cholesterol
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
are triglycerides or phospholipids more polar?
phospholipids = more polar
is cholesterol or cholesterol ester more polar?
cholesterol = more polar
cholesterol ester = more lipophilic
structure of a chylomicron
outside = cholesterol + phospholipid
inside = cholesterol ester + triglycerides
usually more TG> CE
SATA: which of the following are inside the chylomicron
a) cholesterol
b) cholesterol ester
c) triglyceride
d) phospholipids
b) cholesterol ester
c) triglyceride
SATA: which of the following are outside the chylomicron
a) cholesterol
b) cholesterol ester
c) triglyceride
d) phospholipids
a) cholesterol
d) phospholipids
what happens after the chylomicron enters the circulation?
hydrolysis in tissues by lipases
most of the TG in the core → fatty acids for energy (ATP)
chylomicron core = more CE > TG = remnant chylomicrons
remnant chylomicrons vs chylomicrons
remnant chylomicrons = CE > TG
smaller size
chylomicrons = TG > CE
bigger size
what happens to the remnant chylomicrons after they are formed?
liver
digested by lysosomes into free cholesterol
can become CE by esterification (storage)
or metabolized into bile acids
what does the liver make from recombining the 4 components of the chylomicrons?
VLDL particles
same orientation (TG + CE = inside, C, PL = outside)
TG = very high
what is the purpose of the apo-protein
helps chylomicrons move through circulation
helps with recognition of certain tissues
liver makes a small particle from remnant chylomicron that is mostly of TG
a) low density lipoprotein (LDL)
b) high density lipoprotein (HDL)
c) intermediate density lipoprotein (IDL)
d) very low density lipoprotein (VLDL)
d) very low density lipoprotein (VLDL)
liver makes a small particle from remnant chylomicron that is more CE > TG (after adipose tissue)
a) low density lipoprotein (LDL)
b) high density lipoprotein (HDL)
c) intermediate density lipoprotein (IDL)
d) very low density lipoprotein (VLDL)
c) intermediate density lipoprotein (IDL)
liver makes a small particle from remnant chylomicron that is mostly just CE inside globule. dangerous because of its apo-proteins
a) low density lipoprotein (LDL)
b) high density lipoprotein (HDL)
c) intermediate density lipoprotein (IDL)
d) very low density lipoprotein (VLDL)
a) low density lipoprotein (LDL)
liver makes a small particle from remnant chylomicron that lost all of its TG.
a) low density lipoprotein (LDL)
b) high density lipoprotein (HDL)
c) intermediate density lipoprotein (IDL)
d) very low density lipoprotein (VLDL)
b) high density lipoprotein (HDL)
list the cholesterol lowering agents or antihyperlipoprotein drugs
nicotinic acid
gemfibrozil
statins
bile
cholesterol transport inhibitors
what is the most commonly used class of cholesterol lowering agents
statins
what is the most effective cholesterol lowering agent
nicotinic acid
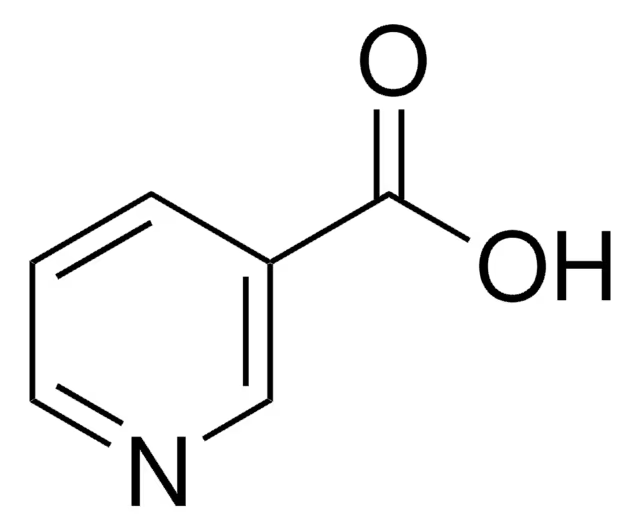
what is this drug?
nicotinic acid
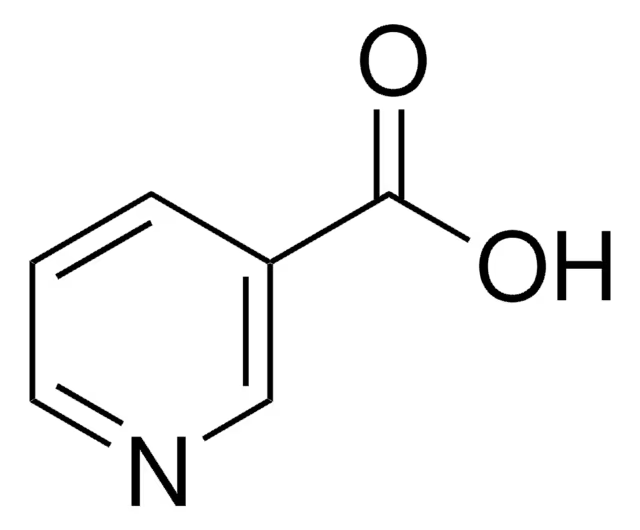
what is the difference between nicotinic acid and nicotine
replaced pyrrolidine ring in nicotine with COOH
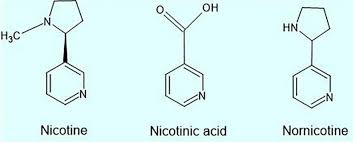
Nicotinic acid is also known as ______
vitamin B3 (niacin)

how is nicotinic acid absorbed? how is it metabolized
good oral absorption
possibly active transport because it is small and polar
poor lipophilicity
metabolized in liver → nicotinamide
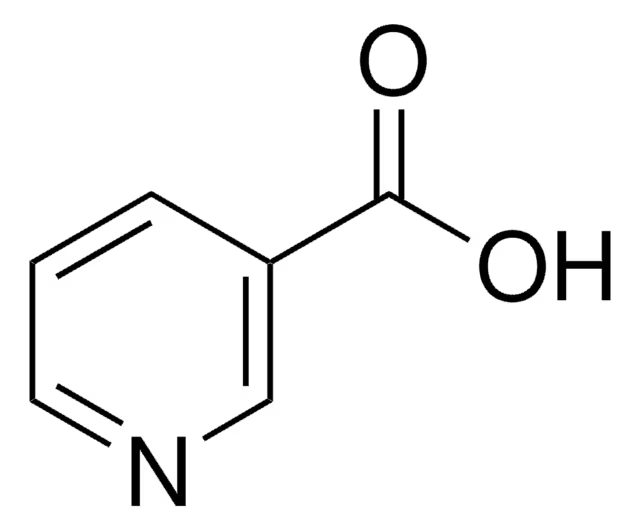
what is a side effect of nicotinic acid? why?
flushing
peripheral vasodilator effects as well
effects of nicotinic acid
effective in lowering LDL + raising HDL levels
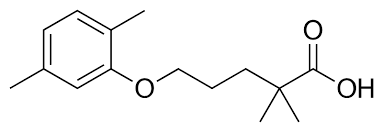
what type of drug is this?
aryloxyisobutyric acid derivative
gemfibrozil
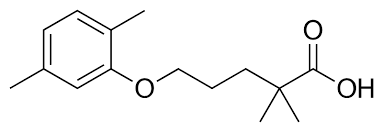
how is gemfibrozil metabolized?
aliphatic hydroxylation → conjugation

gemfibrozil effects
lowers both cholesterol and triglycerides
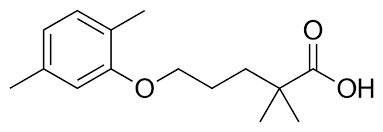
gemfibrozil absorption + administration
orally
high PPB
smaller particle lipid cycle order
VLDL → IDL → LDL → HDL
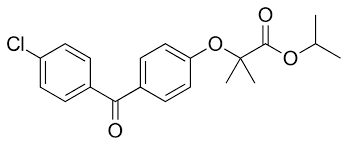
what type of drug is this?
aryloxyisobutyric acid derivative
fenofibrate
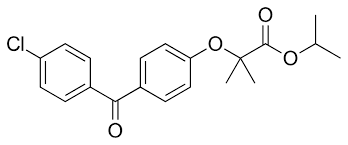
fenofibrate MOA
enhances catabolism of TG-rich particles + reduces secretion of VLDL → hypotriglyceridemic effects
statin MOA
HMG CoA reductase inhibitors
block rate-limiting step (HMG CoA → mevalonic acid) = blocks production of cholesterol
T/F: statins decrease endogenous and exogenous cholesterol levels
false
statins only inhibit endogenous cholesterol biosynthesis in the liver (decreases LDL)
does not affect dietary cholesterol
cholesterol synthesis steps
acetyl CoA
HMG CoA (3 acetyl CoA together + acetyl cos)
(HMG CoA reductase)
mevalonic acid
(20 steps)
cholesterol
how many carbons are in acetyl CoA?
2 carbons
how many carbons are in HMG CoA
6 carbons (3 acetyl CoA combined)
how many carbons are in mevalonic acid?
6 carbons
how many carbons are in cholesterol?
27 carbons
what is the full name for HMG CoA
3 hydroxy-3-methyl gluteryl CoA
what is a common structure in statins
5 carbon backbone with hydroxyl + carboxyl groups
similar structure to HMG
T/F: statins have coenzyme A part replaced with highly lipophilic area connected to mevalonic acid
describe the absorption of statins
absorbed well (good oral absorption)
high PPB
lipophilicity > hydrophilicity
all have similar potency
how are statins metabolized?
high FPM = low bioavailability
phase 2 conjugation
further hydroxylation
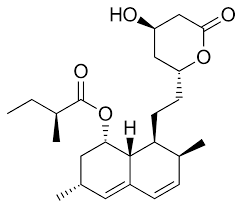
what type of drug is this?
Statin
lovastatin
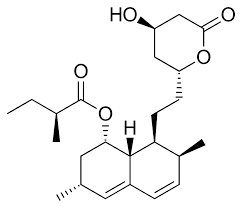
what type of ring does lovastatin have?
naphthalene ring
which statins are prodrugs?
lovastatin
simvastatin
which statin is more hydrophilic than the others?
a) lovastatin
b) rosuvastatin
c) pravastatin
d) simvastatin
c) pravastatin
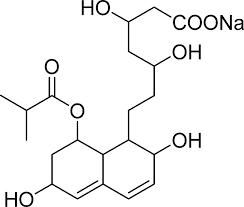
what type of drug is this?
statin
pravastatin
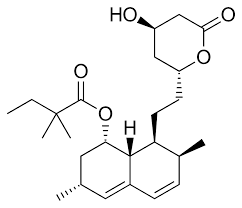
what type of drug is this?
statin
simvastatin
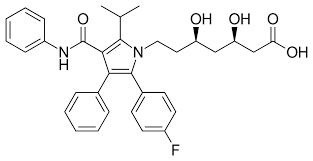
what type of drug is this?
statin
atorvastatin

what type of drug is this?
statin
fluvastatin
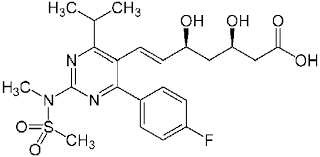
what type of drug is this?
statin
rosuvastatin
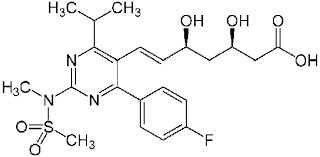
what structure in rosuvastatin makes its metabolism a little different? how does it affect its dose?
sulfonamide group
liver does not like sulfonamide
lower dose than other because of liver metabolism resistance
what are bile acids
metabolites of cholesterol
what happens when bile acids are sequestered in the GIT?
liver cholesterol will be depleted
common structure in bile acid sequestrants
positively charged N
decrease absorption in GIT = localized action
polymeric lipophilic area
polymers = not absorbable = localized action
what structure in bile acid sequestrants react with the carboxylic group?
quaternary nitrogen
what structure in bile acid sequestrants react with the bile acid lipophilic backbone ?
polymer lipophilic area
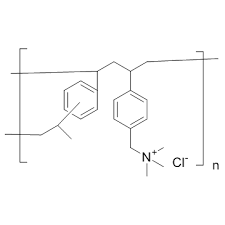
what type of drug is this?
bile acid sequestrant
cholestyramine chloride
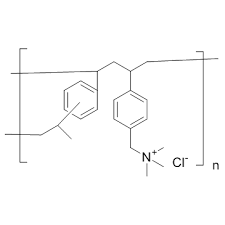
what is an ADE of cholestyramine chloride? why?
severe constipation
quaternary ammonium loves water = absorbs water in GIT = severe constipation
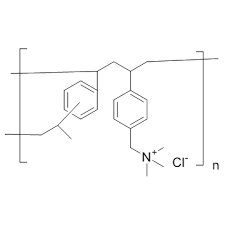
why might cholestyramine have problems with drug-drug interactions?
nonselectivity → sequesters anything highly lipophilic

what specific drugs can cholestyramine have drug-drug interactions with ?
anything highly lipophilic
contraceptives (steroid hormone supplement) → ineffective
vitamin K → clotting
decrease absorption of all non-water soluble vitamins (ADEK)
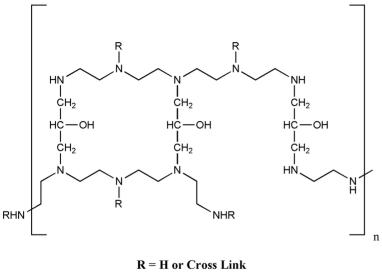
what type of drug is this?
bile acid sequestrant
colestipol HCl
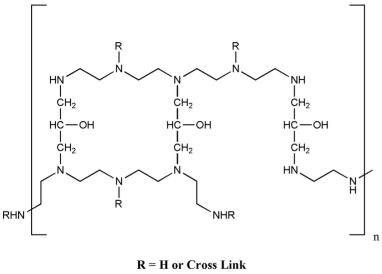
describe the structure of colestipol
polymer of tetraethylenepentamine
non-quaternary (2 + 3 amines)
but is protonated in GIT
side effects + concerns of colestipol
constipation (less than cholestyramine)

what type of drug is this?
cholesterol transport inhibitors (CTI)
ezetimibe
MOA of ezetimibe
cholesterol transporter-inhibitors
inhibits absorption of cholesterol at the brush border of the small intestine in the GIT
inhibits EXOGENOUS cholesterol absorption
compensatory mechanism of cholesterol transporter-inhibitors (CTI)
compensation mechanism to increase cholesterol
upregulates LDL receptors
increases HMG-reductase
T/F: cholesterol transporter-inhibitors are often given in combination
true
prevent compensatory mechanisms
what is in Vytorin combination drug
simvastatin
ezetimibe
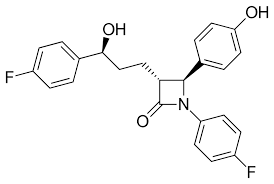
describe the absorption of ezetimibe
very lipophilic = poor dissolution
conjugated in phase 2 → goes back to GIT → interact with transporter
ADE of cholesterol transporter inhibitors
affects muscle buildup
sexual impetus
sperm needs lipids
which of the following drugs inhibits exogenous cholesterol absorption?
a) ezetimibe
b) cholestyramine chloride
c) rosuvastatin
d) fenofibrate
a) ezetimibe
which of the following drugs inhibits endogenous cholesterol biosynthesis?
a) ezetimibe
b) cholestyramine chloride
c) rosuvastatin
d) fenofibrate
c) rosuvastatin
which of the following drugs is effective in lowering LDL and raising HDL levels?
a) nicotinic acid
b) cholestyramine chloride
c) rosuvastatin
d) fenofibrate
a) nicotinic acid
which of the following drugs is effective in lowering cholesterol and triglycerides?
a) nicotinic acid
b) cholestyramine chloride
c) gemfibrozil
d) fenofibrate
c) gemfibrozil
which of the following drugs is effective in lowering trglyceride-rich particles and secretion of VLDL?
a) nicotinic acid
b) cholestyramine chloride
c) gemfibrozil
d) fenofibrate
d) fenofibrate
which aryloxyisobutyric acid derivative has the isobutyric acid given as an ester form?
fenofibrate