RADT W12 Ch 3 (pink), 28 (black) Normal Anatomy - Periapical Films
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Cortical bone aka compact bone is the dense outer layer of bone. It appears _____ on a radiograph.
Radiopaque (white)
Cancellous bone aka Spongy bone is between two layers of dense cortical bone. It appears primarily _____ on radiographs but the trabeculae will appear ______.
Cancellous bone appears primarily radiolucent with the trabeculae appearing radiopqaue.
Process: marked prominence or projection of bone
Radiopaque
Ex. Coronoid Process of mandible.
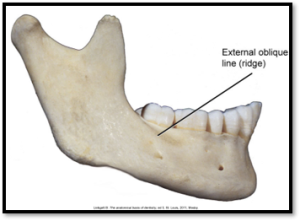
Ridge: linear prominence or projection of the bone; might also be called a “line”.
Radiopaque
Ex. External Oblique Ridge
Spine: sharp, slender projection of bone
Radiopaque
Ex. Anterior Nasal spine
Radiographic Landmark used in Lateral Head Films for Ortho
Tubercle: small rounded projection, small bump or nodule of bone
Radiopaque
Ex. Genial tubercles
Tuberosity: Rounded projection of bone
Radiopaque
Ex. Maxillary Tuberosity
What are the 4 space/depression bone landmarks?
Canal
Foramen
Fossa
Sinus
Canal: Tubelike passageway through bone that contains nerves and blood vessels
Radiolucent
Ex. mandibular canal
Foramen: Short round or oval tube-like opening through a bone that allows the passage of nerves and blood vessels
Radiolucent
Ex. Mental Foramen, Incisive Foramen
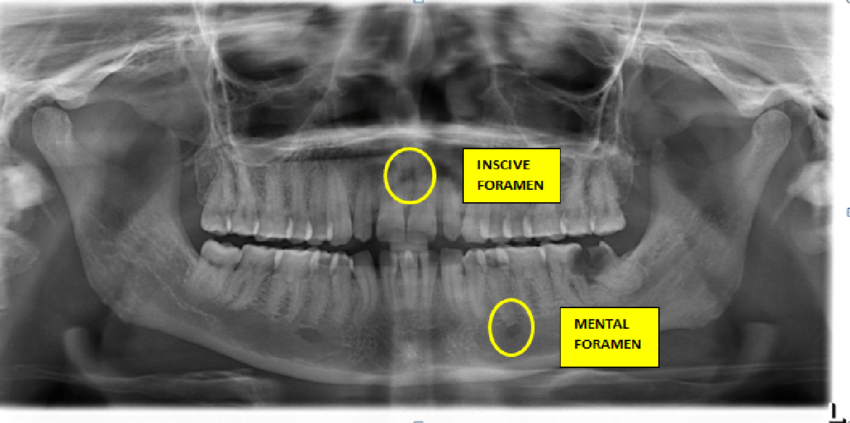
Fossa: shallow, basin-like depression
Radiolucent
Fossa are mainly for the purpose of muscle attachment
Ex. Submandibular fossa
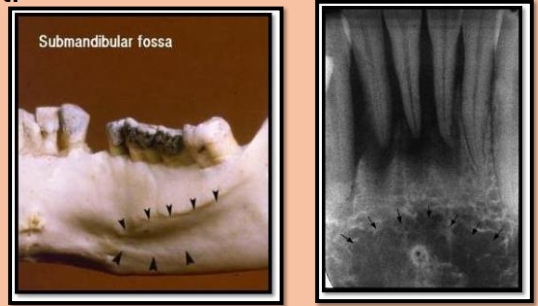
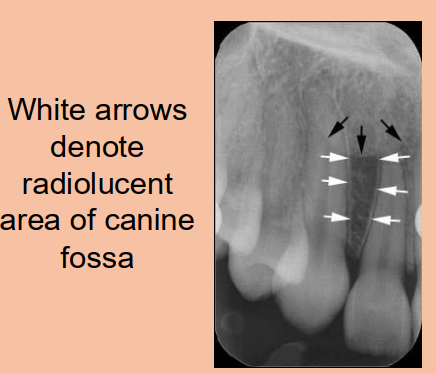
Canine Fossa is…
The depression in the maxillae lateral to the canine
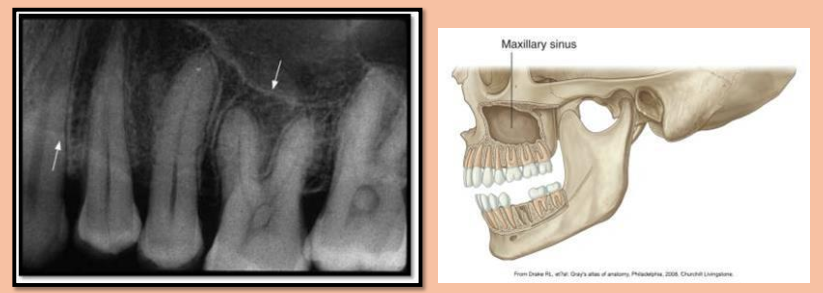
Sinus: a hallow space/cavity within a bone.
Radiolucent
Ex. Maxillary sinus
**when sinuses are infected, they will appear more radiopaque (grayish or white within the sinus area on xray)
Septum: a bony wall or partition that divides two spaces or cavities.
May be present within the space of a fossa or a sinus.
Radiopaque
Ex. Nasal Septum
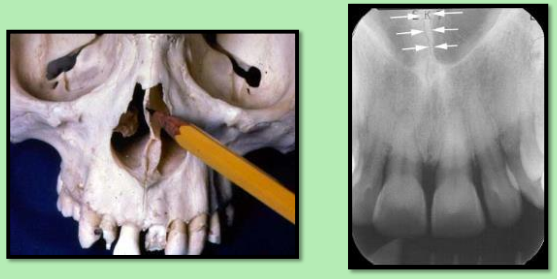
Suture: an immovable join representing a line of union between adjoining bones of the skull.
Only found in the skull !
Radiolucent
Ex. Medial palatal suture
What is the rules of shadow casting?
The further an object is from the film packet, the more likely the object will appear magnified.
ex. tip of the nose is further from the intraoral film packet, then it will appear magnified.
How does soft tissue appear on a radiograph?
On a radiograph, soft tissue (like the nose, lips, tongue) appears as a faint, lighter gray shadow—less radiopaque than bone/teeth, but more radiopaque than air.
Example: the nose shows as a soft-tissue outline or shadow overlying the anterior maxilla, without distinct internal detail.
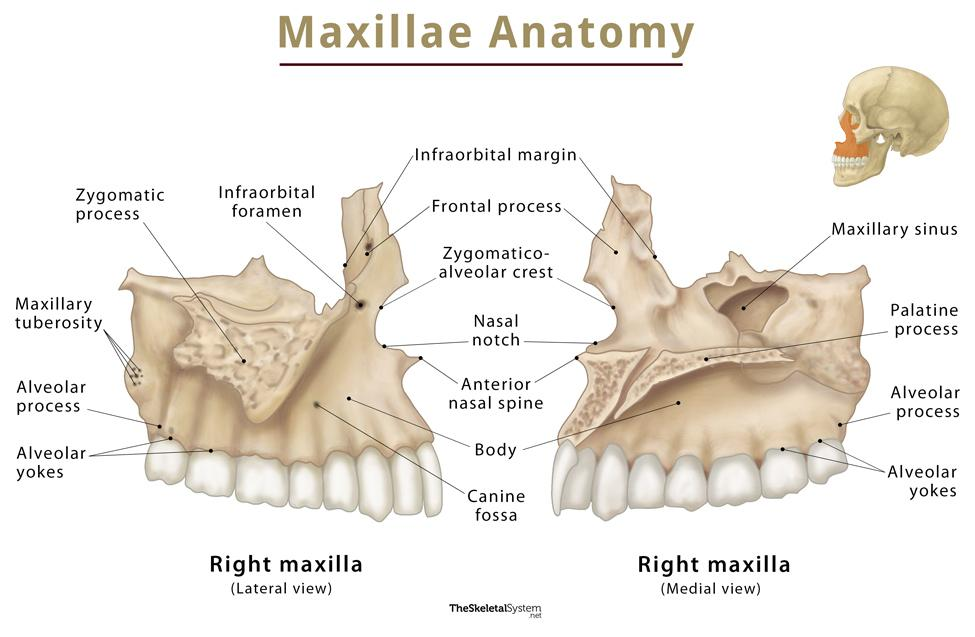
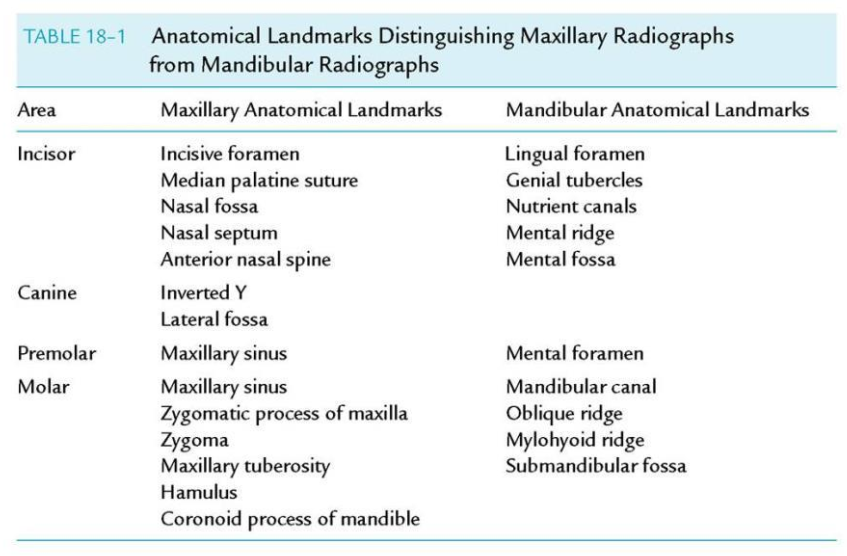
16 Bony landmarks of the maxilla
Incisive foramen
Superior foramina of the incisive canal
Medial palatal suture
Lateral (canine) fossa
nasal cavity
nasal septum
floor of the nasal cavity
anterior nasal spine
inferior nasal conchae
maxillary sinus - septa
maxillary sinus - nutrient canals
inverted Y
maxillary tuberosity
Hamulus
Zygomatic process of the maxilla
Zygoma
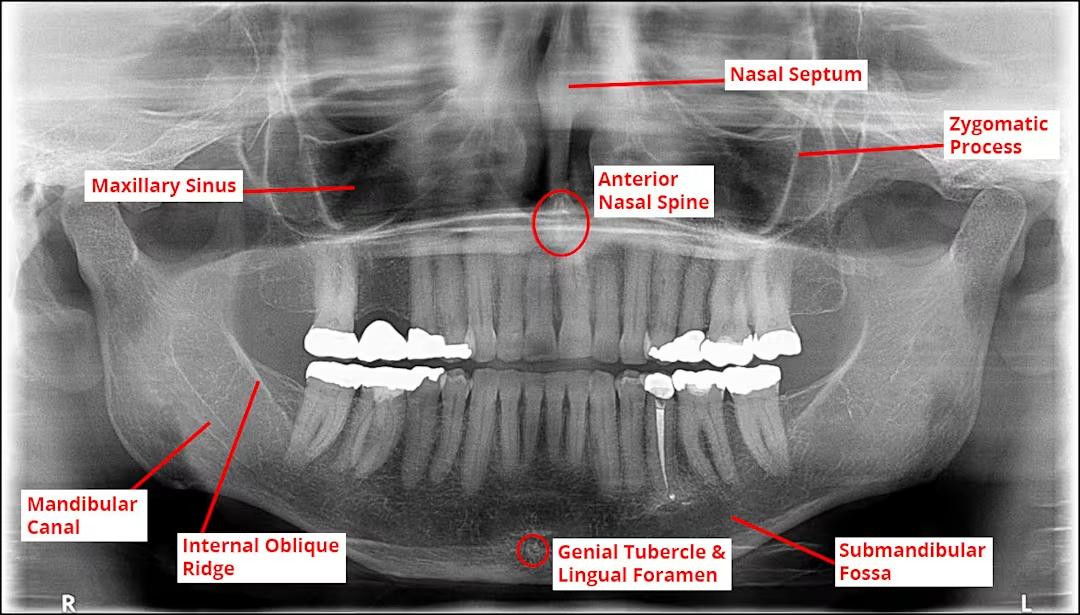
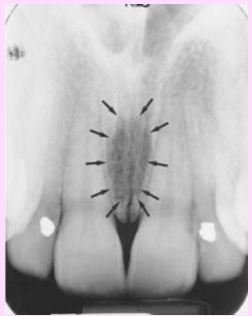
What is the name of this bony landmark?
