RSP 306: Exams Lookover
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
PEEP is used primarily to:
prevent atelectasis
Positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) is most therapeutic for ___ due to ___
hypoxemia, intrapulmonary shunting
which of the following physiological benefits dose PEEP offer?
increased functional residual capacity, improves V/Q mismatch, lowers all distending pressure
the physician is concerned about the risk of barotraumas and asks you to outline some potential criteria for more prudent ventilator management. you would recommend all of the following criteria except
keeping the PEEP less than 5 cmH2O
PEEP is usually indicated in severe restrictive lung disease because it can:
reduces alv distending pressure and correct refractory hypoxemia
complications and hazards of increasing PEEP include all of the following except:
Decreased intracranial pressures
When the p-v loop moves towards the right, what is the lung characteristic changes
Decreased static compliances
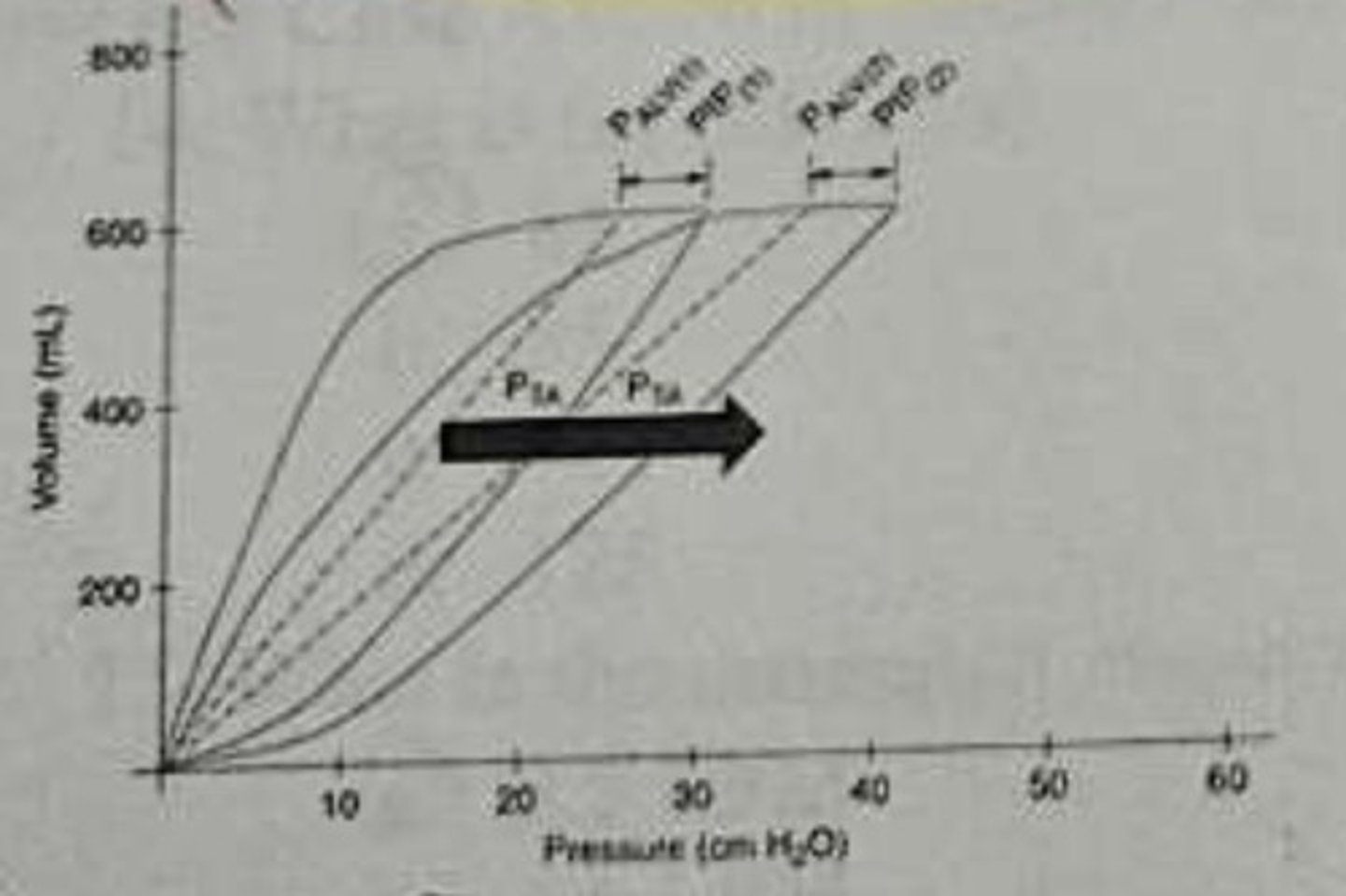
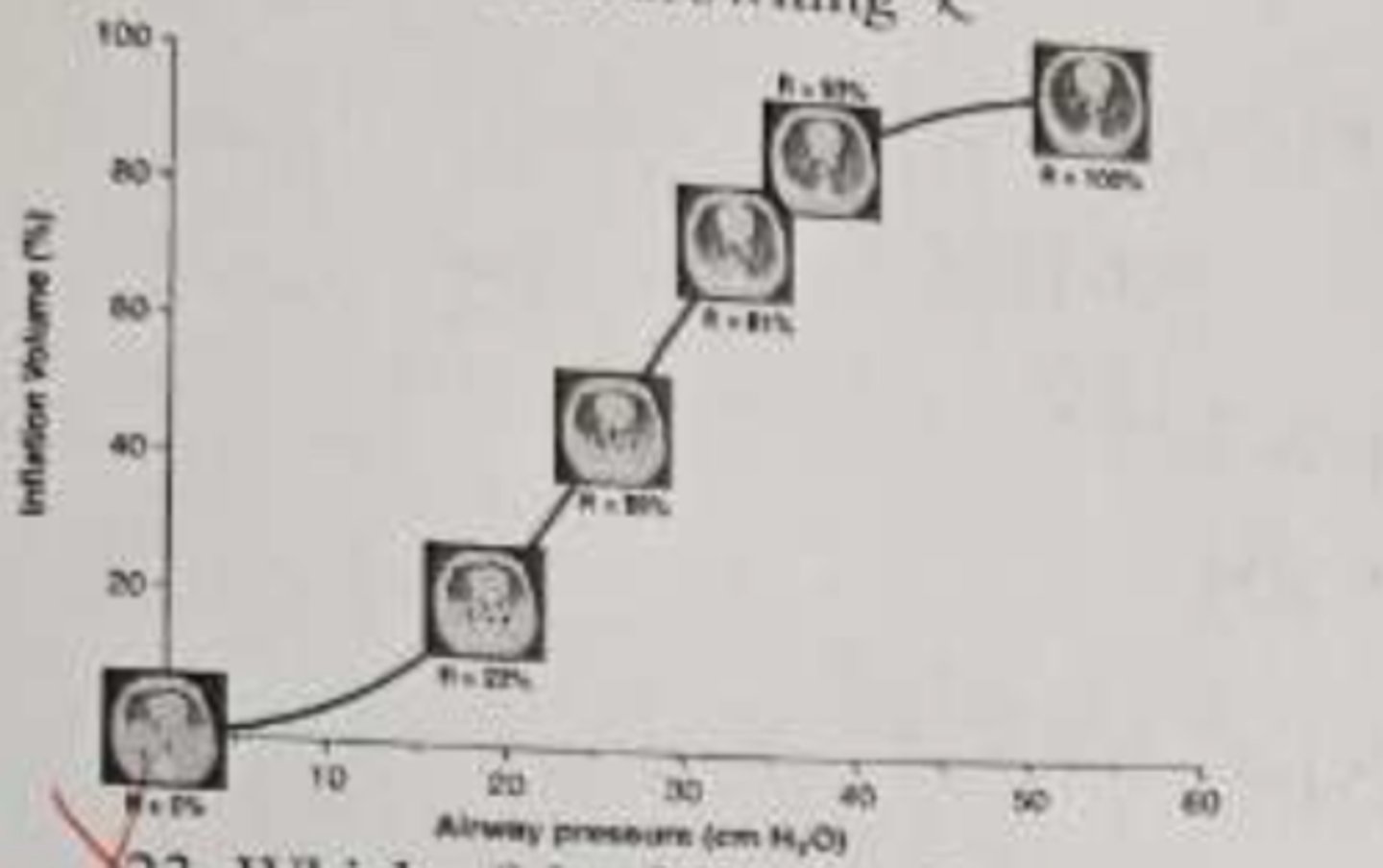
