Cell Bio HW 1
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Secondary structure characteristics in alpha helix only
cylindrical structure, one full turn every 3.6 amino acids
Secondary structure characteristics in beta sheets only
consists of antiparallel or parallel strands, side chains alternating above and below the structure
Secondary structure characteristics in both alpha helix and beta sheets
can be formed by many sequences, formed by hydrogen-bonding between backbone atoms
predict what would happen to the secondary structure of a protein if an alcohol that disrupts hydrogen-bonding were added
The β sheets would unfold, disrupting protein structure, the α helices would unfold, disrupting protein structure.
What is the term for the segment of a eukaryotic gene consisting of a sequence of nucleotides that will be represented in mRNA?
Exon
How do cellular RNA polymerases differ from the DNA polymerases involved in DNA replication?
RNA polymerases don’t need a primer.
Actin is a major constituent of the cytoskeleton. Which one of the following statements correctly describes actin’s structure and location?
Actin forms helical filaments in the cell.
What is the term for the common structural motif in proteins in which different sections of a polypeptide chain that run alongside each other are joined together by hydrogen bonds between atoms of the polypeptide backbone?
Beta sheets
What is the term for the final folded structure of a polypeptide chain, which is generally the one that minimizes its free energy?
Conformation
Disulfide bonds (S–S bonds) are covalent cross-linkages that stabilize the structure of some proteins. Where do disulfide bonds most commonly form?
Disulfide bonds form in the oxidizing environment of the endoplasmic reticulum.
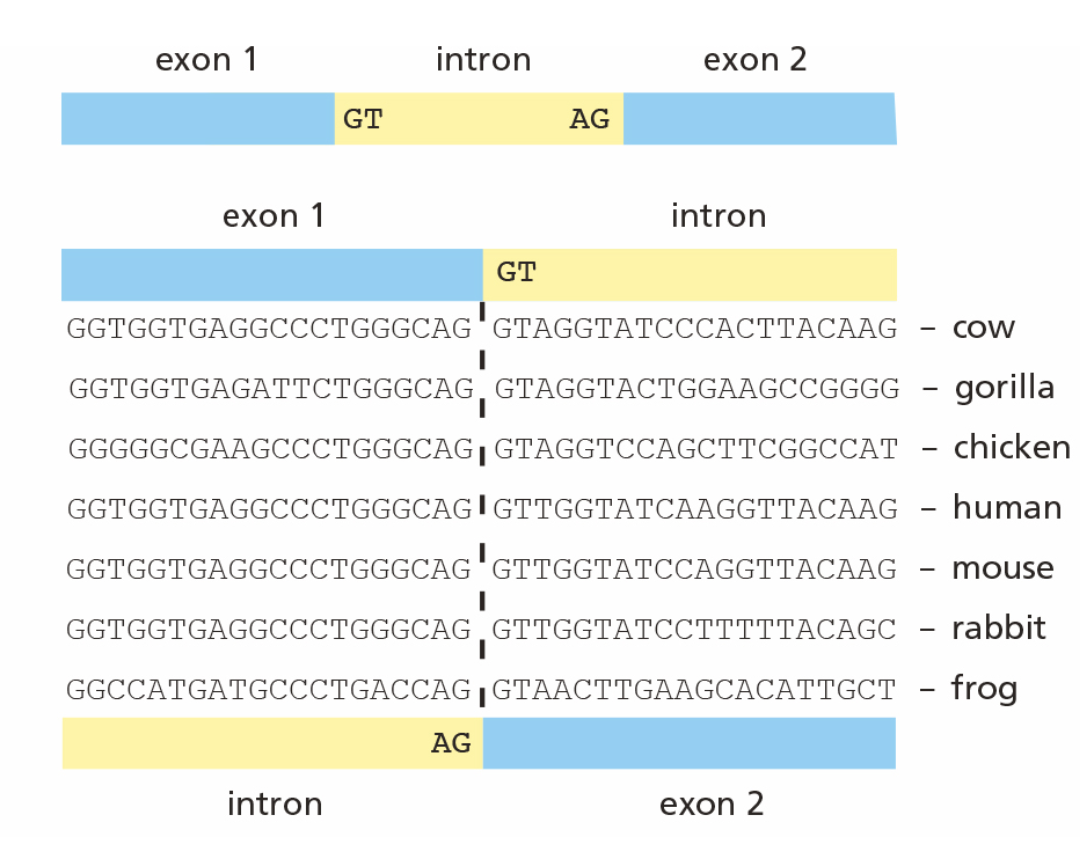
You have printed out a set of DNA sequences around an intron/exon boundary for several genes in the β-globin family, but you have forgotten to mark which side is the exon and which is the intron (see the figure). You know that introns begin with the dinucleotide sequence GT and end with AG, but these particular sequences would fit either as the start or the finish of an intron. The DNA sequences could come from the boundary of exon 1 with the intron (shown above), or from the boundary of the intron with exon 2 (shown below).