Incisive foramen (nasopalatine foramen)
Opening in the bone that is located midline of anterior portion of the hard palate, directly posterior to the maxillary central incisors
Radiography: small ovoid or round radiolucent area between the roots of the maxillary central incisors.
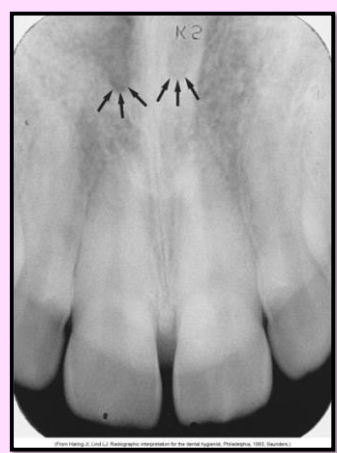
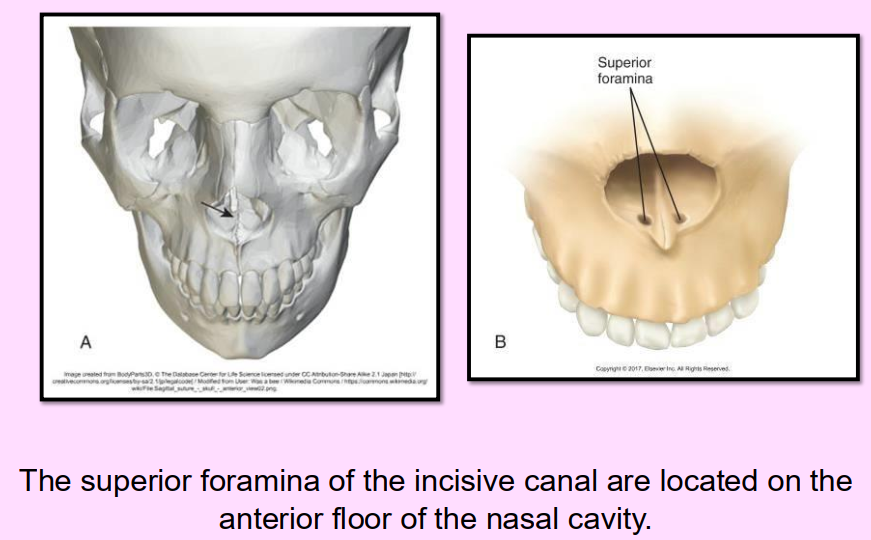
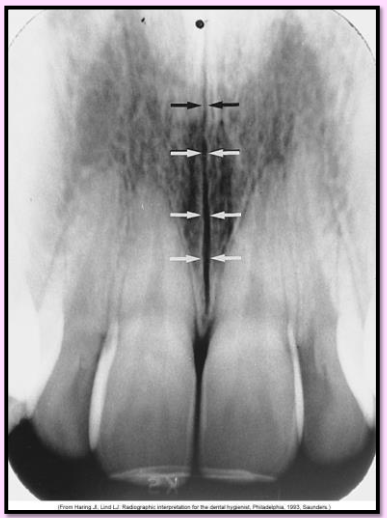
What is the name of this bony landmark?
Superior Foramina of the Incisive Canal
Two tiny openings in the bone that are located on the floor of the nasal cavity that join together to form the incisive canal
Radiography: 2 small round radiolucent openings located superior to the apices of the maxillary central incisors
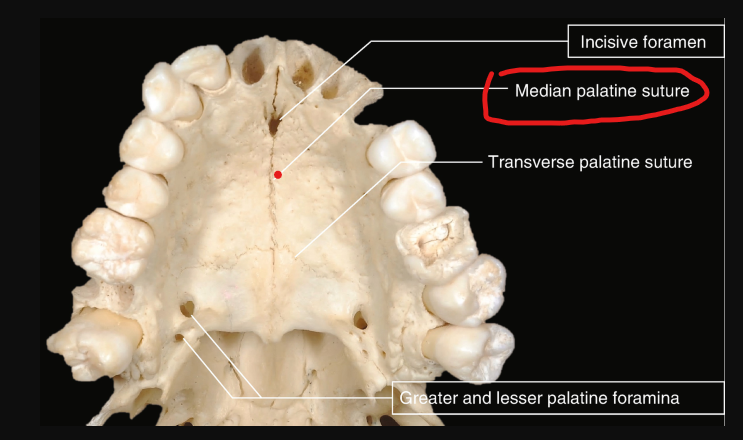
What is the name of this bony landmark?
Median palatal suture
immovable joint between the two palatine processes of the maxilla
Radiography: thin radiolucent line between the maxillary central incisors
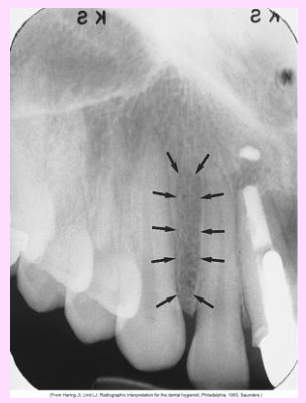
What is the name of this bony landmark?
Lateral (canine) fossa
smooth, depression of the maxilla located just inferior and medial to the infraorbital foramen between the canine and lateral incisors
Radiography: radiolucent area between the max canine and max lateral incisors
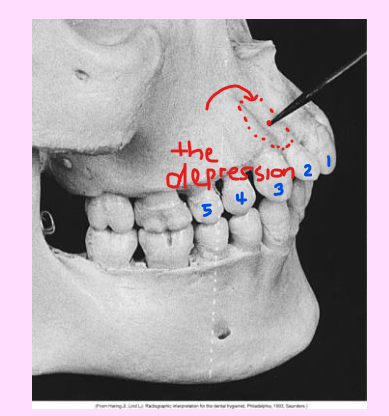
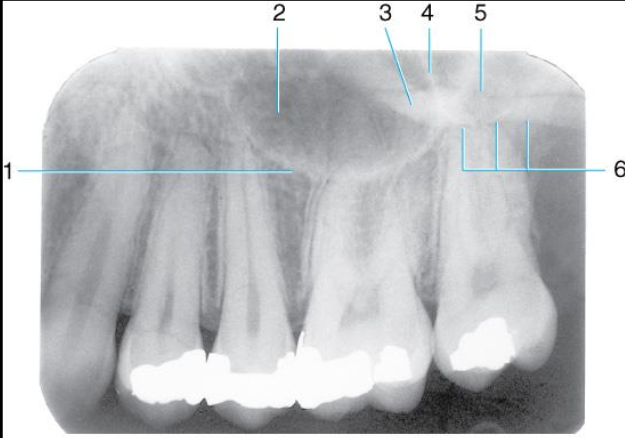
Label all the structures 1-5 of the Maxillary canine area.
Lateral fossa
Nasal fossa
Inverted Y
Maxillary sinus
Dense radiopaque area caused by overlapping
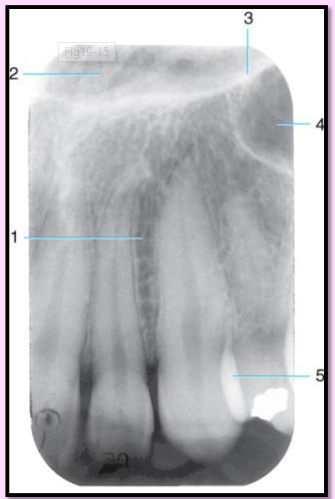
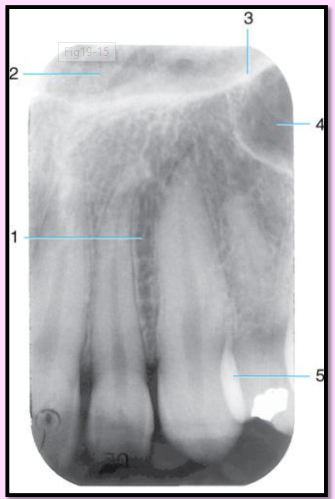
What is the name of this bony landmark?
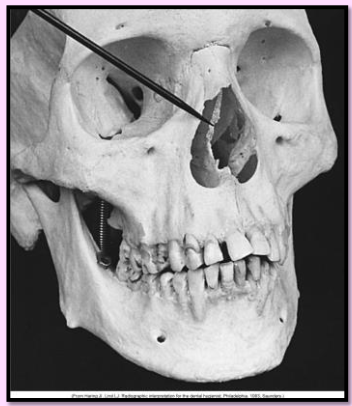
Nasal cavity
pear shaped compartment of bone located superior to the maxilla
inferior portion formed by the palatal processes of the maxilla and horizontal portions of the palatine bone.
