Skeletal System Teas Prep
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
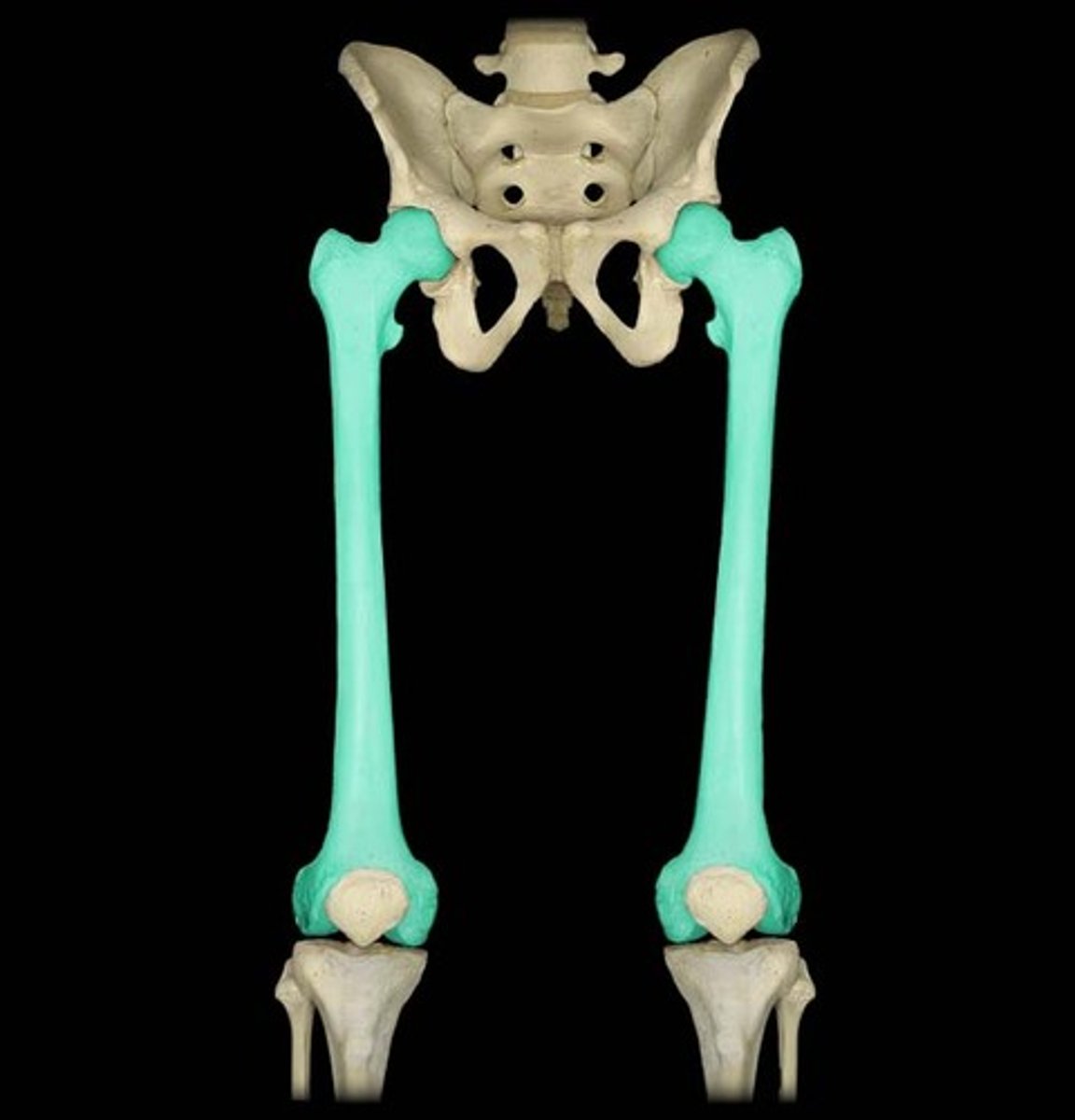
long bones
bones that are longer than they are wide; function primarily in movement and supporting the body weight; rod shaped; extremities (epiphyses) are covered in articular cartilage and are wider than the shaft (diaphysis); most of bones of upper and lower limbs are this as well as collar bones
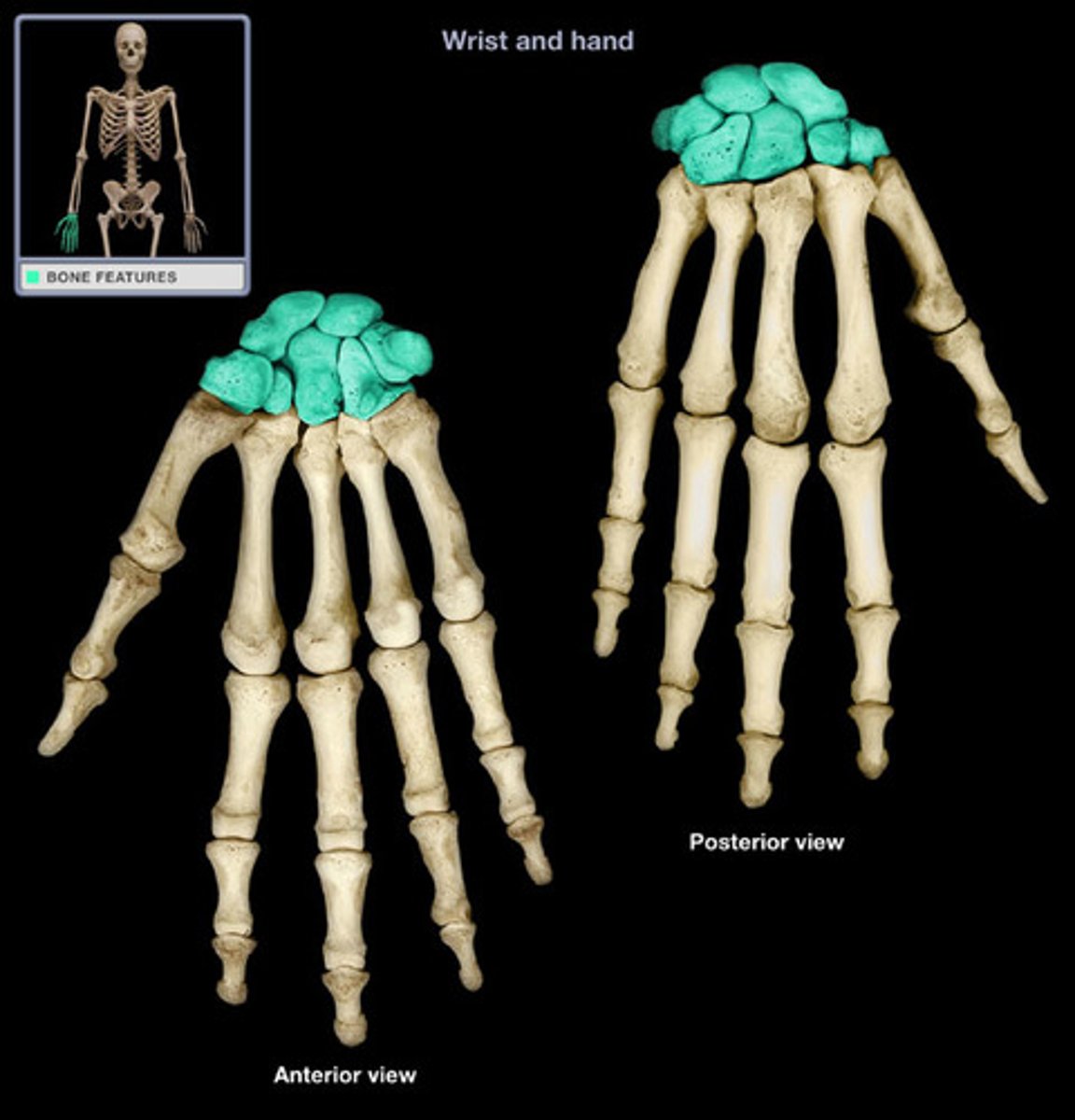
short bones
roundish or cube-shaped bones; have little to no role in movement; function in support and stability; ex: carpals, tarsals of wrist and ankle
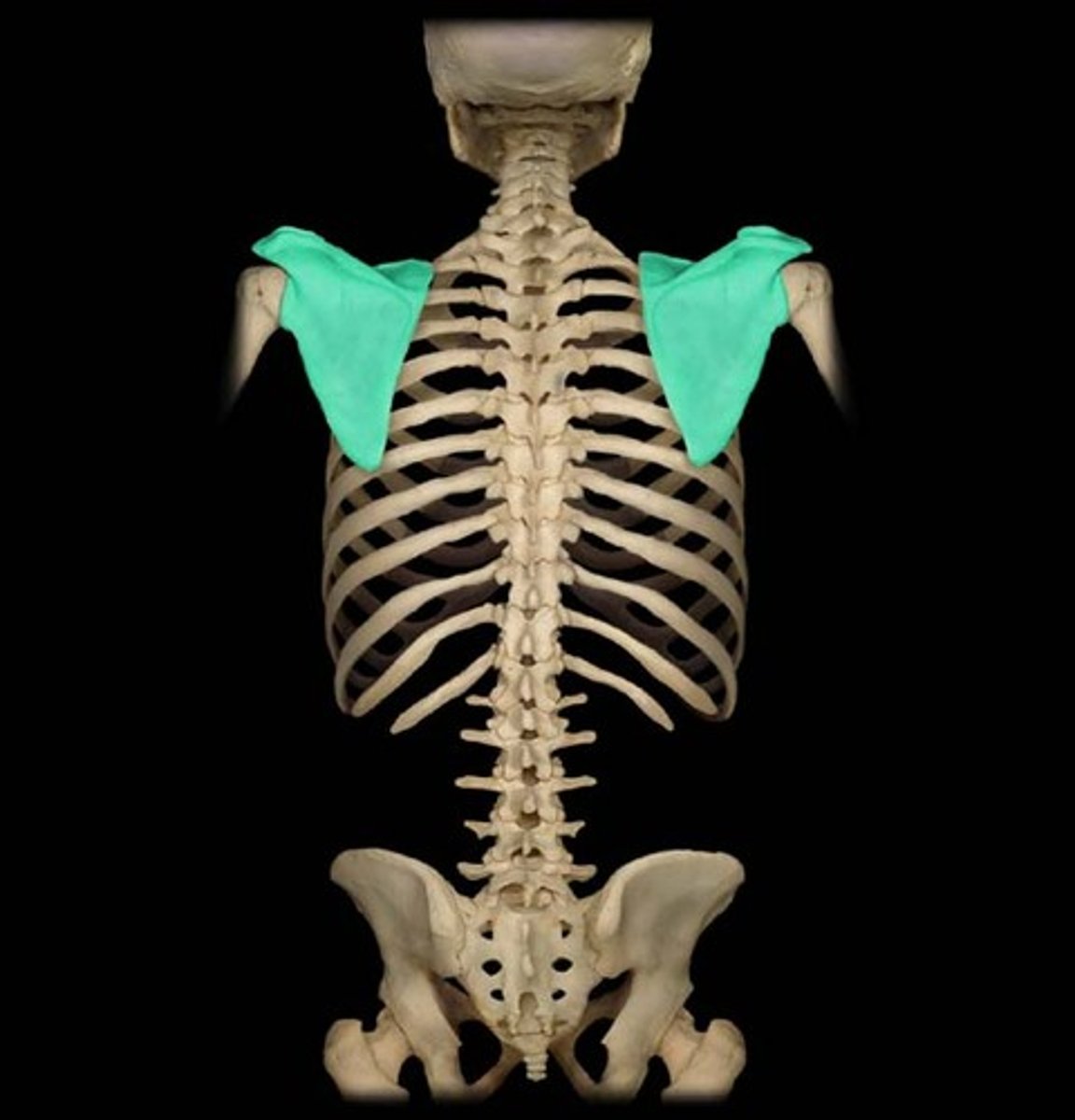
flat bones
