microbio 2125 unit 6 part 2
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Flexible cell membrane is penetrated by whole virus or its nucleic acid by:
Fusion or Endocytosis
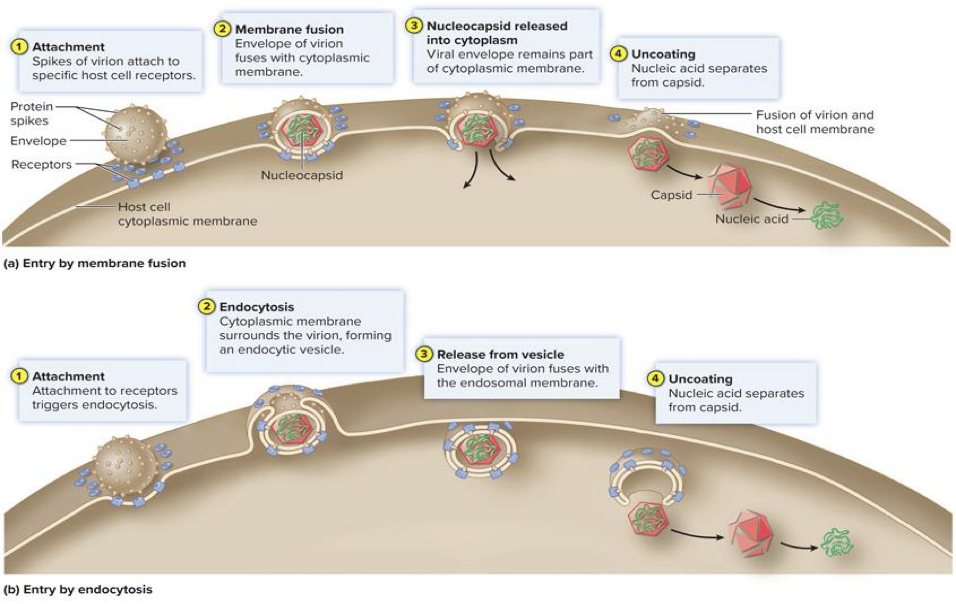
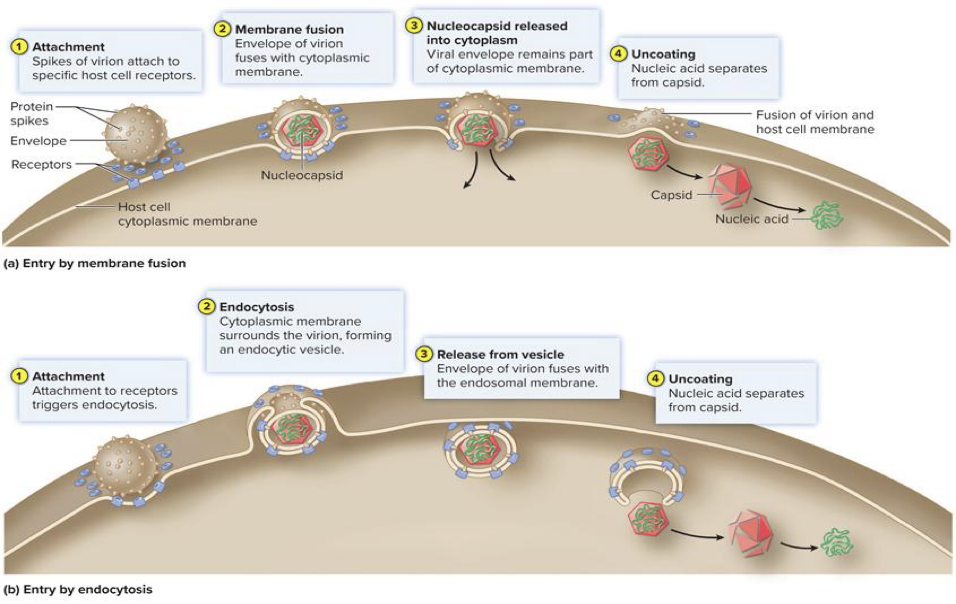
Fusion
envelope merges directly with membrane resulting in nucleocapsid’s entry into cytoplasm
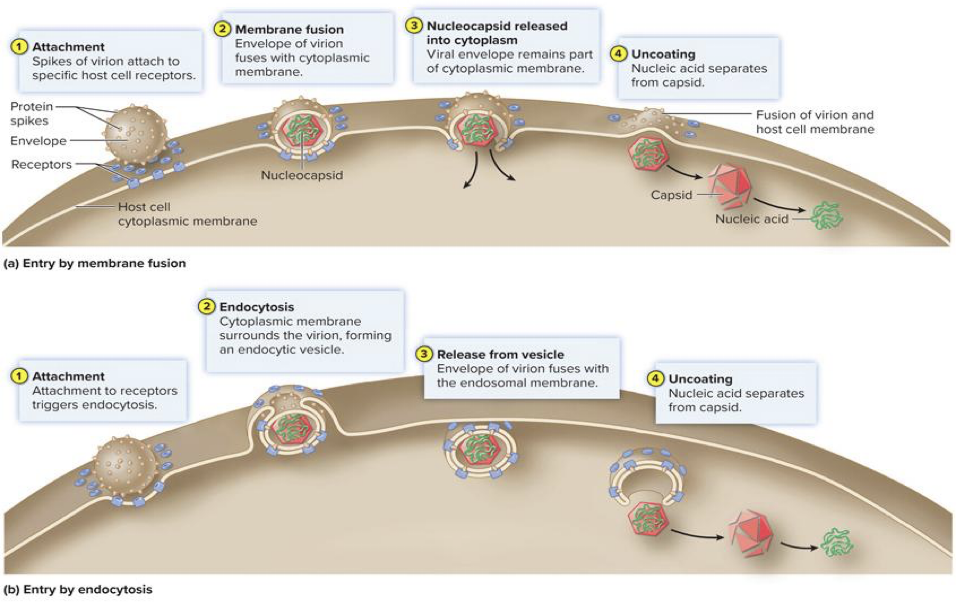
Endocytosis
entire virus is engulfed and enclosed in vacuole or vesicle
Synthesis and Assembly
Require DNA or RNA replication and protein production
Mechanism varies depending on whether virus is DNA or RNA virus
DNA viruses generally are replicated and assembled in…
nucleus, from which they bud
RNA viruses generally are replicated and assembled in…
cytoplasm, from which they bud
