Clinical conditions Final
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Stroke (CVA) definition
interruption in the blood flow to the brain from a blocked or ruptured blood vessel - inadequate supply of oxygen and nutrients to the brain that leads to brain damage
Ischemic stroke
Thrombotic- blood clot forms within one of the arteries of the brain causing obstruction where it is formed
Embolic- clot has formed elsewhere and breaks off and travels to the brain, reached an artery too small to pass through and blocks that artery
Hemorrhagic stroke
caused by a rupture in a blood vessel with resultant bleeding into or around the cerebral tissue (aneurysm)
intracerebral (ICH)- bleeding into brain substance
Subarachnoid (SAH)- bleeding within the brains surround membranes and CSF
Thrombosis stroke
most common cause of CVA - blood clot forms within one of the arteries of the brain causing obstruction where it is formed
Lacunar stroke
small infarcts on the deep brain structures - very small and symptoms can go undetected
Embolism stroke
clot has formed elsewhere and breaks off and travels to the brain, reached an artery too small to pass through and blocks that artery
typically occur during daytime activities- can be evoked by sudden movements which raise blood pressure and dislodges clot
Transient Ischemic attacks (TIA)
“mini strokes” - blood supply to your brain is briefly blocked by a clot or narrowed artery - caused by a plaque
blockage is temporary and blood flow returns on its own
Risk factors for stoke
Modifiable- high blood pressure, smoking, atherosclerosis, waist-to-hip ratio, cardiac, alcohol
Non-modifiable- mexican and african americans, age, genetics
Right vs Left middle cerebral artery
Right- hemiplegia on left side of body, hemianesthesia (impaired sensation) on left side, apraxia
Left- hemiplegia on right side of body, hemianesthesia, aphasia, dysarthria (problems with speech)
stroke implications (ADLS and IADLS)
ADLS- dysfunction in motor system, decreased sense of touch, temp, etc, decreased stereognosis, difficulty completing 2 hand tasks, decreased balance
IADLS- impact on visual field, impact on language, impact on functional cognition
Quadriplegia vs paraplegia
Quad- any degree of paralysis of all four limbs and trunk (C1-C8 injuries)
Para- any degree of paralysis of the lower extremities with involvement of the trunks and hips depending on the level of the lesion (T1-T12, L1-L5, S1-S5)
Complete vs incomplete
complete- absence of motor or sensory function of the spinal cord below the level of injury
incomplete- some spinal cord function may be partially or completely intact
American spinal injury association levels (ASIA)
A- complete- no sensory or motor function below level of injury
B- incomplete- sensory function preserved below the level of injury, no motor function
C- incomplete- motor function preserved more than half of key muscles have a grade <3
D- incomplete- motor function preserved, muscles have a grade >3
E- normal
functional limitations by level of injury

Complications associated with SCI
Neurogenic Shock (loss of Sympathetic nervous system, bp and heart rate drop), Spinal Shock (muscles flaccid), Autonomic Dysreflexia (increase in BP), Pressure Ulcers, Respiratory Complications, Spasticity (increased muscle tone), Bladder and Bowel Dysfunction, Sexual Dysfunction
Orthostatic hypotension (drop in bp when stand to fast), deep vein thrombosis (DVT- increased risk of blood clots), osteoporosis, psychosocial implications
Traumatic brain Injury
nondegenerative, non congenital alteration in brain function caused by an external force - loss of consciousness, post traumatic amnesia, disorientation and confusion
