1. Amber Book Panic Notes - PjM
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
The Owner is responsible for...
Everything site-related and programming
The Architect is responsible for...
Completing construction documents, including specifications
Code, zoning requirements
Delivering a project on-time and on-budget
The Contractor is responsible for...
Building the project as per contract documents
Means & methods of construction, work site safety, shop drawings, operations manuals, submittals
Privity
No direct contract between architect and contractor, meaning it is difficult to sue
Indemnity
Contractual obligation by which one person or entity agrees to reimburse another for loss or damage arising
from specified liabilities
Betterment
Improvement that enhances property value more than replacement
Subrogation
The process by which an insurer can, after it has paid a loss under the policy, recover the amount paid from any party (other than the insured) who caused the loss or is otherwise legally liable for the loss
Agency relationship
Fiduciary relationship where agent acts on behalf of principal
Duty
Obligation imposed by law or contract
Warranties
Pose unacceptable risk; work to a standard of care instead
Contract terminology to avoid...
"as required", "as necessary"
create a guarantee that is not covered by liability insurance
"hold harmless", "indemnification"
imply that the architect will take liability for things they wouldn't normally be responsible for
Examples of high-risk situations include...
- unknown clients
- inexperienced owners
- clients with a history of litigation
- anything related to condos
Contract Type: A Series
owner - contractor
contractor - subcontractor
Contract Type: B Series
owner - architect
Contract Type: C Series
architect - consultants
Contract Type: D Series
miscellaneous documents
Contract Type: E Series
electronic communications
A101 and B101 are specific to...
- project location
- date
- dispute resolution (mediation, arbitration, litigation; select one)
- fees and pricing
A132
Owner - Contractor
CM as Agent or Advisor
A133
Owner - Contractor
CM as Constructor
A195
IPD Agreement
A201
General Conditions of the Contract for Construction
- architect owns drawings
- process for keeping schedule of values
- process for contractor's application of payment
- substantial completion definition
A701
Instructions to Bidders
C401
Agreement Between Architect and Consultant
G601
RFP - Land Survey
G602
RFP - Geotechnical Services
G201
Project Digital Data Protocol Form
G202
Project BIM Protocol Form
G701
Change Order
G702
Application for Payment
G703
Continuation Sheet - used in conjunction with G702
provides a detailed breakdown of the various component of the work and the scheduled value for each component for which payment request is made