Radiography: large radiolucent area above the max incisors
What is the name of this bony landmark?
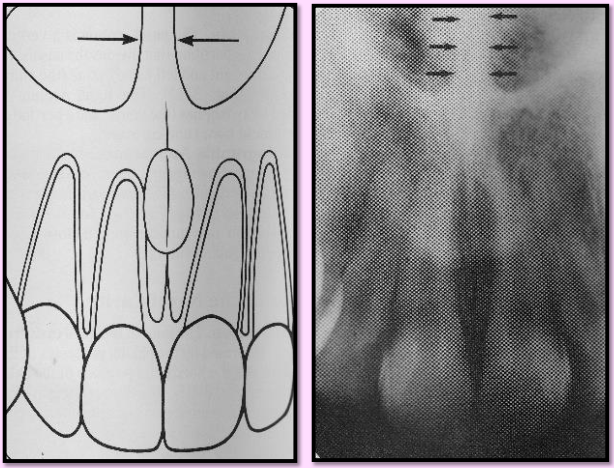
Nasal Septum - made up of the perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone, vomer, and cartilage
vertical bony wall dividing the nasal cavity into left and right nasal fossa
Radiography: vertical radiopaque partition\
What is the name of this bony landmark?
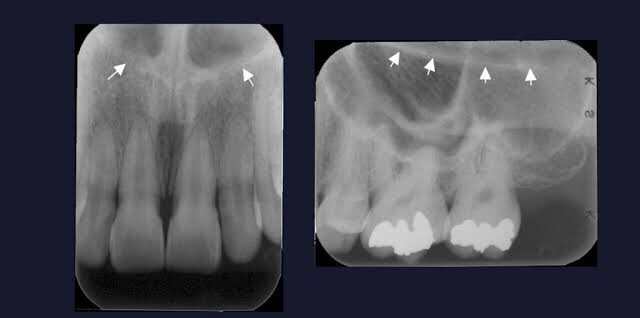
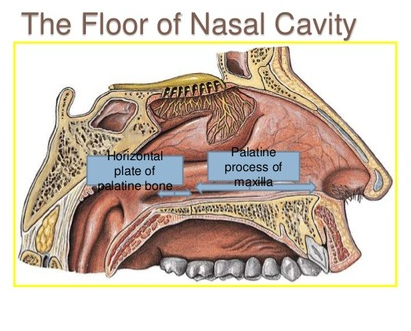
Floor of the Nasal cavity
bony wall formed by the palatal process of the maxilla and the horizontal portions of the palatine bones
Radiography: dense radiopaque band of bone above the maxillary incisors.
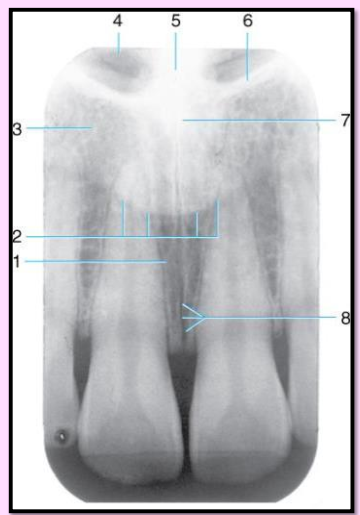
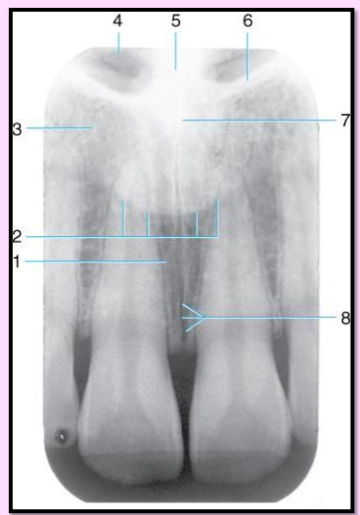
Label the structures 1-8 found in the Maxillary midline area.
Incisive foramen
outline of the nose
lateral fossa
nasal fossa (radiolucent)
nasal septum (radiopaque)
border of nasal fossa
anterior nasal spine
medial palatine suture
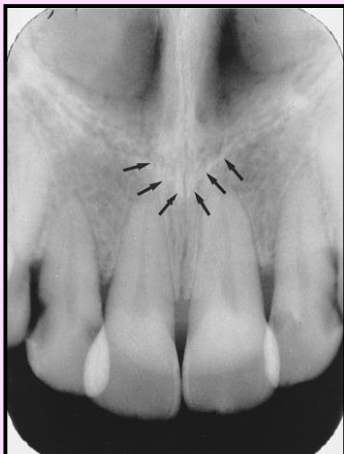
What is the name of this bony landmark?
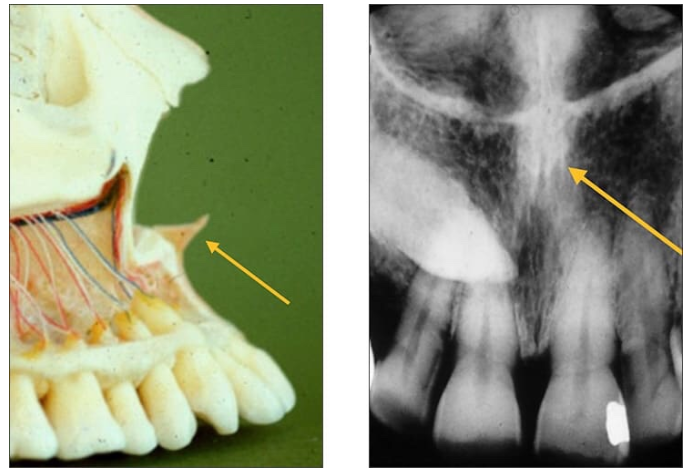
Anterior nasal spine
a sharp projection of the maxilla located at the anterior and inferior portion of the nasal cavity
Radiography: V-shaped radiopaque area located at the intersection of the floor of the nasal cavity and nasal septum.
What is the name of this bony landmark?
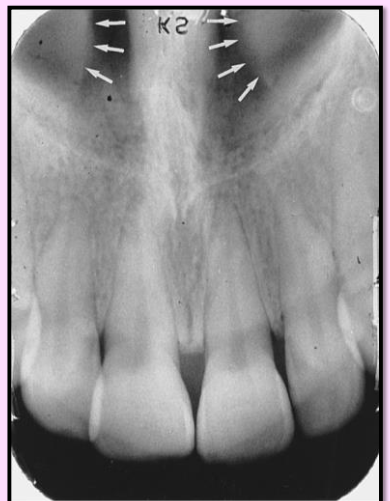
Inferior nasal conchae
wafer-thin, curved plates of bone that extend from the lateral walls of the nasal cavity
Radiography: diffuse radiopaque mass of projection within the nasal cavity Z
What is the name of this bony landmark?
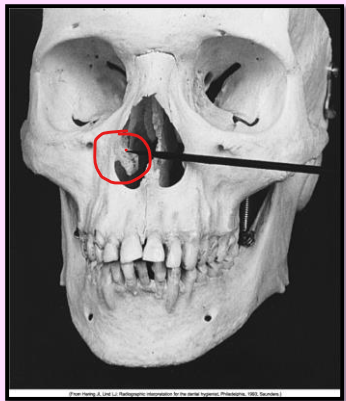
Maxillary sinus
paired cavities of the bone located within the maxilla above the maxillary premolar and molar teeth
Radiography: radiolucent area located above the apices of the max premolar and molars.
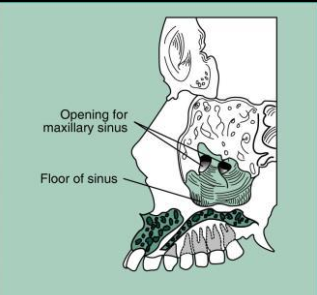
What is the name of this bony landmark?
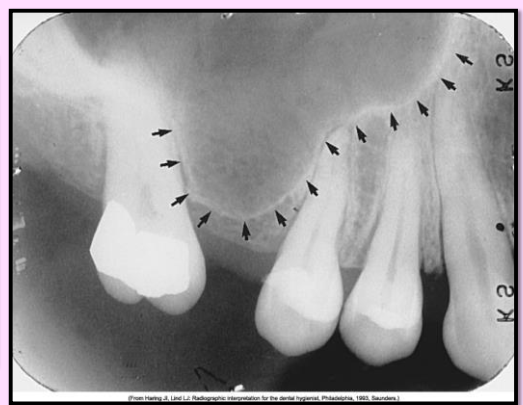
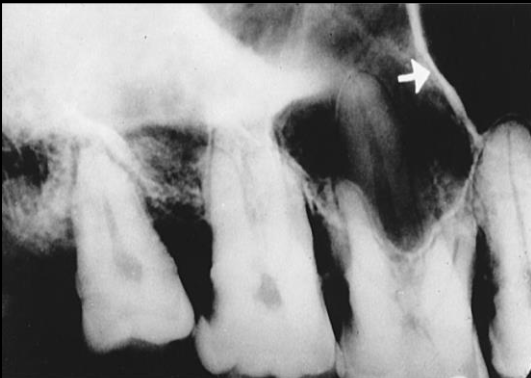
Septa within maxillary sinus
bony wall that appears to divide the maxillary sinus into compartments
Radiography: radiopaque lines within the maxillary sinus
**number and presence of septa vary depending on the anatomy of the individual
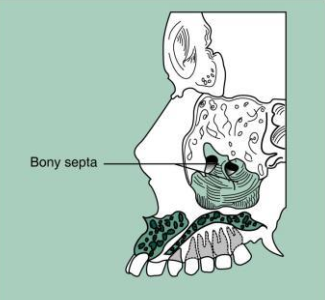
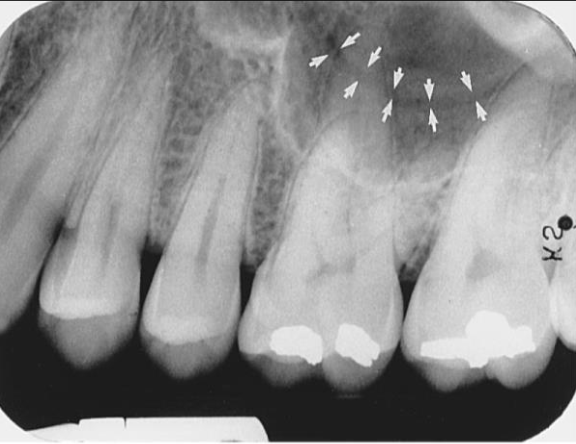
What is the name of this bony landmark?
Nutrient canals within maxillary sinus
tiny, tube-like passageways through the bone that contain blood vessels and nerves
Radiography: narrow, radiolucent band bound by two thin radiopaque lines.
