Exam
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
1
New cards
problem of univariance
different wavelength combinations elicit the same response from a single photoreceptor
2
New cards
young helmholtz theory
trichromatic colour vision
3 photoreceptor’s sensitivity to particular wavelength
3 photoreceptor’s sensitivity to particular wavelength
3
New cards
opponent colour theory
colour perception is based off of red-green, blue-yellow, black-white
4
New cards
achromatopsia
inability to perceive colour
5
New cards
deuteranope
no M cones
6
New cards
protanope
no L cones
7
New cards
tritanope
no S cones
8
New cards
Reichardt detector
hypothetical neural circuits for how the brain can track motion.
a cell in the brain receives input from two receptors in the eye (A then B), the input from A is delayed
a cell in the brain receives input from two receptors in the eye (A then B), the input from A is delayed
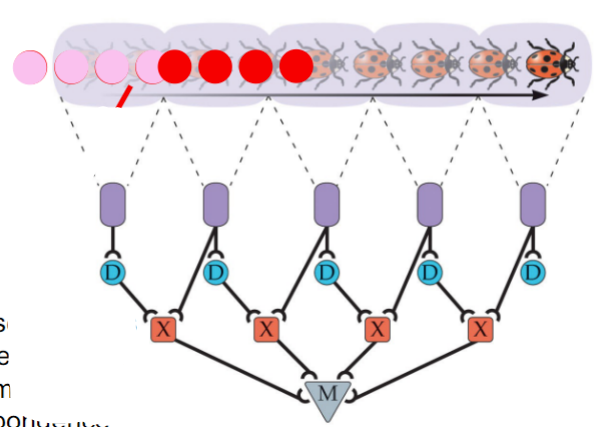
9
New cards
MT / V5
selective for motion in a particular direction
directionally tuned
directionally tuned
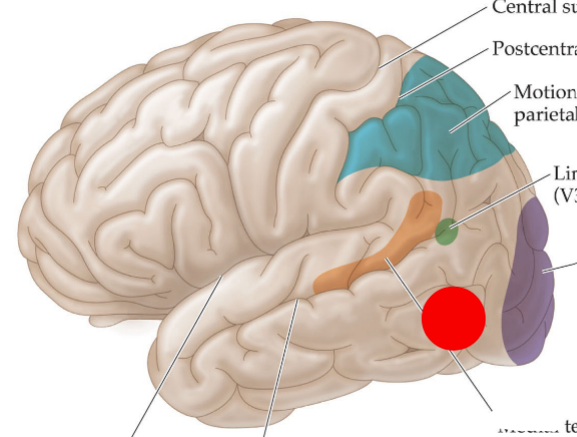
10
New cards
optic flow
perceptive changes as you move through the world
11
New cards
akinetopsia
no reception of motion
MT lesions
MT lesions
12
New cards
superior colliculus
midbrain area that guides eye movement
13
New cards
compensation theory
information about eye movement is discounted from retinal image
efference copy sent to comparator
efference copy sent to comparator