On the following P-V loop what does lower inflation point indicate?
ALV recruitment
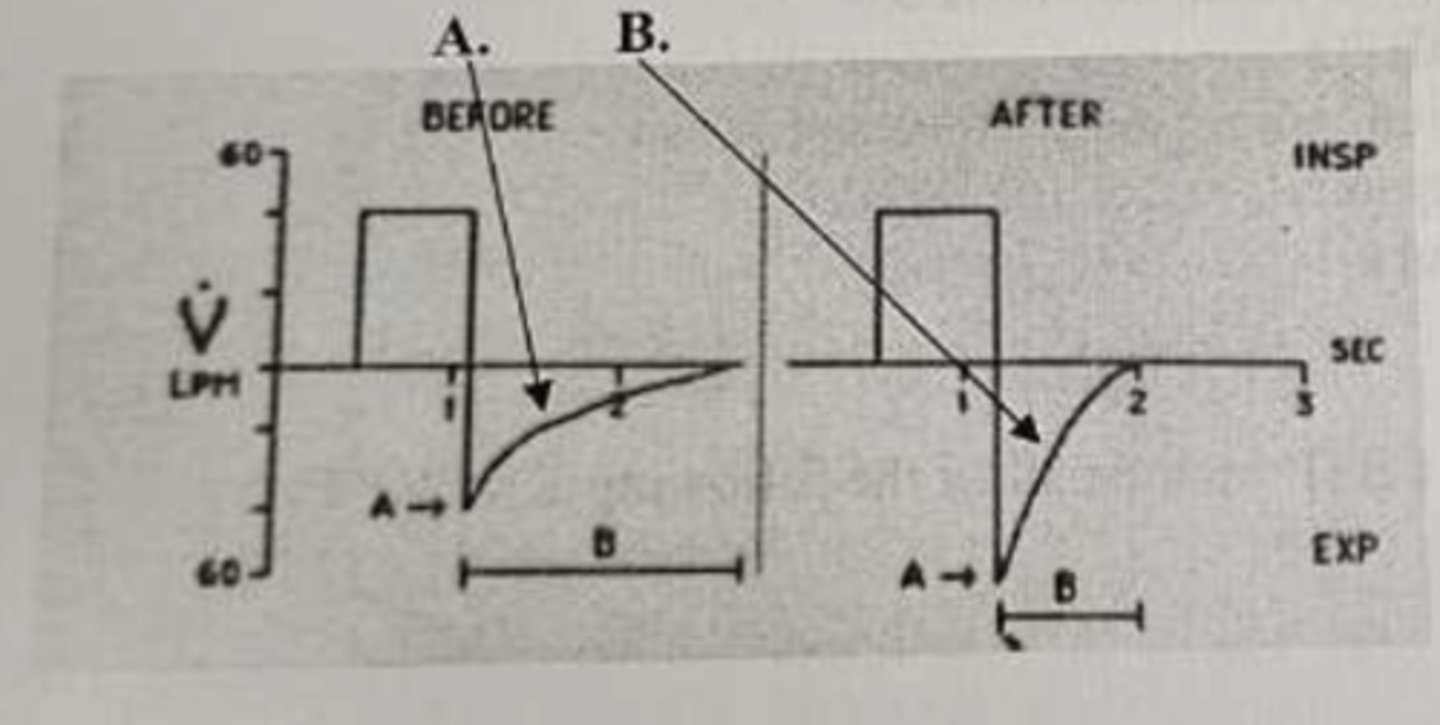
which graphic would tell you if a bronchodilator was effective
flow-time scalar
What action should be taken to improve flow-time scalar waveform in image A to look more like image B
Administer a bronchodilator
P-V loops what does the upper inflection point indicate
overdistention of the lungs
Increased RAW vs decreased CL
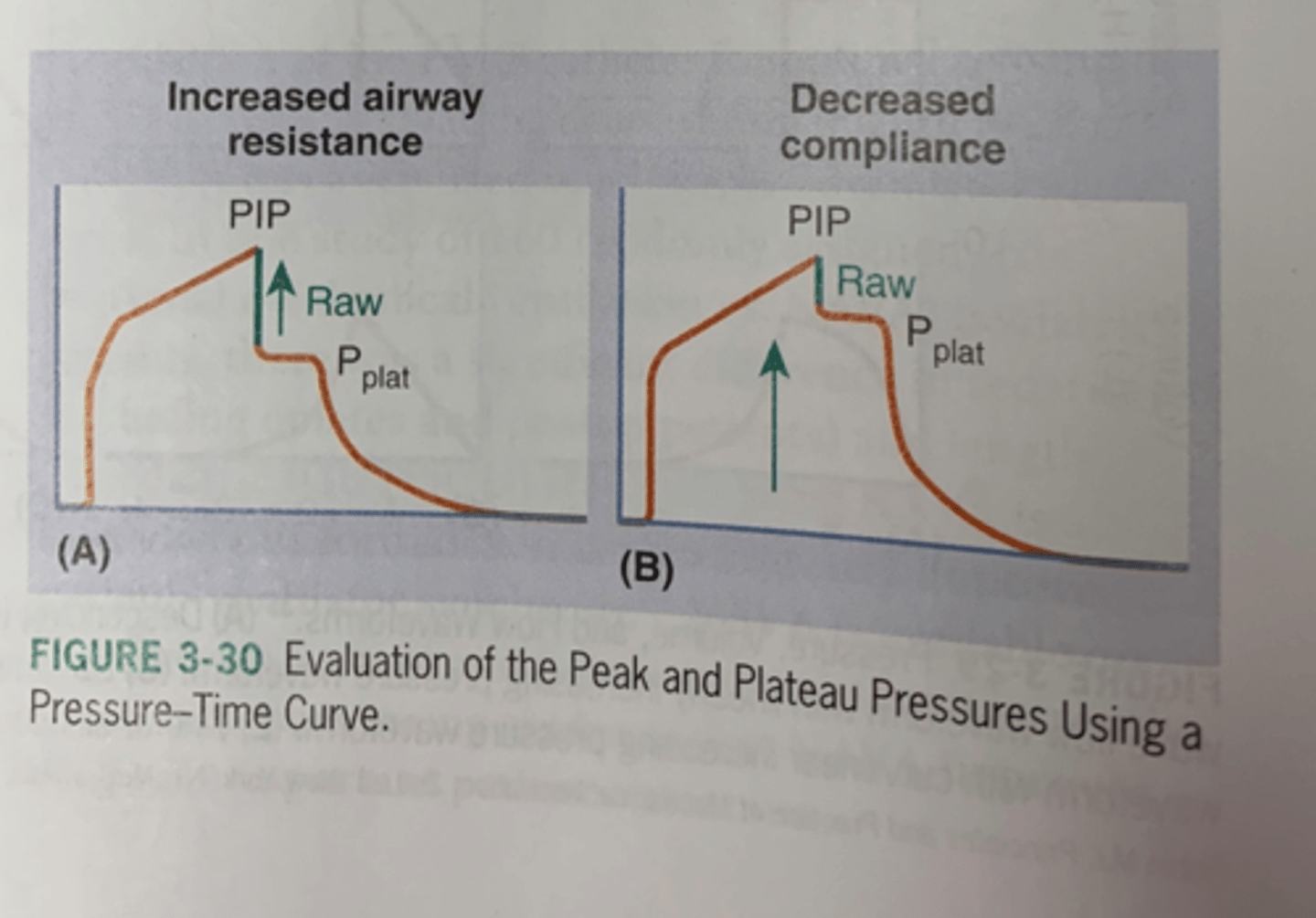
What is the P/F ratio
- PaO2/FiO2
- 83