bones that are flattened, thin and usually curved; broad shape for protection and muscle attachment; ex: scapulae, sternum, ribs, ilia of pelvic girdle, and certain cranial bones
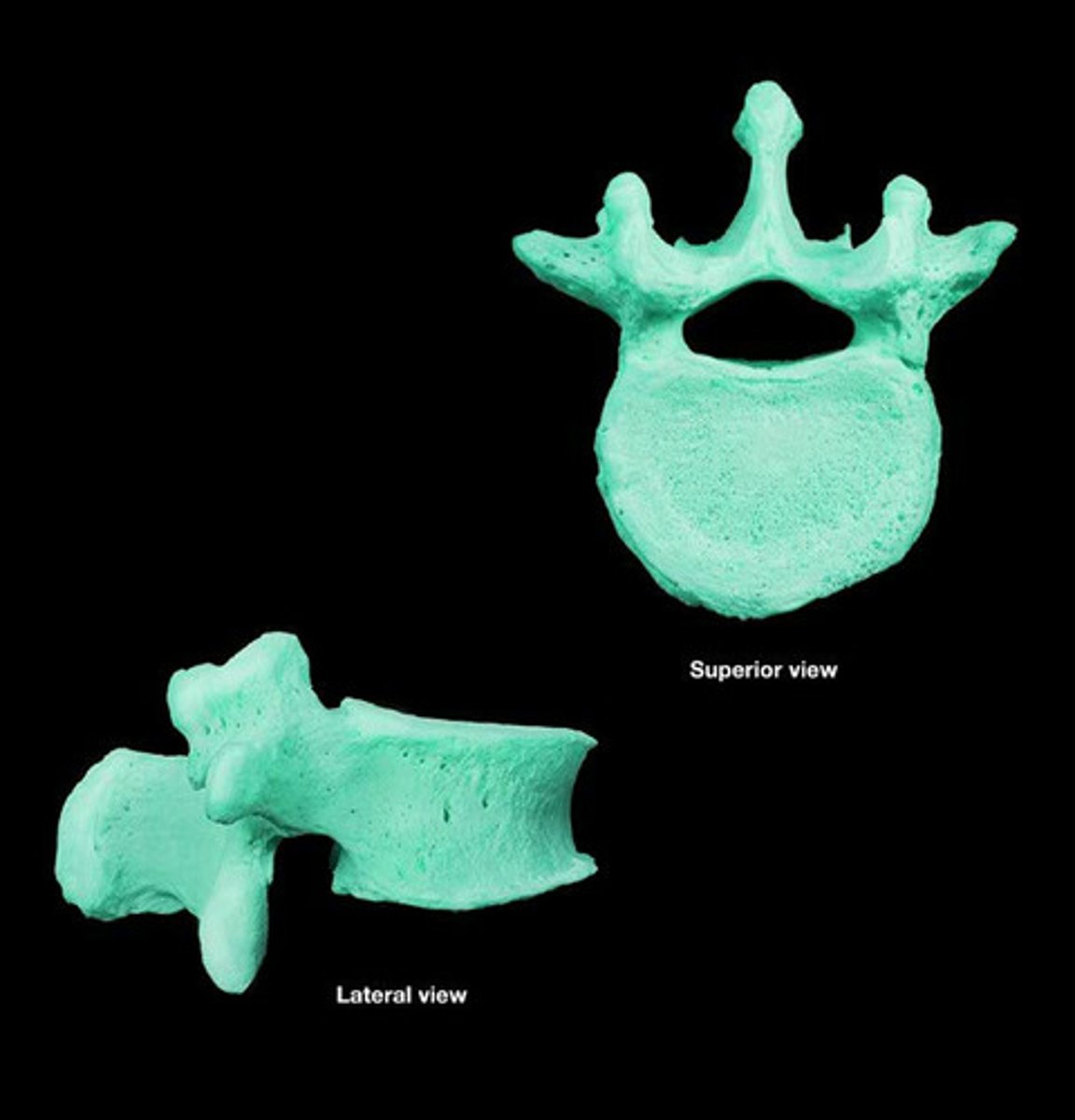
irregular bones
bones that have complex shapes with short, flat, notched or ridged surfaces; examples are vertebrae that form the spinal column and several bones in the skull; their form is suited for their specific function
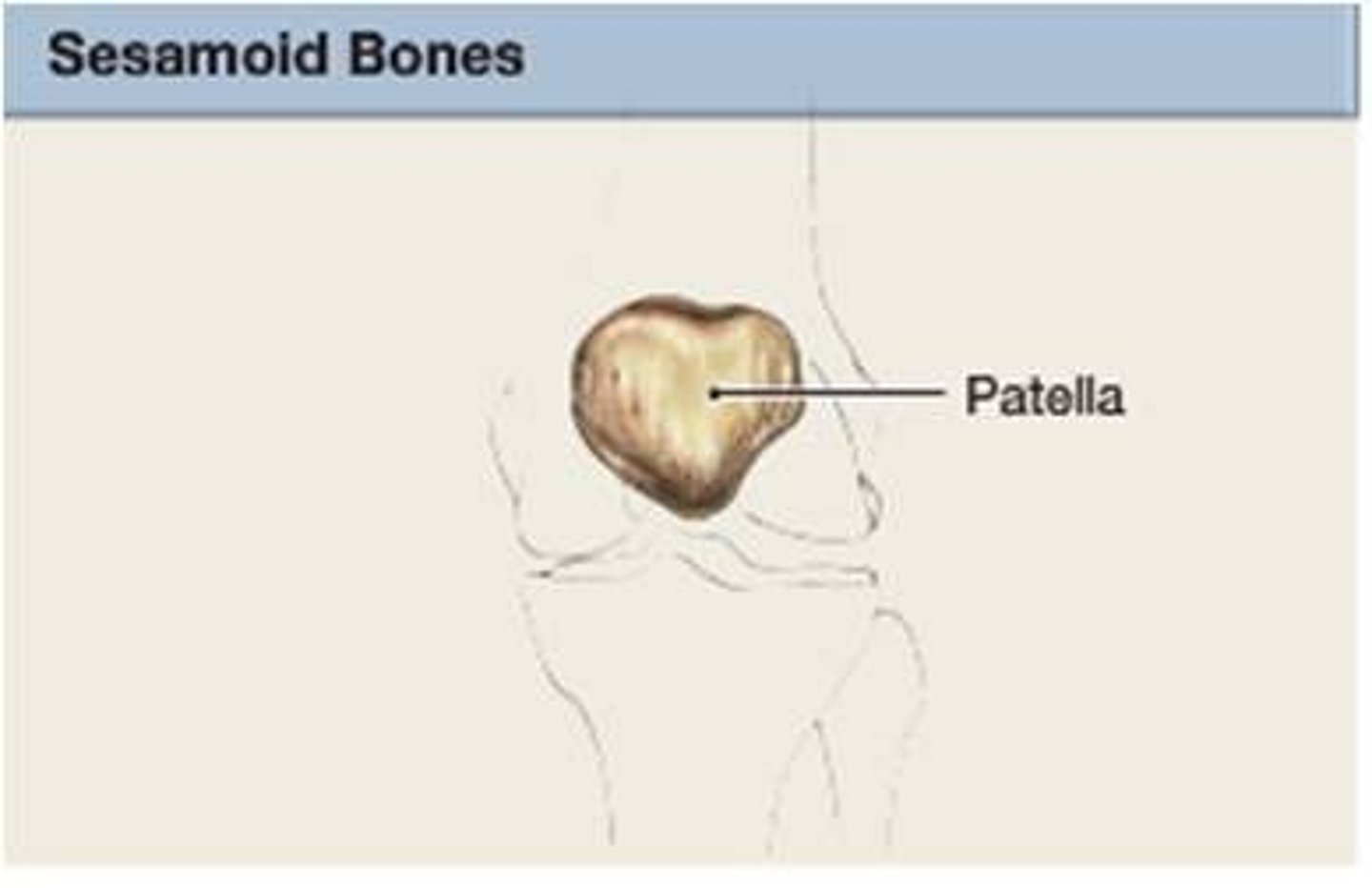
sesamoid bones
bones that are found embedded in tendons where there is a considerable amount of mechanical stress; ex: kneecap
compact (cortical) bone
hard, dense bone tissue, usually found around the outer portion of bones as well as the shafts of long bones; consists of cylindrical structures of osteons (Haversian systems)
