Chapter 4: Integumentary System
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Exocrine Glands: Sweat glands
Apocrine and merocrine
unctions of the integumentary system
integument -"covering"
Integumentary System Functions
- protects against environmental hazards,
- helps regulate body temperature,
- provides sensory information
- excretes salts, water, and wastes
- produces melanin
- produces keratin
- synthesizes Vit D3
- Stores lipids
- Defat sensory info
- Coordinates immune response
Integumentary System compose:
- Cutaneous membrane
- Accessory structures
Cutaneous membrane
The skin; composed of epidermal and dermal layers
Cutaneous membrane: Epidermis
- Outer layer
-stratified squamous epithelium
Epidermis - primary cell type
Keratinocyte (Keratin) - protein that makes epidermis tough protective layer
Layers of the Epidermis
stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, stratum corneum
Stratum Basale
Deepest cell layer of the epidermis
Def: made of a single row of cells that undergo rapid cell division
Melanin
A pigment that gives the skin its color by spider shaped cells - Melanocytes, found chiefly in the stratum basal
Skin pigment: Melanin
-a dark brown to black pigment (hair, skin, and iris of the eye)
- produced from melanocytes located in stratum basal
- Packaged into melanosomes; transferred to keratinocytes where it offers protection for nucleus against UV radiation
Skin Pigments (Carotene)
Carotene: yellow-orange pigment
• Most apparent in stratum corneum of light-skinned people
• Found in orange vegetables
Stratum Spinosum
a layer of the epidermis that provides strength and flexibility to the skin
contains dendritic cells
Stratum Granulosum
-Grainy layer
- Most cell stops diving
- Produce keratin
- cells grow thinner
- Flatter,
- Thick
- less permeable membranes
Stratum Lucidum
"Clear layer"
- found only in the thick skin (fingers, palms, and soles)
Stratum Corneum
outermost layer
- consists of flattened,
