thermal physics
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
define internal energy
the sum of randomly distributed kinetic and potential energies of the particles in a body
how does internal energy increase
through heating or work being done on the system as energy is transferred to the system
energy changes when a substance changes state
potential energy of particles change
kinetic energy constant
energy changes when a substance changes temperature
kinetic energy of particles change
potential energy constant
why do molecules have kinetic energy
due to their random motion
why do molecules have potential energy
due to the chemical bonds holding them together and the bonds within their nuclei
thermal equilibrium
two bodies are at the same temperature so there is no flow of thermal energy
specific heat capacity definition
thermal energy required to raise the temperature of a body of mass 1kg by 1K
specific latent heat definition
amount of energy required to change the state of 1 kg of material, without changing its temperature
ideal gas assumptions
all molecules of a particular gas are identical
internal energy of the gas is entirely kinetic
all collisions between molecules and the walls of the container are completely elastic
Newton’s laws of motion apply
molecules take up negligible volume
gravitational and electrostatic forces can be ignored
motion of all molecules is random
all molecules travel in straight lines
absolute zero
the temperature at which particles have no kinetic energy and the volume and pressure of a gas are zero
in the equation pV = NkT what is N
total number of molecules of gas
in the equation pV = nRT what is n
number of moles of gas
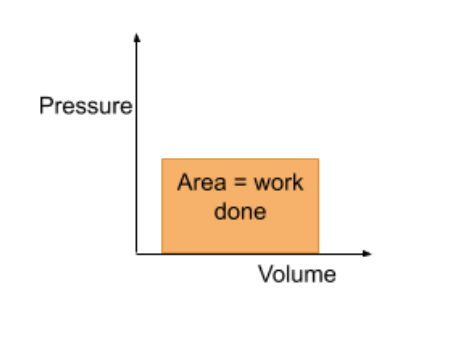
work done from pressure volume graph
area
brownian motion
random motion of larger particles in a fluid caused by collisions with surrounding particles
can be observed through looking at smoke particles under a microscope
evidence for the existence of atoms and molecules
assumptions in the kinetic theory model
no intermolecular forces act on the molecules
the duration of collisions is negligible in comparison to time between collisions
the motion of molecules in random, and they experience perfectly elastic collisions
the motion of the molecules follows Newton’s laws
the molecules move in straight lines between collisions
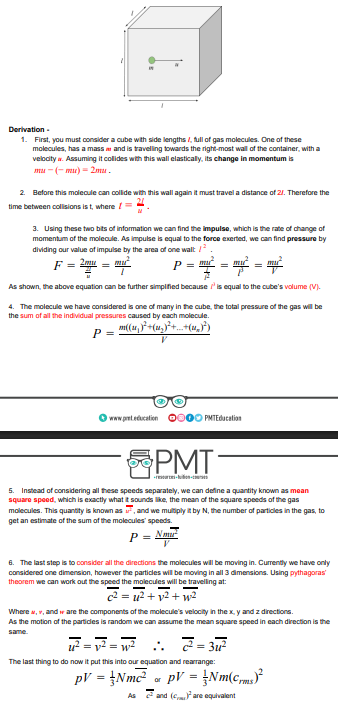
derivation of kinetic theory model