TBI classifications
Mild TBI- less than 30 min LOC, concussions
Moderate TBI
Severe TBI- LOC more than 24 hours, PTA more than 7 days
classification based on Glasgow coma scale

Types of TBI
Closed- damage to head caused by blunt force
Penetrating- damage to brain caused by a foreign object (bullet)
Blast Brain Injury- damage to brain caused by energy waves from an explosion
Types of brain damage
Primary damage-- occurs at time of injury and created by direct impact of intrusion into brain, cellular level damage
Secondary damage- occurs within hours to day of impact as a result of physiological response to injury, neuroinflammation
Coup-contrecoup injury- impact of brain against skull and the rebounding of brain to opposite side of skull
complications of TBI
post-concussion syndrome- symptoms began or have gotten worse since concussion and may be persist for 3 or more months
cumulative trauma disorder- more times a person sustains a mild TBI, the more severe the symptoms
symptoms/deficits of TBI
Sensorimotor Deficits- Muscle Tone Issues and Movement Coordination
Visual and Perceptual Deficits-Cognitive Deficits, Memory, Executive Functioning,Attention
Psychosocial Impairments- Behavioral Changes, Emotional Issues
Neurodegenerative conditions
progressive conditions that affect the brain and spinal cords nerve cells or neurons
gradual loss of neurons - leads to decline in brain functions like memory, movement, and cognition
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
autoimmune disease that causes demyelination (immune system attacks the myelin sheath) common in females
weakness in legs, spasticity, ataxia, facial weakness, visual blurring, diplopia, areas of numbness, burning, tingling, trouble chewing or swallowing
Parkinson’s disease (PD)
Degeneration of dopamine- producing neurons in part of the brain, dopamine is crucial for coordinating smooth and balanced muscle
Motor Symptoms- bradykinesia, tremors, rigidity, postural instability, gait difficulties
Non-Motor Symptoms- fatigue, muscle weakness, decreased change in facial expression, cognitive impairments
Medications: Levodopa and dopamine agonists to manage symptom
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)- electrode implanted in brain to modulate abnormal neural activity
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
motor neuron disease that attacks motor neurons located in the brain, brain stem, and spinal cord - causes death to nerve cells controlling voluntary muscles
DISTAL TO PROXIMAL: slurred speech, trouble breathing, twitching, tripping, muscle cramps, clumsy hands and fingers
damage to Lower Motor Neuron: Muscle weakness, atrophy, cramps, and fasciculations.
loss of Upper Motor Neuron: Spasticity, hyperreflexia, dysphagia, and dysarthria.
Cognitive Changes: Some patients may experience frontotemporal dementia.
Delirium
short term disorientation
occurs when a person is being treated or in need of treatment; high fever, UTI, symptoms end when medical condition clears unless there is pre existing dementia then the changes may not be reversable
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)
exclusion diagnosis, brain shrinks, memory loss, changes in mood, changes in personality
pre-dementia (memory and mood), mild (language and praxis), moderate (sensory changes/need more care/poor new learning/BPSDs),severe (profound cognitive loss/incontinence/verbal loss) terminal (end stage complete dependence/weight loss/bedridden/sleeping)
Lewy bodies dementia
Lewy bodies- round collections of proteins in brain, early changes in attention and executive function, visual hallucinations, sleep disturbances, parkinsonian traits
