CLINMIC LEC SWEAT AND STOOL
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
Cystic fibrosis
Sweat is usually performed for the diagnosis of:
Sodium
Chloride
Sweat of cystic fibrosis patients are rich in:
Pilocarpine
Alkaloid that promotes sweating which possesses strong sialogigic and diaphoretic properties
Sweat glands are stimulated to sweat profusely
Sample is either collected on preweighed cause or filter paper as above and analyzed for chloride or it can be measured directly on skin using chloride specific electrode
10-40 mEq/L
Normal levels of sweat chloride in children
60 mEq/L
Indicative of cystic fibrosis
Chloride
Pilocarpine iontophoresis measures what analyte of sweat?
Increased
Cystic fibrosis affects exocrine glands that causes to have sticky sweat.
In this case, chloride is (increased/decreased)
P. aeruginosa
Most common cause of RI in px with cystic fibrosis
P. aeruginosa
Burkholderia cepacia
Staph aureus
Haemophilus influenzae
Px with cystic fibrosis are prone to infections with the following organisms: (PBSH)
¾ water
Feces is composed of ______ water
Gram negative anaerobic bacteria
Common bacteria in GIT
Small intestine
Where the final breakdown and reabsorption of ingested proteins, carbohydrates and fats take place under the influence of digestive enzymes and bile salts
Pancreas
Digestive enzymes are produced by what organ?
Trypsin
Amylase
Lipase
3 enzymes that are responsible for digesting most of the food from the diet
Bile salts
Produced by the liver, sent into the duodenum via bile duct
Needed by Lipase
Emulsifier to promote digestion of fat
Large intestine
capable of reabsorption up to 3000mL or 3L of water
Diarrhea
Occurs when less water is reabsorbed by large intestine
Constipation
occurs when fecal material stays a long time in the large intestine providing time for additional water to be reabsorbed
3-day stool collection or timed collection
Spx collection for quantitative testing
Cammidge method
Diaper scraping method
Jallife method
Insertion of thick walled glass in rectum
used for px that have difficulties to defecate (mga na budlayan mag poopy)
Large intestines
What part of the GIT is no longer capable of digesting?
Water and cellulose
These 2 forms the bulk of the stool
Stool would be acidic, urine would be alkaline
In a protein rich diet, the stool would be (acidic/alkaline) and the urine would be (acidic/alkaline)
Stercobilin
Urobilin
Gives stool its normal color (2)
Pale
VARIATIONS IN STOOL COLOR
Signify blockage of bile duct
Use of barium sulfate
Black and tarry
VARIATIONS IN STOOL COLOR
Upper GI tract bleeding
Takes 3 days to appear in stool (Hgb degradation)
Ingestion of iron, charcoal, and bismuth
Most clinically significant color
Acholic stool
Associated with bile duct obstruction
Bright red
VARIATIONS IN STOOL COLOR
Lower GI tract bleeding (colon or rectum)