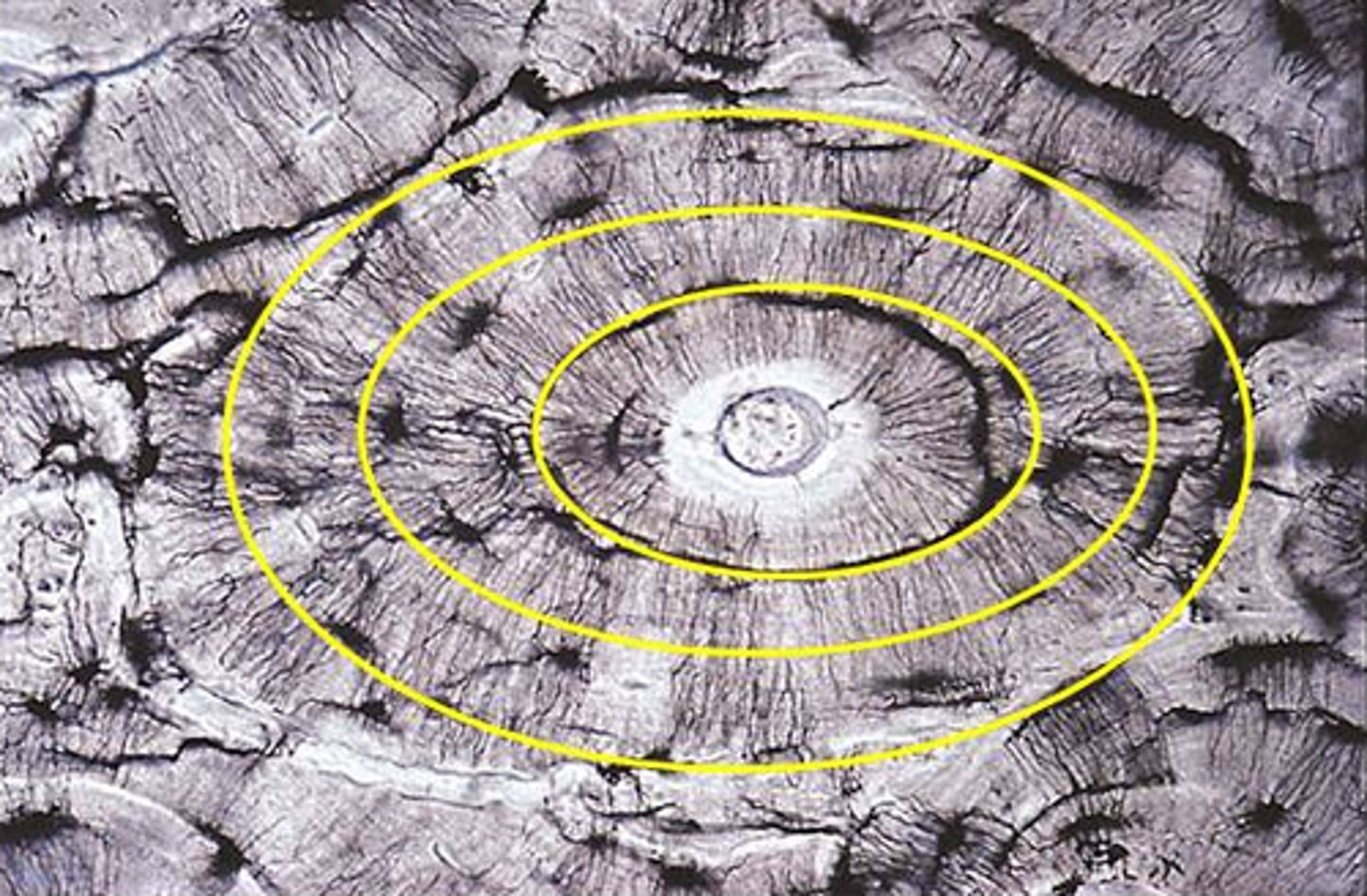
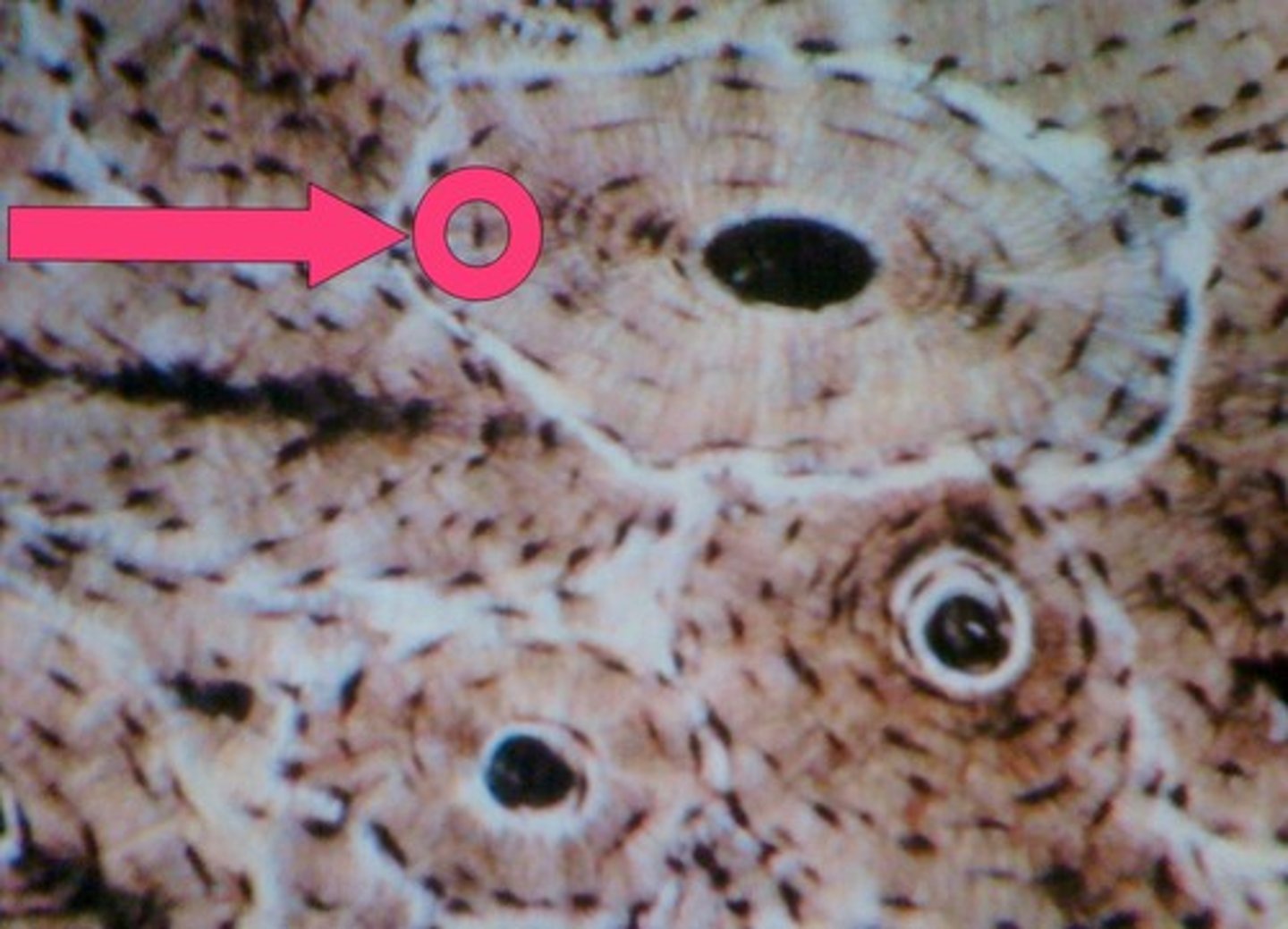
Osteon (Haversian system)
structural unit of compact bone; each consists of haversian canal that contains nerve fibers and blood vessels
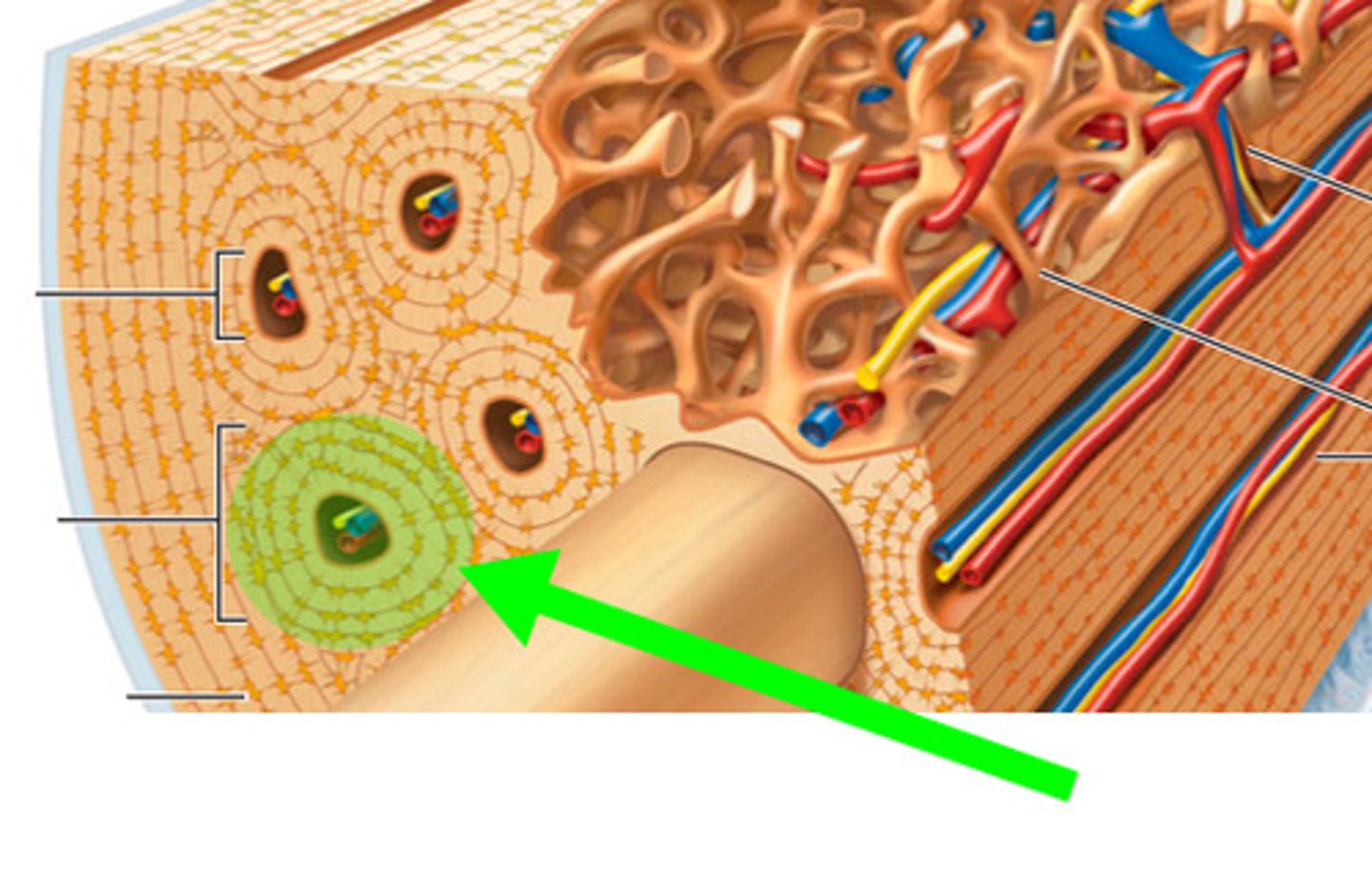
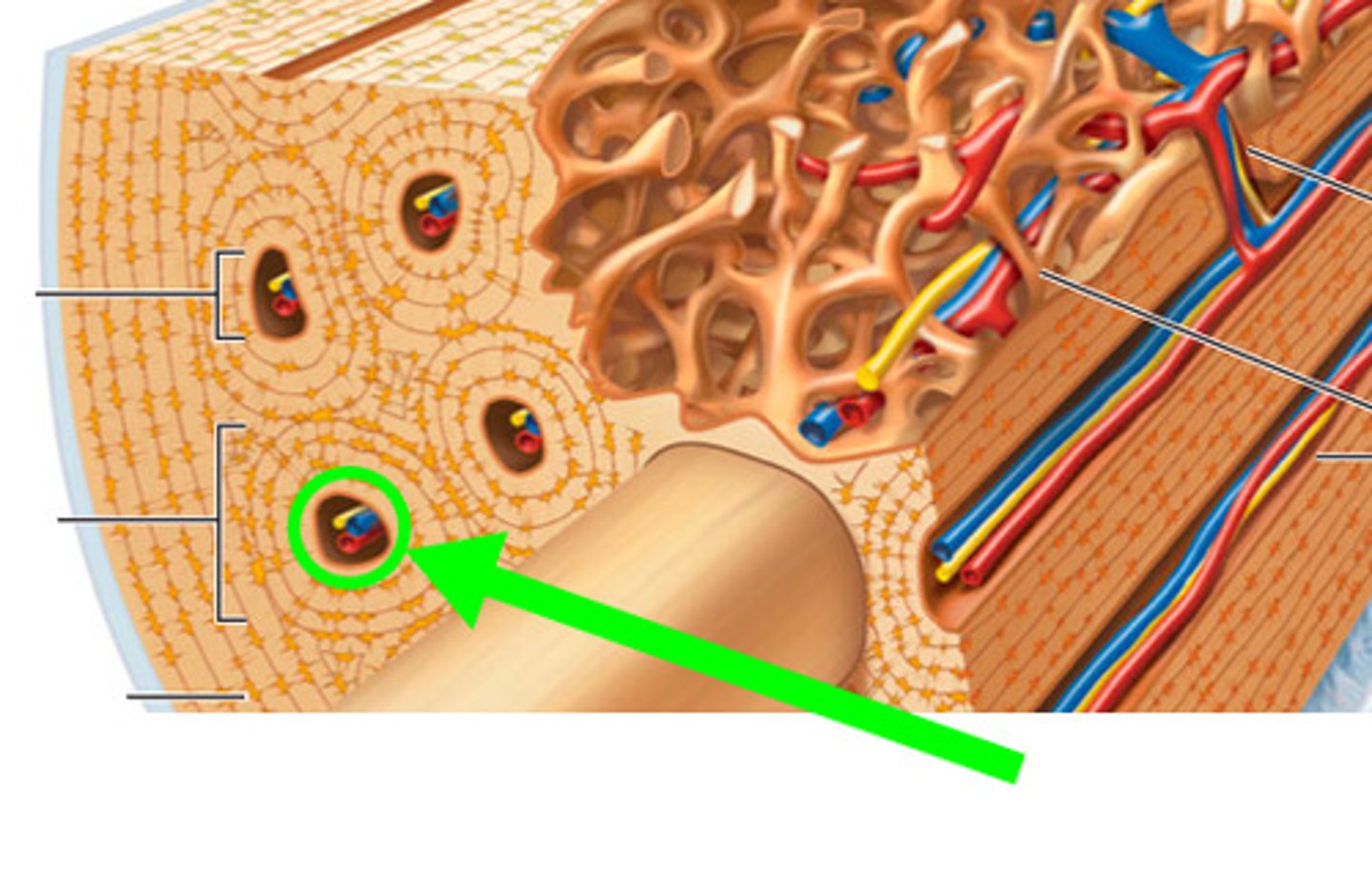
Haversian canal
one of a network of tubes running through compact bone that contains blood vessels and nerves; connect though perforating canals (Volkmann's canals); surrounded by concentric layers of calcified lamellae with small spaces of lucanae
perforating canals (Volkmann's canals)
Connect the haversian canals with each other and the periosteum.