Vascular dementia
cognitive impairment is abrupt in onset, associated with stroke
slowing down of mental processing, impaired judgement, personality changes
Parkinson’s disease dementia
occurs in person with parkinson’s disease
rest tremors, hypokinesia, masked facial expression, tiny handwriting, gait problems
Frontotemporal dementia
fast decline and common in clients younger than 65
lose interest in socialization, self-care, personal responsibility, display socially inappropriate behaviors, insight is impaired, changes in political, social, or religious values
Recommendations for Brain Health (Alzheimer’s Association)
S = Sleep 7-8 hours
H = Handle Stress
I = Interaction /Socialize
E = Exercise
L = Learn new things/ hobby/Music
D = Diet for Brain Health
Cancer
old or damaged cells continue to divide without control or develop abnormally - too many new cells grow = tumor
Cancer classification
classified by site or origin by tissue type and by stage and severity of cancer
benign- cells are genetically like the original cell, unable to spread
Malignant- invasive cancerous cells that have grown into surrounding tissues but are capable
Metastasize- when tumor cells spread to distant tissues, organs,
Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL):
Most common in children ages 3-5; overcrowds white blood cells, originates in bone marrow.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML):
Affects myeloid cells, leading to low blood cell counts; common in adults over 65
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL):
Slow-growing; affects older adults (age 70+)
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML):
Abnormal myeloid cells grow slowly; seen in adults, men more common : high exposure to radiation is a risk factor
Hodgkin vs non-hodgkins lymphoma
Hodgkin Lymphoma: B cells with Reed-Sternberg cells, enlarged lymphocytes
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: Affects B or T cells; more common than Hodgkin’s
Cancer diagnosis and staging
diagnosis- blood tests, MRI, ultrasound, PET scan, CT scan
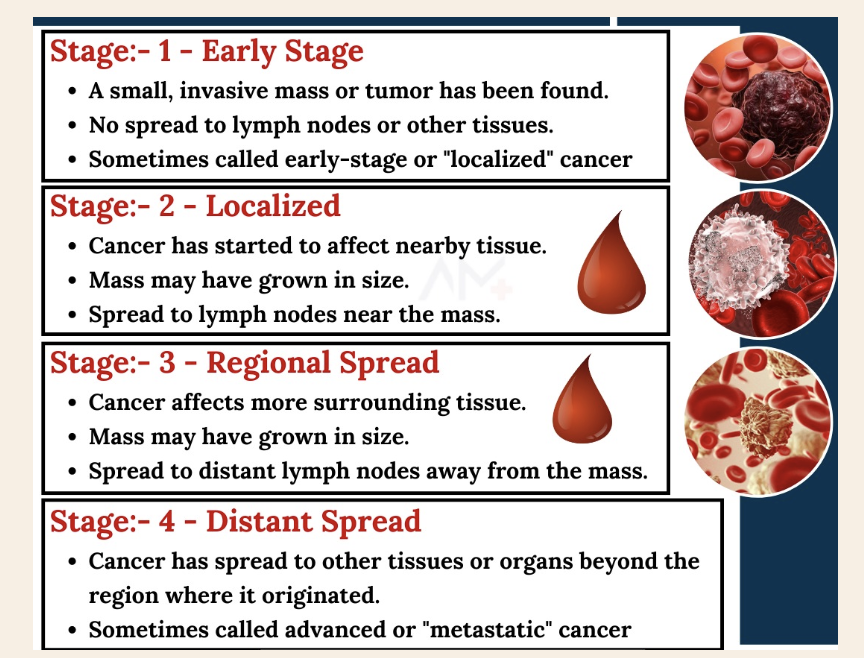
Cancer treatments
Surgery- remove the tumor
Radiation Therapy- high energy rays kill cancer cells
Chemotherapy- drugs are used to destroy cancer cells
Bone Marrow Transplant- stem cells donation
Cancer complications
Cancer-Related Fatigue (CRF)
Cancer-Related Cognitive Impairment (CRCI)
Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy (CIPN)- peripheral nervous system is damaged by chemotherapeutic drugs- weakness/pain in hands, feet
Compromised Bone Health
Cancer Pain and Lymphedema
Nutrition and Psychological Concerns- Nutrition Issues and Psychological Impact
Zones of injury
Zone of Coagulation- Area exposed to the most heat and endures the most damage, area of irreversible tissue destruction
Zone of Stasis- Damage results in decreased tissue
perfusion, Tissue in this zone may be salvageable, Try to increase perfusion
Zone of Hyperemia- Tissue is damaged but with proper care can heal and recover
Burn classification by depth
Superficial Burn (First Degree)- only epidermal layer of skin, redness and pain
Partial-Thickness Burn (Second Degree)- destroys epidermal layer, blisters, blanching
Full-Thickness Burn (Third Degree)- destroys entire epidermal and dermal layers of skin, leathery in texture, residual scar
Deep Full-Thickness Burn (Fourth Degree)- destroys all skin layers, extends into muscle tendon or bone, challenging to close and leads to amputations
Burn assessment and complications
Total Body Surface Area (TBSA): Estimation using the "Rule of Nines" to
determine the percentage of body burned.