What is the estimated ALV min vent?
- (VTe-VD)xRR
- 3.5

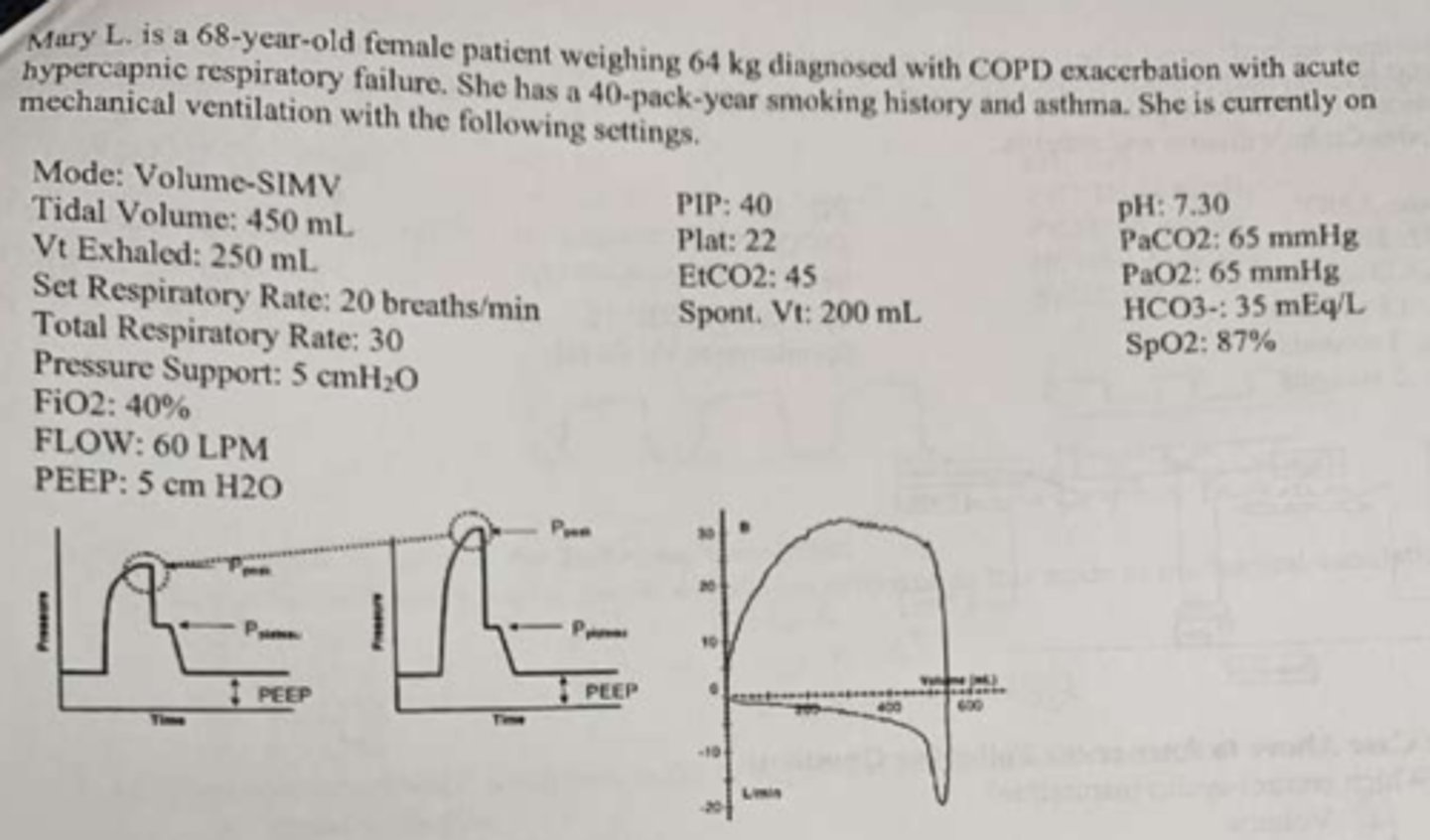
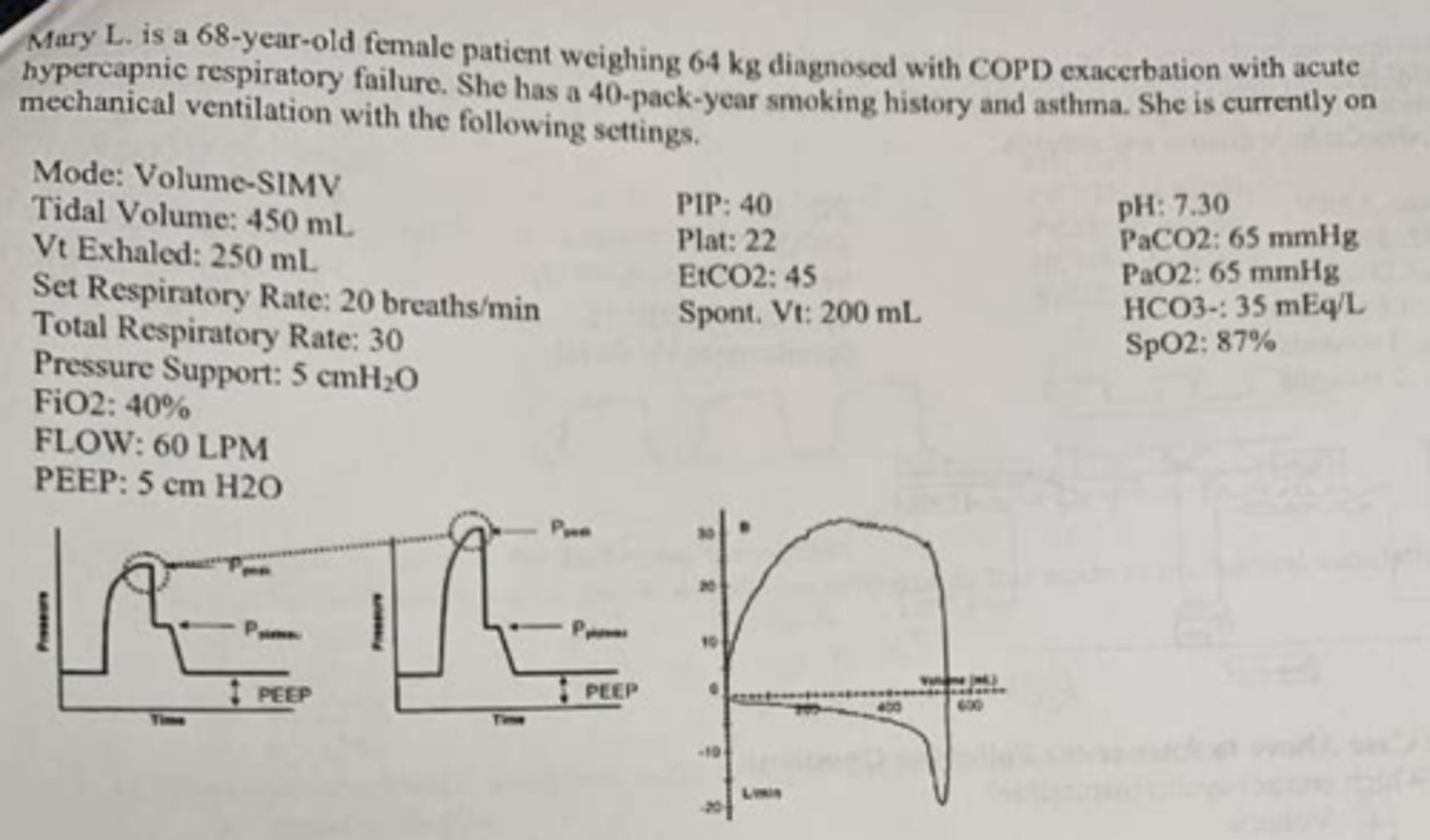
what the ABG & what mode would you switch it to correct FRIST.
- uncomp resp ACD with uncorrected hypoxemia
- Increases RR