- keratinized cells aka cornfield or horny cells
Cutaneous membrane: Dermis
Papillary of areolar tissue
Reticular Layer of dense irregular connective tissue
Dermis: Papillary Layer
-Areolar connective tissue
-nuorishes & supports epidermis
Dermis: Reticular Layer
-Deepest skin,
- stores lipid reserves
- sensory receptors, detect touch, pressure, pain, vibration & temp
Consists of:
-Blood vessels
-Glands
-Nerve receptors
Cutaneous membrane: Hypodermis (subcutaneous layer)
Deep to the dermis;
made of adipose tissue;
helps insulate
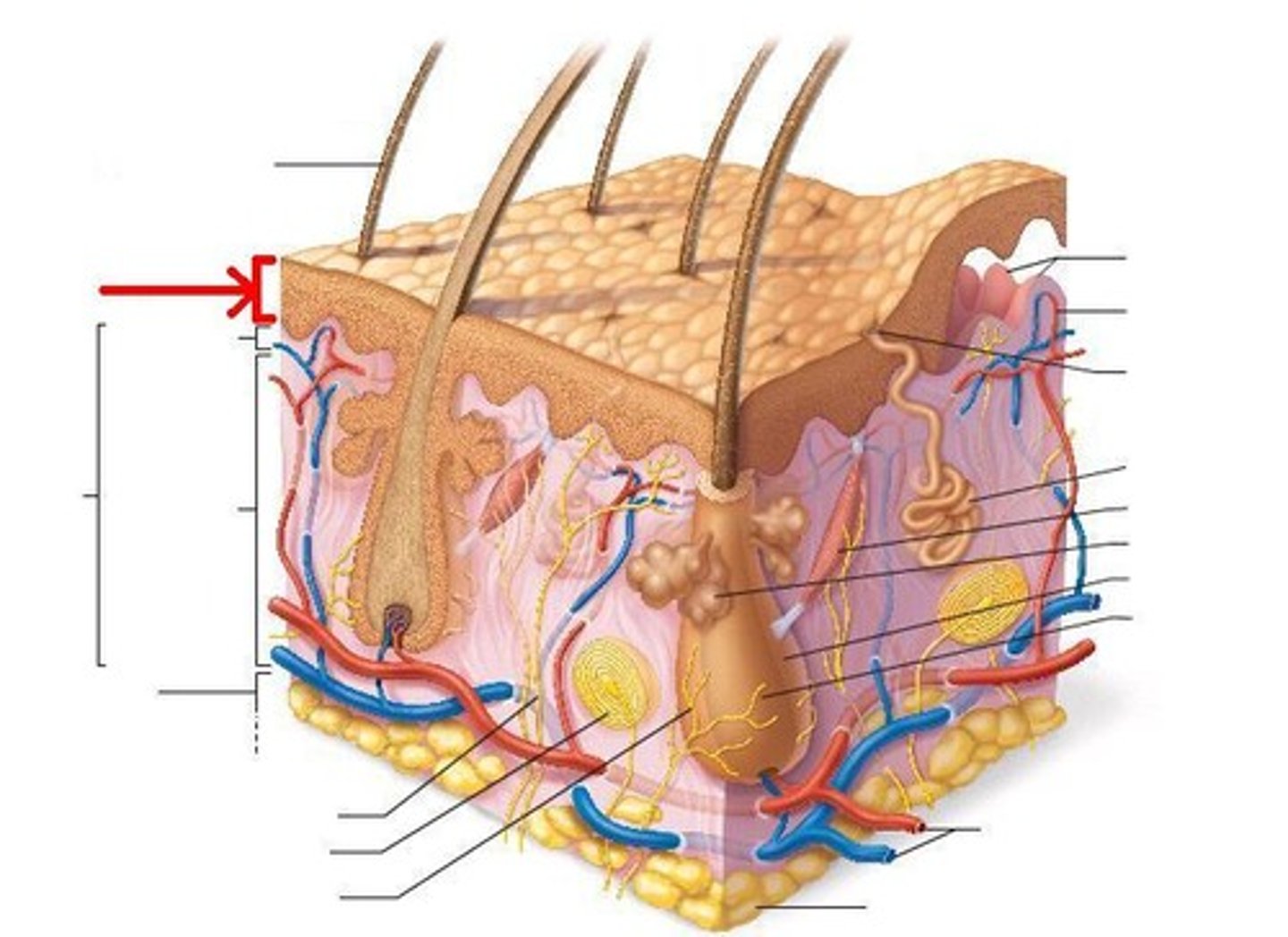
Skin Appendages
include nails, sweat glands, sebacous (oil) glands, and hair follicles and hair.
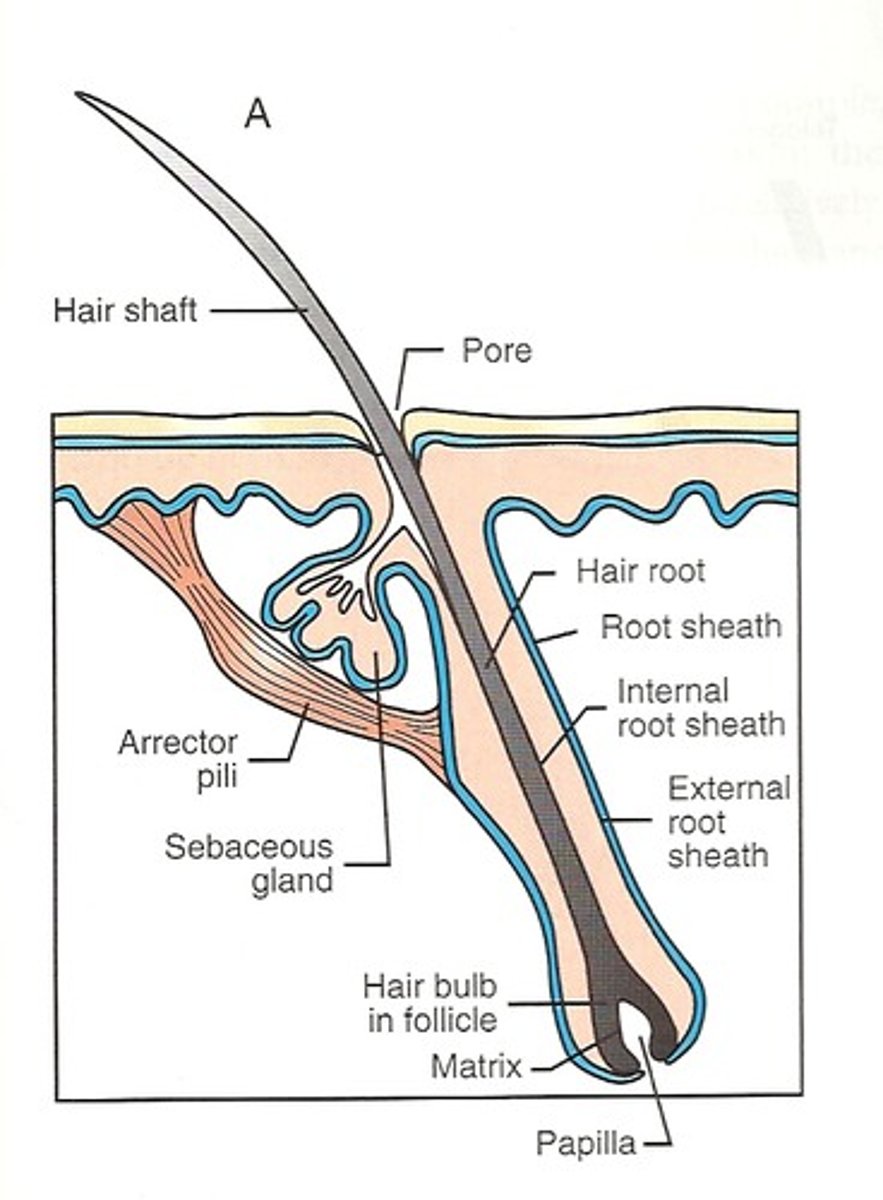
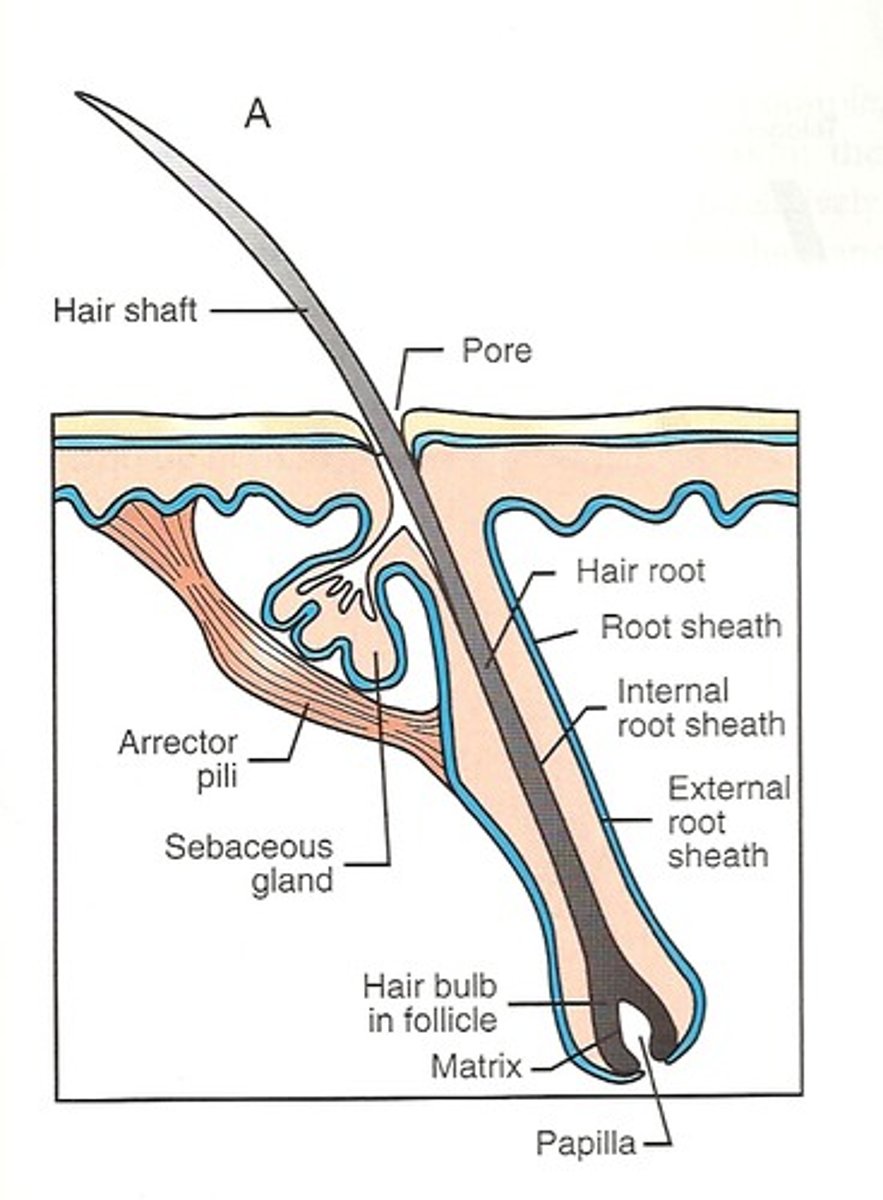
Accessory Organs: Hair Follicles
•Hair papilla: Peg of connective tissue filled with blood vessels and nerves at
base of follicle
•Matrix: Growth zone of hair
•Medulla: Core of hair at center of hair matrix & Contains flexible, soft keratin.
