Chemistry- year 9
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What are atoms made up of?
Atoms are made up of protons, nutrons and electrons.
What is an electron?
A negatively charged particle.
What is a proton?
A positively charged subatomic particle in the nucleus of an atom.
What is a neutron?
A neutral (no change) subatomic particle in the nucleus of an atom.
Define subatomic particles.
Particles that are smaller than atoms. Inside the atom.
Examples of indicators.
Litmus paper and litmus solution are examples of indicators.
What colour does litmus turn when it is a acid or alkali?
Litmus is red in acid. litmus is blue when in alkali.
Limitation of litmus.
Does not show if the acid or alkali is strong or weak.
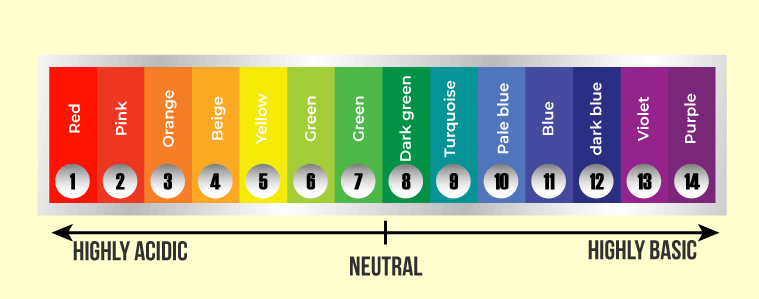
What is a universal indicator?
Universal indicator has a range of colours that show how weak or strong the acid or alkali is.
how does a universal indicator look like?
Write the word equation for the reactions with acid?
Acid+base→ metal salt+ Water (neutralisition).
Write a word equation for reaction with acids.
Acid+metal→Metal salt+Hydrogen gas.
Write a word equation for reaction with acid.
Acid+ Carbonate→ Metal Salt+ Water+ Carbon dioxie.
What are the three types of nuclear radition?
Alpha, Beta and gamme.
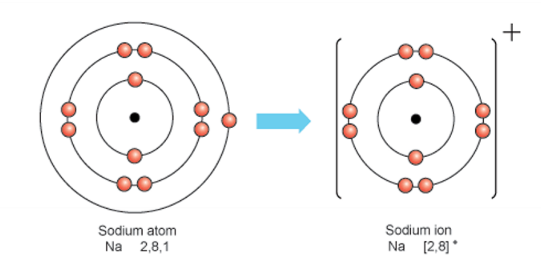
Define an ion and how they are formed.
Ions are charged atoms, they are formed when electrons are lost or gained by the atom.
Explain the difference between cations (positive) and anions (negative).
Cations are positive ions that have lost electrons, while anions are negative ions that have gained an electron.
Explain evidence for electron shells using the flame test experiment.
The tiny electrons sit in shells, when we put a chemical in a flame, the fire gives the electrons extra energy. it’s like the electronsget really exited and jumper into higher shells. But they don’t like staying up there for long. They quickly fall back down to their old seats. When they fall, they drop their extra energy as light. That’s why the flame glows in a special colour, and it is a different colour depending on element,( how many electrons in the atom).
Explain how the periodic table is arranged in groups and periods.
The periodic table is ordered on how many protons the atoms have. The groups (vertical) are elements that behave similalry, chemical ways. Then there are periods that are horizontal.
Use the position of an element in the periodic table to predict its proporties.
periods show the number of shells and groups are put in similar behaver and how many ourter electrons.
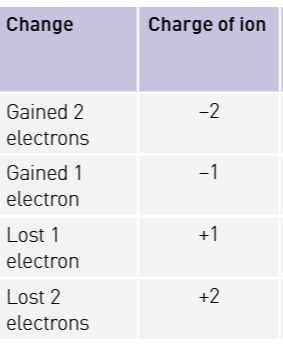
Caculate the charge on an ion from its electron gain/loss
Electrons are negativley charged so when an atom gains an electron, the charge on the whole atom becomes negative. If two electrons are gained, then there is an overall charge of negative two. But when they loss one or two it becomes positive one or two.
Draw diagrams to show ion formation (electron transfer for metals and non-metals)
Define isotopes as atoms of the same element with different numbers of electrons.
An isotope is a form of a chemical element that has the same number of protons in its atomic nucleus but a different number of neutrons compared to other forms of the same element. Protons and nucleaus usally have the same amount. For example carbon has 12, so 6 protons and 6 neutrons, but for isotopes it can be different and it can have 6 protons and 8 neutrons.
Decribe the different proporties of acids and bases.
Acids are sour, corrosive substances that turn blue litmus paper red, have a pH below 7, and react with metals to produce hydrogen gas. Bases are bitter, slippery, and alkaline substances that turn red litmus paper blue, have a pH above 7, and feel slippery to the touch.
Explain Thomson’s plum model and the key experiment that led to it.
J.J. Thomson's "Plum Pudding Model" describes the atom as a sphere of diffuse positive charge with negatively charged electrons embedded within it, like plums in a pudding. This model was a result of his cathode ray experiments, which demonstrated the existence of negatively charged subatomic particles, the electrons. These experiments showed cathode rays were deflected by electric and magnetic fields, indicating their negative charge and particle nature, and that they came from all types of atoms.
Explain the Rutherford’s nuclear model and the key experiment that led to it.
Rutherford's nuclear model proposes the atom has a small, dense, positively-charged nucleus at its center, with electrons orbiting at a distance, and the atom is mostly empty space. This model was a result of the Geiger-Marsden experiment (also known as the Rutherford gold foil experiment), where alpha particles were fired at a thin gold foil. The key observation was that while most alpha particles passed through undeflected, a small number were scattered at large angles, some even bouncing back, which indicated a concentrated, massive positive charge within the atom.