G704
Certificate of Substantial Completion
G716
RFI
Addendum
change made after bid, but before bids are received
Change Order
change after contract is signed
Construction Change Directive
owner and contractor disagree about who pays for something, so the architect issues CCD to the contractor to keep project moving along
Submittals
items contractor submits to the architect for their approval
- product data sheets
- shop drawings
- product samples
Bonds
Bid bonds and performance bonds protect owner if contractor defaults
Invited Bid
prequalified contractors are preselected and given the opportunity to bid
Phased Bid
used during fast-track, allows systems with long lead times to be bid first (and thus fabricated earlier)
Negotiated Bid
contractor brought on at the beginning of the project to provide feedback
after CDs, the bid is negotiated between the owner and contractor
Masterformat vs Uniformat
masterformat = specs organized by material or process (concrete, excavation)
uniformat = specs organized by system (foundations, stairs)
Surety Bond
similar to insurance, protect the owner if the contractor does not follow through on a project
third party insurer will pay the owner to finish the project if a contractor walks away
two types of surety bonds include
bid bond = pay difference between the accepted bid and the next lowest bid if the lowest bidder taps out
- before contract is signed while contractor is still being selected
performance bond = pay for the project to be completed if the contractor defaults
- after contract is signed / contractor is selected
Project Timeline Order
1. RFP
2. Architect Selected
3. Pre-Design (no drawings yet)
4. Schematic Design
5. Design Development
6. Construction Documentation
7. Bidding
8. Contract Awarded
9. Construction Administration
10. Punch List
11. Certificate of Occupancy
12. Substantial Completion
13. Final Completion
Substantial Completion
When a building can be used, even if there are a few last minute items that still need to be completed (before punch list has been completed)
Final Completion
After punch-list has been done and the contractor has completed the contract requirements
Now the contractor can apply for final payment
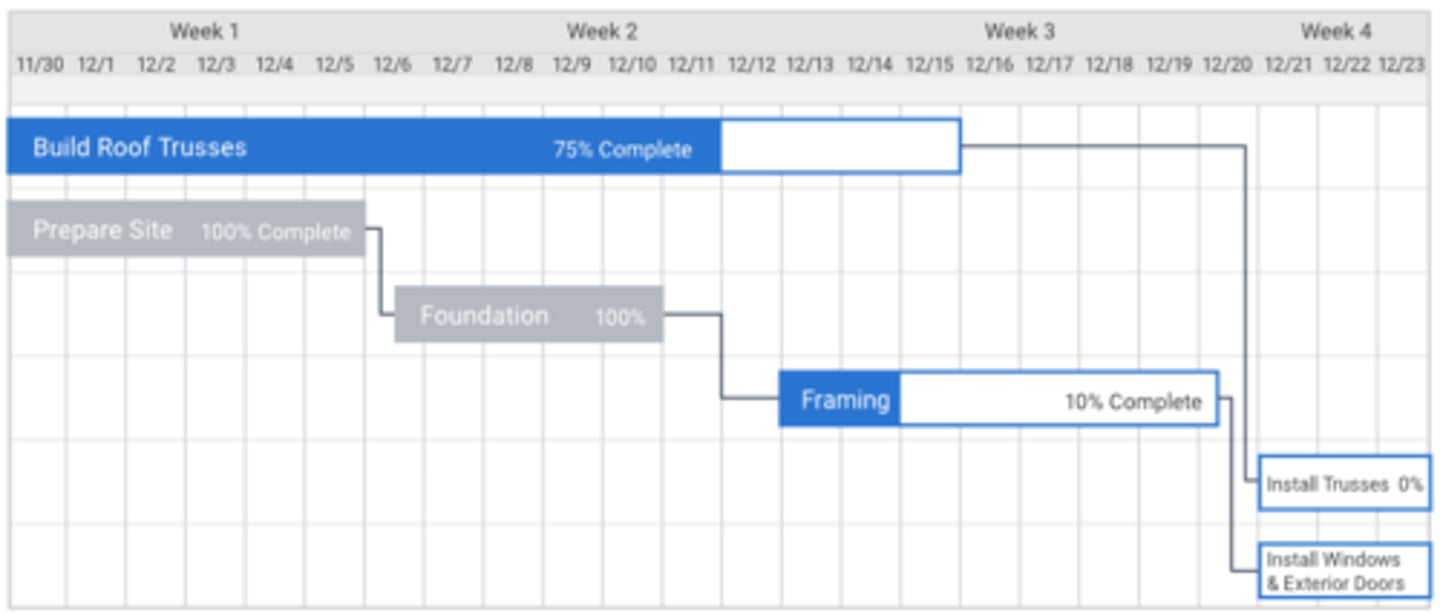
Gantt Chart
Scheduling tools to depict start and end dates of tasks, sequencing of items in a construction schedule
PERT Chart
Network diagram showing tasks and their dependencies
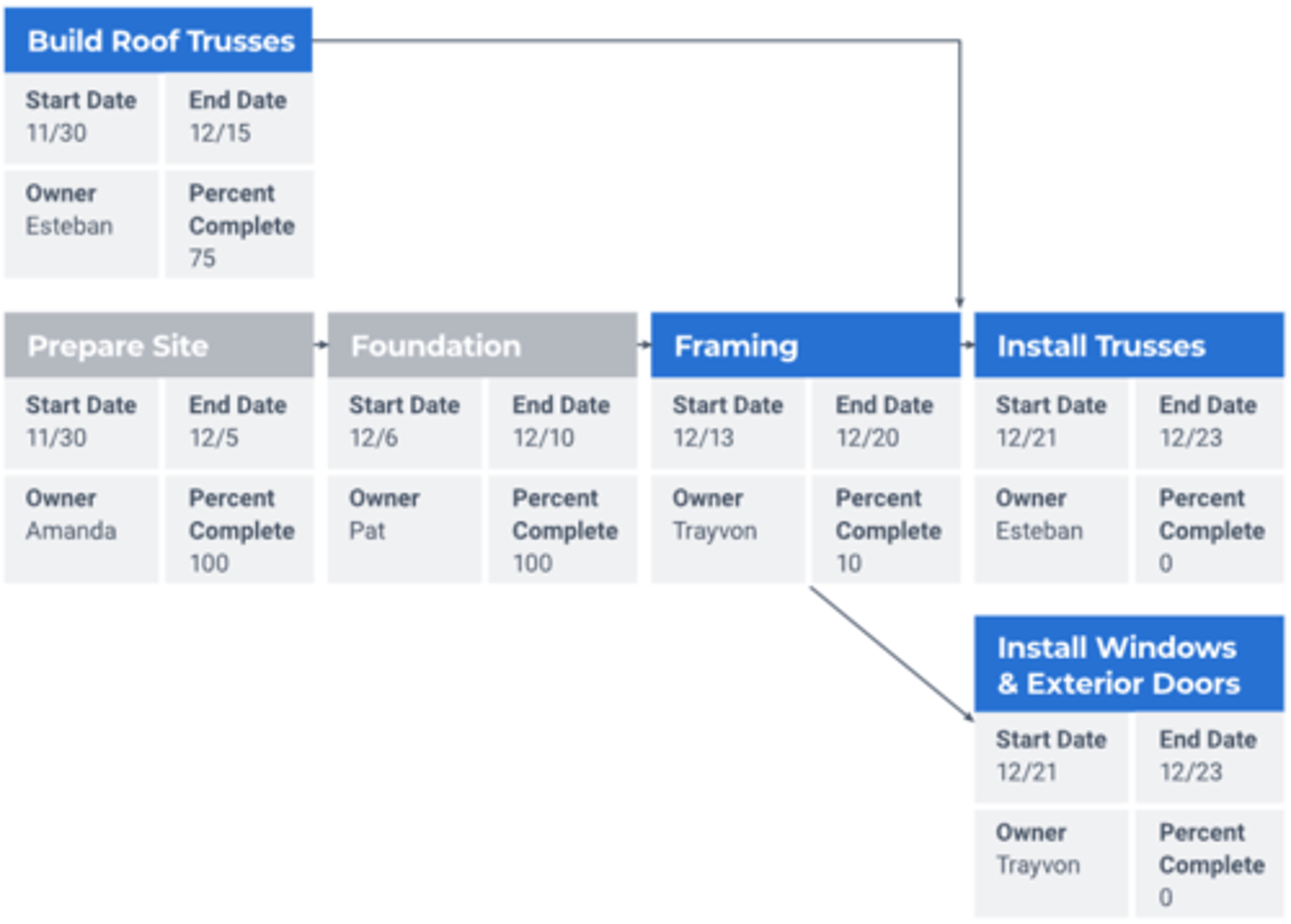
Critical Path Chart
diagrams which tasks are dependent on other tasks
Slack (float)
how much time is built into the project schedule to account for unexpected, extra time required to complete a task
Free Float Time
the amount of time that a task can be delayed without affecting the start date of subsequent tasks