14
New cards
parallax
information taken from 2 eyes at the same time is different
uses stereopsis (two different 2D images on retina create 3D perception)
uses stereopsis (two different 2D images on retina create 3D perception)
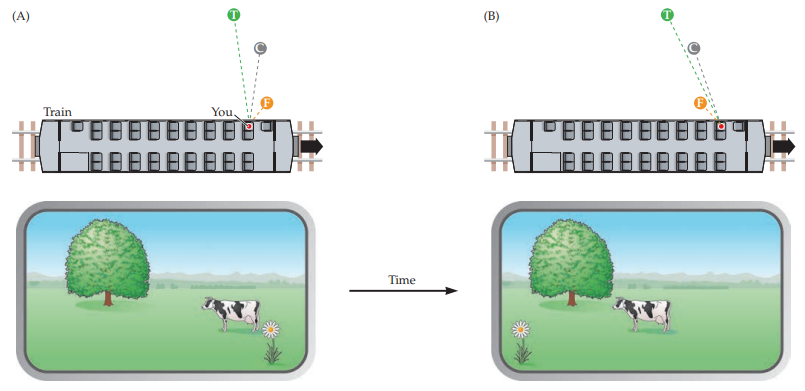
15
New cards
stereopsis
using binocular disparity as depth cues
16
New cards
texture gradient
same sized objects appear smaller the farther they are from the viewer
17
New cards
anamorphosis
specific POV is needed to view a distorted image

18
New cards
motion parallax
objects appear to move faster the closer they are to the viewer
19
New cards
strabismus
the eyes are misaligned, childhood visual disorder
20
New cards
inhibition of return
difficulty getting attention back to recently attended location
peripheral/exogenous/stimulus driven cues have this
peripheral/exogenous/stimulus driven cues have this
21
New cards
feature integration theory
preattentive stage - basic features are processes in parallel
attentive stage - binding features to items in serial search
attentive stage - binding features to items in serial search
22
New cards
guided search theory
items are searched based on basic features
23
New cards
premotor theory of attention
covert attention - inhibiting oculomotor program
overt attention - allowing eye movement
overt attention - allowing eye movement
24
New cards
dorsal attention network
endogenous + exogenous attention
goal directed
goal directed
25
New cards
ventral attentional network