You know you could look it up on your computer, but you wonder if knowing that introns evolve faster (suffer more nucleotide changes) than exons would allow you to identify which side corresponds to introns?
Yes, the less conserved sequences—introns—are on the right side
Most nonpolar amino acid side chains in folded proteins are buried in the interior, forming a tightly packed core of atoms that are hidden from water. Which one of the following influences is chiefly responsible for this phenomenon?
Hydrophobic forces
Each one the following structures is capable of self-assembly from a solution of its component macromolecules EXCEPT:
a cilium
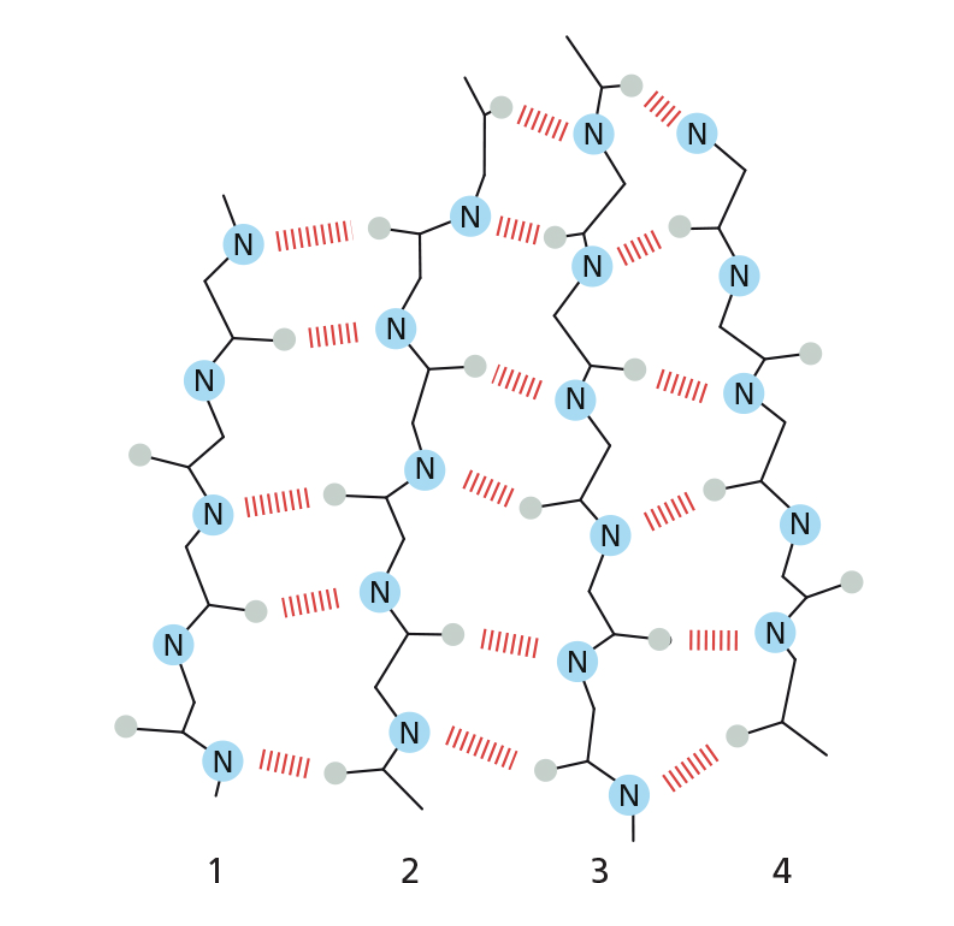
Examine the segment of β sheet shown in the figure. Which two neighboring strands are parallel to one another?