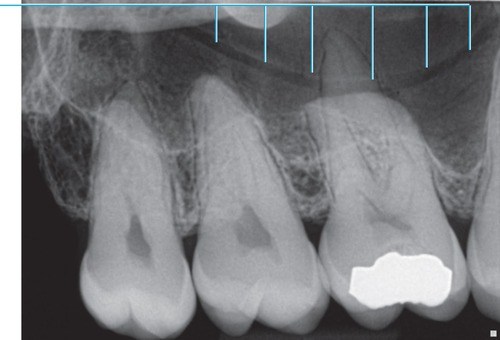
What is the name of this bony landmark?
Inverted Y
intersection of the maxillary sinus and the nasal cavity
Radiography: radiopaque upside-down Y located above the maxillary canine
formed by the intersection of the lateral wall of the nasal fossa and anterior border of the maxillary sinus
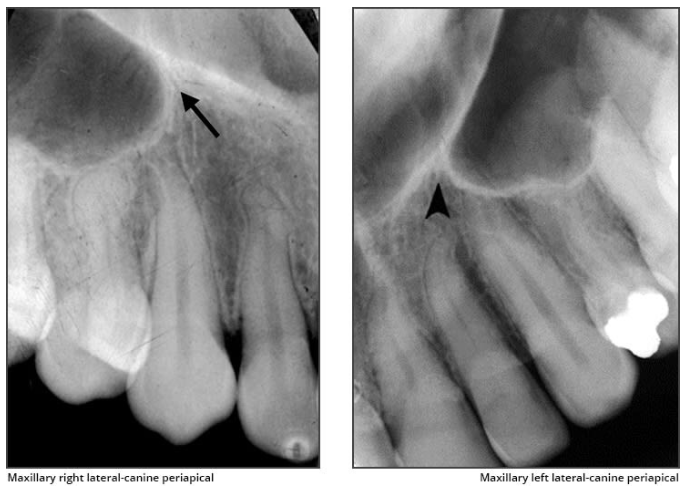
What is the name of this bony landmark?
Maxillary tuberosity
rounded prominence of bone that extends posterior to the third molar region
Radiography: radiopaque bulge, distal to the third molar region
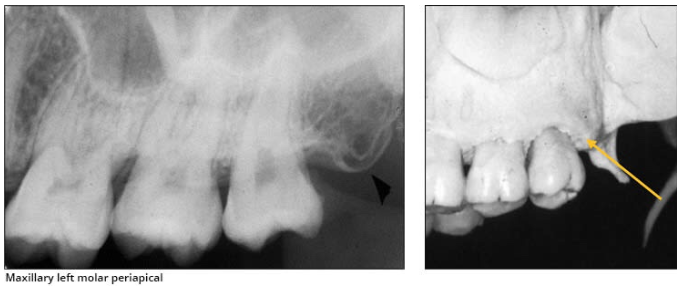
What is the name of this bony landmark?
Hamulus (Hamular process)
small hook-like projection of bone extending from the medial pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone
Radiography: radiopaque hook-like projection posterior to the maxillary tuberosity area
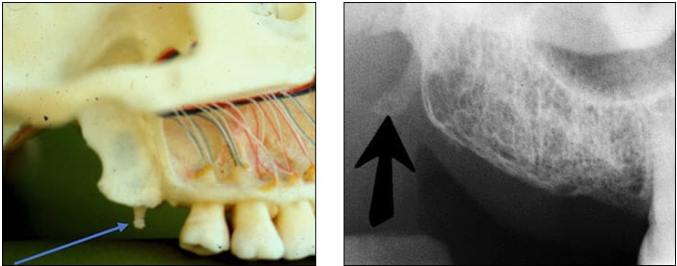
What is the name of this bony landmark?
Zygomatic process of the maxilla
bony projection of the maxilla that articulates with the zygoma or malar (cheek) bone
Radiography: J or U shaped radiopaque structure located superior to the max first molar region.
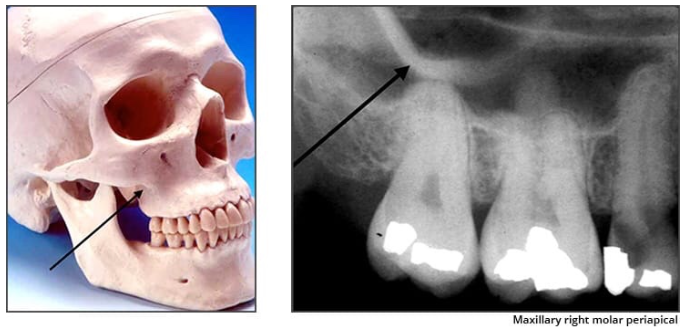
What is the name of this bony landmark?
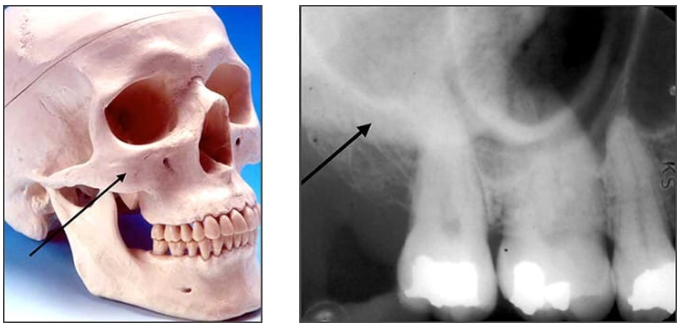
Zygoma/Zygomatic bone
articulates with the zygomatic process
Radiography: diffuse, radiopaque band extended posteriorly from the zygomatic process of the maxilla
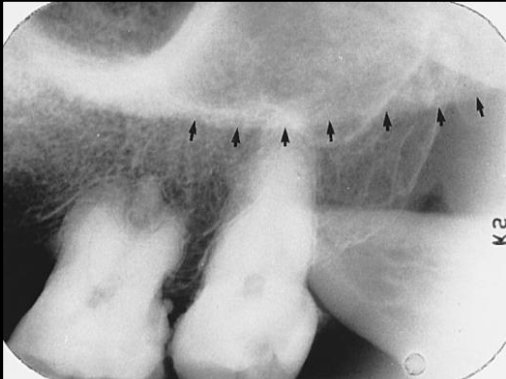
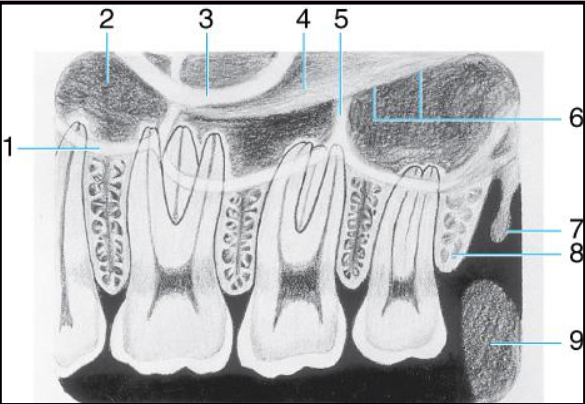
Label the structures 1-6 of the Maxillary premolar area
Floor of max sinus
maxillary sinus
zygomatic process
septum in maxillary sinus
zygoma
inferior border of the zygomatic arch.
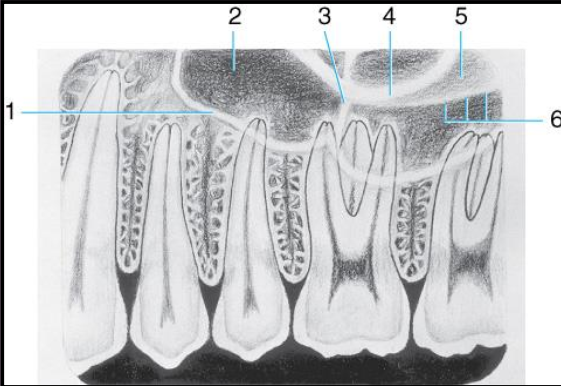
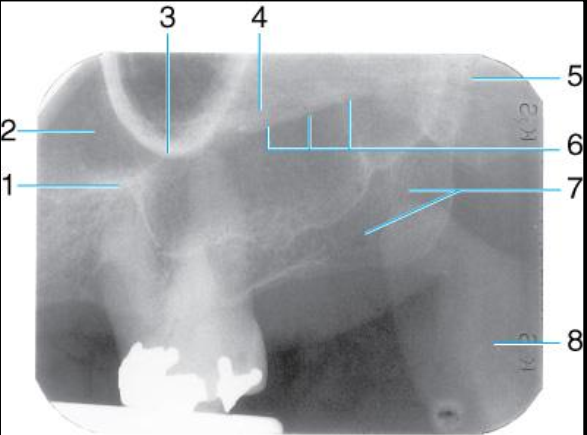
Label the structures 1-8 of the Maxillary molar area
border of max sinus
maxillary sinus
zygomatic process
zygoma
septum in max sinus
lower border of zygomatic arch
hamulus
maxillary tuberosity
coronoid process (mandible)
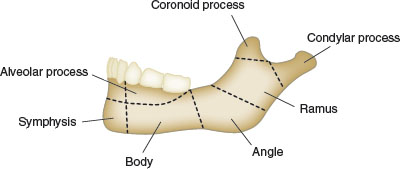
What are the 3 main parts that make up the mandible?
Ramus - vertical portion, posterior to the third molar
Body - horizontal u-shaped portion from ramus to ramus
alveolar process - encases and supports the teeth
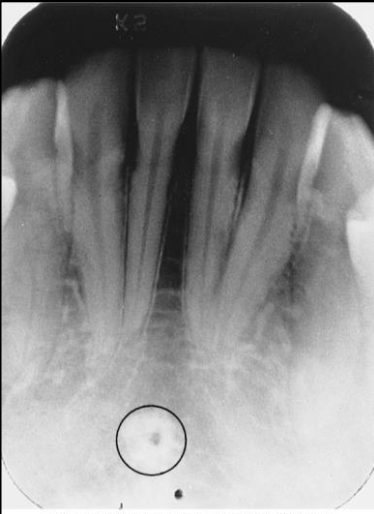
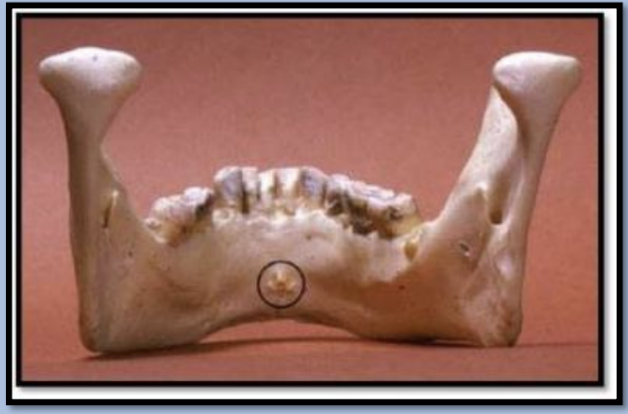
Genial tubercles
tiny bumps of bone on the lingual aspect of the mandible
attachment site for genioglossus and geniohyoid muscles
Radiography: ring-shaped radiopaque structure below the apices of the mandibular incisors
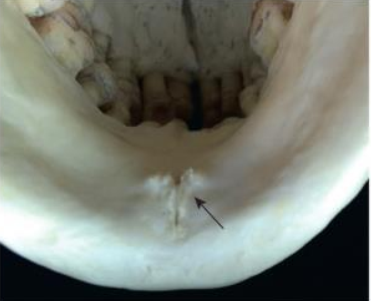
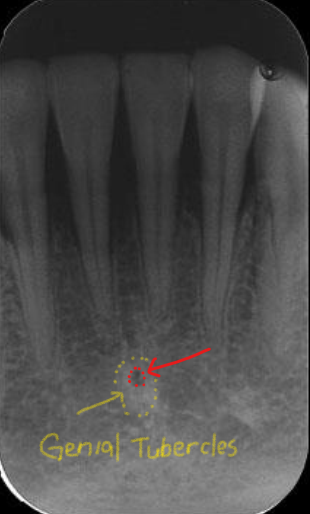
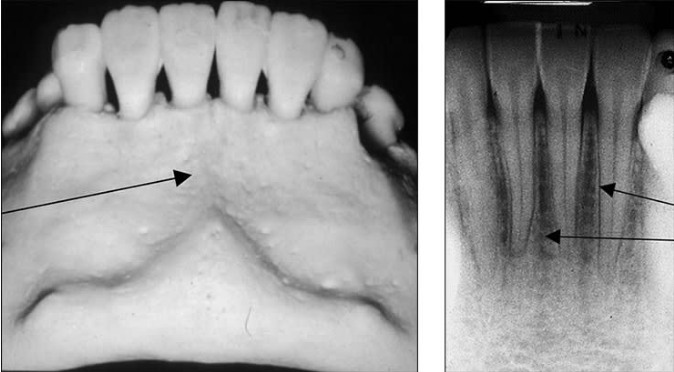
Lingual Foramen
tiny opening or hole in the bone located on the internal surface of the mandible (lingual)
inside the genial tubercles
Radiographic: small radiolucent dot inferior to the apices of the mandibular incisors
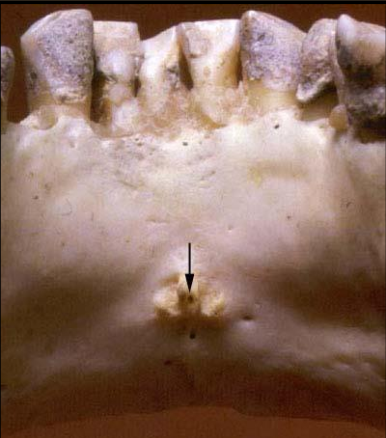
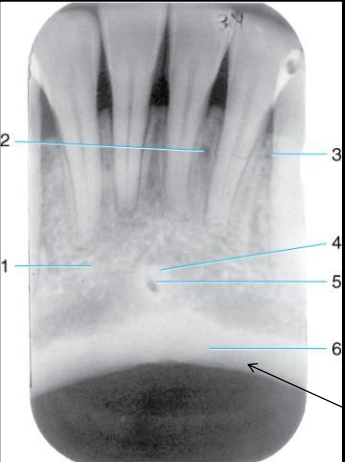
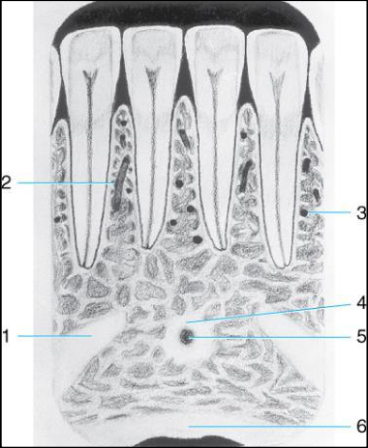
Label the structures 1-6 of the Mandibular midline area.
mental ridge
nutrient canal
nutrient foramen
genial tubercles
lingual foramen
inferior border of the mandible
Nutrient canal of mandible
vertical radiolucent lines seen in thin areas of bone.
most often seen in anterior portion of mandible.
Mental ridge
linear prominence of cortical bone located on the external surface of the anterior portion of the mand.
Radiography: thick radiopaque band from premolar region to the incisal region
often appears superimposed over the mandibular anterior teeth