Small channels in bone that transmit blood vessels from the periosteum into the bone and that communicate with the Haversian canals; provide energy and nourishing elements for osteons.
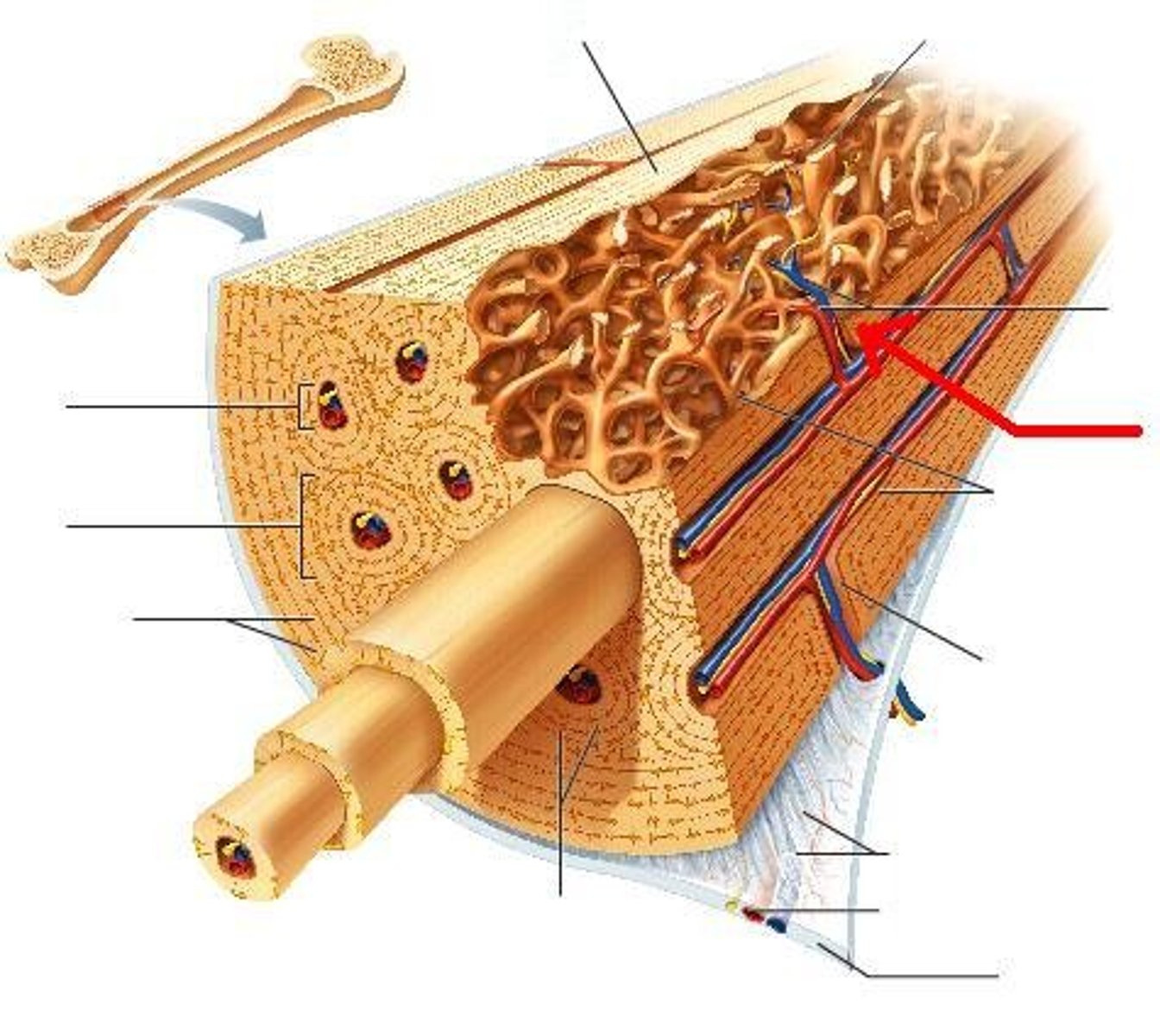
lamellae
calcified concentric rings made up of groups of hollow tubes of bone matrix; surround haversian canals
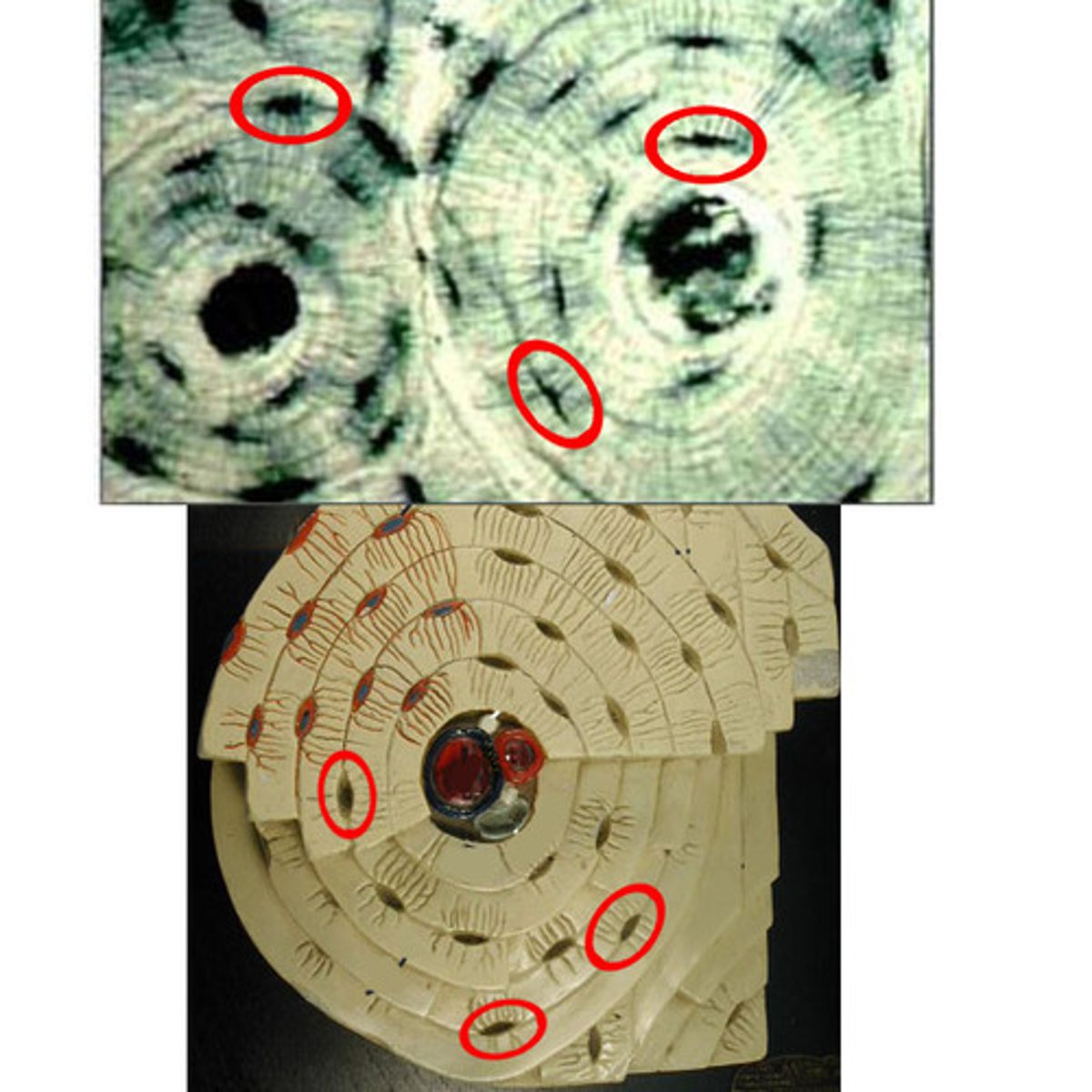
lacunae
small cavities in bone that contain osteocytes; connected to others by canaliculi to allow oxygen and nutrients to reach the osteocytes and for wastes to be removed
trabeculae
supporting bundles of bony fibers in cancellous (spongy) bone; flattened interconnected plates of spongy bone
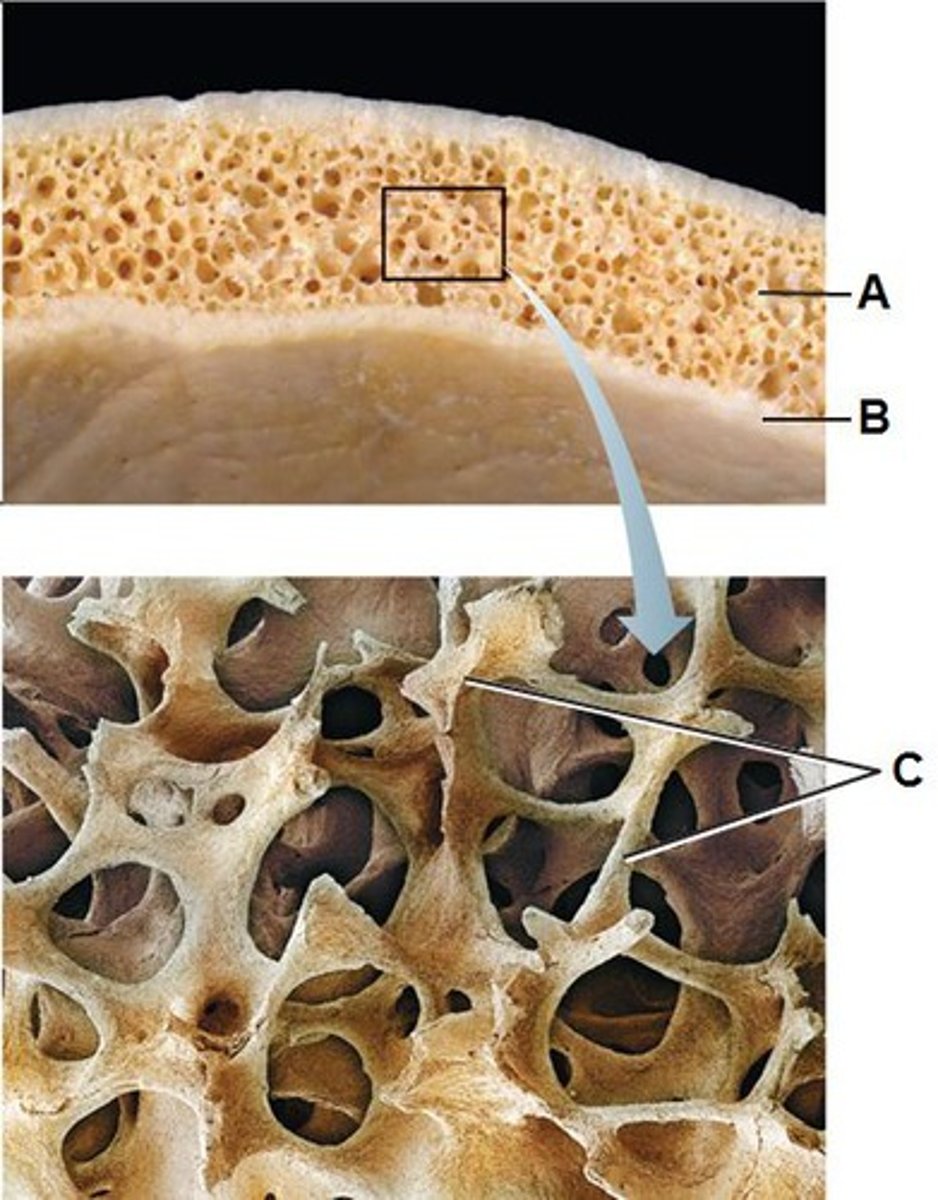
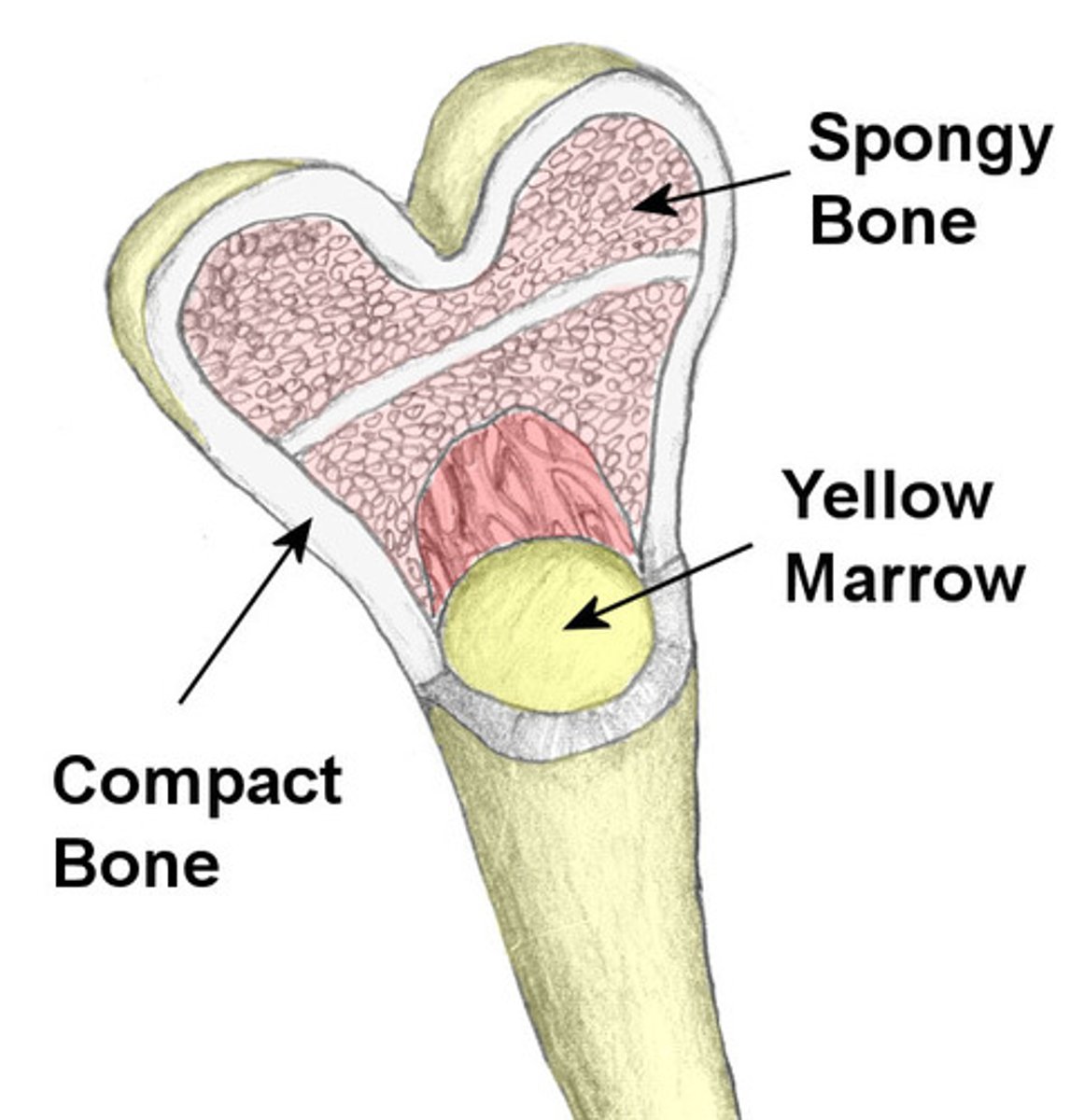
spongy (cancellous) bone
Bone tissue that consists of an irregular latticework of thin plates of bone called trabeculae; porous tissue; found inside short, flat, and irregular bones and in the epiphyses of long bone; not as strong or abundant as compact bone and does not contain osteons; no central canals but osteocytes reside in lacunae that are connected by canaliculi
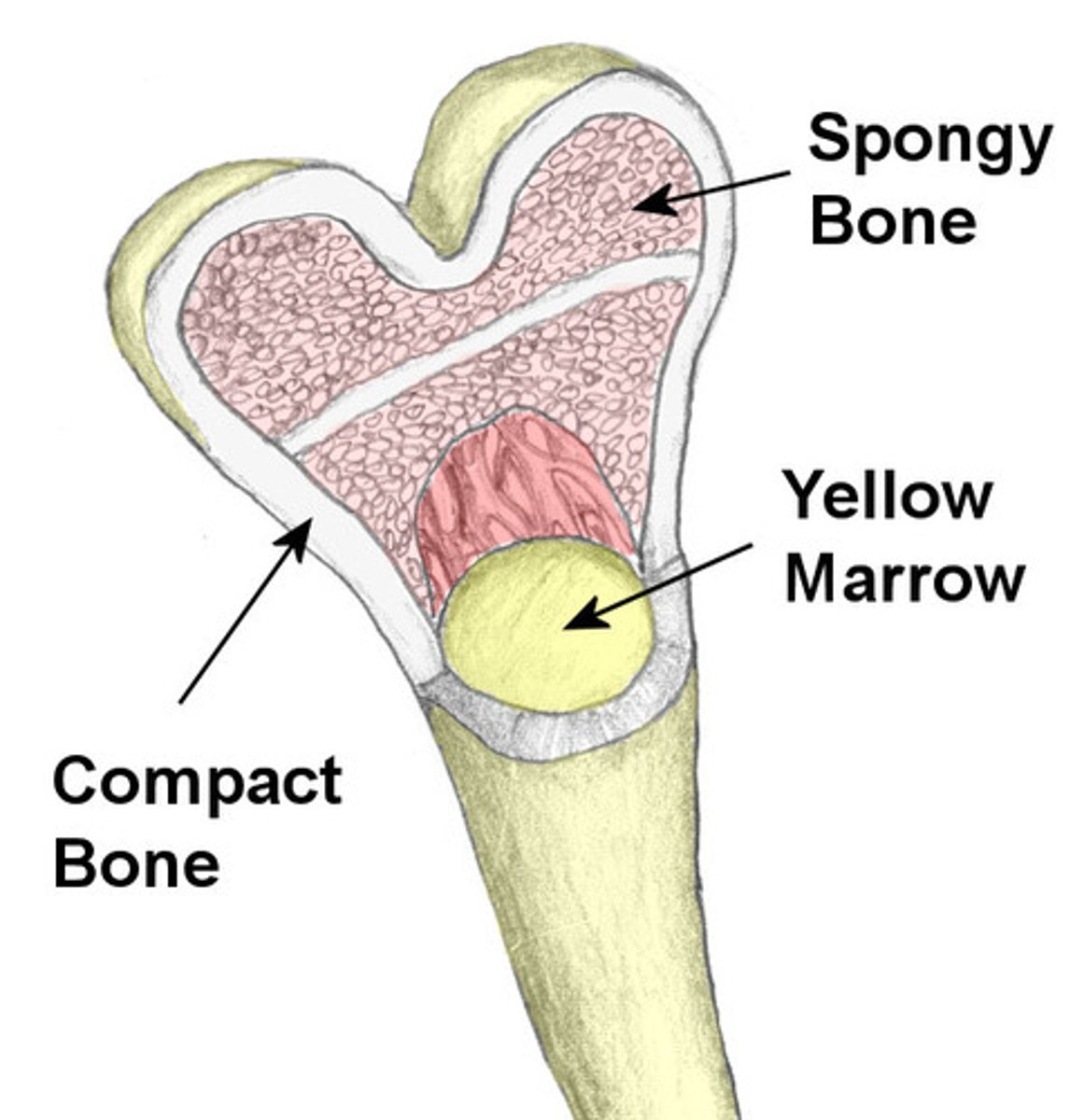
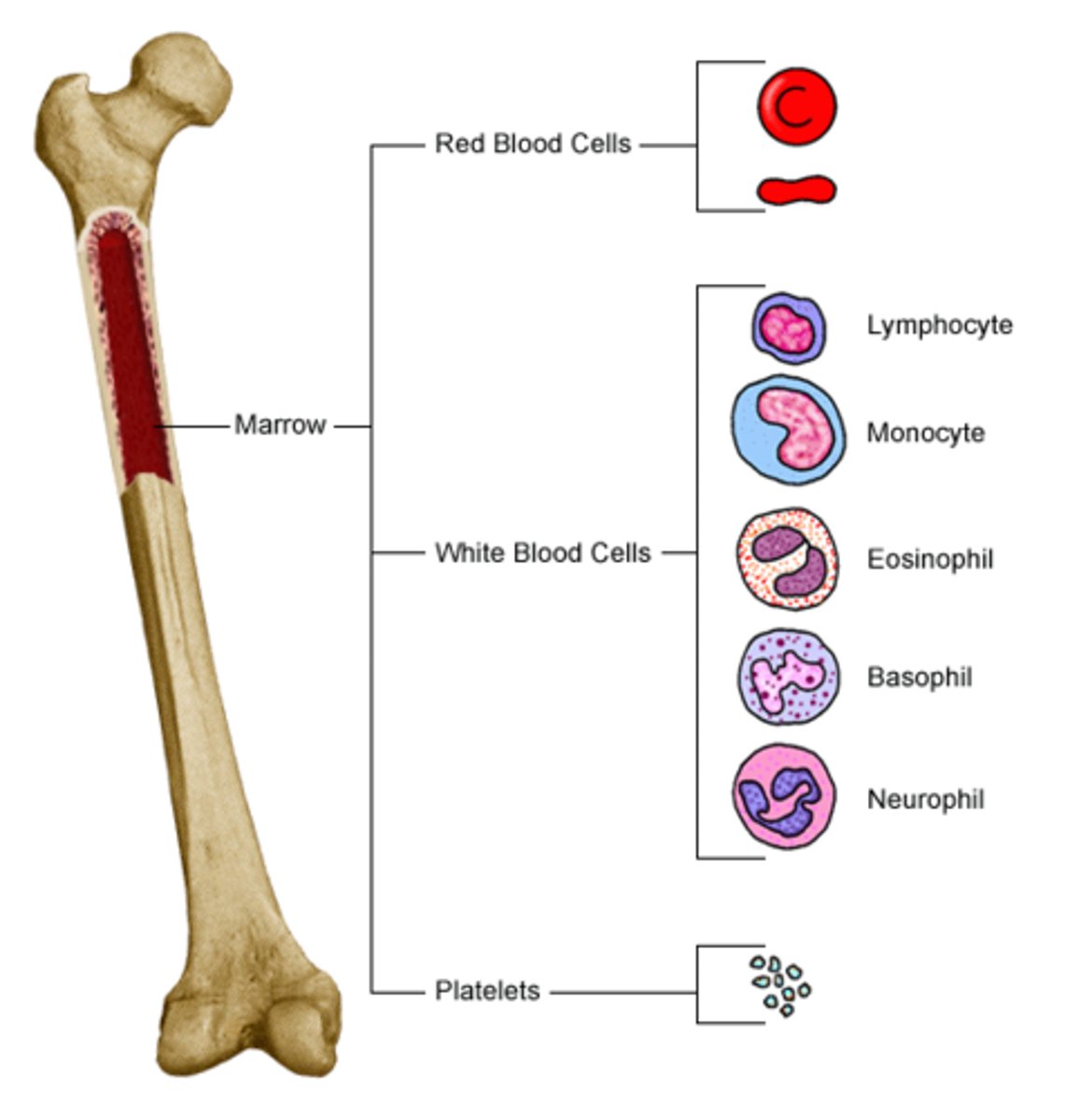
red bone marrow
located within the spongy bone, is hemopoietic tissue that manufactures red blood cells, hemoglobin, white blood cells, and thrombocytes
osteoblasts
bone forming cells derived from osteoprogenitor cells; take calcium from blood and produce the matrix (including collagen fibers) that form bone; differentiate into mature bone cell when it is completely encased in matrix