Strands 3 and 4
Prion diseases can spread from one organism to another, when the second organism eats tissue that contains the gene encoding the protein involved in formation of amyloid fibrils. True or False
false
Which of the following statements about how enzymes enhance reaction rates is true?
I When they bind substrates, enzymes increase the equilibrium constant, giving rise to more product.
II When an enzyme binds, it often distorts the substrate, changing its shape to more closely resemble the transition state.
III Enzymes can bind two substrates in close proximity, increasing their local concentration and promoting the reaction.
IV Enzymes often participate directly in the reaction by transiently forming a covalent bond with the substrate.
II, III, and IV
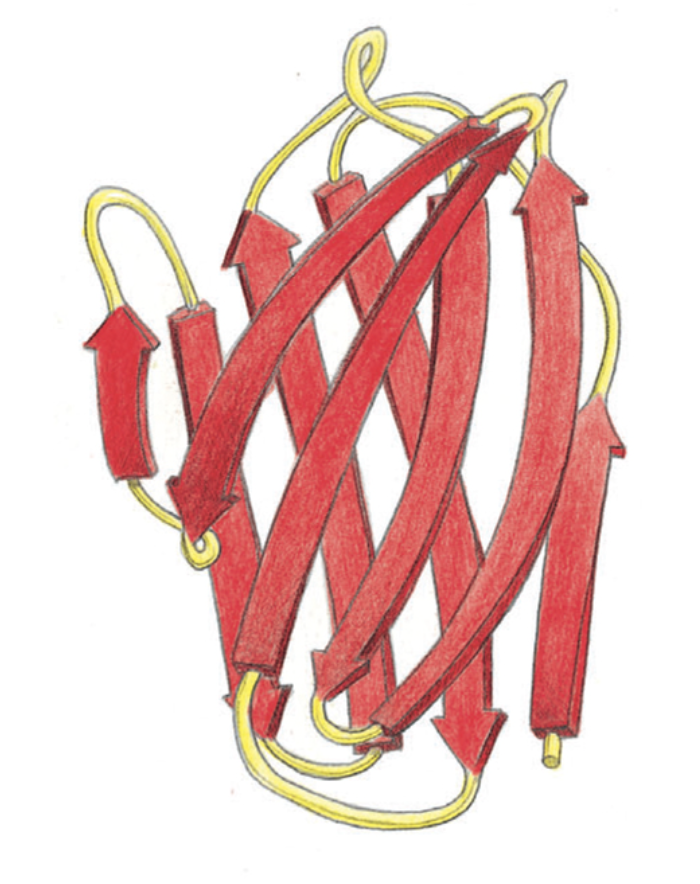
The ribbon model of the variable domain of an immunoglobulin (antibody) light chain is shown in the figure. What folding pattern constitutes most of this protein?
Antiparallel β sheets
Which one of the following statements correctly describes the way adjacent strands in a β sheet are commonly connected to one another?
Parallel strands are connected together by an α helix.
Which one of the following amino acids has an uncharged polar side chain?
A. Valine (V) B. Aspartic acid (D) C. Histidine (H) D. Glutamine (Q)
Glutamine (Q)
What does the expression “central dogma of molecular biology” refer to?