Positive-sense RNA contain message for translation
Negative-sense RNA must be converted into positive-sense message
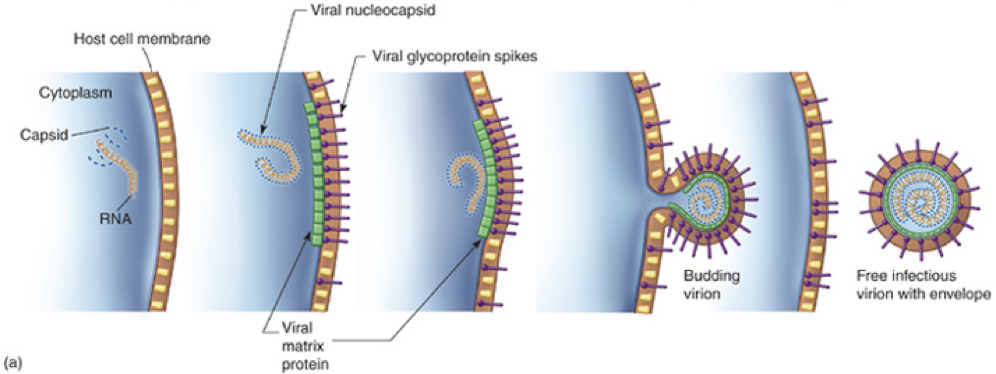
release: Budding
exocytosis; nucleocapsid binds to membrane which pinches off and sheds viruses gradually; cell is not immediately destroyed
release: Lysis
nonenveloped and complex viruses released when cell dies and ruptures
Number of viruses released is variable
3,000-4,000 released by poxvirus
>100,000 released by poliovirus
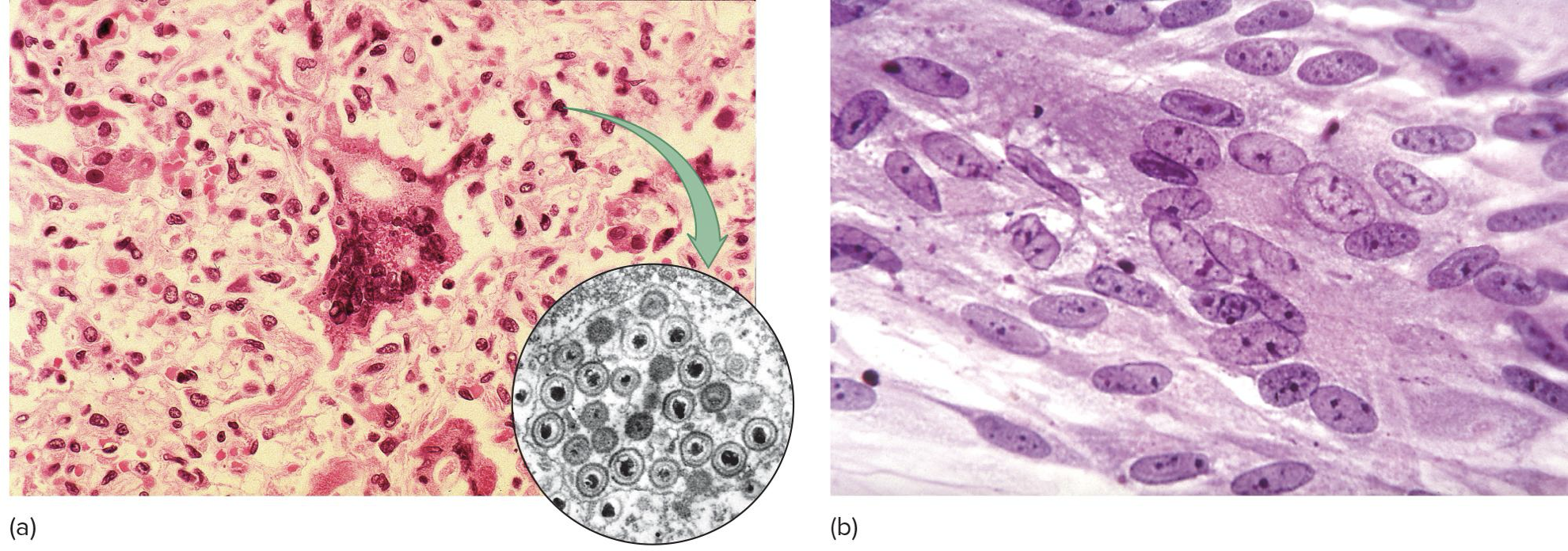
Cytopathic Effects
virus-induced damage to cells
Changes in size and shape
Cytoplasmic and nuclear inclusion bodies
Cells fuse to form giant multi-nucleated cells (syncitia)
Cell lysis
Alter DNA
Transform cells into cancerous cells
Persistent infections
cell harbors virus and is not immediately lysed