based on the PEEP study above, what is the optimal PEEP by CL
15
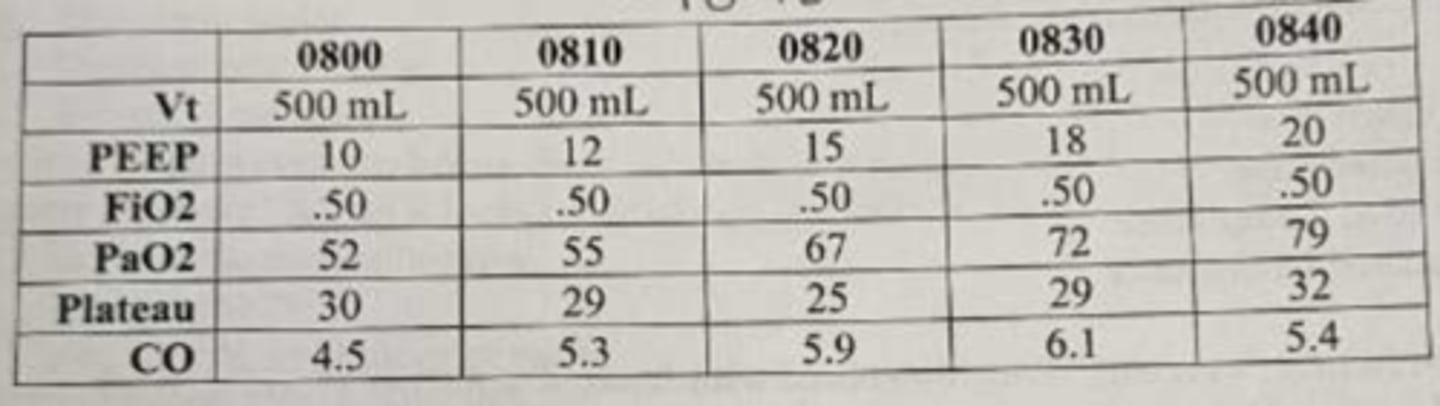
what is contributing to the worsening hypoxemia despite oxygen therapy
refractory hypoxemia due to atelectasis
the absolute contraindication to mech vent
untreated tension pneumothorax
which of the following P-V segments above is most likely to reflect the highest driving pressure
R-93% - R100%
what the ABG
uncomp resp ACD with uncorrected hypoxemia