exogenous attention
salient, right hemisphere only
salient, right hemisphere only
26
New cards
milan cathedral experiment
visual imagery is impaired in spatial neglect patients

27
New cards
extinction
inability to detected contralesional stimuli when presented with ipsilesional one
28
New cards
ataxia
reduced spatial localization
29
New cards
simultanagnosia
inability to perceive more than one object at a time
30
New cards
apraxia
reduced eye movement
31
New cards
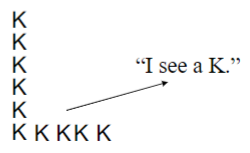
Balint’s syndrome
ataxia, simultanagnosia, apraxia
loss of global perception
loss of global perception
32
New cards
idealism
reality is inseparable from perception
reality is a mental construct
reality is a mental construct
33
New cards
superior temporal sulcus pathway
biological motion & social perception
34
New cards
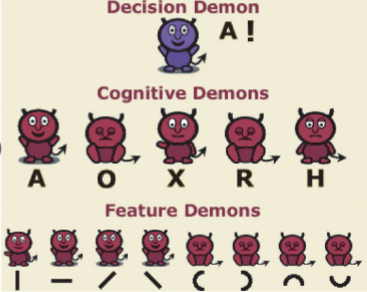
peceptual committe models
middle vision is a collection of “specialists” who vote on their opinion
pandemonium model
pandemonium model
35
New cards
minimum visual angle
0\.017deg
36
New cards
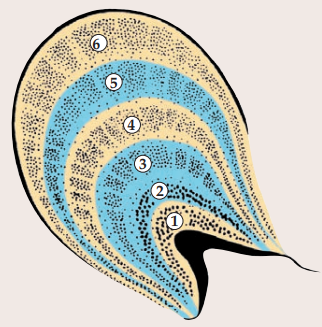
magnocellular
layers 1 & 2 of LGN
high luminance sensitivity & motion
take in rod information
high luminance sensitivity & motion
take in rod information
37
New cards
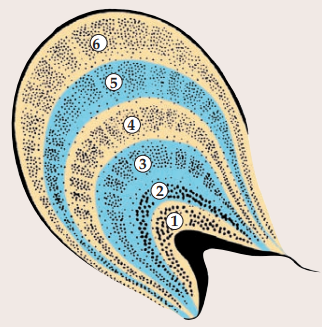
parvocellular
layers 3-6 of LGN
high spatial frequency & colour
take in cone information
high spatial frequency & colour
take in cone information
38
New cards
235