The central dogma refers to the idea that the flow of genetic information goes from DNA to RNA to protein.
What is the term for the type of metabolic regulation in which the activity of an enzyme acting near the beginning of a reaction pathway is reduced by a product of the pathway?
Feedback inhibition
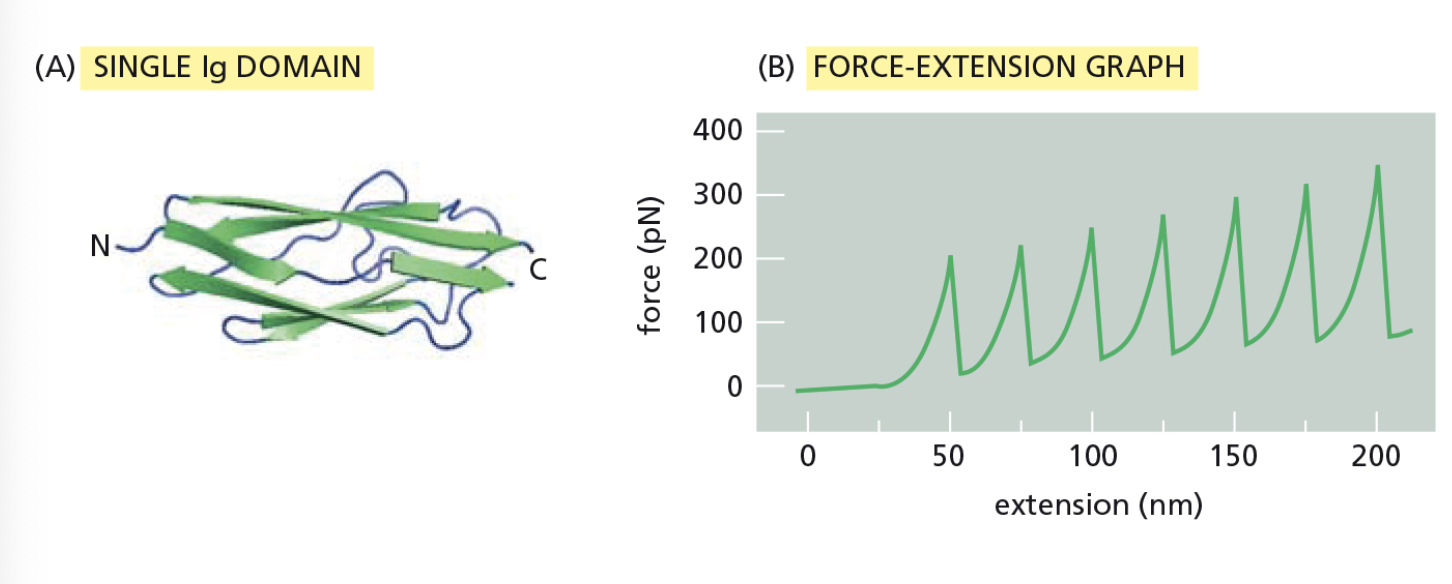
The largest protein yet described is titin, which has a mass of about 3 × 106 daltons. Titin molecules act as springs to keep muscle thick filaments centered in the sarcomere. Titin is composed of a large number of repeated immunoglobulin (Ig) sequences, each of which is 89 amino acids long and folded into a 4-nm domain (see the figure Part A).
To test your hypothesis that the springlike behavior of titin is caused by the sequential unfolding (and refolding) of individual Ig domains, you use atomic force microscopy to pick up one end of the protein and pull with an accurately measured force. For a fragment of titin containing seven repeats of the Ig domain, this experiment gives the sawtooth force-versus-extension curve shown in Part B.
Why is each successive peak in Part B a little higher than the one before?
Domains that are less stable are the first to unfold.
What is the term for the protein produced by the immune system in response to a foreign molecule or invading microorganism?