Rifampin (anti-TB drug)
Beets (genetically predisposed)
Green
VARIATIONS IN STOOL COLOR
Seen in patients taking oral antibiotics
Biliverdin increased
Green veg and food coloring
Yellow
VARIATIONS IN STOOL COLOR
Milk dirt
Corn meal
Rhubarb
Fats
Bristol’s chart
drawing ka buli search sa net
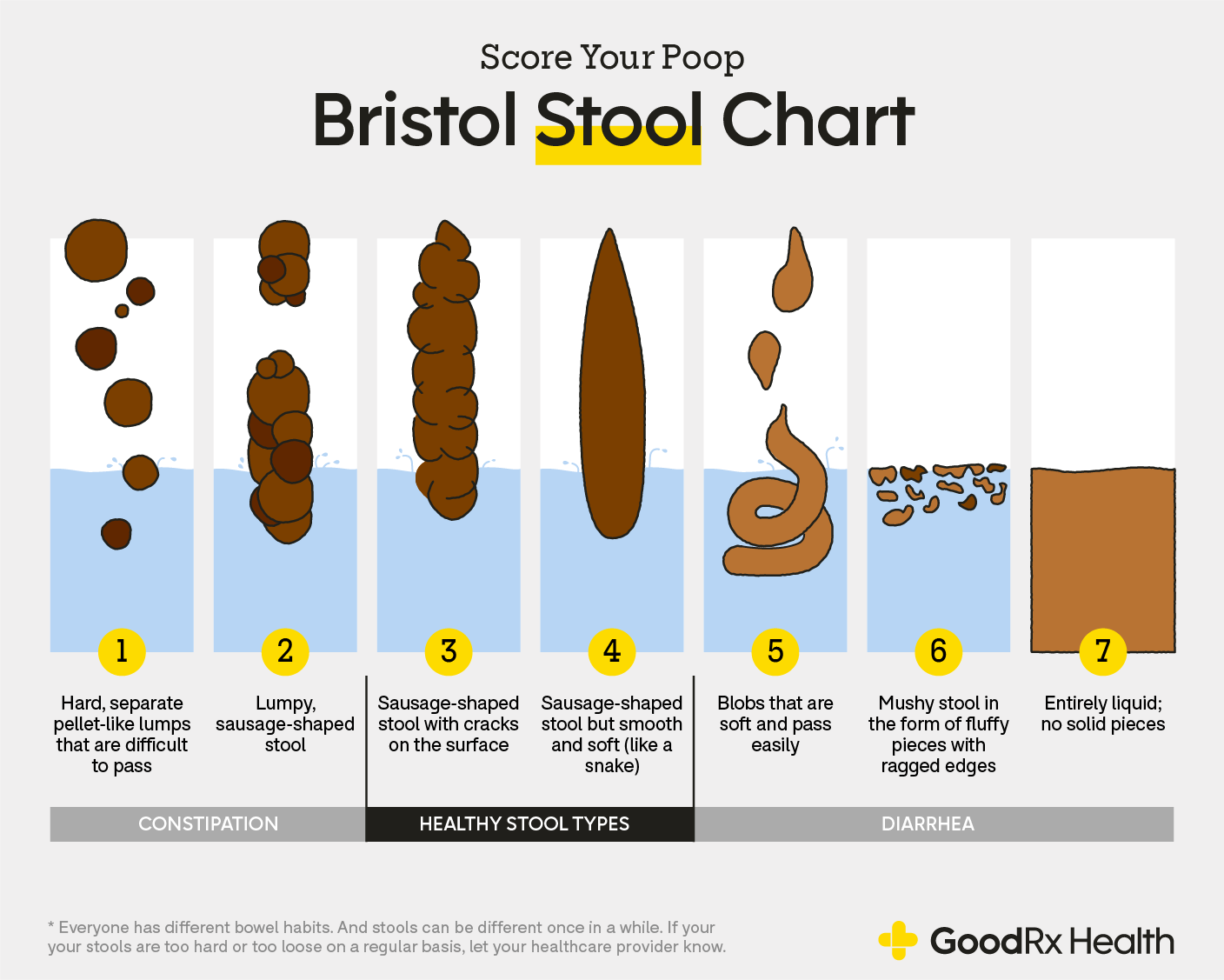
3 and 4
What number on the Bristol’s chart is considered normal?
Pea soup stool
Typhoid fever stool
Rice water stool
Cholera stool
Noodle-like stools
Stool consistency associated with cancer
Soft to well-formed
Normal consistency of stool
Constipation
STOOL APPEARANCES
Small and hard/Goat droppings
Slender and flattened/Ribbon-like
STOOL APPEARANCES
Intestinal constriction, malignancy
Bulky, frothy, greasy and may float
STOOL APPEARANCES
Steatorrhea and biliary obstruction
Mucus-coated stools
STOOL APPEARANCES
Intestinal inflammation or irritation, pathologic colitis (excessive straining during defecation)
Blood-streaked mucus
STOOL APPEARANCES
Damage to intestinal walls
Dysentery
Malignancies
Small caliber
STOOL APPEARANCES
Cancer tumor
Ulcer
Hirschsprung’s disease
A stool of a large caliber is associated with what disease?
Invasive bacteria
ex. Shigella, Enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC), Campylobacter, Salmonella, Yersinia (SECSY)
Neutrophils present is a sign of:
Toxin producing bacteria, viruses, parasites
ex. S. aureus, Vibrio spp.
Neutrophils absent is a sign of:
Fresh specimen
Slide preparation for leukocyte counting must be performed on:
Methylene blue
WET PREP
Faster
Difficult to interpret
Gram stain
DRY PREP
Permanent slide
Gram differentiation = initial treatment
Better in differentiating the organism that causes diarrhea
Lactoferrin latex agglutination test
Detects fecal leukocytes which remains sensitive in refrigerated and frozen specimens
Lactoferrin is a component of the secondary granules of leukocytes
Positive result is indicative of bacterial pathogen
Muscle fibers
examined within 24 hours of collection
Can be helpful in diagnosis and monitoring of patients with pancreatic insufficiency
Patients should be instructed to include red meat in their diet to produce a representative sample
10% alcoholic eosin
What is used to stain the striations or identification of muscle fibers?
Creatorrhea
It is defined as an increase in undigested muscle fibers.
>10/hpf
For muscle fibers, presence of _________ undigested fibers is reported as increased.
Undigested fibers
both horizontal and vertical striations are still present
Qualitative fecal fat
Microscopic screening for presence of excess fecal fat from patients suspected of having steatorrhea
Monitor patients undergoing treatment for malabsorption disorders
Oil Red O
Sudan IV
Sudan III - most common
In qualitative fecal fat, lipids are stained using: (3)
Among the 3, which is the most common?