Can last weeks or host’s lifetime; several can periodically reactivate (chronic latent state)
examples of persistent infections
Measles virus: may remain hidden in brain cells for many years
Herpes simplex virus: cold sores and genital herpes
Herpes zoster virus: chickenpox and shingles
Transformation
some animal viruses enter host cell and permanently alter genetic material resulting in cancer
Transformed cells have increased rate of…
growth, alterations in chromosomes, and capacity to divide for indefinite time periods resulting in tumors
Mammalian viruses capable of initiating tumors are called…
oncoviruses
Papillomavirus: cervical cancer
Epstein-Barr virus: Burkitt’s lymphoma
Bacteriophages
bacterial viruses (phages)
Most widely studied are those that infect Escherichia coli – complex structure, DNA
Only nucleic acid enters cytoplasm - uncoating is not necessary
Phage replication step 1 Adsorption
binding of virus to specific molecule on host cell via tail fibers
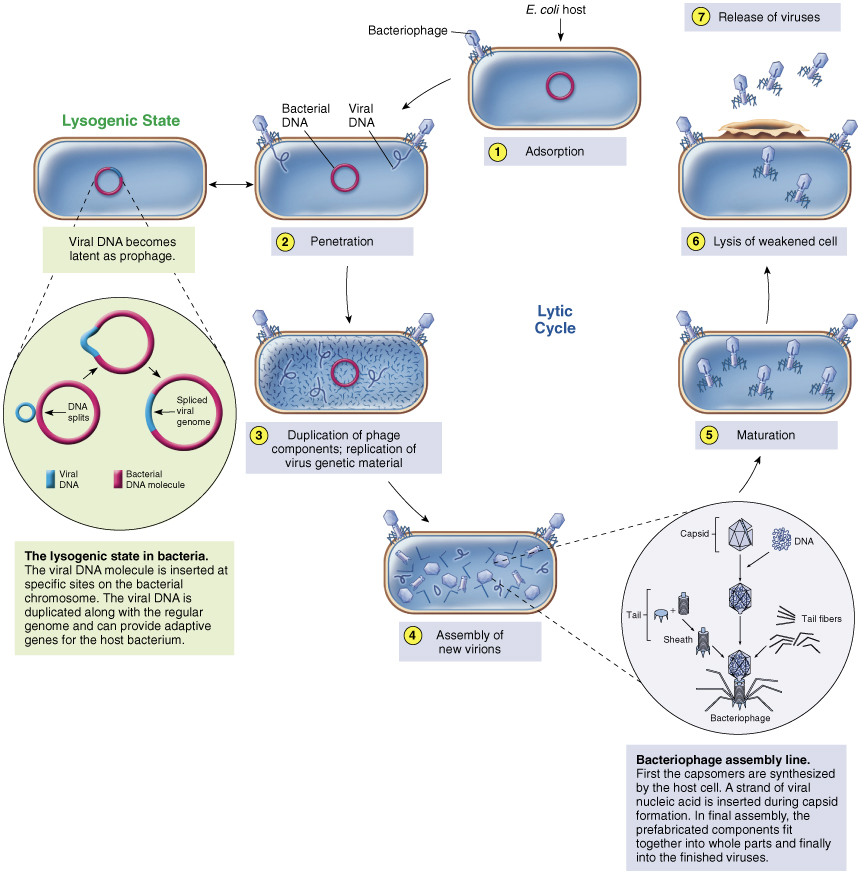
Phage replication step 2 Penetration
genome enters host cell
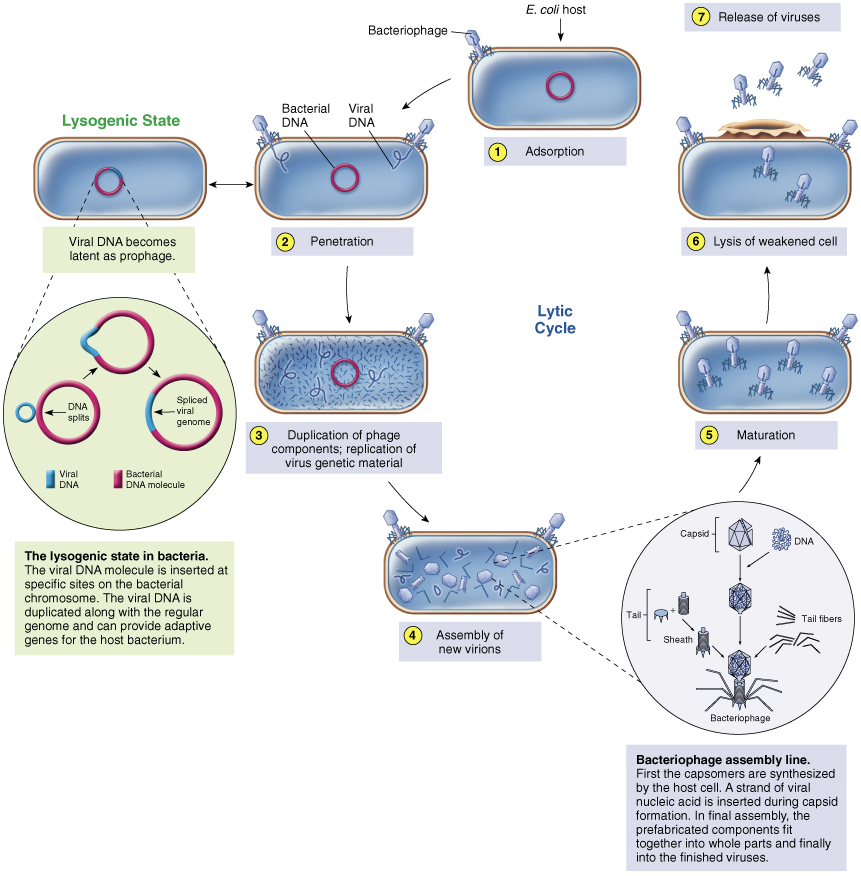
Phage replication step 3 Replication
viral components produced
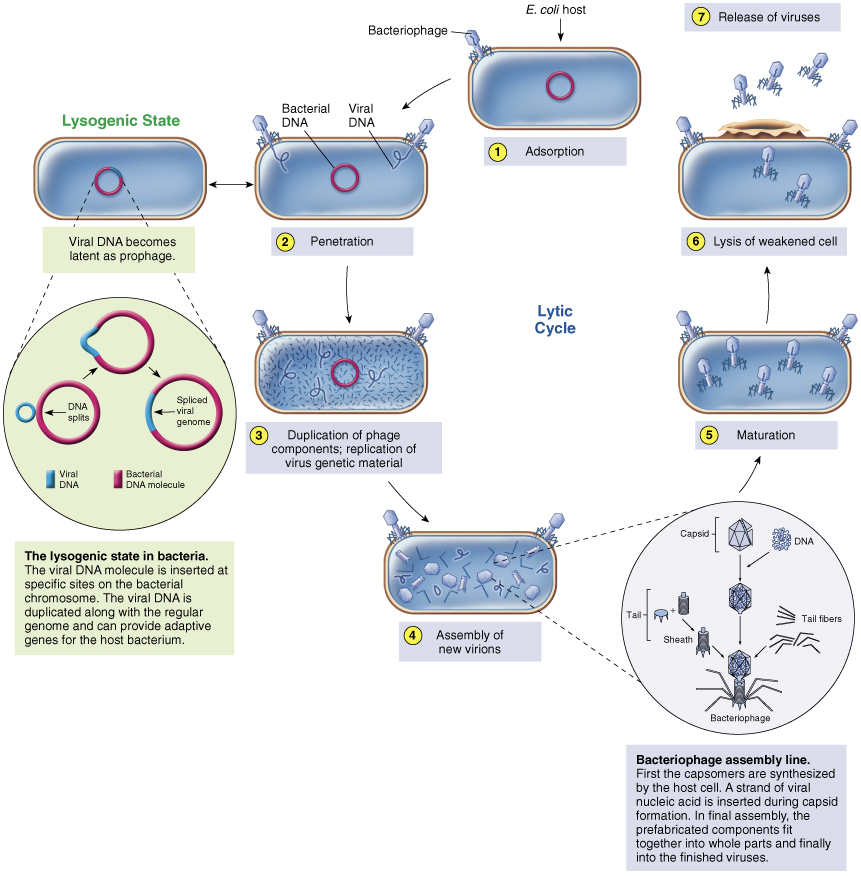
Phage replication step 4 Assembly
viral components assembled
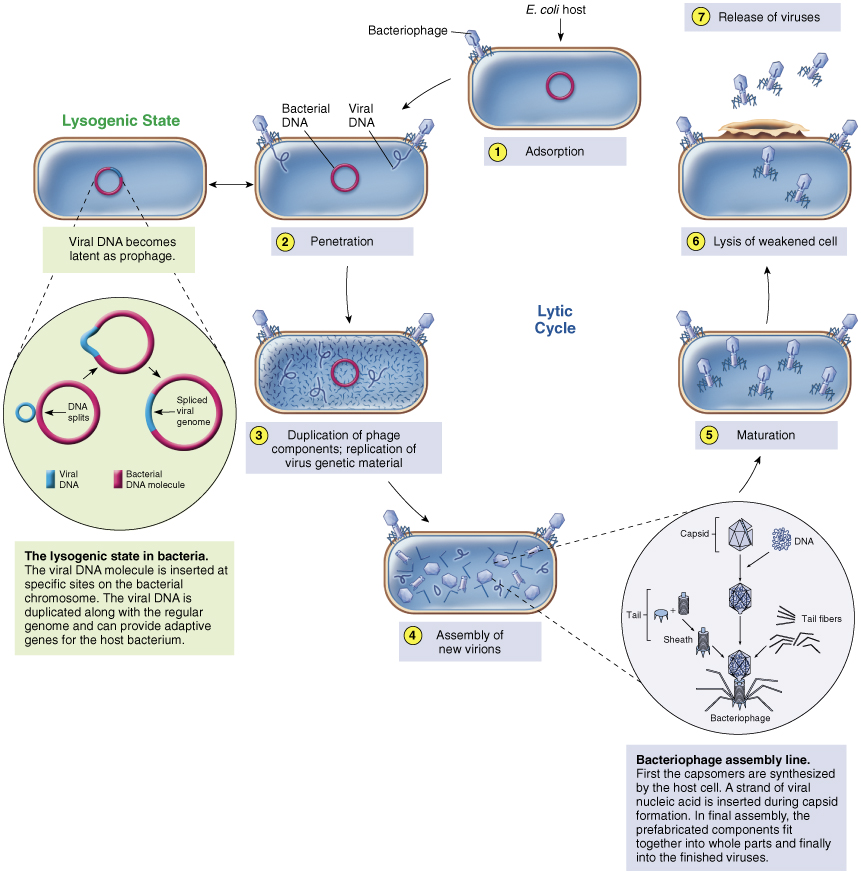
Phage replication step 5 Maturation
completion of viral formation
Phage replication step 6 Release
viruses leave cell to infect other cells
Lysogeny
The Silent Virus Infection
Not all phages complete lytic cycle
Some DNA phages, called ______ _____, undergo adsorption and penetration but don’t replicate