ipsilateral LGN layers
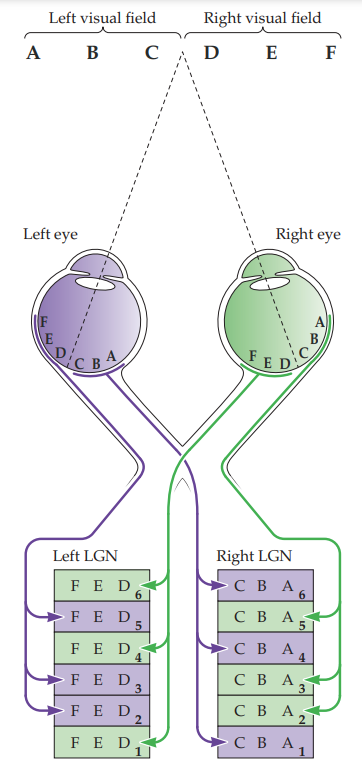
39
New cards
146
contralateral LGN layers
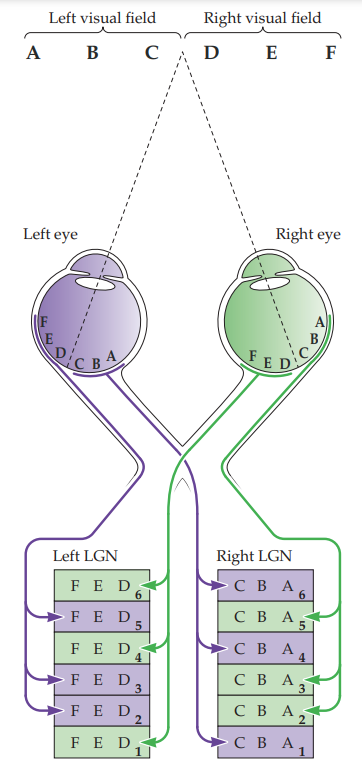
40
New cards
doctrine of specific nerve energies
sensation depends on which neurons are stimulated, not how they are stimulated
41
New cards
spectrum
representation of the relative energy present at each frequency
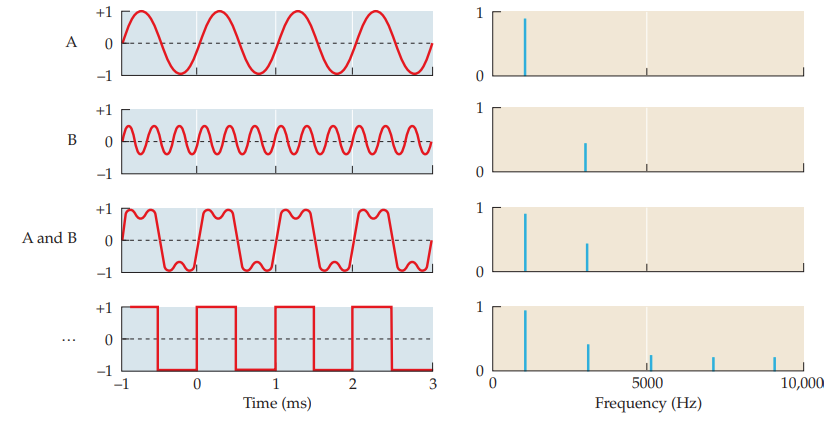
42
New cards
place code
location stimulated in cochlea determines frequency coded
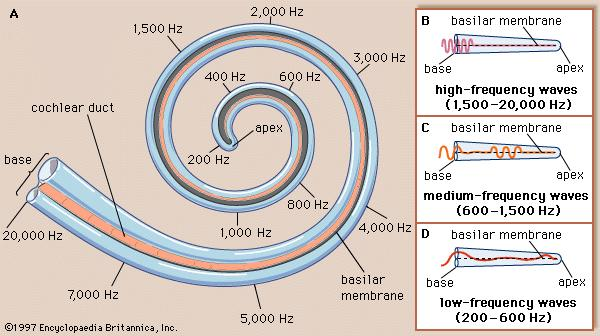
43
New cards
threshold tuning curve
map of neural response to sine waves at lowest intensity
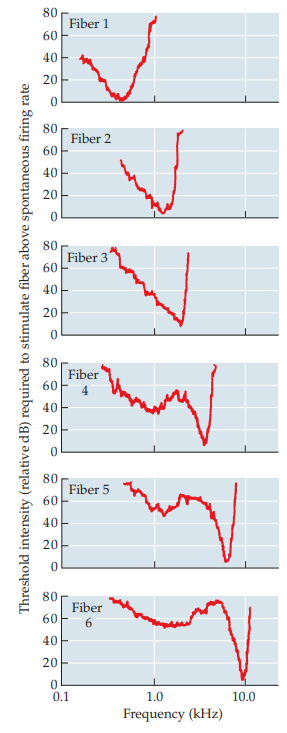
44
New cards
isointensity curve
fibers firing rate to many frequencies at same intensity
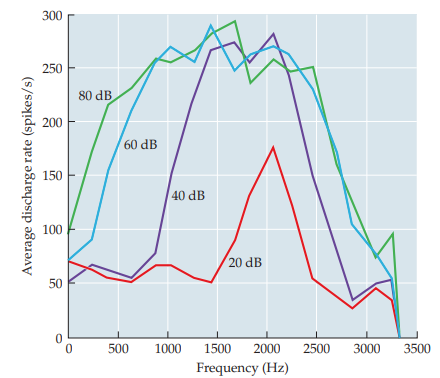
45
New cards
phase locking
firing of a single neuron at a distinct point in the sine wave at a given frequency
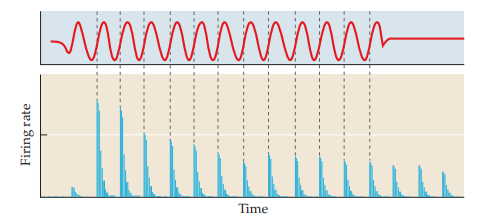
46
New cards
volley principle
multiple neurons fire at distinct points in the sine wave at a given frequency which codes for a distinct sound
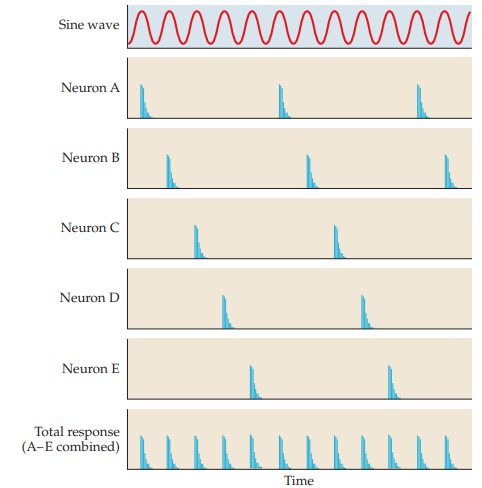
47
New cards
equal loudness curve
sounds placed at a constant level are perceived as louder when played for longer
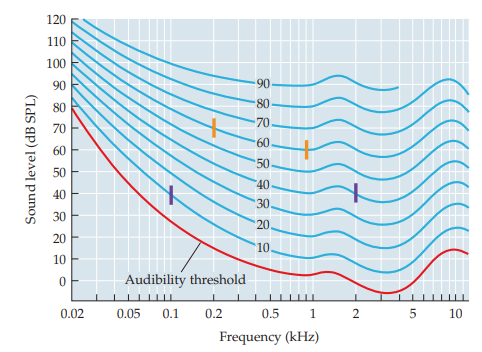
48
New cards
head directional transfer function
different intensities of the same sound hit the ear based on how they traveled (azimuth & elevation), providing depth to auditory cues
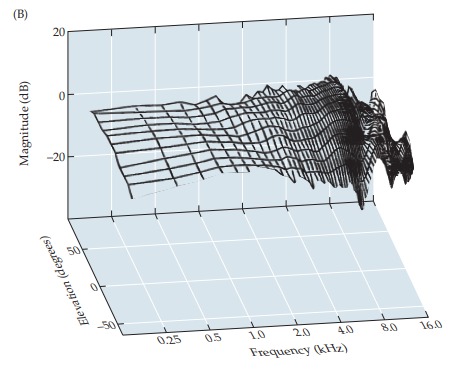