which of the following conditions contributes to the results noted in the ABG
increased in RAW

the following are vent management recommendation that are reasonable EXCEPT
changing to HFOV mode mech vent

estimated ALV VE
13.4

all of the following signs on chest radiograph indicate COPD except
increased vascular marking
all the following breaths types are available in PRVC and SIMV except
intermittent
all vent parameters should be considered when managing a TBI patient except
utilize permissive hypercapnia
prime risk of hyperventilating a TBI patient is
ischemic brain injury
total min vent
7
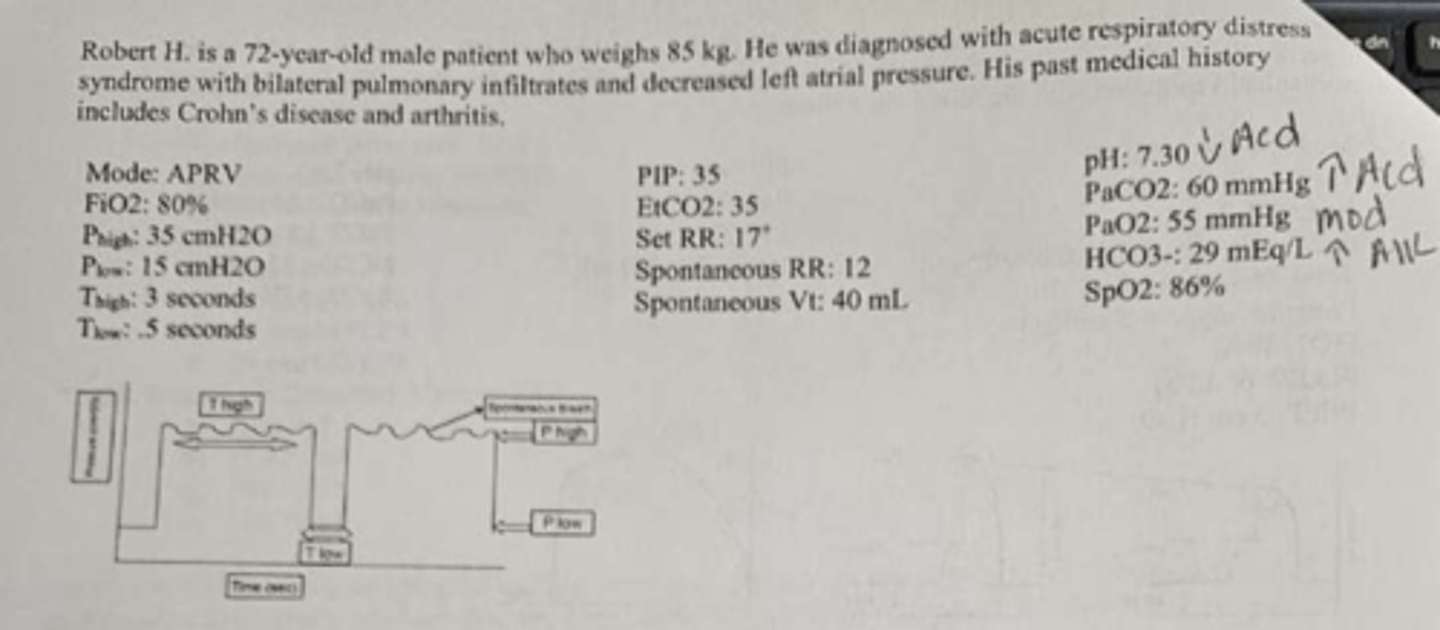
All of the following approaches should be considered EXCEPT
increases the PEEP or changing to APRV mode
Which control cycles inspiration
time
according to the Berlin definition of ARDS, the p/f ratio indicates
Severe ARDS
How is RR determined in ARDV mode?
total cycle time
what's the ABG and how would you NOT correct it
- partially comp resp ACD uncorrected hypoxemia
- decrease the Plow
all o the following contribute to the benefits of proning except
reduced surface area in the alveoli
what is the ALV min vent and how to improve it
- 1.5
- Increase the pressure support

which of the following is the limiting variable on the vent setting above?
pressure