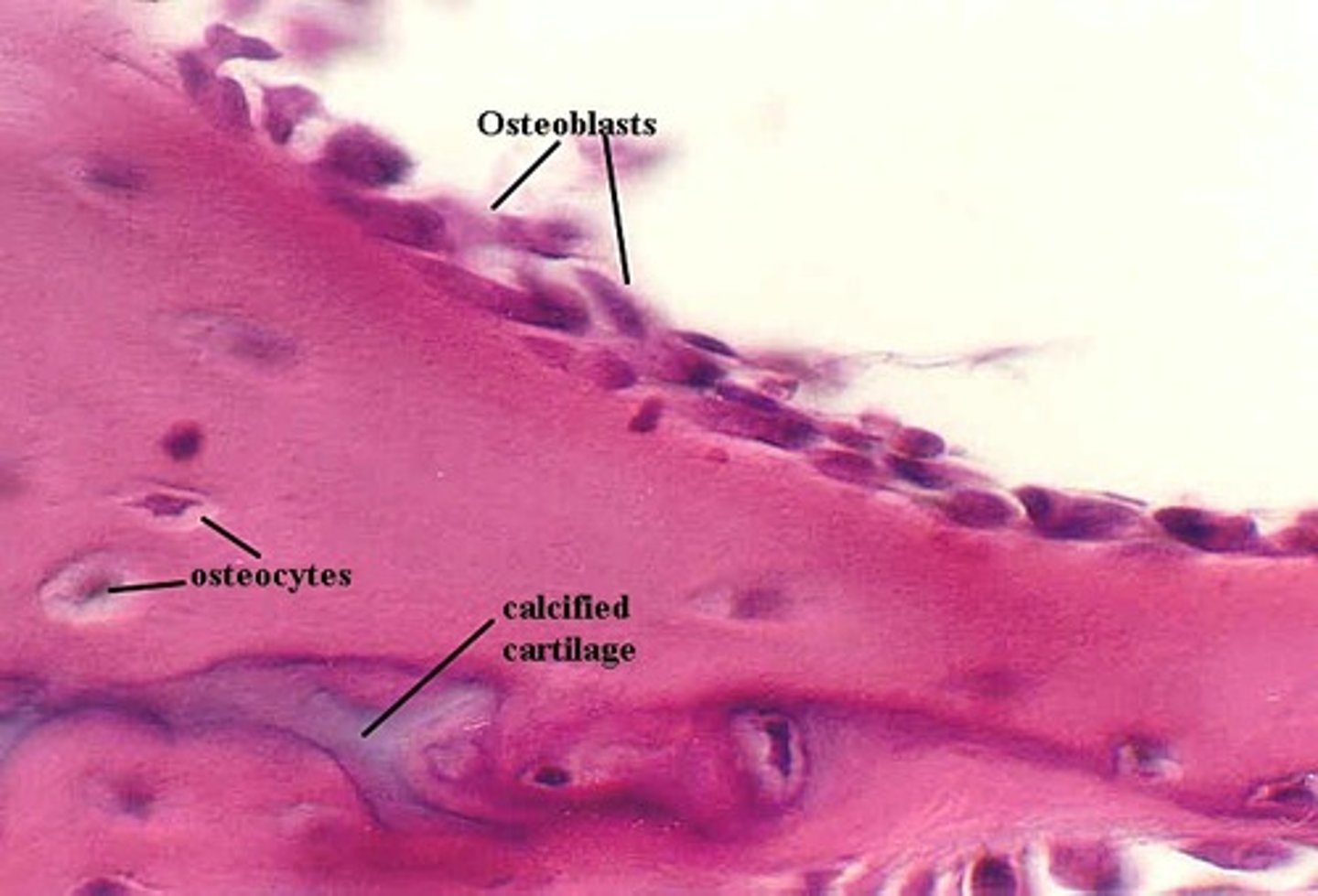
osteocyte
mature bone cell formed from differentiation of osteoblasts; most abundant bone cells; maintain matrix by recycling calcium slats
osteoclasts
large multinucleate cells that are formed by fusion of monocytes (large WBC); reside on bone surfaces and secrete acid and digestive enzymes that break down and return calcium to blood
joint
A place in the body where two bones come together/connect; classified by material holding it together (structure) and range of motion (function)
fibrous joint
immoveable and held together by ligaments (fibrous connective tissue) only
types: suture, gomphosis, syndesmosis
cartilaginous joint
held together by cartilage
types: synchondrosis, symphysis
Synovial joint
most common type of joint; characterized by joint cavity filled with synovial fluid
types: pivot, hinge, saddle, gliding, condyloid, ball and socket
suture joint (fibrous)
type of fibrous joint; immovable - ex: skull
Gomphosis joint (fibrous)
type of fibrous joint immovable - ex: teeth/mandible
Syndesmosis joint (fibrous)
type of fibrous joint - slightly moveable - ex: distal tibiofibular joint
synchondrosis joint (cartilaginous)
type of cartilaginous joint- hyaline cartilage, nearly immovable - ex: first rib/sternum
symphysis joint (cartilaginous)
type of cartilaginous joint - fibrocartilage, slightly moveable - ex: intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis
pivot joint (synovial)
type of synovial joint; allows for rotation - ex: atlantoaxial joint
hinge joint (synovial)
type of synovial joint; allows movement in one plane (ex: knee)