temperate phages
Viral genome inserts into bacterial genome and becomes…
inactive prophage – cell is not lysed
Prophage is retained and copied during normal cell division resulting in transfer of temperate phage genome to all host cell progeny
lysogeny
Induction
can occur resulting in activation of lysogenic prophage followed by viral replication and cell lysis
Lysogeny results in?
spread of virus without killing host cell
Phage genes in bacterial chromosome can cause production of toxins or enzymes that cause pathology
lysogenic conversion
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Vibrio cholerae
Clostridium botulinum
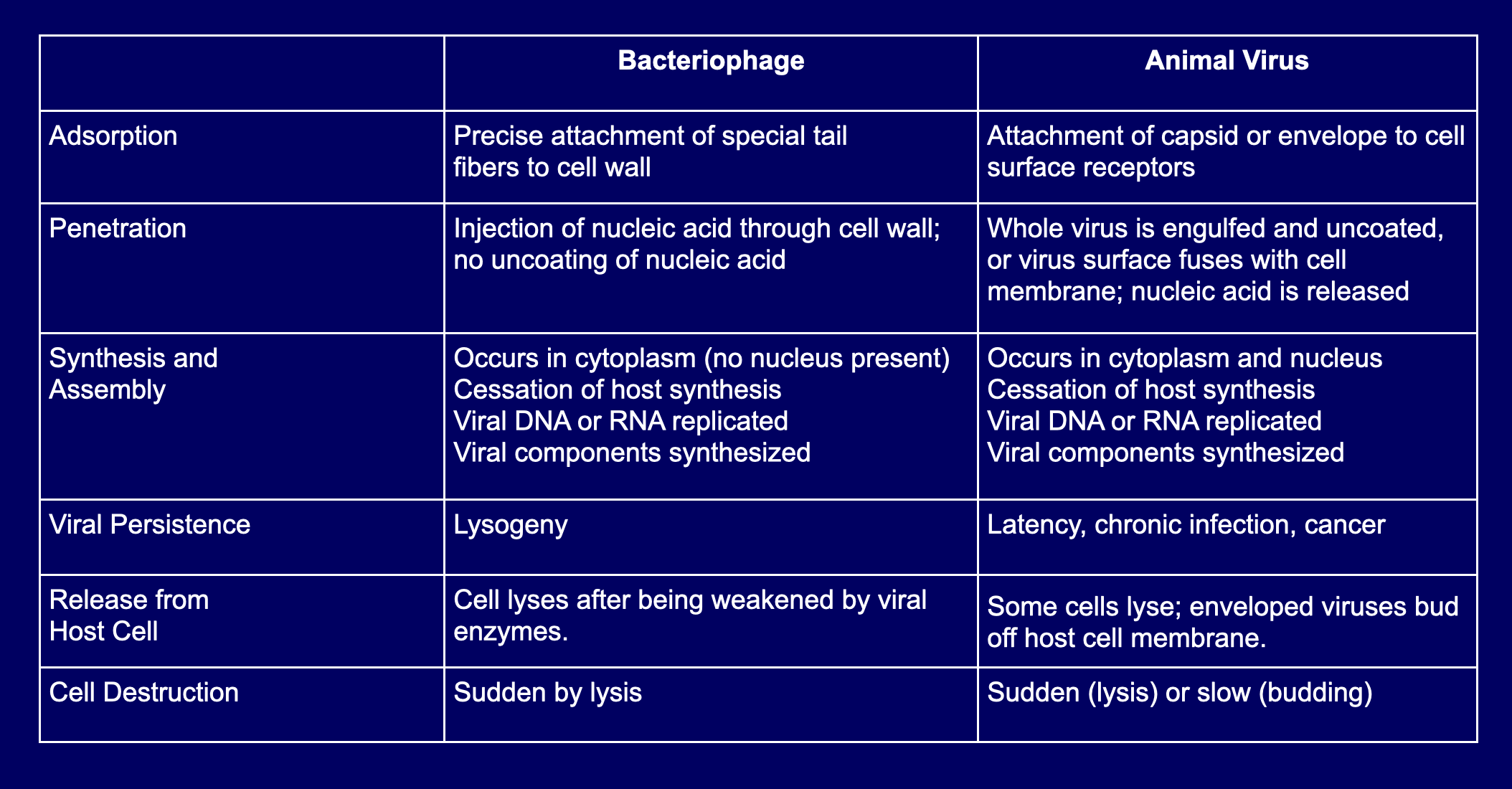
Bacteriophage versus Animal Viral Multiplication table 6.4
Viruses are limited to….
