Mains electricity part 2: safety
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What are some common electrical safety hazards?
Damaged insulation — contact with an exposed wire could mean electric shock
Overheating of cables — passing too much current through too small a wire (e.g having too many devices functioning) or leaving a long length of wire tightly coiled. May cause fire or melt the insulation and exposing the wires
Damp conditions — if moisture comes into contact with live wires it could conduct electricity causing a short circuit within device (fire) or posing an electrocution risk
Name the safety devices in mains electricity
Fuses
Earth wires
Insulation or double insulation
Circuit breakers
What is the structure of a fuse?
It is usually a cylinder or a cartridge which contains a thin piece of wire made of a metal with a low melting point
How does a fuse work?
When a current that is too large passes through the circuit
the fuse wire becomes overheats and melts. The fuse 'blows'.
Breaks the circuit by stopping the current
What is a purpose of a fuse?
Prevents
overheating in circuit
current exceeding a value
Switches off the circuit
Prevents you getting a shock and reduces the possibility of an electrical fire
If the current in a circuit is 2A then what size fuse should you use?
One that allows a current that is a bit larger, e.g in this case 3 or 4 or 5
Modern safety devices, such as those found in the consumer units are often in the form of circuit breakers.
How do these work?
If a current that is too large passes through the circuit, a switch automatically opens making the circuit incomplete
What are the advantages of circuit breakers? (Compared to fuses) starred one are preferred ones
Can be easily reset
Turn off circuit more quickly *
Allow does not need to be replaced (unlike the fuse) *
What is the characteristic does the replacement fuse must have?
The new fuse replacing the melted one must be the same size as the previous one
A circuit breaker has a rating of 16A.
Suggest a reason why the heater may switch off before it reaches its normal operating current
Idea that there are likely to be other appliances in same circuit
Fuse in heater net be rated less than 16A
Idea that heater may have a thermal safety cut out
Idea that thermostat turn off heater
What do ALL devices with metal casings have to have?
An earth wire
How do earth wires work?
If the live wire breaks and comes into contact with the casing, the earth wire provides a low-resistance path for the current to the ground/earth.
A surge of current happens in the earth wire and hence also in the live wire
The current is likely to be large enough to blow the fuse in the live wire and turn the circuit off
by cutting the supply of electricity to the appliance
Basically prevents buildup of charge
What are the colours of the live, neutral and earth wire?
Live — brown
Neutral — blue
Earth — green and yellow stripes

Label the diagram
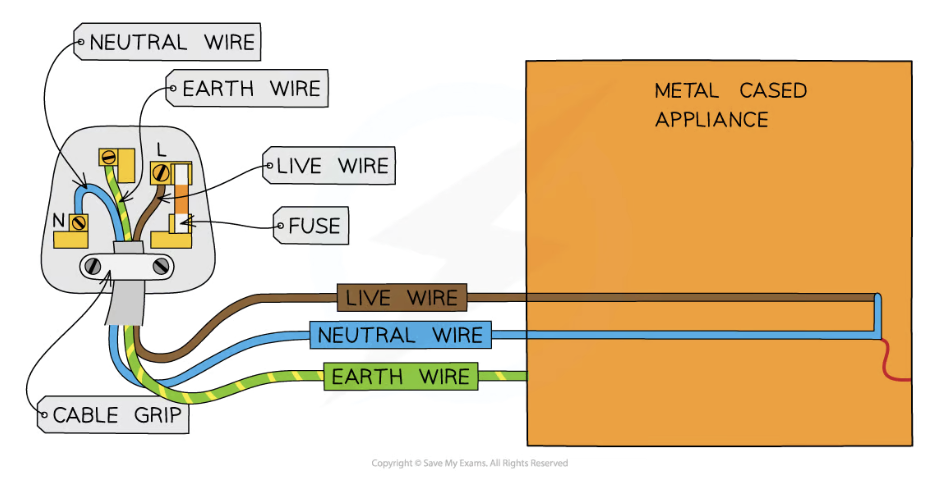
Explain what would happen to devices with metal casings that do not have an earth wire if the live wire is damaged?
Without the earth wire anyone touching the casing of the faulty appliance would receive an electric shock as the current passed through them to earth
What is double insulation?
Many electrical appliances have casing made from an insulator such as plastic, rather than metal. All electrical parts are insulated this wasy so that they cannot be touched by the user.
How is the wire used in an device with double insulation different from another one without (just the metal casing)?
Appliances with double insulation use a two-wire flex (cable with only a live and neutral wire) as there is no need for an earth wire
Switches: in which wire should a switch be placed in? Why?
The live wire so that when the switch is open no electrical energy can reach an appliance
What would happen if the switch is placed in the neutral wire?
Electrical energy would still be able to enter a faulty appliance and could possibly cause an electric shock.