Burn Shock- capillaries are more permeable which allows plasma to leak into surrounding tissues resulting in edema
Hypermetabolism- prolong stress in the body
Infection-barrier is injured, risk for sepsis
Burn scarring
Hypertrophic Scars- raised, red, rigid- fibrous tissue replaces normal tissue
Keloid Scars- excessive fibrosis, tender and painful and can be difficult to treat
Contractures- shortening and hardening of burn scar, permanant shortening of the muscle
Management of burns
Fluid Resuscitation (give IV fluids), Debridement (cleaning and removing nonviable tissue), Grafting (mesh graft, sheet graft, - allograft (person), xenograft (animal)
Compression Therapy (helps reduce hypertrophic scarring), Moisturization & Stretching (prevents tightness and maintains flexibility), Pain Management
Vital signs
Pulse rate (HR)- number of times a heart beats in one minute (60-100)
Respiratory rate (RR)- number of breaths per minute (12-20)
Blood pressure (BP) - systolic- top, blood being pushed out, diastolic- heart rests between beats (110/70)
hypertension- consistently 140/90 or higher “silent killer”
Oxygen saturation (SpO2)- amount of hemoglobin in blood that is saturated with oxygen (96-100%)
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
coronary arteries become damaged over time - angina (pressure in left shoulder), SOB, nausea, rapid or irregular heart rate, complete blockage= heart attack
Coronary artery bypass graft- takes a vessel from another part of body and reroutes the blood around the CAD artery
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
decrease in cardiac efficiency and output affecting the body’s ability to circulate blood, chronic and progressive
dyspnea, depression, decreased alertness, cognitive decline
medication- diuretics, beta-blockers
Chronic Obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Emphysema- walls between alveoli are damaged
Chronic Bronchitis- inflammation in the bronchioles
shortness of breath, wheezing, chest tightness, chronic cough: symptoms don’t occur until lung is already damaged
Myocardial infarction (MI)
blood flow bringing O2 to the heart muscle is severely reduced, prolonged lack of O2 to cardiac tissue, atherosclerosis
chest pain, dyspnea, diaphoresis, gastric discomfort, syncope, impaired cognition
Stenting- put an expandable coil to keep the artery open and keep from narrowing
Osteoarthritis (OA)
progressive deterioration of articular cartilage and its underlying bone and overgrowth of periarticular bone - obesity linked -
swelling of cartilage, reduction in thickness of the joint surface, loss of elasticity of the cartilage, pain worsens with activity, joint stiffness, swollen and tight joints
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
chronic, systemic, inflammatory autoimmune disorder - significant joint inflammation- also affects internal organs - genetic and environmental factors
fatigue and generalized weakness, morning stiffness, some exacerbations and remission, can be symmetrical or asymmetrical

GOUT
crystalline form of inflammatory arthritis that is marked by significant pain the in big toe - build up of uric acid in body
flares and goes into remission, joint feels on fire, pain may last 5-10 days, attacks suddenly
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
Chronic disease with no cure that causes pain and inflammation in any part of body- autoimmune where the body attacks otherwise healthy tissue
fatigue, stiffness in hands, wrist, elbows, fever, butterfly rash, sunlight sensitivity
Juvenile Arthritis
arthritis but in kids
Oligoarticular JIA: Affects 4 or fewer joints
Polyarticular JIA: Affects 5 or more joints
Systemic JIA: Involves joint swelling along with systemic symptoms like fever, rash, and organ involvement
Arthritis intervention
joint replacement- shoulders, hiips, knees - fully remove the damage bone and ultimately provide significant pain relief
Musculoskeletal pain
discomfort from impairment to the structural integrity of bones, joints, muscles, tendons etc : radiating, throbbing, burning, shooting
chronic pain- lasting 3 or more months
Myofascial pain syndrome
chronic pain disorder characterized by presence of myofascial trigger points in muscles: localized muscle pain, stiffness, muscle weakness
muscle overuse, trauma, stress, poor posture
Fibromyalgia
chronic condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, sleep problems, memory, and mood disturbances - “fibro fog”
rule out diagnosis
Low Back and Neck Pain
Low Back Pain: radiates from back and hip to legs and spine, Sciatica= pain, weakness or tingling in legs
Neck Pain: May radiate down the arms
Common Spinal Conditions
Herniated Disc- intervertebral disc bulges or leaks out compressing adjacent nerves
Spinal Stenosis- degenerative condition where spinal openings begin to narrow causing pressure on the spinal cord
Shoulder conditions
Rotator Cuff Tendonitis/Bursitis- shoulder impingement, inflammation of shoulder muscles and bursa inflamed
Rotator Cuff Tear- one or more tendons torn and become detached from head of humerus
Adhesive Capsulitis (Frozen Shoulder)- CT of shoulder joint become thickened, stiff, inflamed- scar tissue forms in shoulder capsule limiting mobility
Elbow conditions
Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow)- overuse of wrist extensors
Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer’s Elbow)- overuse of wrist flexors
Olecranon Bursitis- bursa becomes inflamed and fills with fluid and causes inflammation at tip of elbow
Hand and Wrist conditions
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome- compression of median nerve within carpal tunnel
DeQuervain’s Tenosynovitis- inflammation of the tendons of the thumb, repetitive wrist motion requiring radial abduction
Bone Conditions
Osteopenia: Mild bone density reduction, reversible with diet and exercise.
Osteoporosis: Severe bone density loss, increasing fracture risk
Amputations
removal of a limb or part of a limb due to trauma, disease, or surgical intervention
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)- circulatory problem narrowing arteries and reduced blood flow to limbs
Foot Ulcers and Infection Management-
Phantom Limb Pain
Pain the feels like its coming from a body part that is no longer there- burning, throbbing, stabbing or shooting pain in amputate limb
Mirror Therapy helps
Pre-Prosthetic and Prosthetic Management
Pre-Prosthetic Care- needs to be a good shape, decrease in swelling
Types of Prostheses- body powered, myoelectric, cosmetic
Selection Criteria- based on level of amputation, patient goals, and functional needs
Low vision
progressive diseases that lead to chronic loss of eyesight or blindness
Age-related vision changes- difficulty focusing on reading and intermediate objects, increased dryness in eyes, increased need for light, need more time to adjust from light to dark
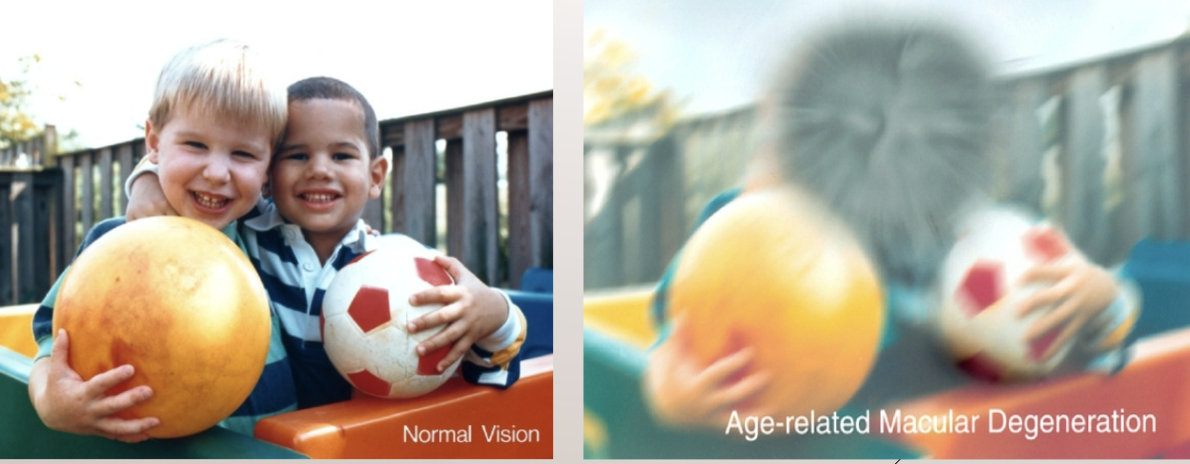
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD
affects retina and central vision- loss of central vision, loss of visual acuity, increased glare

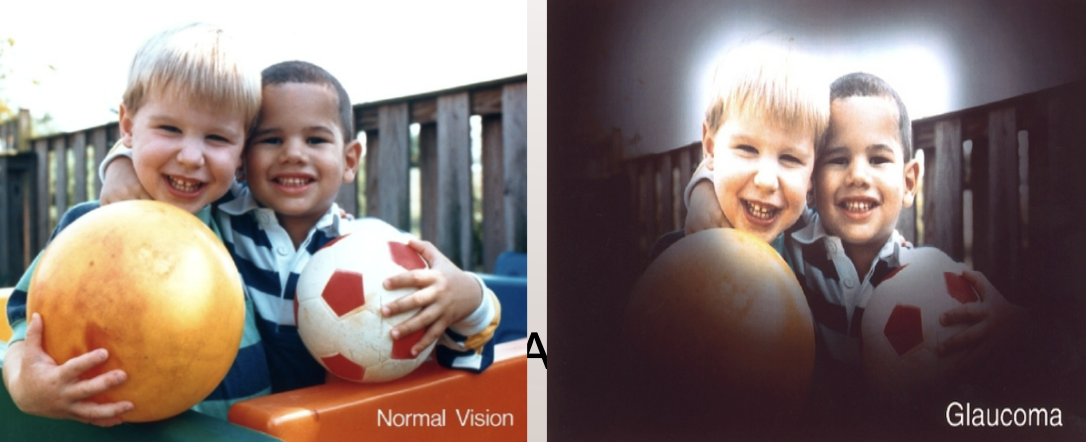
Glaucoma
diseases affecting the optic nerve caused by increased pressure in eye - can cause blindness
slow loss of peripheral vision, decreased ability to see in dim light, blurred vision, tunnel vision

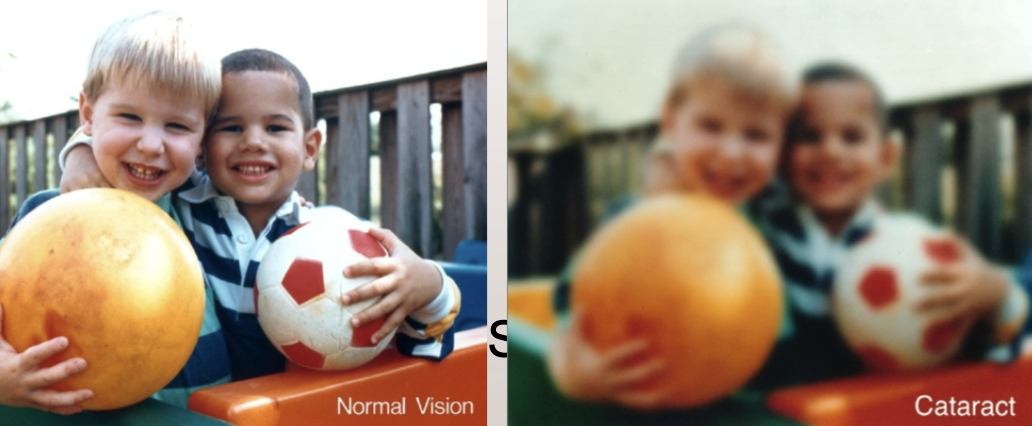
Cataracts
buildup of opaque, broken proteins that stick together and form obstructions that decrease the amount of light reaching the retina - clouding
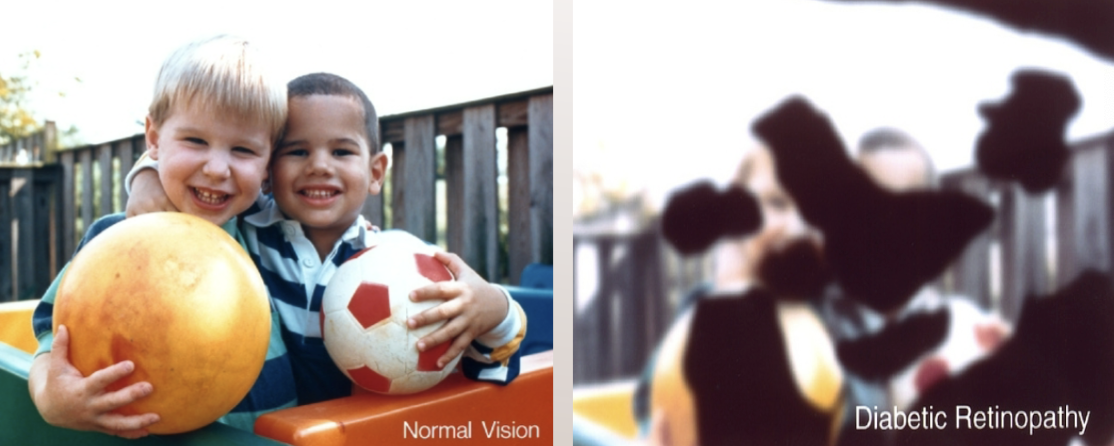
Diabetic retinopathy
complications of diabetes- too much sugar in blood damages retina -
floaters, loss of central vision, eye pain, blind spots, blurred vision

Obesity
being overweight
Social Determinants of Health- the environments raised in, access to medical care, healthy food etc, socioeconomic status
Contributing Factors- health behaviors, diet, physical inactivity, and genetic
Health risks w obesity
Modifiable Risk Factors- type II diabetes, cardiovascular, liver disease, sleep apnea
Metabolic Syndrome: group of risk factors that result in an “apple shape” high bp, high blood sugar, high triglycerides
Body Mass Index (BMI)- does not account for muscle mass, age, sex etc & Waist Circumference- indicates the amount of fat distribution in the abdominal area
Childhood and elder obesity
Childhood Obesity- Defined as a BMI at or above the 95th percentile for age and gender, Can lead to psychological stress, poor self-esteem, and reduced quality of
life.