saddle joint (synovial)
type of synovial joint; type of joint found at the base of each thumb; allows grasping and rotation; allows pivoting in 2 planes and axial rotation: ex: 1st metacarpal/trapezium
gliding joint (synovial)
type of synovial joint that allows one bone to slide over another; found in wrist and ankles (carpals)
condyloid joint (synovial)
type of synovial joint that does everything except rotating; allows pivoting in 2 planes but no axial rotation; ex: radiocarpal joint
ball and socket joint (synovial)
type of synovial joint that has the highest range of motion; ex: hip
synarthrosis joint
immovable joint - either fibrous or cartilaginous: ex: skull sutures, teeth/mandible (type of joint by function)
amphiarthrosis joint
slight range of motion, either fibrous or cartilaginous; ex: intervertebral discs, distal tibiofibular joint (type of joint by function)
diarthrosis joint
freely movable joint - always synovial; ex: wrist, knee, shoulder (type of joint by function)
bones
provide a resting ground for muscles (attachment points for muscles) and protection of vital organs and body; reservoir for calcium
ligaments
Connect bone to bone and help stabilize joints; composed of dense regular connective tissue consisting of bundles of collagen fibers and elastic fibers; more elastic than tendon; yellow due to protein elastin
tendons
Connect muscle to bone; composed of dense regular connective tissue consisting fo bundles of collagen fibers and elastic fibers; tougher than ligament
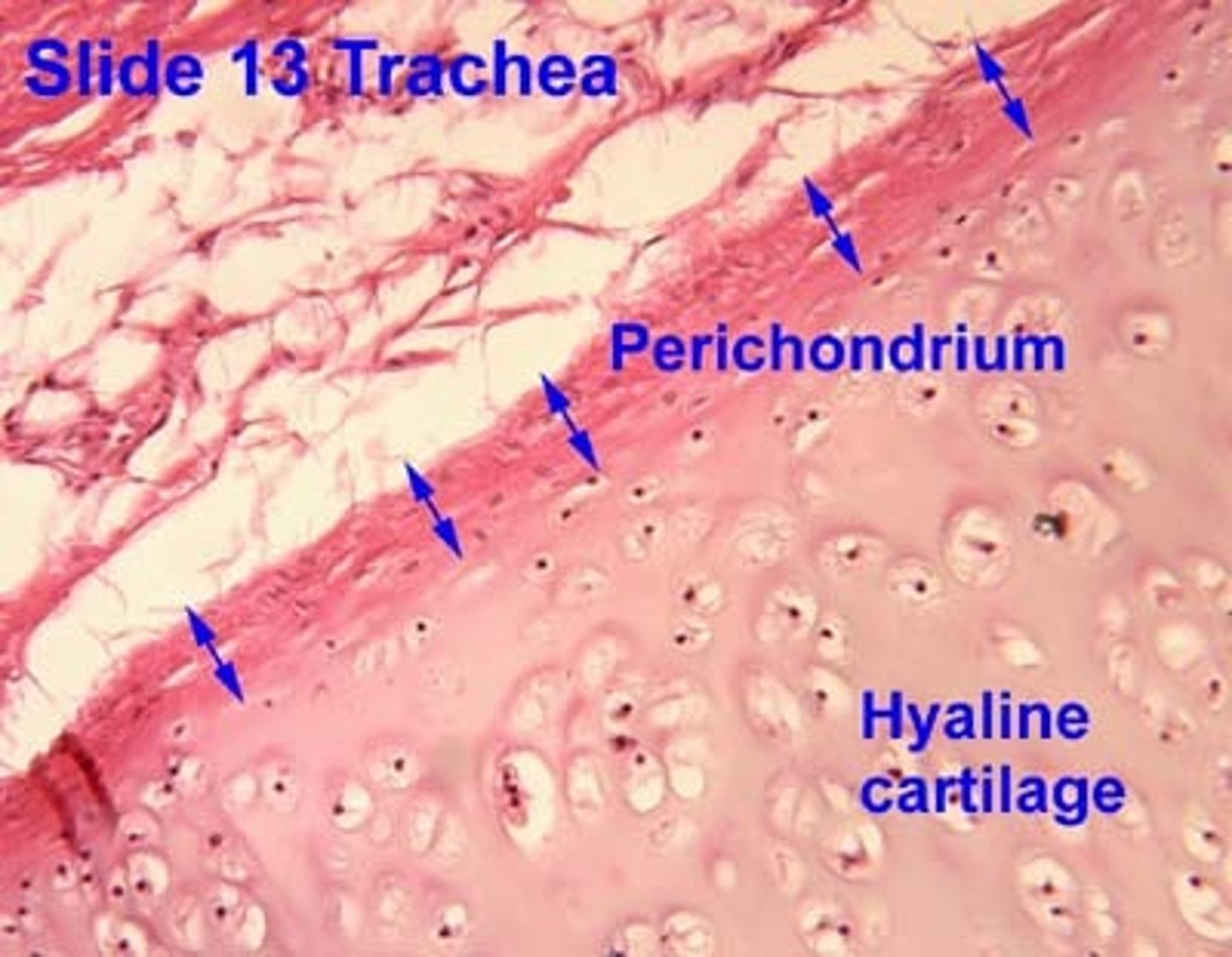
cartilage