particular host or cell type
Many viruses are strictly human in origin, others are zoonoses transmitted by vectors
Viral infections range from..
asymptomatic to mild to life-threatening
Several viruses can cross placenta causing developmental disturbances and permanent defects
teratogenic
Course of disease
invasion at portal of entry and primary infection; some viruses replicate locally, others enter circulation and infect other tissues
Common manifestations
rashes, fever, muscle aches, respiratory involvement, swollen lymph nodes
Body defenses
combined action of interferon, antibodies, and cytotoxic T cells; frequently results in lifelong immunity
Diagnosis of viral diseases
symptoms, isolation in cell or animal culture, serological tests for antibodies; some tests for antigens
Some viruses establish long-term persistent infections that last many years or lifetime
2 types of persistent infections:
Many viral infections have rapid course; lytic cycle
Chronic infections
Latent infections
Some persistent viruses are oncogenic
Chronic infections
virus is detectable in tissue samples, multiplying at slow rate; symptoms mild or absent
Latent infections
after lytic cycle, virus enters dormant phase; generally not detectable, no symptoms; can reactivate and result in recurrent infections
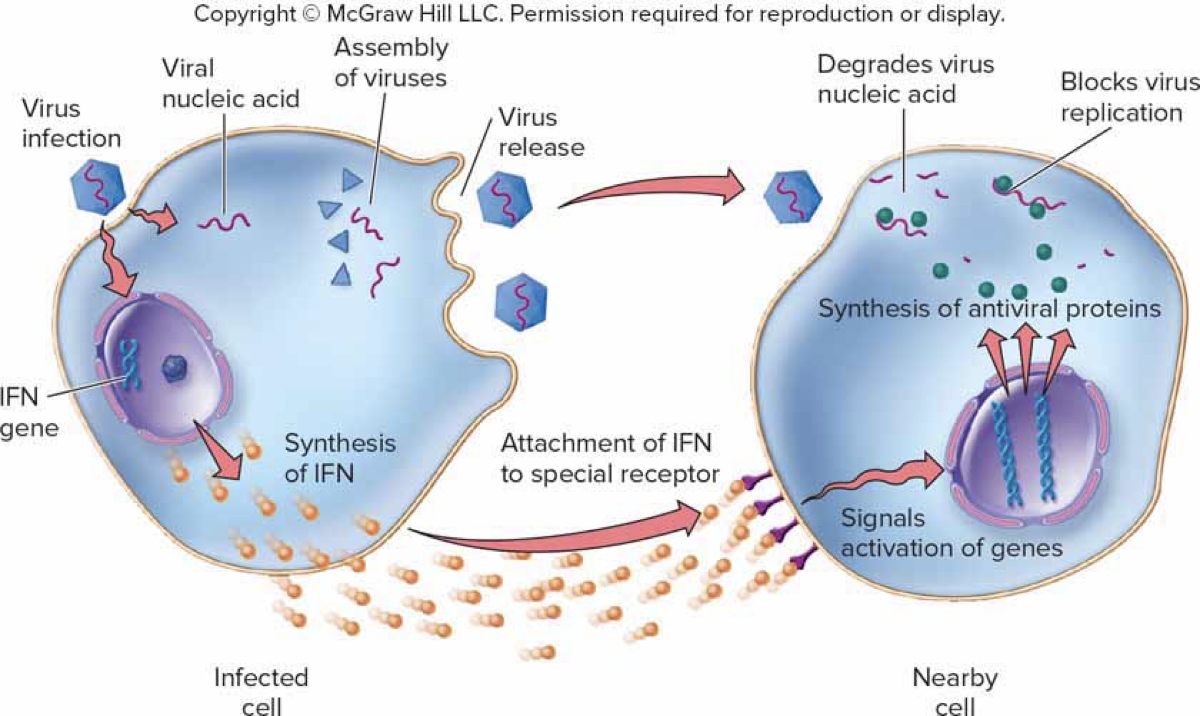
Interferon (IFN) – A Natural Antiviral Protein
Potent antiviral cytokine
Antiviral Mechanism 1
Infected cell releases IFN
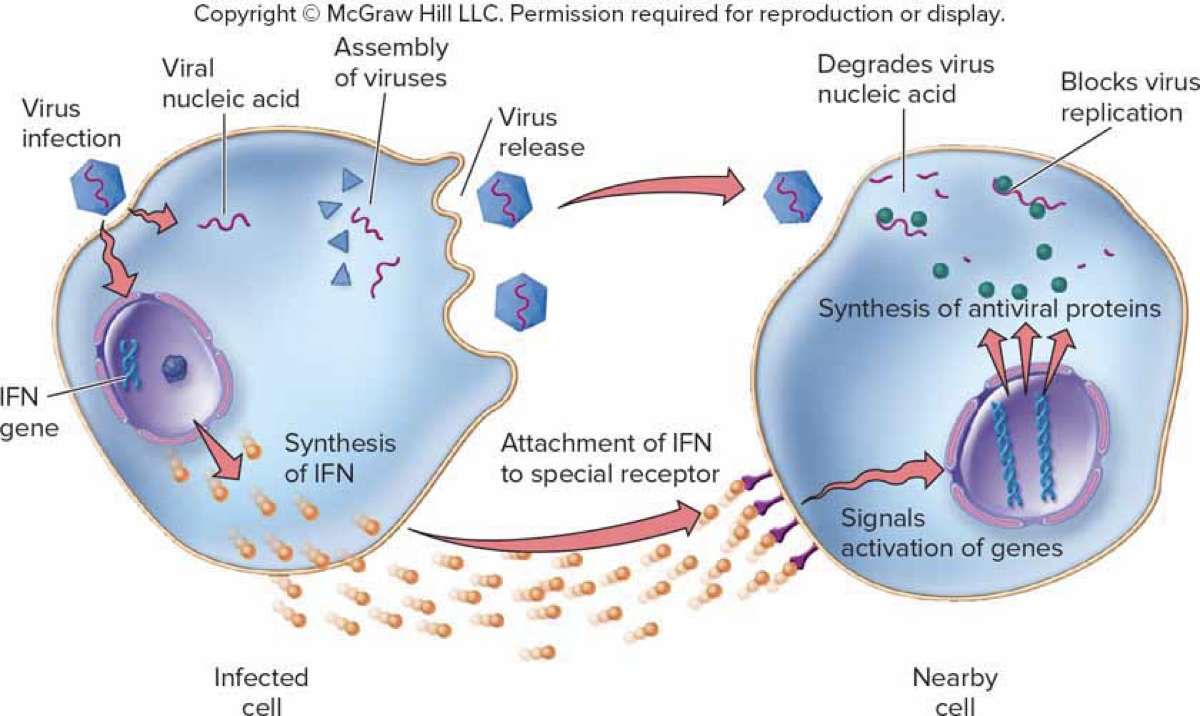
Antiviral Mechanism 2
IFN signals neighboring cells to produce other factors that suppress transcription and increase RNase expression in infected cell
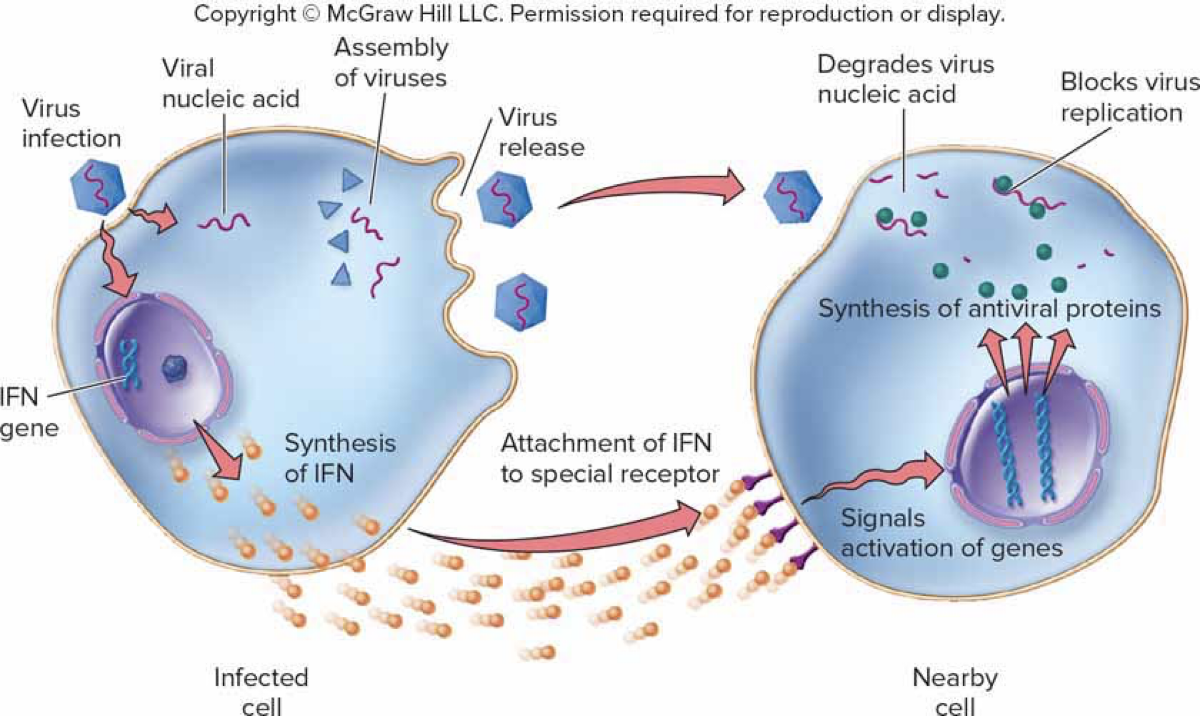
Antiviral Mechanism 3
IFN also increases MHC production, increasing presentation of viral antigens to T-cells
Animal viruses are categorized according to..