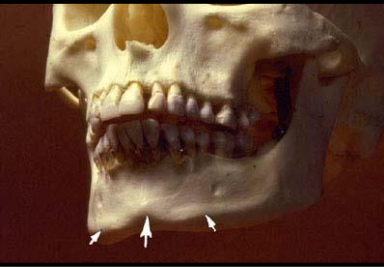
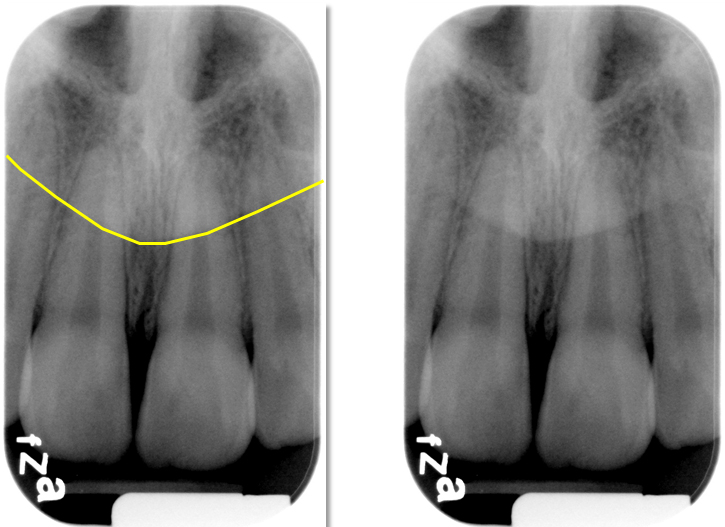
Mental fossa
scooped-out, depression of bone located on the external surface of the anterior mandible
Radiography: radiolucent area above the mental ridge
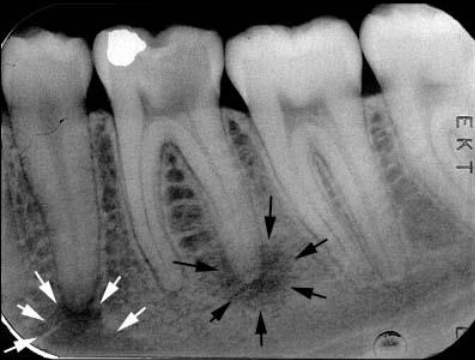
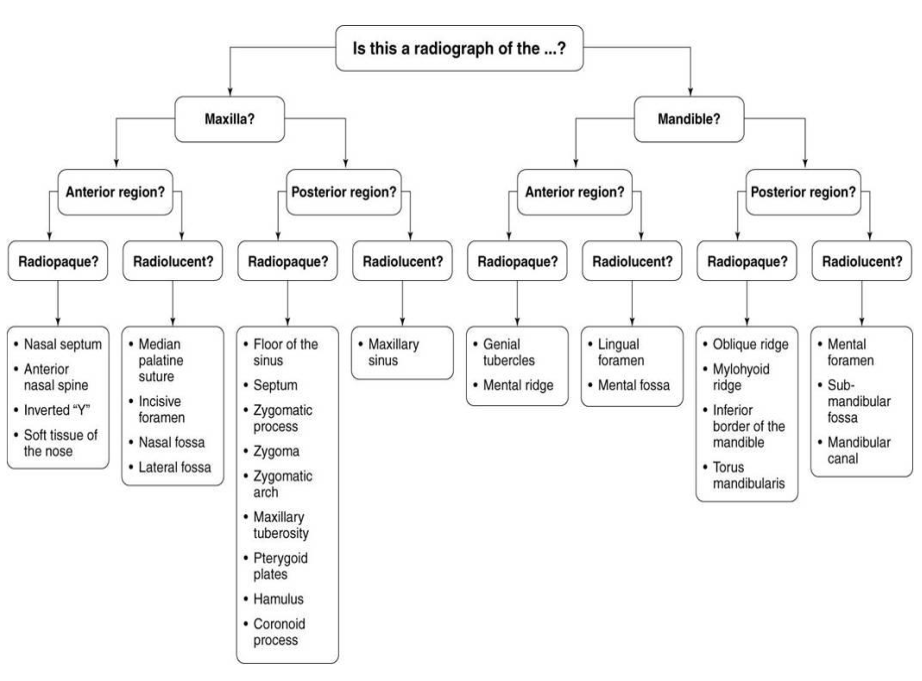
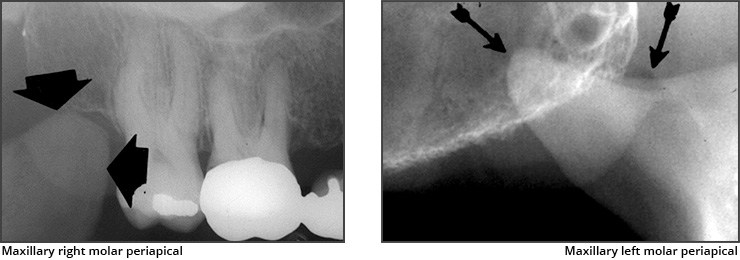
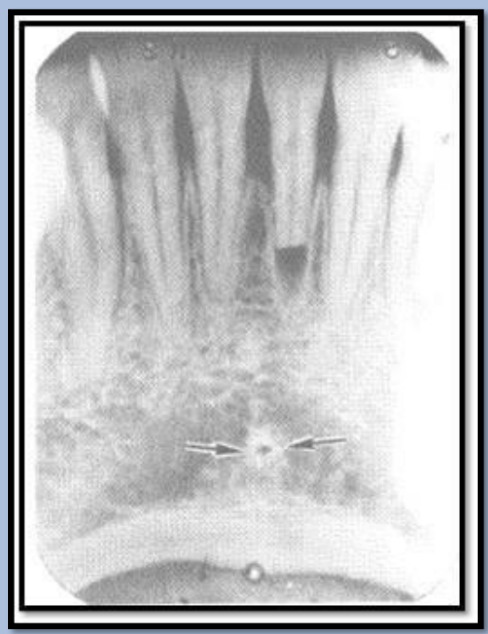
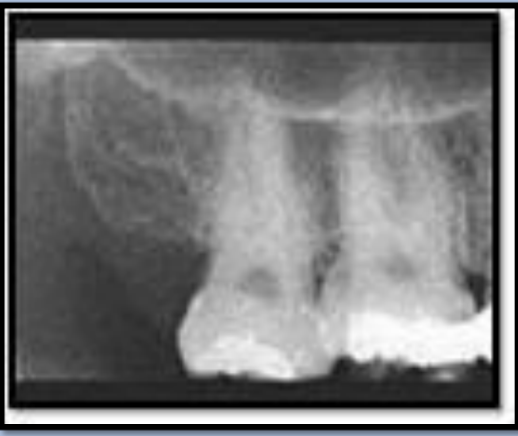
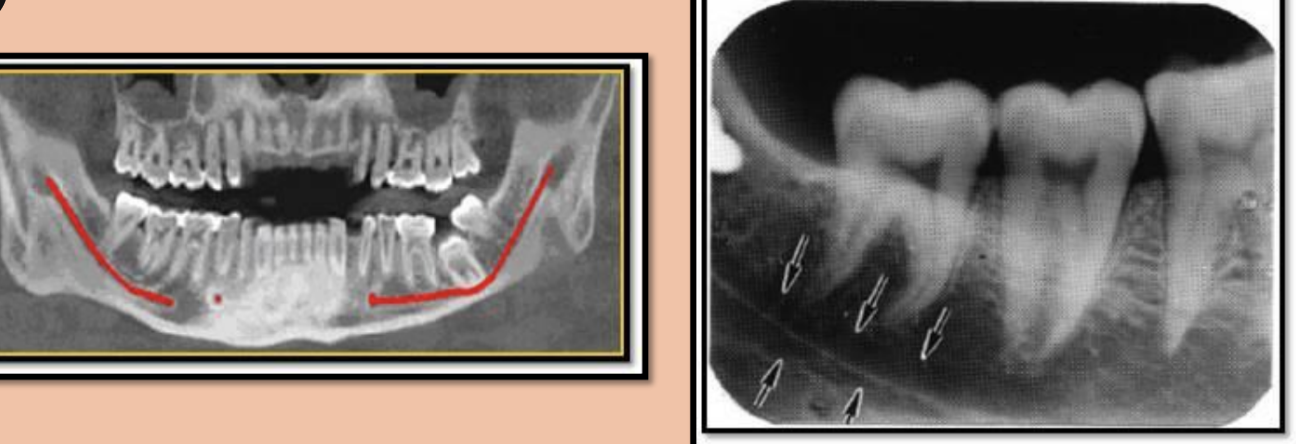
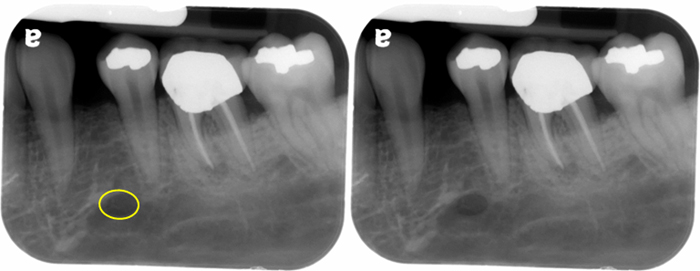
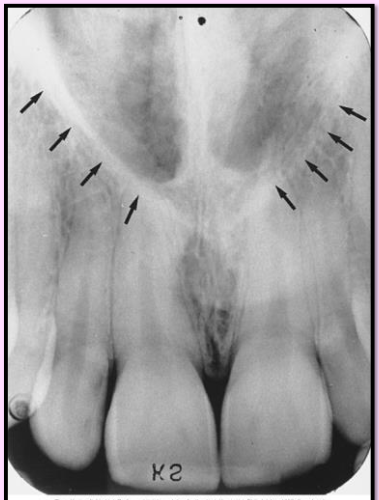
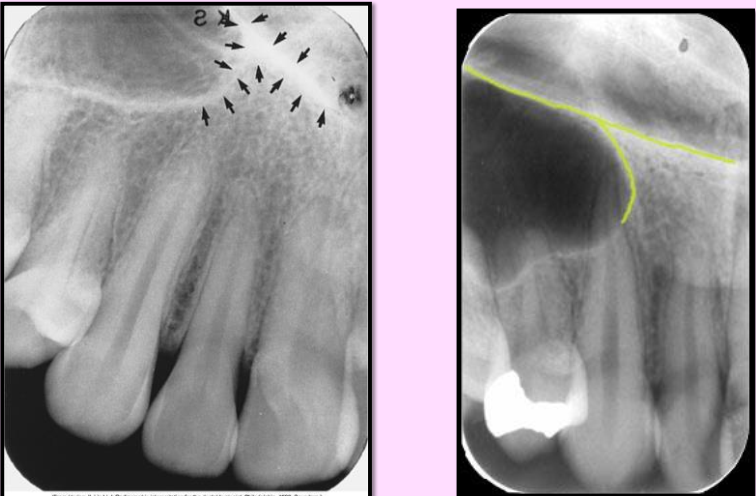
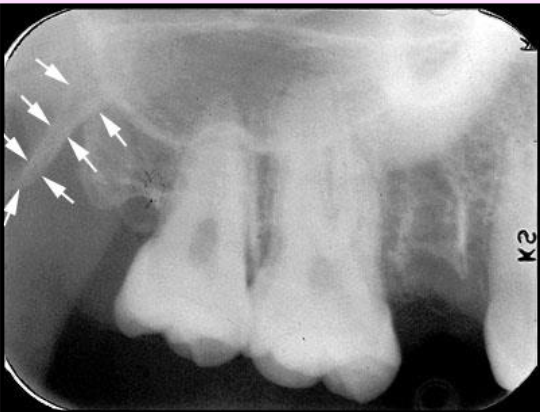
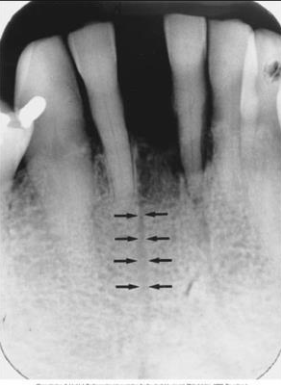
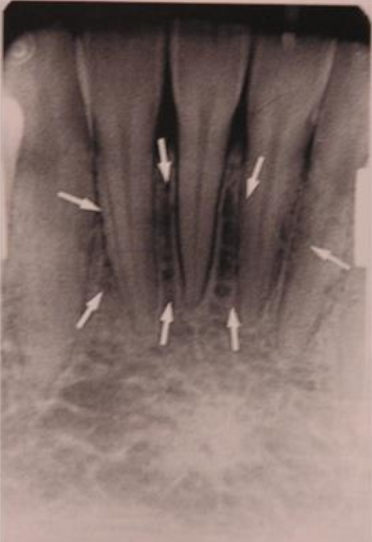
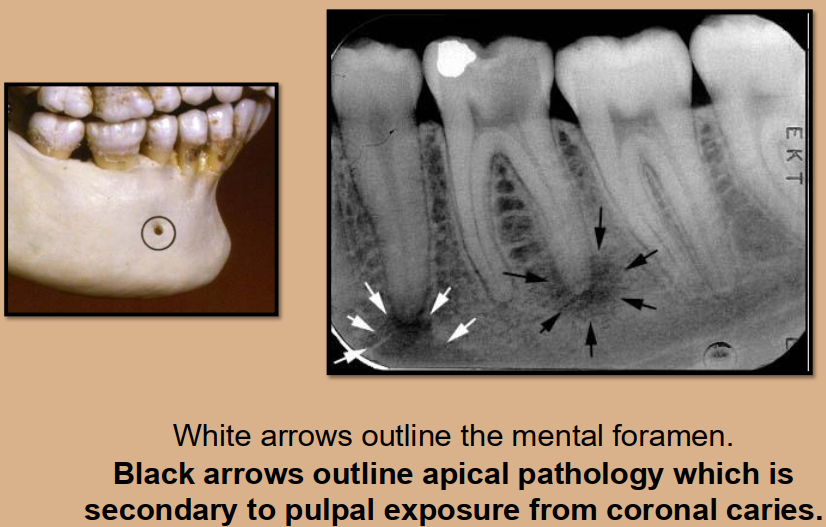
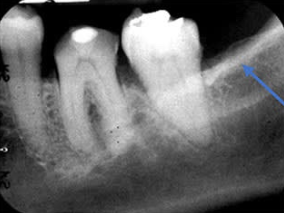
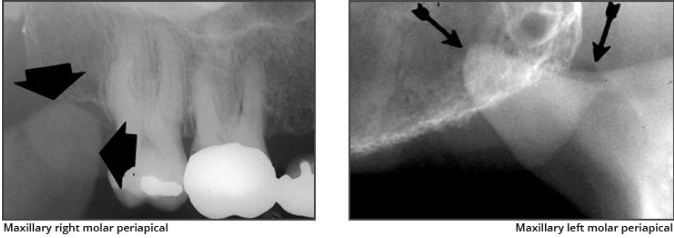
What is the bony landmark that the white arrows are pointing to?
Mental foramen
opening or hole in bone located by the mandibular premolar region
Radiography: small ovoid or round radiolucent area located in the apical region of the mand. premolars.
**frequently misdiagnosed as periapical lesion. → black arrows point to a real apical lesion
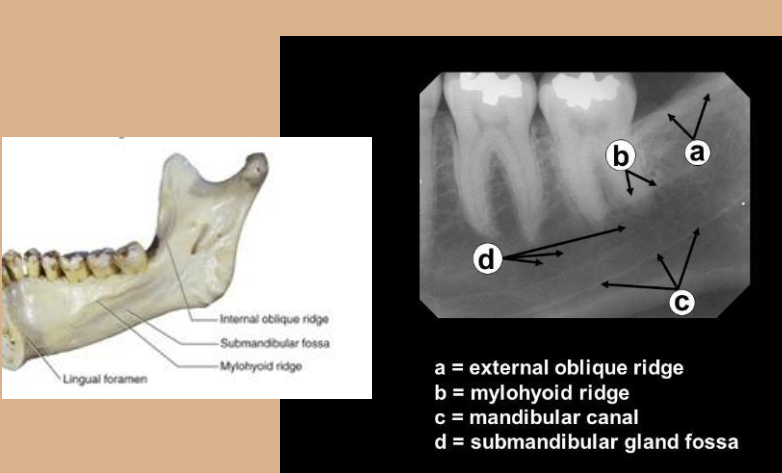
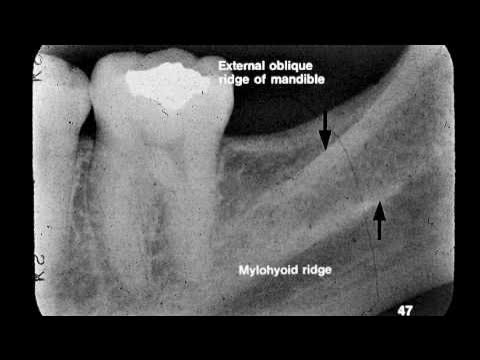
Mylohyoid ridge
linear prominence of bone located on the internal surface of the mand
Radiography: dense radiopaque band that extends downwards and forward from the molar region.