A connective tissue that is more flexible than bone and that protects the ends of bones and keeps them from rubbing together; flexible yet resistant to stretching; not innervated and has no blood supply except for perichondrium that forms surfaces of nearly all cartilage
bone matrix
hard acellular matrix produced by bone cells composed of 35% collagen and 65% inorganic material
hydroxyapatite
type of calcium phosphate that makes up most of the inorganic matter in bone
fracture
caused when a force against the bone that is greater than the bone can sustain, causing it to splinter, fracture, or break
closed fracture
when bone breaks but does not puncture through the skin ad protrude through to the outside
open fracture
when bone breaks and punctures skin protruding to outside of the body
comminuted fracture
when bone breaks in multiple areas - often seen in trauma
greenstick fracture
when part of bone bends and does not fully break - often occurs in young children because their bones are more flexible, soft, and still developing
spiral fracture
when bone is twisted or rotated like a corkscrew
avulsion fracture
when a tendon or ligament is taxed and pulled to hard causing it to pull away and break the bone
oblique fracture
break of a bone at an angle cause by outside force coming at a right angle to the bone
transverse fracture
when the fracture is perpendicular to the shaft of the bone
pathological fracture
caused by disease making the bone so weak that it may break without warning simply by putting minimal pressure on it
perichondrium
Dense irregular connective tissue membrane covering cartilage
chondroblast
