Biology- Nutrition in plants
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
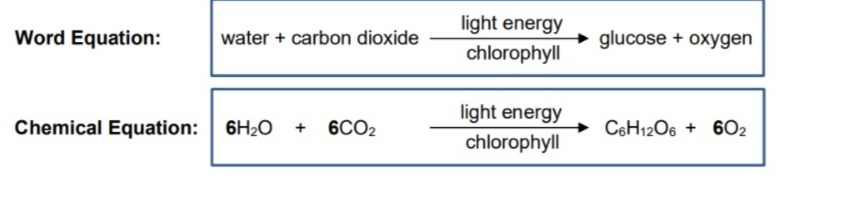
Photosynthesis equation
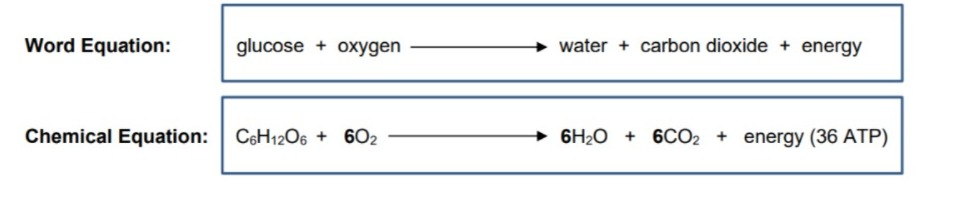
Respiration Equation
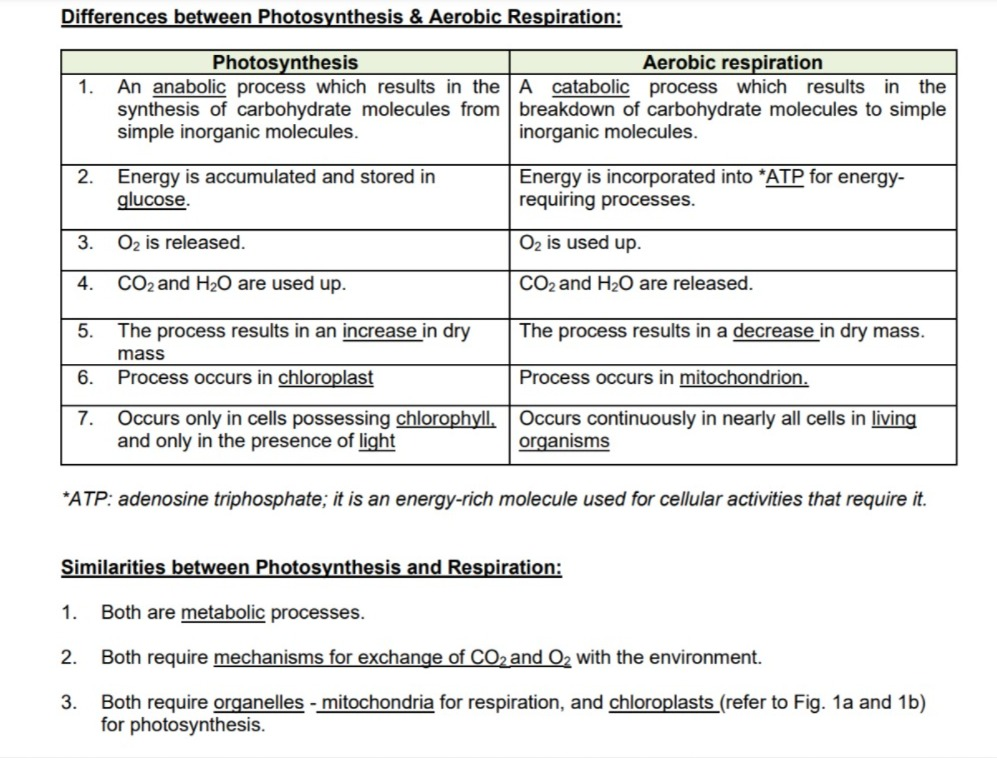
Differences and similarities b/w photosynthesis and respiration
Upper epidermis structure
One-cell thick layer
covered by a waxy cuticle
has no chloroplasts
stomata present in fewer numbers than in lower epidermis
Upper epidermis function
Waxy cuticle reduces water loss due to evaporation of water from the epidermal cells
Protects against mechanical damage
Transparent to allow light to pass through to the palisade layer
Palisade mesophyll cells structure
Densely packed cylindrical-shaped palisade cells are arranged at right angles to the upper epidermis of the leaf
Palisade cells have thin cell walls and contain more chloroplasts than other types of leaf cells
Palisade mesophyll cell function
main site of photosynthesis in the leaf due to highest concentration of chloroplasts
Thin cell wall and cytoplasm → allow rapid diffusion of water and CO2 into chloroplasts
Spongy mesophyll cells structure
Irregularly-shaped cells containing fewer chloroplasts.
Loosely packed cells form loose network of large intercellular air spaces
Spongy mesophyll cells function
Allows rapid diffusion of carbon dioxide and oxygen in and out of leaf
Some photosynthesis occur here
Vascular tissue structure
Veins in the leaf contain the xylem and phloem tissues
Xylem → comprises of lignified vessels
Phloem → consists of sieve tubes and companion cells
Vascular tissue function
Veins provide necessary support for the leaf
Xylem transports water and dissolved mineral salts from the roots to the leaves
Phloem transports the synthesized food from the leaves to all parts of plant
Lower epidermis structure
One-cell thick layer
covered by waxy cuticle
many stomata present
Lower epidermis function
Stomata allow for gaseous exchange between air spaces in the spongy mesophyll and the surrounding atmosphere
Protects the underlying cells
Stomata (singular: stoma) structure
Each stoma is surrounded by a pair of specialized guard cells
Stomata function
Guard cells regulate the size of stomata to control the gaseous exchange between the leaf and the atmosphere and to regulate the amount of water loss
Limiting factor
any factor that directly affects a process if its quantity is changed.
Factors affecting rate of photosynthesis - Light intensity
As light intensity increases, the rate of photosynthesis increases
Light intensity is the limiting factor
Beyond a certain point, light intensity is no longer the limiting factor.
Rate of photosynthesis remains constant, even as light intensity increases
Other factors may become the limiting factor
Factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis - Light Quality
Red and blue light → highest rate of photosynthesis
Green light → lowest rate of photosynthesis
Factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis - Concentration of CO2
As the co2 conc increases, rate of photosynthesis increases
Under normal conditions, co2 is an impt limiting factor as atmospheric co2 is usually low
Factors affecting rate of photosynthesis - Temperature
Photosynthesis is an enzyme-controlled reaction, hence it is an enzyme-sensitive process.
Rate of photosynthesis doubles for every 10 ºC increase.
Different types of plants grow best in different optimum temperatures
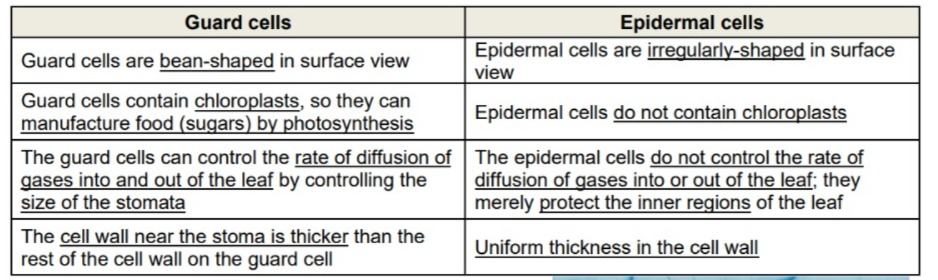
Guard cells vs epidermal cells
How do guard cells control the size of the stomata?
In the presence of sunlight, conc of K+ increases in the guard cells
Chloroplasts in the guard cells photosynthesize. The light energy is converted into chemical energy used to pump potassium ions into the guard cells from neighbouring epidermal cells.
This lowers the water potential in the guard cells.
Water from neighbouring epidermal cells enters the guard cells by osmosis → they swell and become turgid.
The guard cells have a thicker cellulose wall on one side of the cell
The swollen guard cells become more curved and pull the stoma open.
Guard cells at night
K+ accumulated in the guard cells during the day diffuse out of the guard cells.
This increases the water potential in the guard cells and water leaves them by osmosis.
The guard cells become flaccid and the stomatal pore closes
On extremely hot days excess evaporation of water causes the guard cells to become flaccid → stomatal pore closes → reduces the amount of water vapour escaping from the leaf
Effect of climate change on plant distribution and adaptation
As temperature rises, plants distribution may shift upwards to higher altitude where temperature is lower.
However, plant species that are already at the peak of the mountain will have nowhere to go if temperature rises beyond their survival range.
Boreal forest could also shift into the tundra, while the forests temperate regions could shift into the boreal region
Warmer temperatures effect on plants
warmer spring temp cause some plants to start producing pollen earlier
warmer fall temp extend the growing season for some plants(e.g. ragweed)
warmer temp and increased co2 concentrations also enable ragweed and other plants to produce more pollen, in larger quantities
Higher levels of co2 effect on plants
Elevated carbon dioxide levels may partly offset the adverse impacts of climate change on plants by the co2 fertilization effect → suggests that the increase of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increases the rate of photosynthesis in plants
Trees are expected to be favoured over tropical grasses, and may already be contributing to observed increases in tree invasions into savannas.
Increase in leaf sugars, which may influence flowering time and fitness of the plants.
Plants produce larger no. of mesophyll cells, chloroplasts, longer stems and extended length, diameter and no. of large roots, forming good lateral root production with different branching patterns; in some agricultural food crops, resulting in increasing root to shoot ratios.
Increase co2 and temp may cause the stomata to close in order to reduce transpiration → increase efficient use of water by plants, may increase photosynthetic productivity in some plants.