•Cortex: Intermediate layer deep to cuticle & has thick layers of hard keratin
•Cuticle: Forms surface of the hair & hard keratin
Accessory Organs: Hair Growth Cycle
Active phase: new hair added to hair root by dividing cells of hair matrix (can last for weeks to years)--determines hair length differences
Resting phase: cells of hair matrix and hair follicle inactive (1-3 months)
-New active phase: hair follicle produces new hair, pushes out old club hair
Accessory Organs: Hair Color
Variations in hair color are caused by melanocytes.
Accessory Structures: Cutaneous glands
sebaceous glands and sweat glands
Exocrine Glands: Sebaceous glands (oil glands)
Glands connected to the hair follicles that secrete sebum;
- provides lubrication (soft)
-can kill bacteria
Exocrine Glands: Sweat glands
apocrine and merocrine
Exocrine Glands: Apocrine glands
-In the pubic & underarm, nipples areas that secrete thicker sweat on hair follicles,
- produce odor when come in contact with bacteria on the skin
Exocrine Glands: Merocrine glands
• highest concentration in palms & soles
• Secrete directly onto skin surface
• Produce watery secretions with electrolytes to help regulate body temperature
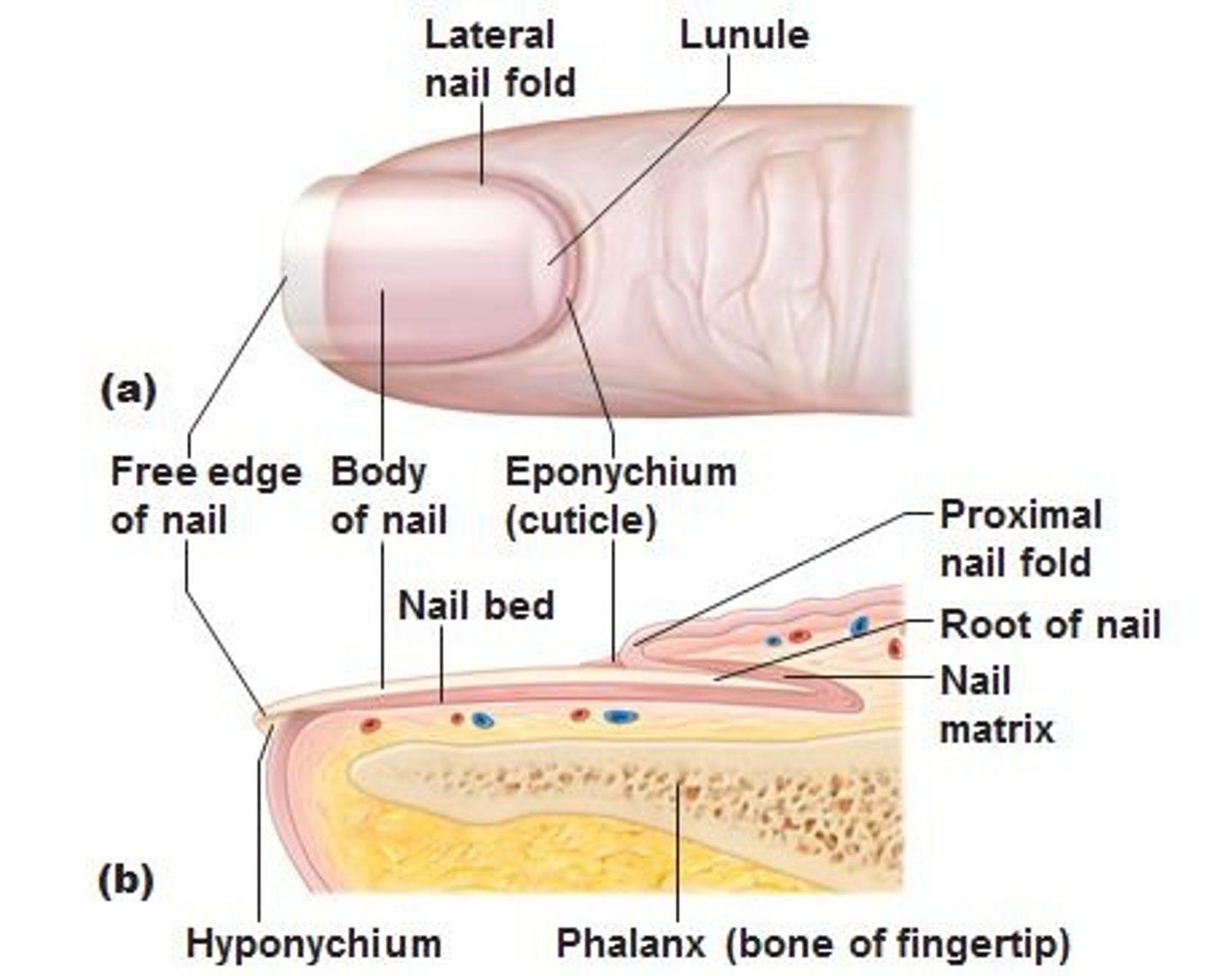
Nails structure
• Nail body is thick sheets of dead, keratinized epidermal cells
• Nail bed is area of epidermis under nail body
• Nail production occurs at nail root
• Cuticle is portion of stratum corneum of nail extending over nail root
• Pale arched area near nail root is lunula
Integument Repair
Initial Injury
-Mass cells trigger inflammatory reponse
After several hours:
- Scab forms at the surface
- patrolling macropoasges
- rapid cell division and migration along wound edges
- formation of granulation tissue
One week
- deeper portions of the clot dissolve
- fibroblasts deposit collagen fibers & ground substance
Several weeks:
- scar tissue formation
a. After taking a long bubble bath or doing dishes by hand, your fingers often appear wrinkled, or "pruny." Explain why.