ARDSnet guideline require specific modes of mechanical vent
False
ARDSnet Guidlines utilize tables that include a lower peep/higher Fi02 and higher PEEP/Lower FiO2 to improve management of type 1 resp failure
Ture
ARDSnet guidelines publish oxygenation goals of
PaO2 55-80mmHg
Relative contraindications of PEEP therapy includes all of the following except
untreated tension pneumothorax
High frequency oscillatory vent utilizes all of the following except
high tidal volumes
which of the following condition is affecting your patient? and how would you correct it?
- Obstructive
- bronchial hygiene, bronchodilator, and corticosteroid

which of the following are true regarding PC vent
- used for time-triggered and patient-triggered mechanical breaths
- flowrate is variable
PS Is an adjunct mode that supports spontaneous tidal volume by decreasing work of breathing
Ture
in VC vet, what is set by the clinician
Tidal volume
In PC vent, which parameter is fixed
Pressure
Pressure support cannot be used with which of the following modes
CMV
Mr. Camper is being vent mech with control mode. which of the following parameters is determined by the pt
a. Vt
b. insp flow rate
c. RR
d. none
d. none
Mrs. Smith being vent with assist control mode at a set rate of 6 breaths per min and an assisted rate of 4 breaths per min. Under this mode, a vent-triggered breath will be delivered every ___ sec.
10
the major advantage of assist control mode ventilation is that the patient can:
breath at a min volume necessary to normalize the PaO2
during SIMV, the breaths delivered may be:
a. mandatory
b. assisted
c. spontaneous
d. all
d. all
when the pressure is released in APRV, it stimulates an effective _____ maneuver.
Exhalation
when pt are being vent in APRV, spontaneous breathing is available
true
all of the following problems concerning the artificial airway and ventilator circuits that would increases airways resistance EXCEPT
increasing the PS
CPAP provides positive airway pressure during the ____________ phase and it _______________ include mechanical breaths
Inspiratory and expiratory; does not
which of the following conditions is affecting your pt
restrictive disorder

what FiO2 would you select to normalize the PaO2?
.70

The p/f ratio is used to evaluate the severity of ARDS based on the Berlin def to determine mortality risk
ture
id ti was determined that switching form VC to PC mode was appropriate for your pt, how would you set the insp pressure
use the monitored plateau pressure
In a VC mode, the _____ is preset by therapist with a variable ____ depending on the compliance and airway resistance of the lung
- VT
- PIP
Which of the following modes delivers mandatory breaths and allows spontaneous breathing?
SIMV
Which of the following modes delivers pt-triggered and time-triggered mandatory breaths?
Assist control
for a pt who are placed on mech vent for non-cardio complications where no ABG has been taken, the initial FiO2 may be set at
40%
what range is recommended for Vt in pt with severe ARDS who is being mech vent
4-6 ml/kg
what peak insp pressure should be avoided when managing vent pt
40 cmH2O
what static (plateau) pressure should be avoided when managing mech vent pt
30 cmH2O
Refractory hypoxemia is preset when the PaO2 is less then ___ mmHg at an FiO2 of greater than ____ percent
60; 50
ALV min vent
5.5

What's the ABG and how to fix
- uncomp resp ACD with corrected hypoxemia
- increase RR

how would you protect the trachea for this pt who is anticipated to be on mech vent for extended period
Monitor cuff pressure
what the condition based on ABG and how to correct it first
- increased RAW
- increase the insp pressure

all of the following recommendation would be reasonable to make to a physician regarding vent management EXCEPT
changing to ASV mode

adaptive and combo modes of mech vent may not be appropriate for this pt due to
higher risk of irregular breathing patterns

due to the need for extended vent support, the cuff pressure should not exceed
20-15 mmHg
Airway care should include all of the following EXCEPT
routine suctioning
Total min vent
9.9

VD %
13%

P[a-et]CO2 difference
5 mmHg

what mode for when pt wake up after surgery
SIMV