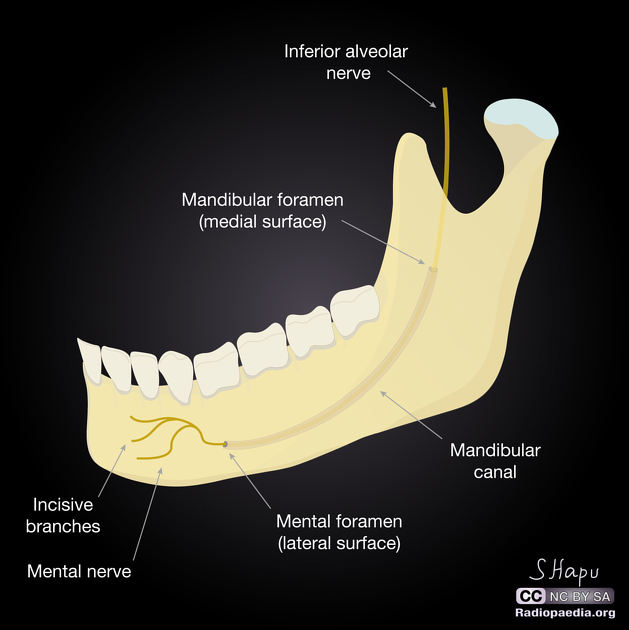
Mandibular canal
tube-like passageway through the bone travelling the length of the mandible; houses the inferior alveolar nerve and blood vessels
Radiography: a radiolucent band outlined by two thin radiopaque lines
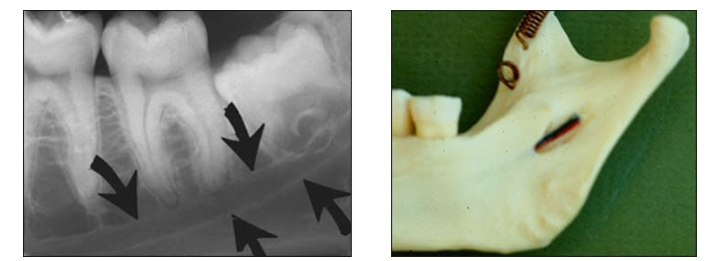
*not mylohyoid ridge
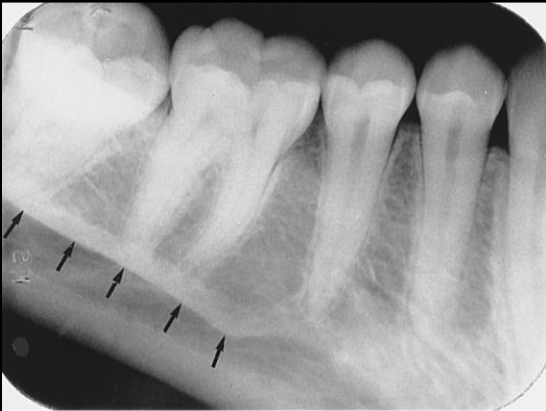
Internal Oblique Ridge
a linear prominence of the bone on internal surface of ramus
*also where mylohyoid ridge is; used for muscle attachment of the tongue
Radiography: radiopaque band that extends downward and forward from ramus
** when both internal and external oblique ridge is present, external is superior to internal
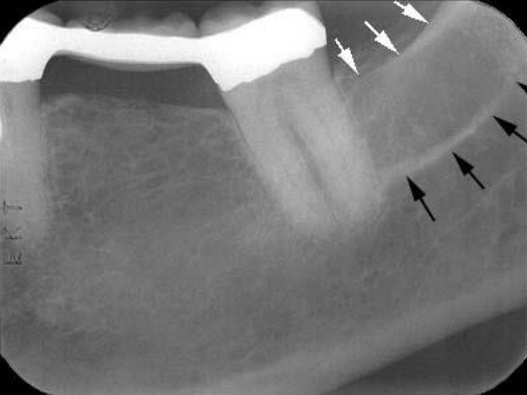
*white arrows
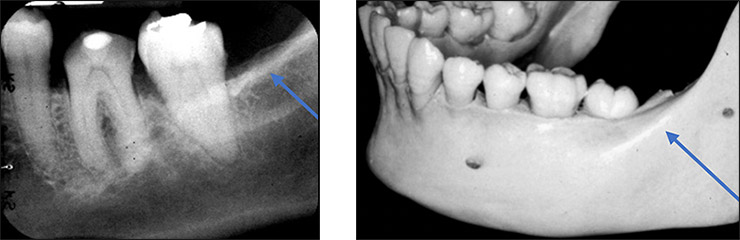
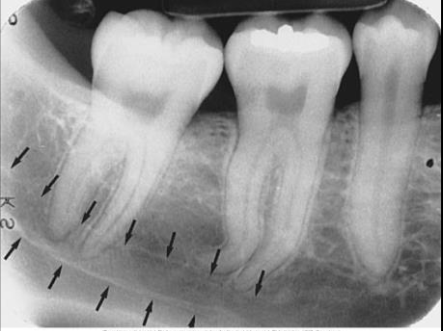
External Oblique Ridge
linear prominence located on the external surface of the body of the mandible
Radiography: radiopaque band extended downwards and forward from the anterior border of the ramus
** when both internal and external oblique ridge is present, external is superior to internal
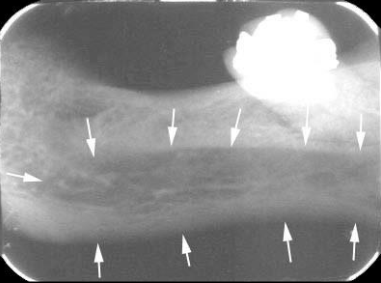
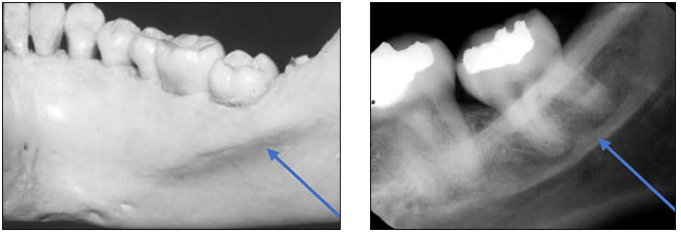
Submandibular fossa
scooped-out depression of the bone located on the internal surface of the mandible, inferior to the mylohyoid ridge
location of the submandibular salivary gland
Radiography: radiolucent area in the molar region below the mylohyoid ridge
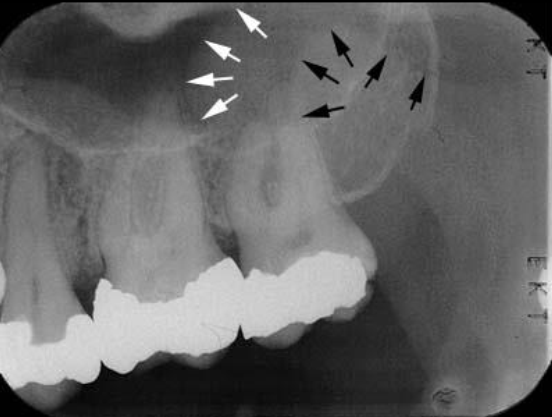
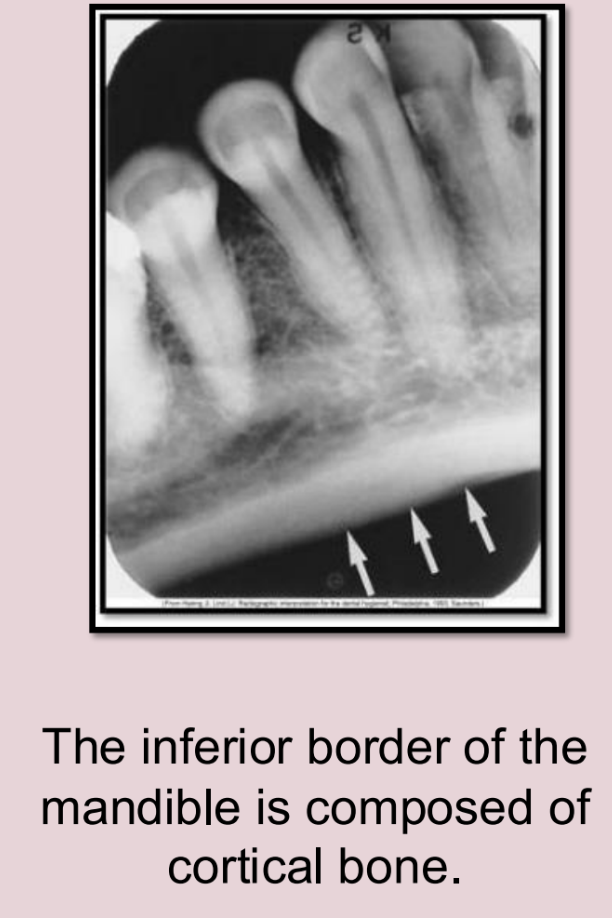
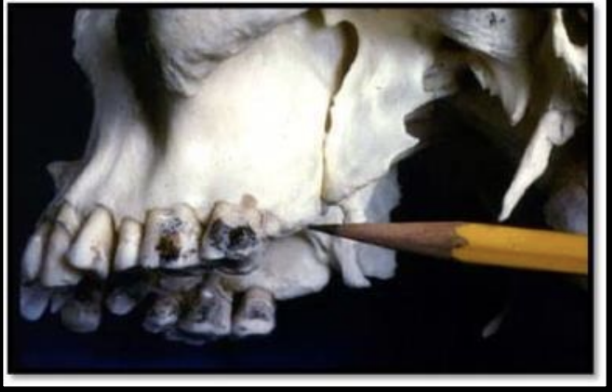
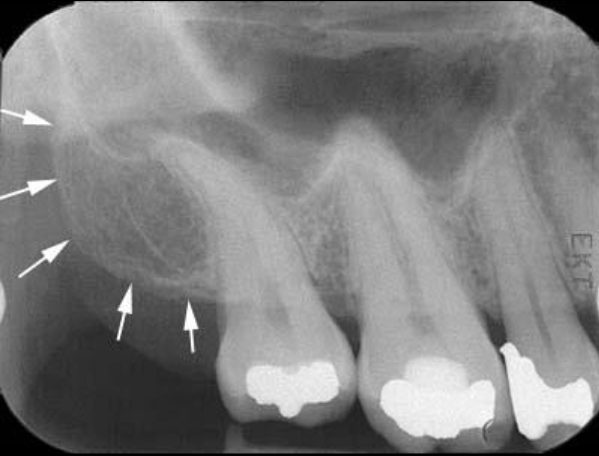
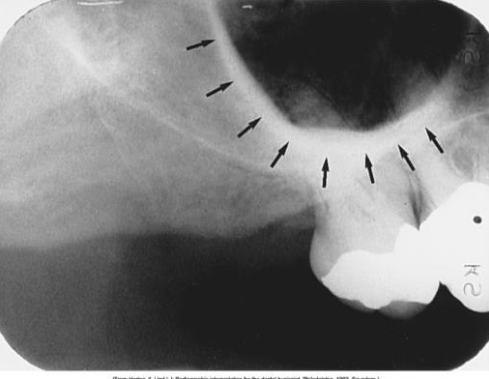
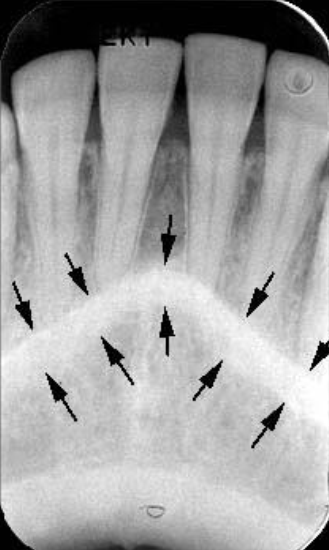
What is the bony landmark indicated by the black arrows?