nucleic acid, capsid, and presence or absence of envelope
Survey of DNA Viruses
7 DNA families
DNA viruses causing human disease:
Enveloped DNA viruses
Nonenveloped DNA viruses
Nonenveloped ssDNA viruses
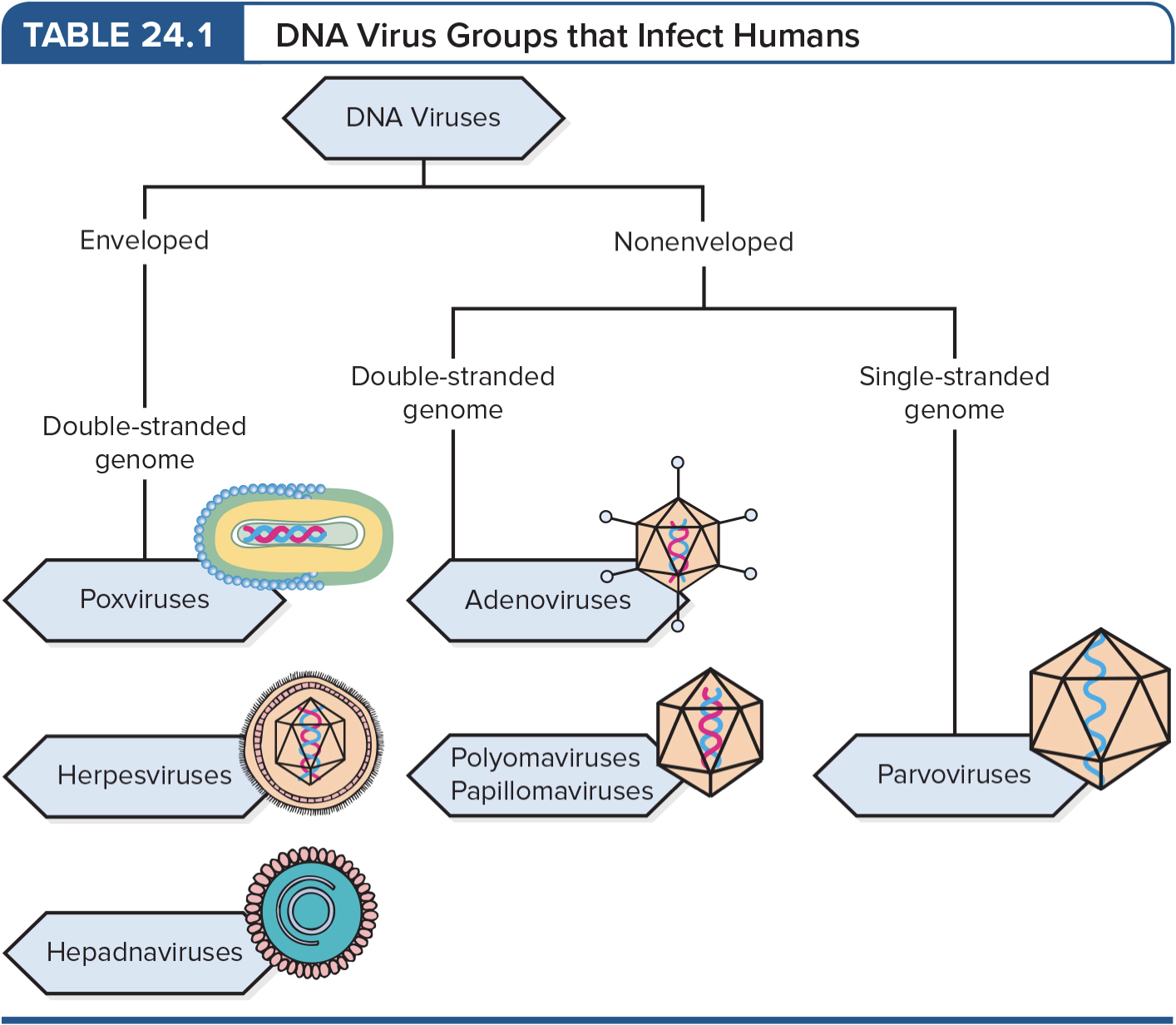
Smallpox - History
Throughout history, smallpox has devastated populations, particularly naïve (never exposed before) populations
One of deadliest diseases of past, now only found in government labs (U.S.A. & Russia)
1999 - World Health Organization recommended that all smallpox stores be destroyed, but…
gov’ts scoffed, maintaining smallpox should be tested and used in research
Russia has reported developing resistant strain that would..
withstand delivery by bomb or missile
There is concern that all Russian stores may not be accounted for and CDC in US had scare with…
discovery of long-term inappropriate storage of smallpox samples in the 2010’s