Elder Obesity: Often due to decreased physical activity, chronic conditions, and changes in independent living. Can lead to deconditioning, muscle loss, and social isolation
Medical complications and obesity
Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome- sleep apnea, excess weight compression decreases air flow when sleeping
Lymphedema- Excess fat can impair lymph drainage, causing swelling, especially in
lower extremities.
Joint Stress & Arthritis- Extra weight increases stress on joints, accelerating cartilage degeneration.
Weight loss can reduce knee pain and decrease the need for joint surgeries.
Diabetes
group of metabolic conditions meaning a malfunction in the way the body produces insulin, uses insulin, or both
insulin- pancreas makes insulin, hormone that helps transport glucose from food into body’s cells to be used for energy, helps regulate glucose levels
Type 1 vs Type 2 diabetes
Type 1- complete or absolute insulin deficiency- autoimmune b cell destruction that requires insulin replacement
Type 2- body does not produce insulin properly due to a progressive loss of B-cell insulin secretion - does not make enough
prediabetes- blood glucose levels within range of normal to high- obesity, hypertension
Signs and symptoms of diabetes
hypoglycemia- low blood surgar (below 70 mg/dL)
hyperglycemia- high blood sugar above 125, too little insulin or body cant use it properly
diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)- diabetic emergency, ketones are made by the bodys liver from the breakdown of fats for energy formed where there is not enough insulin to use glucose - buildup of ketones in blood stream
Complications of diabetes
Macrovascular Complications- cardiovascular system, HTN, CVD, PAD
Microvascular Complications- diabetic retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy
Diabetic Retinopathy- blurred vision, floaters
Diabetic Nephropathy- impaired kidney function
Diabetic Neuropathy- burning, tingling, pain, numbness loss of protective sensation
Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Periodontal Disease- chronic inflammation of the gums due to bacteria
General deconditioning
physiological changed caused by a decline in activity that results in decreased functional participation - happens from an illness, physical disability, hospital stay, ICU stay
signs and symptoms of deconditioning
muscle weakness, pain, disrupted sleep patterns, nutritional deficits
mild (cant do physical exercise), moderate (cant do IADLS) , severe (cant do ADLS)
Management of deconditioning
Prevention and Early Intervention:
Exercise and Rehabilitation:
Trauma
An emotional wound or shock that creates lasting damage to a person's
psychological development or a distressing event that disrupts normal
functioning
Complex Trauma & Developmental Trauma Disorder
complex- chronic exposure to multiple traumatic incidents that occur within a relational system in early childhood - body cannot recover to baseline
Developmental Trauma Disorder
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Develop in response to a traumatic experience such as a life-threatening or extremely distressing situation that causes a person to feel intense fear, horror or a sense of helplessness
DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria-
A. Exposure to actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violence in one (or more) of the following ways:
B. Presence of one (or more) of the following intrusion symptoms associated with the traumatic event(s), beginning after the traumatic event(s) occurred:
Long-term Effects of Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs)
-Toxic Stress:- Overactivation of stress response systems can lead to changes in brain structure, hormonal imbalances, and health issues.
Dose-response relationship: More ACEs correlate with higher risk for
chronic health conditions, mental illness, and substance abuse.