Total Float Time
the amount of time that a task can be delayed without affecting the completion date of the entire project
7 days
amount of time the architect can give the owner before they will stop providing services
architect or owner can terminate the contract after_____ time of written notice to the other party, if the other party violated their agreement
amount of time to approve or dispute the contractor's application of payment
14 days
time the contractor has to inform the owner and architect if previously concealed site conditions are unveiled
amount of time the architect has to notify the contractor if they don't approve of their subcontractor
30 days
amount of time the owner has to provide final payment to the contractor; issued after the final certificate of payment
60 days
amount of time after substantial completion before the architect's construction administration services end
amount of time that disputes sit between the owner and architect before advancing to arbitration or litigation
90 days
amount of time the owner can suspend a project before the architect can terminate or re-negotiate the contract
1 year
amount of time after substantial completion that the owner is entitled to make any corrections or fix any construction defects
within this amount of time after substantial completion, the owner can request to meet with the architect to discuss building operations and performance (without additional compensation)
the amount of time after substantial completion before the owner-architect contract is terminated
10 years
the amount of time after substantial completion before all claims between the owner and architect (or the owner and contractor) are dropped
Application for Payment includes...
- change order summary
- how much money is needed to complete the project
- amount of retainage for work-in-place
- amount of retainage for stored materials
- certification that the contractor's subs have been paid
Retainage
money owed to the contractor, but intentionally not paid until substantial completion of the project
Mechanic's Liens
portion of the property is owed to the little guy (subcontractor, consultants, etc.) in the event that whoever is responsible for paying them (contractor, e.g.) walks away before payment
requires the owner to sell the property to get enough money to cover little guy costs
Allowances
funds set aside to pay for items that can change frequently or are difficult to narrow down a price far in advance
Alternate
item that is priced for the owner's understanding, but is not included in the base cost of the project
could be added to the project later if the owner gets enough money
Unit Prices
items in the bid that are priced by unit when you aren't sure of total quantities
per square foot, linear foot, cubic foot, etc.