a. Fingers (and toes) swell up because of the hypotonic osmotic flow of water into the dead, keratinized cells of the outer layer of the epidermis, the stratum corneum. Because the underlying strata and dermis doesn't expand, the larger surface area of the swollen stratum corneum must go somewhere, & it forms folds and creases, or wrinkles. Other areas of the body lack a thick stratum corneum, so little swelling & wrinkling result.
Describe the sequence of events that begins with epidermal cells and UV radiation, and leads to the absorption of calcium and phosphorus by the small intestine.
Epidermal cells in the stratum basale & stratum spinosum convert a cholesterol related steroid to vitamin D3 in the presence of UV radiation. The vitamin enters capillaries in the dermis and is carried to the liver. The liver produces an intermediate product that is released & carried to the kidneys. The kidneys convert that intermediate product into the hormone calcitriol. Calcitriol stimulates the intestinal absorption of calcium & phosphate, which are then available for bone growth and maintenance.
a ___________________ Produce watery, electrolyte-containing secretions b ___________________ Epithelial fold not visible from the surface
c ___________________ Found in the armpit
d ___________________ Blood clot at skin surface
e ___________________ Site of hair production
f ___________________ Decrease in elastic fibers
g ___________________ Oily lipid secretion
h ___________________ Abnormal melanocytes metastasize through the lymphatic system
i ___________________ Causes hair to stand erect
j ___________________ Surface of a hair
a. merocrine sweat glands;
b. nail root;
c. apocrine sweat glands;
d. scab;
e. reticular layer of dermis;
f. wrinkled skin;
g. sebum;
h. malignant melanoma;
i. arrector pili;
j. cuticle
Label hair follicle
a. hair shaft;
b. sebaceous gland;
c. arrector pili muscle;
d. connective tissue sheath of hair follicle;
e. root hair plexus