Coronoid process
a prominence of bone on the anterior ramus of the mandible
Radiography: appears as triangular radiopacity with its apex divided & in the region of the third molar.
**The coronoid process is the only mandibular structure recorded on maxillary molar periapicals.
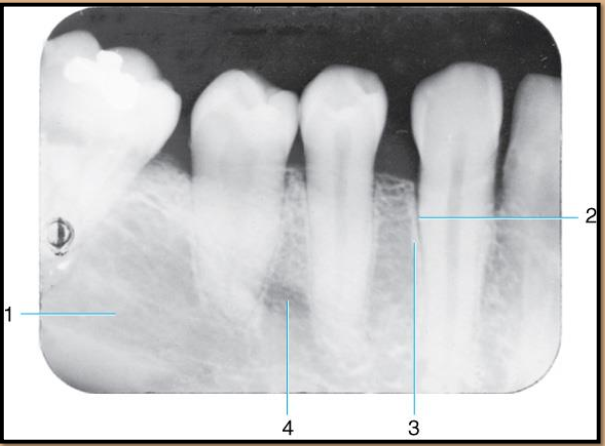
Label the landmarks 1-4 of the Mandibular Premolar Area
Submandibular fossa
PDL space -radiolucent
Lamina dura - radiopaque
Mental foramen
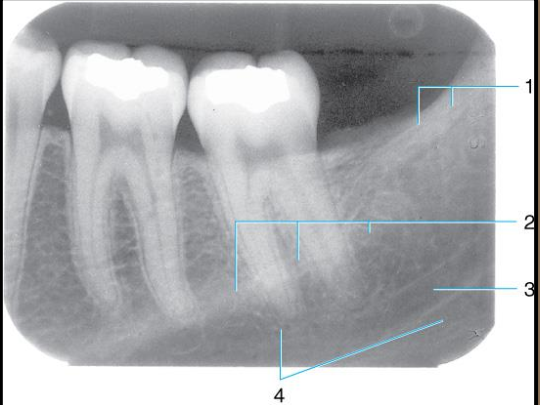
external oblique ridge
mylohyoid ridge or internal oblique ridge
mandibular canal
submandibular fossa
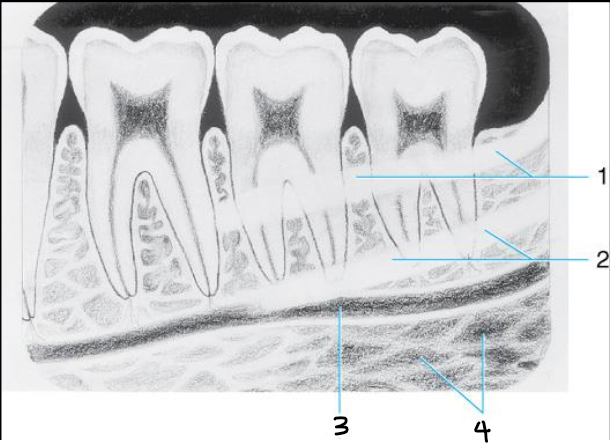
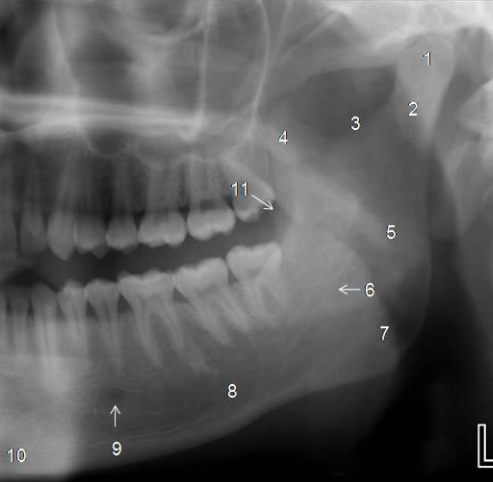
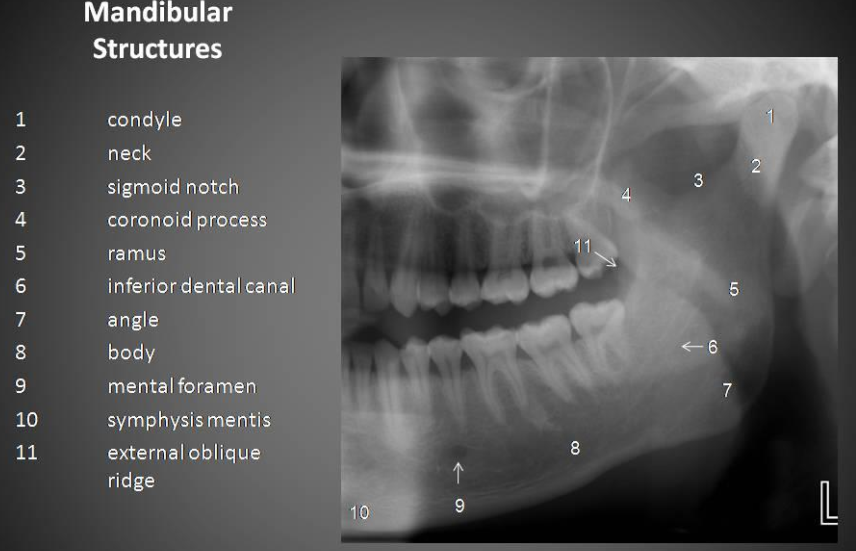
Label all the Mandibular structures.
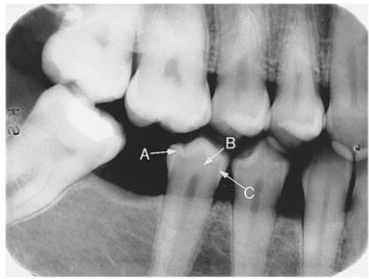
Label the structures
A - enamel
B - dentin
C - dentino-enamel junction
What are the 3 main anatomical landmarks of the alveolar bone? Describe each briefly.
lamina dura - wall of tooth socket; made of dense cortical bone; radiopaque line
alveolar crest - most coronal portion of the alveolar bone between teeth; radiopaque
periodontal ligament space - space between root and lamina dura; thin radiolucent line
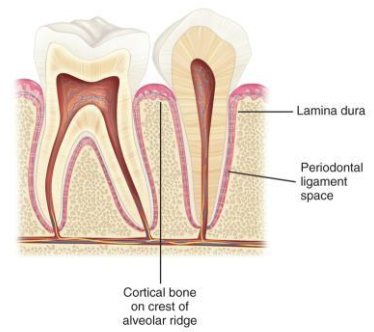
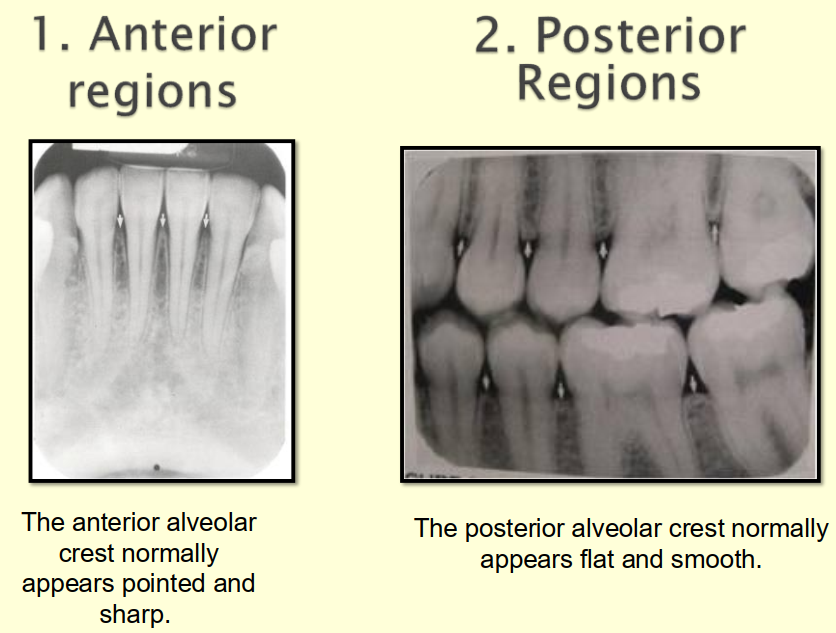
Compare and contrast the anterior and posterior regions of the alveolar bone on a radiograph.
Anterior alveolar bone
dense radiopaque line
Appears as a thin, pointed, corticated crest between teeth.
Height is close to the CEJ line.
Interdental septa are narrow and sharp.
Posterior alveolar bone
less dense and less radiopaque than anterior region
Appears as a broader, flat, less corticated crest between teeth.
Height still follows CEJ but less sharp.
Interdental septa are wider and more rounded.
Arrange these landmarks as radiolucent or radiopaque.