Schedule of Values
line item cost of specific items, including windows, drywall, HVAC, foundations, etc.
ways to calculate architect's fee
- hourly billing
- % of construction cost
- value-based fees
- per SF fees
- fixed fees
Process for filing an ethical complaint
1. File claim through AIA ethics board
2. Advisory board and chair are selected
3. Pre-hearing, hearing, start, claim, defense, end, judgement
claims are confidential; can not result in legal action but can be punished and/or revoke AIA license
Dispute resolution (owner-architect)
1. Mediation -> Arbitration
2. Mediation -> Litigation
Mediation - non-binding, let's talk it out before it gets blown up into something huge
Arbitration - single person makes decision, kept private
Litigation - jury / court decision, made public
Lifecycle costing
Comparison of cost impacts of design decisions
Lifecycle analysis
Comparison of environmental impacts of design decisions
Fair Labor Standards Act
establishes minimum wage, which employees are eligible for overtime, forbids child labor
Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA)
protects workers from job site hazards by establishing safety standards
Affordable Care Act
requires firms with more than 50 employees to provide health insurance
Are measured drawings considered a base service or additional service under AIA B101?
additional service
Is programming considered a base service or additional service under AIA B101?
additional service
Is coordination of owner-hired consultants considered a base service or additional service under AIA B101?
additional service
Restrictive Covenant
(aka non-compete clause) limits what an employee can do after they leave the firm
restrictions include setting up their own business, working for competitors, working with the firm's clients, or sharing confidential information
Consequential damages
I can sue you for the unrealized profits I would have made if the building opened on time
These are not allowed in any standard AIA agreements
Liquidated Damages
Amount you owe for each day the project is delayed (example), established in the contract well before construction starts.
These are only allowed in AIA owner-contractor agreements, NOT owner-architect agreements
Direct damages
Pay for the cost to fix the error
Allowed in all AIA contract agreements
What are the options for the owner if the lowest bid comes in too high?
1. increase the budget
2. authorize rebidding / renegotiating
3. terminate
4. cooperate with the architect to revise scope / quality
5. implement mutually acceptable alternative
What does the cost of work include?
- cost of labor and materials
- architecture management fees
- overhead expenses
- profit allowance
What does the cost of work NOT include?
- professional fees
- land cost
- financing costs
- other owner costs (survey, permits, etc.)
Compensation methods for the owner to pay the architect include...
1. stipulated sum
2. cost plus fixed fee
3. % construction cost
4. unit cost
extras (variation of cost plus):
- multiple of direct personnel expense
- multiple of direct salary expense
- hourly billing rates
Compensation methods for the owner to pay the contractor include...
1. stipulated sum
2. cost plus fixed fee
3. guaranteed max price
4. unit prices
Accessory Occupancies
small spaces (area < 10% of total floor area) that are for spaces of a different occupancy than the main occupancy
example: office in the corner of a large warehouse building
What can the Architect do if the Owner suspends the project?
1. suspend work
2. require payment for work-to-date
3. require payment of delay-caused expenses
4. submit a new schedule
What are the Architect's responsibilities to prepare for bidding?
- complete CDs
- update the cost estimate
- administer bidding (aka assist the owner)
B101, Article 1 - Initial Information
- identify the project
- establish budget
- determine schedule
B101, Article 2 - Architect's Responsibilities
- obtain insurance
- standard of care
B101, Article 3 - Architect's Basic Services
- submit a project schedule / timeline
- design must meet applicable code
- consider sustainable design alternatives
- facilitate bidding
- certify payment to contractor
- review contractor submittals
B101, Article 4 - Additional Services
- anything beyond single drawing set with MEP and structural engineering
B101, Article 5 - Owner's Responsibilities
- everything site related
- everything permit related
- geotechnical engineer
- coordination of owner-hired consultants
B101, Article 6 - Cost of Work
Labor and Materials
Management fees
Overhead expenses
Profit allowance
B101, Article 7 - Copyright and Licenses
architect + architect's consultants own their drawings
B101, Article 8 - Claims and Disputes
two options:
1. mediation --> arbitration
2. mediation --> litigation
B101, Article 9 - Termination / Suspension
- if owner suspends project (or doesn't pay architect) for 90 days, the architect can terminate (after 7 days written notice)
- if owner decides to terminate "because they feel like it", they must pay the architect for work up to that point and to cover expenses (insurance, consultant fees, etc.)
- contract automatically terminates 1 year after substantial completion
B101, Article 10 - Miscellaneous Provisions
architect's consultants can't sue the owner directly; owner's consultants can't sue the architect directly
think privity