Physical Health: Increased risk of cardiovascular disease, obesity, diabetes, and
autoimmune disorders
Autism Specturn Disorder (ASD)
persistent deficits in all areas of social communication and interaction across multiple settings, restricted repetitive patterns of behaviors or interests
must be present in early development
boys are more likely, can be detected as early as 18 mo
levels of autism/ females
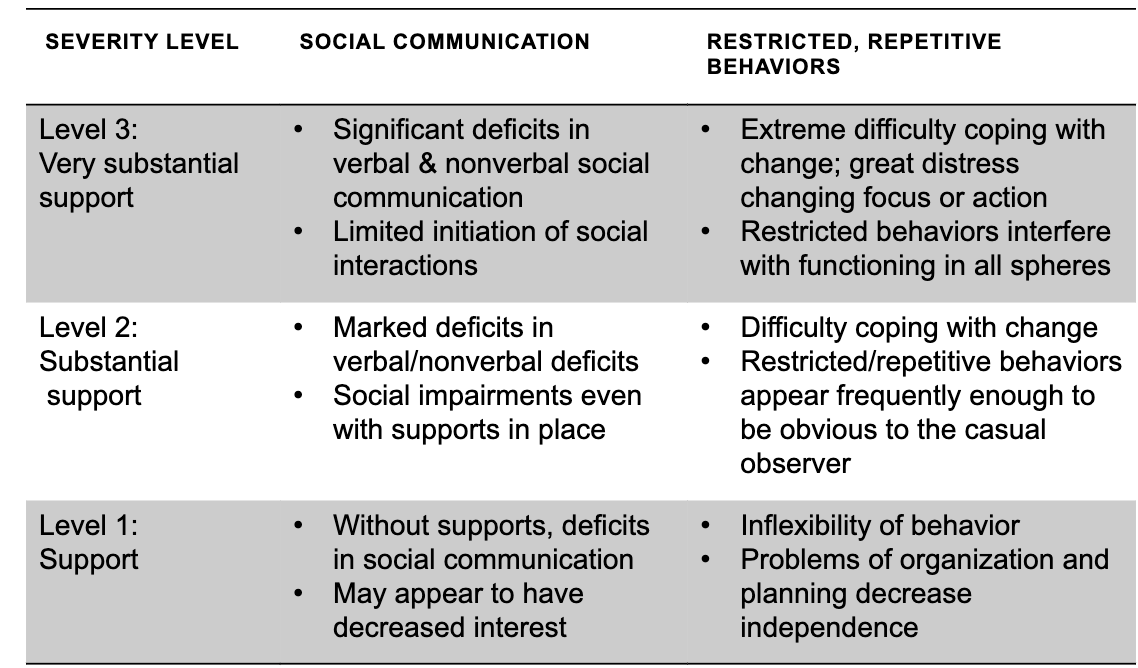
females- typically can mask better than boys, more engaged and talkative, better nonverbal skills, fewer repetitive behaviors
Red flags of autism
does not respond to name by 9 months, does not show facial expressions by 9 mo, uses few gestures by 12 mo, does not show interests by 15 mo, does not play pretend by 24 mo
Intellectual disorder
impairments of general mental abilities in conceptual domain, social domain, and practical domain: genetic causes, birth defects, environmental influences


ID co-occuring occupations
cerebral palsy, epilepsy, autism, ADHD, depression/anxiety
Sensory processing disorder
sensory processing impacts occupations
sensory modulation- hyperreactive (tactile defensiveness, gravitational insecurity) or hyporeactivity (high threshold to sensory input- can be sensory seeking)
depends upon: habituation- recognizing familiar sensory information as unimportant and sensitization- highested awareness important sensory stimulu
Sensory-based motor disorder
vestibular- bilateral dysfunction- inability to use 2 sides of the body together in a coordinated manner, inefficient balance and equilibrium reactions
Dyspraxia- impaired ability to plan and execute non-habitual motor tasks
fundamental concepts of sensory integration
sensory stimulation → processed within brain → appropriate response
Ayres Sensory integration
adaptive responses- challenge is presents in the environment is successfully met, neural plasticity, inner drive (child wants to master their environment), just right challenge (not so complex that they are overwhelmed, not simple so uninterested)
we want child to actively do it - NOT a child receiving passive input
Proprioception
sensory receptors in muscles and tendons - tells where body is in space, can control how much force is needed to complete task, calming impact on other sensory systems