Neutral fat stain
A step in qualitative fecal fat that stains TAG (readily stained by Sudan III)
Split fat stain
A step in qualitative fecal fat that do not stain directly; mixed with acetic acid and heated before staining of Sudan III
Neutral fats (TAG)
LIPIDS OBSERVED IN FECES
Readily stained by Sudan III
Large orange-red droplets located near the edge of the coverslip
Steatorrhea: >60 droplet/hpf
Fatty acids salts/Fatty acids (Soap)
LIPIDS OBSERVED IN FECES
Don’t stain directly with Sudan III
Observed after the specimen has been mixed with acetic acid and heated
Size and number of stained fat droplets are counted
100 small; <4 um in size/HPF
Normal fatty acid salts size and number
100, 1-8 um/HPF
Slightly increased fatty acid salts size and number
100 droplets; 6-75 um/HPF
Increased fatty acid salts size and number
Cholesterol
LIPIDS OBSERVED IN FECES
Stained by Sudan III after heating
As specimen cools forms crystal that can be identified microscopically
Fatty acid salts
Cholesterol
These 2 are considered as SPLIT FATS
Fecal occult blood testing
Most frequently performed chemical screening test for stool
Performed because any bleeding in excess of 2.5 ml/150 g of stool is pathologically significant and no visible signs of bleeding may be present with this amount of blood
150g
How much stool is usually produced in a day?
Colorectal cancer
FOBT is used as a mass screening test for what cancer?
Melena
Large amounts of fecal blood (50-100 ml/day) that turned the stool black and tarry
Pseudoperoxidase activity of hemoglobin
What is the principle of FOBT?
Benzidine
INDICATORS FOR FOBT
not used; overly sensitive; can detect <2.5 ml/150g of blood
Gum Guaiac
INDICATORS FOR FOBT
MOST COMMON but LEAST SENSITIVE
Dietary restrictions
Cannot detect upper GIT
Commonly used because it is cheap
Horseradish
Aspirin
Red meat
Raw broccoli, cauliflower, radish, turnips, melons - should not be eaten at least 3 days prior to treatment
Menstrual and hemorrhoid contamination
False-positive interferences for FOBT (HARRM)
Aspirin
Blocks cyclooxygenase pathway
Red meat
Has myoglobin which is a false-positive interference for FOBT
Vitamin C
False-negative interference for FOBT
Causes false negative if the value is >250 mg/dl
Iron supplement with vitamin C
If Vit C is not in the choices for false-negatives for FOBT, the next best answer is:
Hemoquant
Fluorometric test for hemoglobin based on the conversion of heme to fluorescent porphyrins
Detects blood from upper GIT bleeding
Required dietary restrictions esp to red meat
SENSITIVE AND SPECIFIC
Hemoccult immunochemical test (ICT)
Immunochemical test
Uses a polyclonal anti-human hemoglobin antibody that is specific for the globin portion of human hemoglobin
Does not require dietary or drug restriction
Not good for upper GIT bleeding
immunochemically nonreactive
Blood
Which of the ff is not normally found in stool? Water, Bacteria, Electrolyte or Blood?
Bleeding → Hemoglobin → Normal flora converts hemoglobin → Porphyrins
Porphyrins do not have psuedoperoxidase activity
What is the problem with pseudoperoxidase test?
Quantitative fecal fat
Used as confirmatory test for steatorrhea
At least 3-day specimen in paint cans
What is the specimen needed for quantitative fecal fat?
100g/dL for 3 days
Patient must maintain a regulated intake of fat prior and during the collection period for quantitative fecal fat. How much?
Carmine and activated charcoal
Markers taken on the first and last day of collection for quantitative fecal fat
Van de Kamer titration method
Gold Standard for fecal fat measurement; used routinely
Fecal lipids are converted to fatty acids and content is reported as grams of fat coefficient of fat retention for 24 hours
NORMAL VALUES: 1 to 6 g/dal ot 95% coefficient of retention
Weighing → extraction → titration
What is the general procedure for Van de Kamer method?
Acid steatocrit
A rapid test to estimate the amount of fat excretion; reliable tool to monitor patient's response to therapy and screen for steatorrhea in pediatric population
5N perchloric acid
What is the reagent used in acid steatocrit?
13,000 rpm for 15 minutes in microhematocrit centrifuge
For acid steatocrit, give the rpm, time, and centrifuge used.
<10%
Acid steatocrit result indicative of steatorrhea in children
Near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy (NIRS)
Technique that quantitates water, fat, and nitrogen in grams per 24 hours
Requires a 48 to 72-hour stool collection to exclude day-to-day variation
The result is based on the measurement and computed processing of signal data from reflectance of fecal surface, which is scanned between 1400m to 2600m.
Pros: less stool handling, excluded day to day variability
APT test
Used to distinguish between the presence of fetal blood or maternal blood in infant's stool or vomitus
Distinguishes not only between fetal hemoglobin and hemoglobin A but also between maternal hemoglobin AS, CS and SS, and fetal hemoglobin
1% sodium hydroxide
Reagent used in apt test, added to pink, hemoglobin-containing supernatant
Fetal hemoglobin
APT TEST
Solution remains pink. Interpretation?
Maternal hemoglobin
APT TEST
Yellow-brown supernatant after 2 minute of standing. Interpretation?
Cord blood and adult blood
2 controls used in APT test
Fetal hemoglobin resistance to alkali denaturation
What is the principle of APT test?
>200 g/day
Diarrhea leads to increased daily stool weight of about: