Regulation of Immune Responses: Tregs, Cytokines, and Immune Privilege L. 24
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What are T regulatory cells (Tregs)?
Tregs are a subset of T cells that regulate the immune response by controlling the activity of other immune cells.
What are the main mechanisms that control lymphocyte responses in the periphery?
1. Regulatory T cells, 2. Immunosuppressive molecules, 3. Immune deviation, 4. Immune privilege.
What is the role of T regulatory cells (Tregs) in the immune system?
Tregs help balance protective anti-pathogen and anti-tumor responses while preventing excessive inflammatory and autoimmune responses.
What is the association between aberrant activation of Th1 and Th17 cells?
Aberrant activation is linked to chronic inflammation and autoimmune diseases.
What are the four major subtypes of CD4+ T regulatory cells?
1. nTreg cells, 2. iTreg cells, 3. Tr1 cells, 4. Th3 cells.
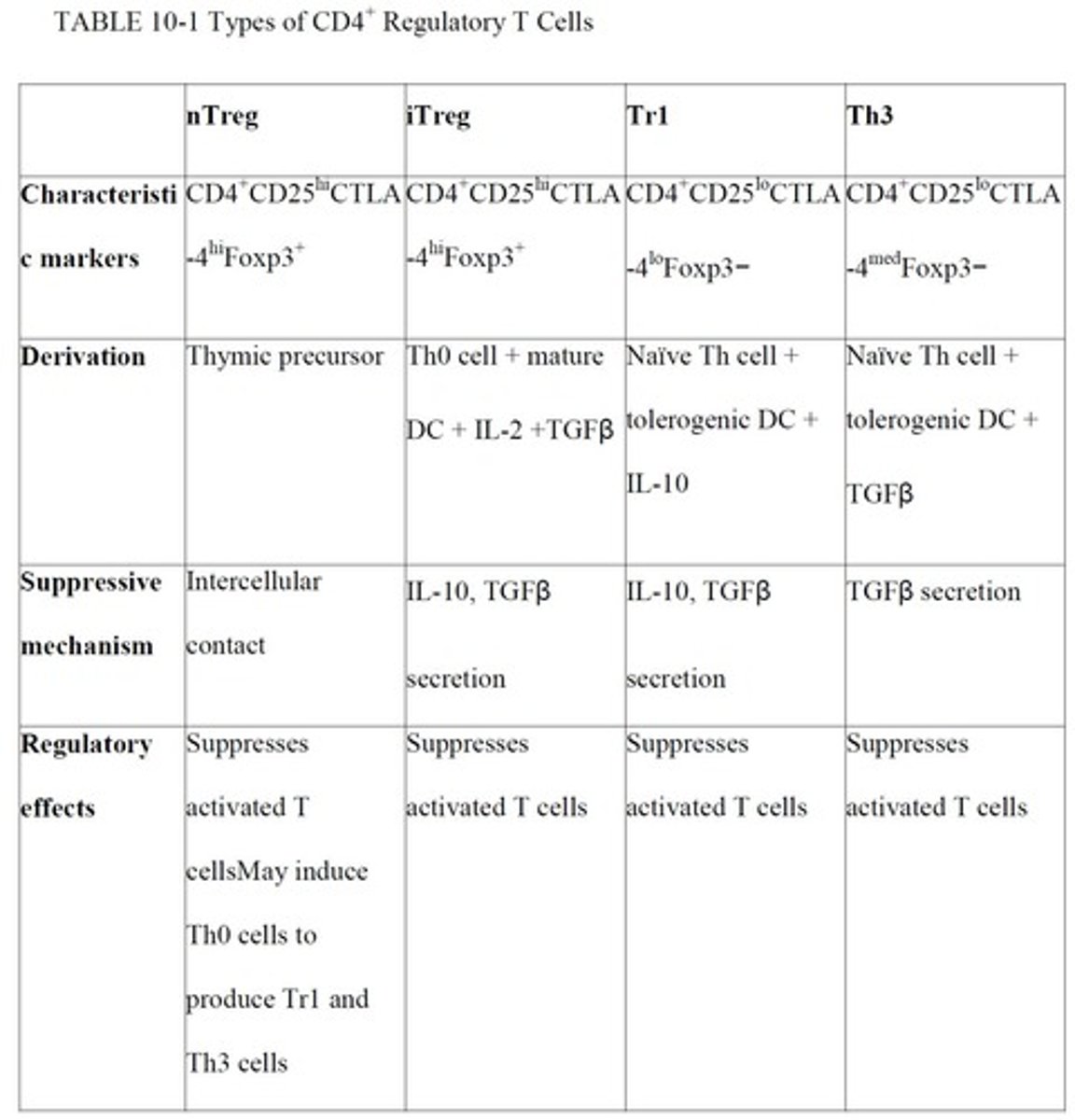
What characterizes natural T regulatory cells (nTregs)?
nTregs comprise about 6-10% of peripheral CD4+ T cells, express Foxp3, and are derived from thymic precursors.
How do nTregs suppress conventional CD4+ T cells?
nTregs block proliferation and IL-2 production through direct intercellular contact, independent of TCRs.
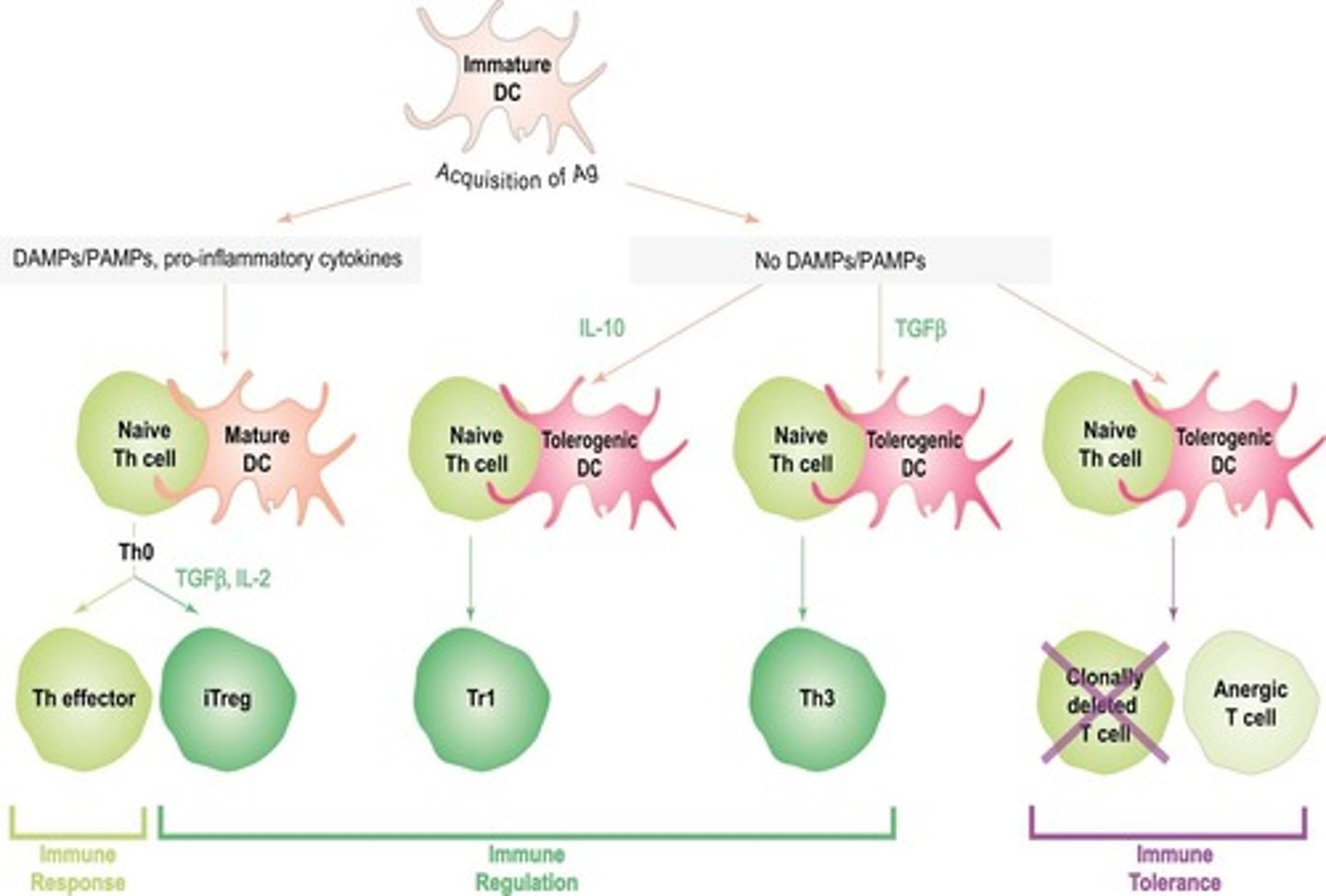
What cytokines are associated with induced regulatory T cells (iTregs)?
iTregs secrete immunosuppressive cytokines IL-10 and TGF-beta to suppress effector T cells.
What is the role of Tr1 and Th3 cells in immune regulation?
Tr1 and Th3 cells suppress activated effector T cells in an antigen non-specific manner by secreting immunosuppressive cytokines.
What distinguishes Th3 cells from Tr1 cells?
Th3 cells preferentially secrete TGF-beta, while Tr1 cells secrete IL-10 and low amounts of TGF-beta.
What are the functions of CD8+ regulatory T cells?
CD8+ Tregs can block the proliferation of naive and effector T cells and can also exert effects on antigen-presenting cells (APCs).
What are the immunosuppressive effects of IL-10?
IL-10 downregulates TCR signaling, inhibits macrophage activation, blocks APC function, and destabilizes mRNAs of various cytokines.
What is immune deviation?
Immune deviation is the process where a potentially harmful adaptive response is redirected to a less harmful response.
How does immune privilege protect certain tissues?
Immune privileged sites, like the CNS and eyes, are less subject to immune responses to prevent collateral damage to sensitive tissues.
What role does intestinal microflora play in immune regulation?
Intestinal microflora maintain gut immune homeostasis and promote oral tolerance to food antigens.
How do commensal bacteria influence dendritic cells (DCs)?
Certain species of commensal bacteria can render DCs tolerogenic and promote differentiation of T cells towards regulatory T cells.
What can trigger autoimmune and inflammatory gut disorders?
Alterations in normal gut microbiota can trigger conditions such as colitis and Crohn's disease.
What is the significance of Fas-FasL interactions in T cell regulation?
Fas-FasL interactions can induce apoptosis in conventional T cells as part of the regulatory mechanisms of Tregs.
What is the primary function of TGF-beta in immune regulation?
TGF-beta inhibits macrophage and NK cell activation and blocks proliferation of activated T cells.
What is the relationship between Th0 cells and induced Tregs (iTregs)?
Th0 cells interacting with tolerogenic DCs in a cytokine-rich environment can differentiate into iTregs.
What are the characteristics of nTreg cells?
nTregs express high levels of CD4 and CD25, develop from thymic precursors, and are characterized by the expression of Foxp3.
What is the impact of immunosuppressive cytokines on T cell activation?
Immunosuppressive cytokines like IL-10 and TGF-beta can inhibit T cell activation and promote anergy.
What is the role of regulatory T cells in preventing autoimmune responses?
Regulatory T cells limit the activity of autoreactive T cells and help maintain self-tolerance.
How do different Treg subsets interact with conventional T cells?
Various Treg subsets interact with Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells to modulate their activities and prevent excessive immune responses.