immature cartilage cell (responsible for matrix production)
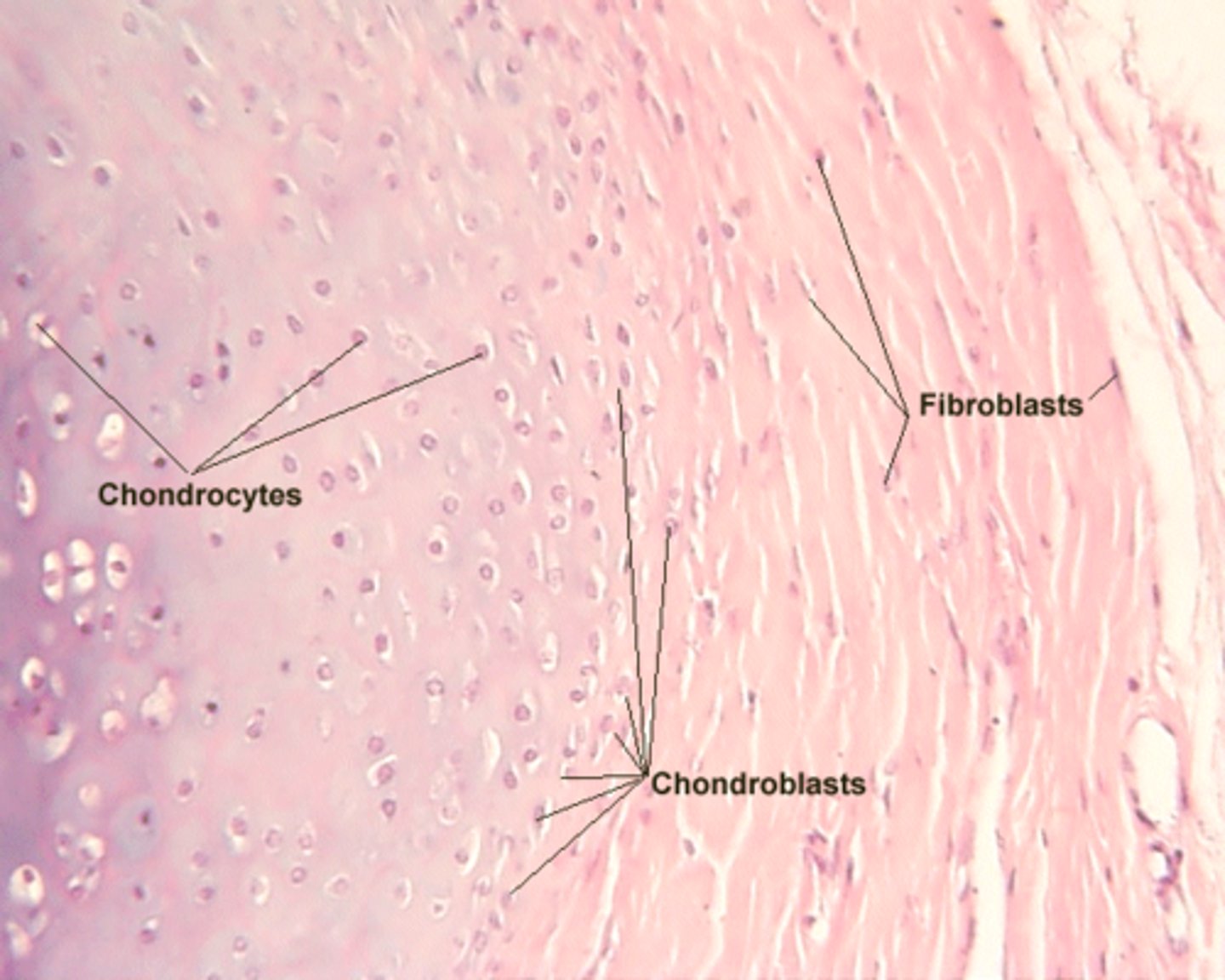
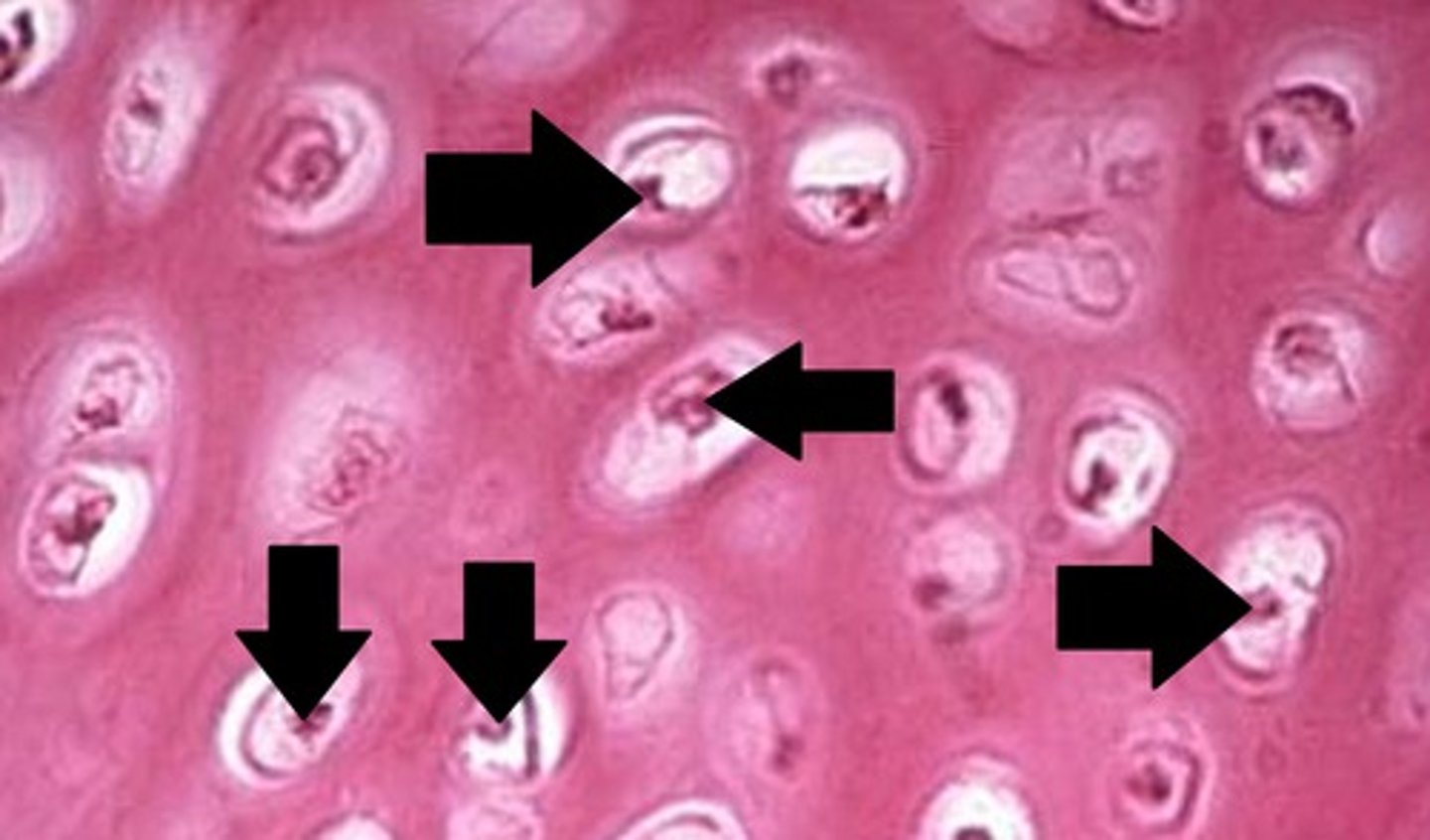
Chondrocytes
mature cartilage cells that reside in lacunae
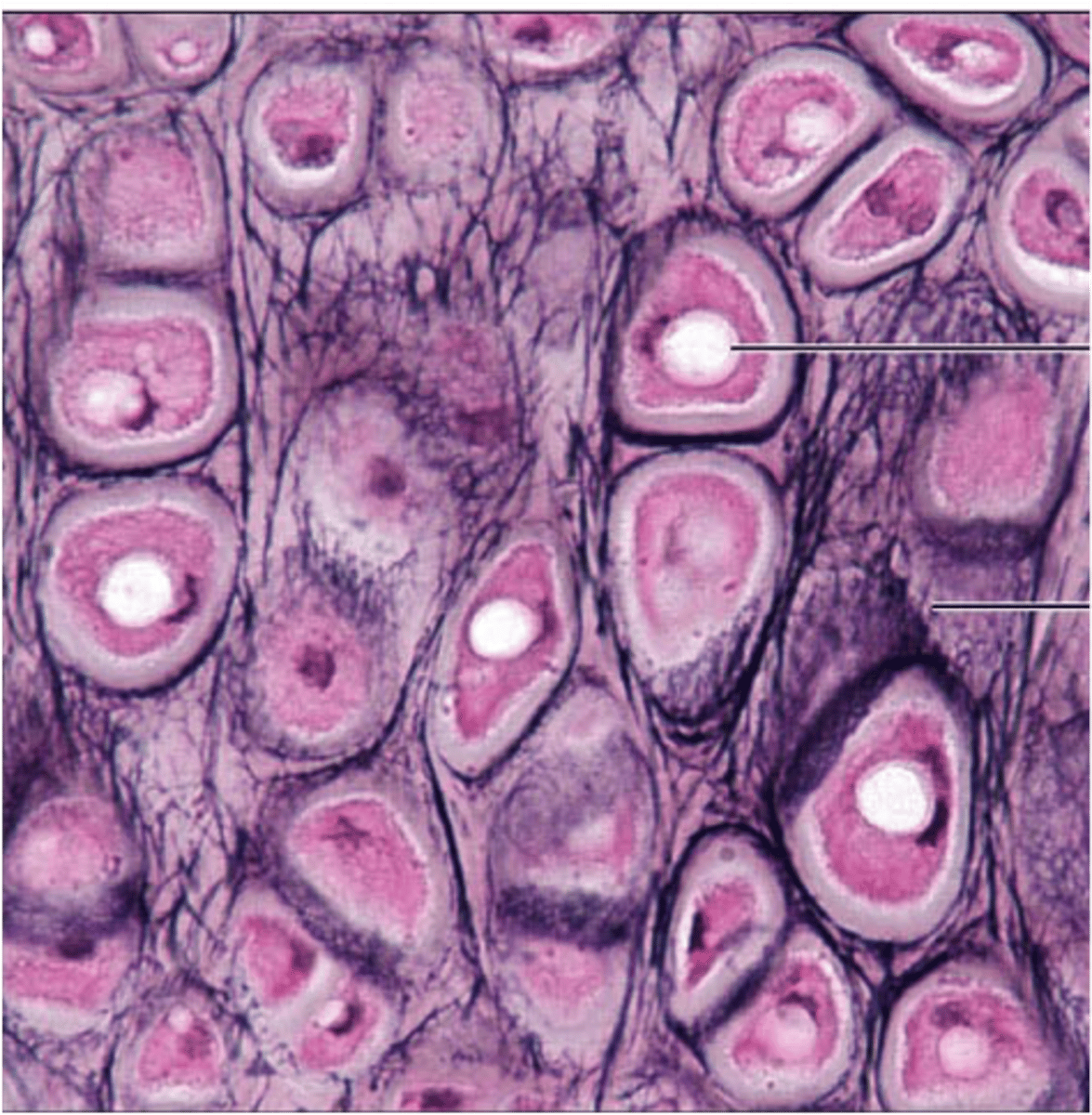
hyaline cartilage
Most common type of cartilage; consists of evenly distributed collagen fibers that explain its glassy appearance; it is found on the ends of long bones, ribs, and nose (found in locations that require strong support with some pliability)
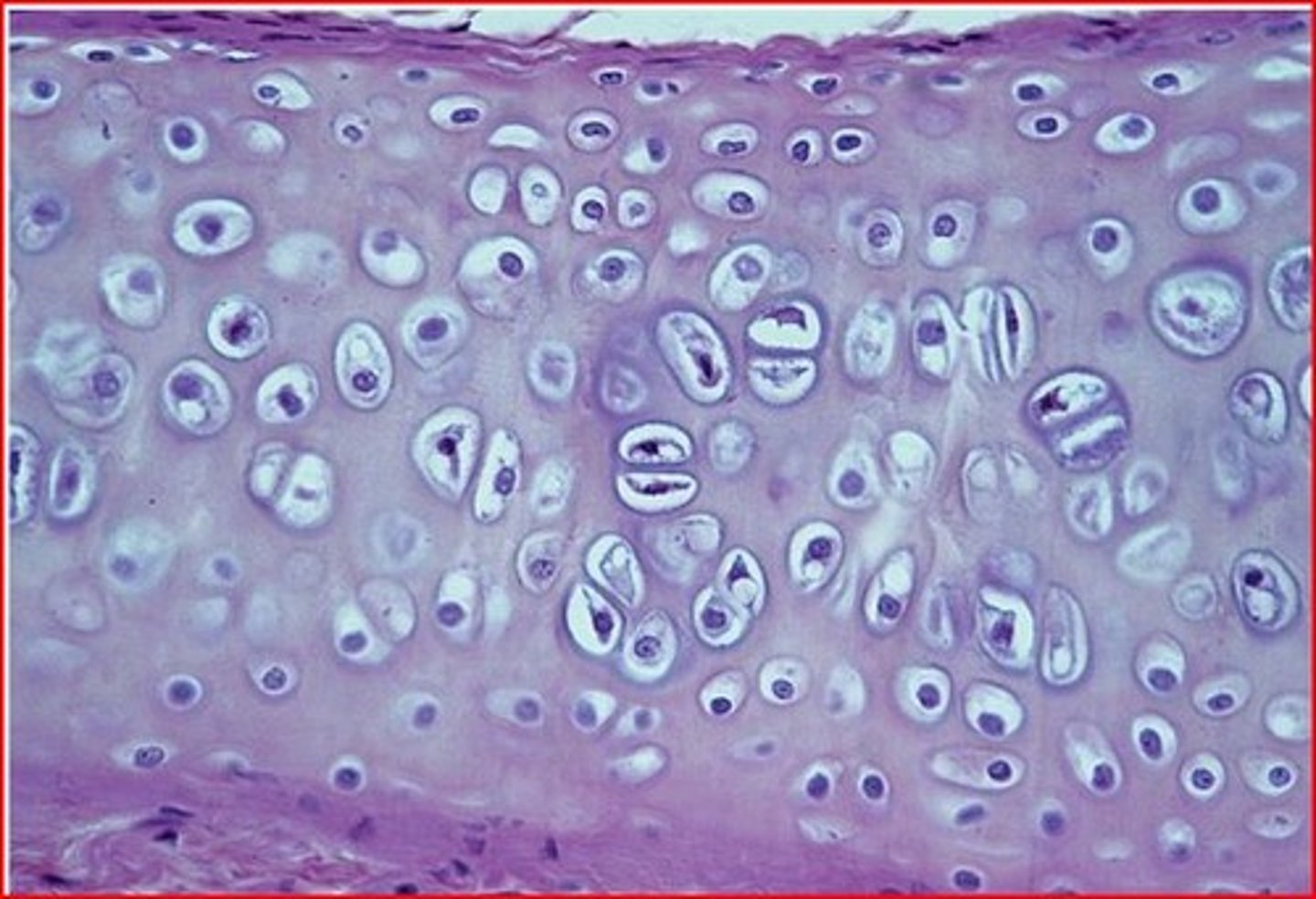
fibrous cartilage
very tough form of cartilage found in the intervertebral disks of the spine and at the junctions where tendons attach to bone; has collagen arranged into thick fibers which allows it to withstand tension and compression; found in jaw, knee, and between vertebrae
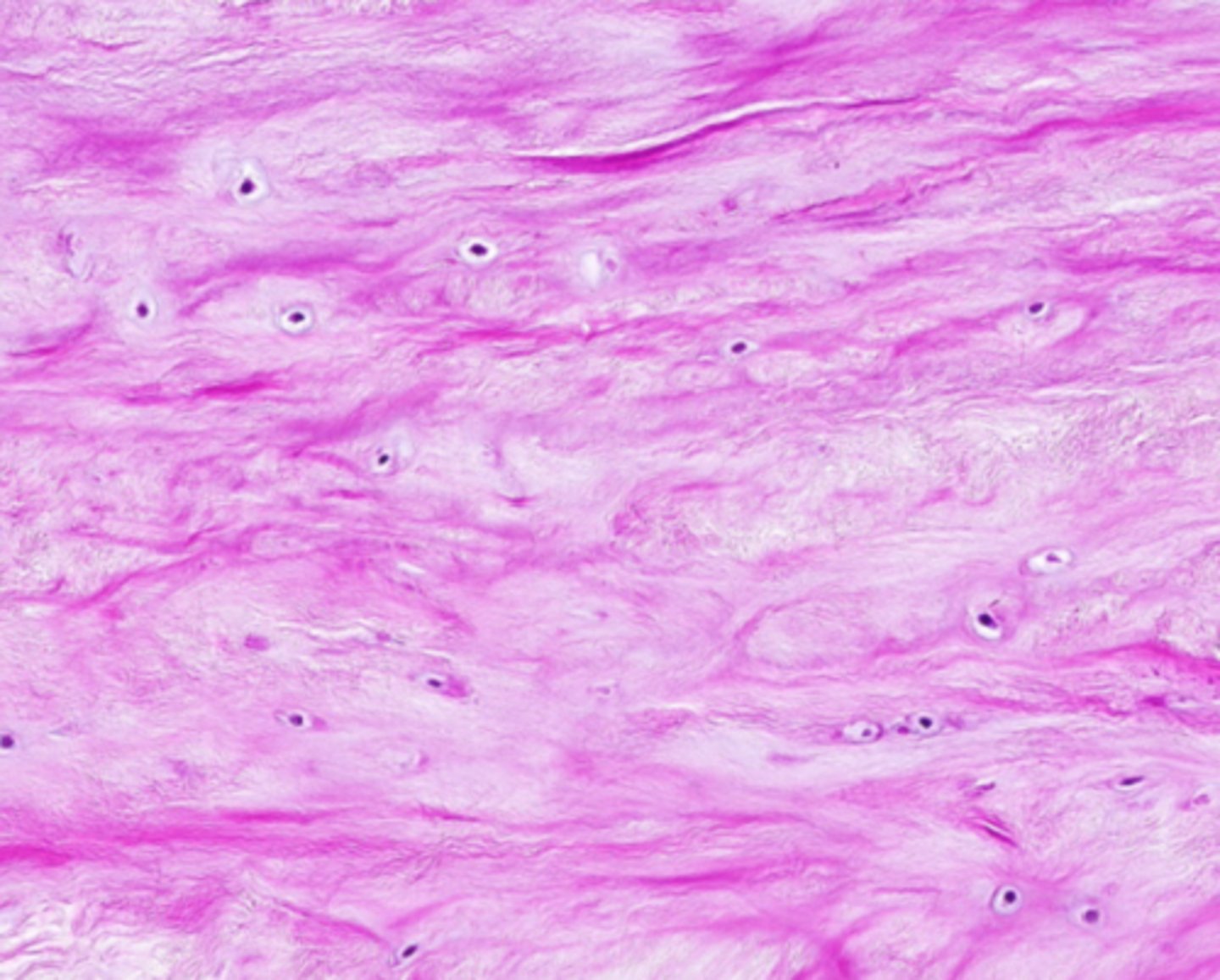
elastic cartilage
cartilage with abundant elastic fibers; more flexible than hyaline cartilage due to presence of elastic fibers; found in epiglottis and external ear
calcitriol
A hormone produced from vitamin D that acts to increase absorption of calcium in intestine that will increase level of calcium in blood; stimulates osteoclasts to break down bone (moves calcium into blood)
calcitonin
peptide hormone secreted by parafollicular cells of thyroid gland when calcium is too high; inhibits activity of osteoclasts and stimulates activity of bone forming osteoblasts
parathyroid hormone (PTH)
peptide hormone produced and secreted by the parathyroid glands in response to low blood calcium levels; increases quantity and activity of osteoclasts