49
New cards
formants
concentrations in energy occur at different frequencies depending on length of vocal tract
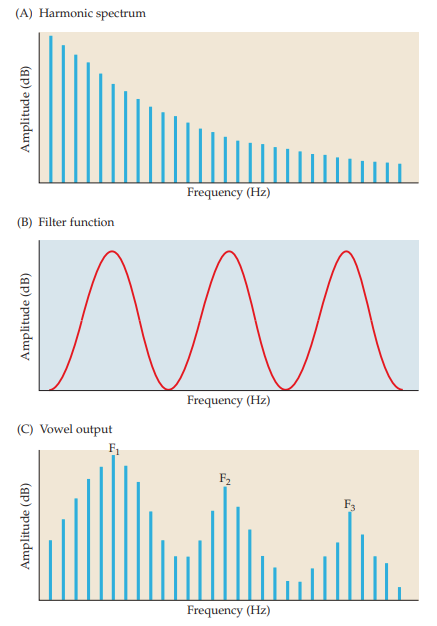
50
New cards
spectral contrast
syllables are perceives based on change of relative energy (change in the spectrum)
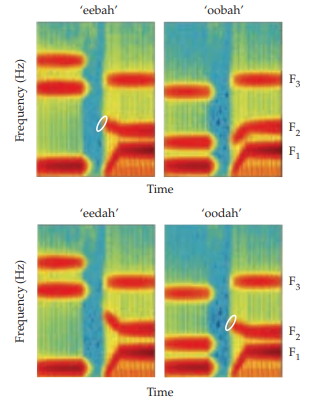
51
New cards
analgesia
decreased pain when conscious
52
New cards
substantia gelatinosa
location of pain feedback circuit
gate control theory of pain
gate control theory of pain
53
New cards
anterior cingulate
responds to hypnotic suggestion of water temperature
54
New cards
haptic perception
active exploration, sense derived from mechanoreceptors
55
New cards
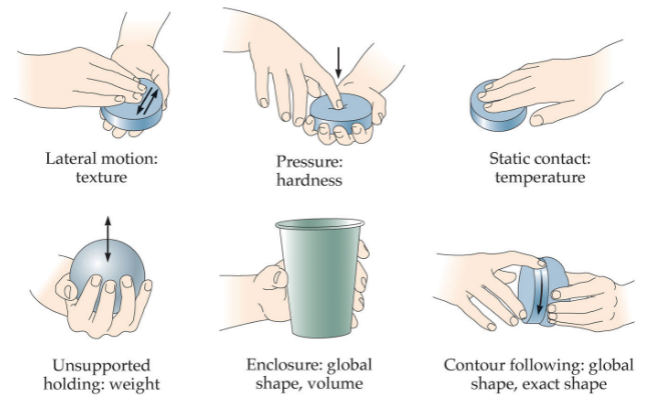
exploratory procedure
hand movement pattern used to contact objects to perceive their properties
56
New cards
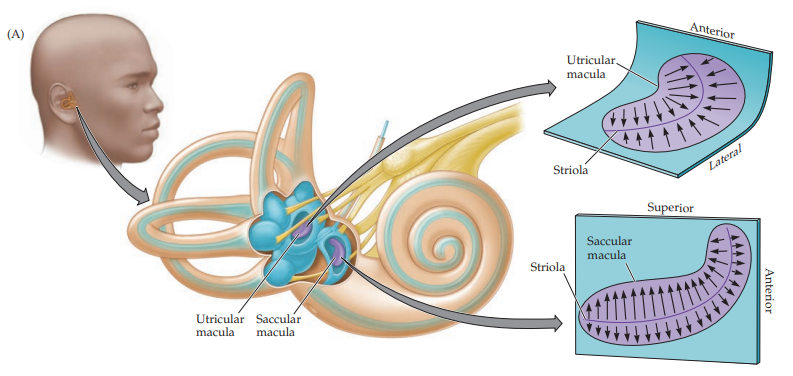
macula
detects linear acceleration and gravity
in otolith organs
in otolith organs
57
New cards
anosmia
loss of smell
58
New cards
entorhinal cortex
mediates information to/from hippocampus
59
New cards
cross adaptation
reduced detection of a new odor after exposure to other odors that stimulate the same olfactory receptors
60
New cards
insular cortex
primary taste processing area
61
New cards
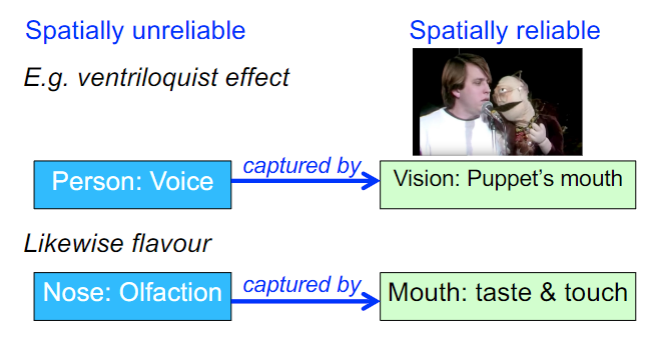
perceptual capture
dominance of one sense over other modalities in creating a percept
62
New cards
angular gyrus
may be the brain region responsible for out of body experiences