Antibody
The common DNA-binding domain called a homeobox is 60 amino acids long and is found in all so-called homeodomain proteins. Comparison of the homeobox domains in two homeodomain proteins from yeast and from Drosophila shows that only 17 of 60 of their amino acids are identical.
How is it possible for a protein to change over 70% of its amino acids and still fold in the same way?
Many different strings of amino acids can fold into the same tertiary structure.
What is the term for proteins that help to position RNA polymerase II correctly at the promoter, to aid in pulling apart the two strands of DNA to allow transcription to begin, and to release RNA polymerase from the promoter into the elongation mode once transcription has begun?
General transcription factors
What is the chemical nature of the 5′ cap in eukaryotic pre-mRNAs?
The 5′ cap is a nucleotide.
What is the term for the portion of each amino acid that gives the amino acid its unique properties?
Side chain
How does RNA differ from DNA?
RNA is a single chain of nucleotides.
The relatively unstructured lengths of polypeptide chain that connect domains of protein can act as flexible hinges between domains. True or False
True
What is the term for the region of an enzyme surface to which a substrate molecule binds in order to undergo a catalyzed reaction?
Active site
What is the term for the three-dimensional structure of a polypeptide chain, including its α helices, β sheets, and other meanderings of the peptide chain?
Tertiary Structure
The shape of a protein can change when the protein interacts with other molecules in the cell. True or False
True
What is the term for the mutual effect of the binding of one ligand on the binding of another that is a central feature of the behavior of all allosteric proteins?
Linkage
What is the main function of the TATA-binding protein?
to promote initiation of transcription
Which of the following events occur when TATA-binding protein binds to the DNA?
A.The DNA backbone is kinked nearly 90 degrees.
B.Binding leads to assembly of the rest of the transcription complex at the initiation site.
C.An eight-stranded β-sheet domain of the TATA-binding protein lies on the DNA helix.
D.Four α helices separate the two strands of DNA.
A.The DNA backbone is kinked nearly 90 degrees.
B.Binding leads to assembly of the rest of the transcription complex at the initiation site.
C.An eight-stranded β-sheet domain of the TATA-binding protein lies on the DNA helix.
How many amino acid residues are there per turn in an α helix?
3.6 amino acids
Generally speaking, two proteins are likely to share the same overall structure if their sequences exceed what minimum percent identity?
25%
Under which one of the following conditions is the complete structure of a protein designated as its quaternary structure?
The protein contains more than one protein subunit.
Which of the following complexes include both RNA and protein as structural components?
I Nucleosome
II Spliceosome
III Ribosome
II and III
Using evolutionary tracing, you have identified a few clusters of invariant amino acids in members of a protein family. Which one of the following statements about such clusters is correct?
They correspond to binding sites for one or more ligands.
What is the term for a structural unit of a protein that folds more or less independently of the rest of the protein and is the modular unit from which larger proteins are constructed?
Protein domain
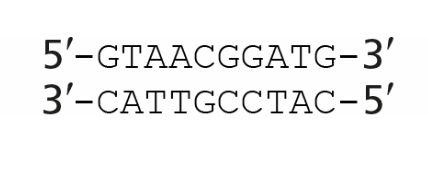
An RNA polymerase is transcribing a segment of DNA that contains the sequence shown in the figure. If the polymerase transcribes this sequence from right to left, what will the sequence of the RNA be?
5′-CAUCCGUUAC-3′

Antarctic notothenioid fish (see the figure) avoid freezing in their perpetually icy environment (–1.9°C) because of an antifreeze protein that circulates in their blood. This evolutionary adaptation has allowed the Notothenioidei suborder to rise to dominance in the freezing Southern Ocean.
It is said that all proteins function by binding to other molecules. To what ligand do you suppose antifreeze proteins bind to keep the fish from freezing?
They bind to small ice crystals and prevent them from growing.
What is the term for a protein that serves both to link together a set of interacting proteins and to position them at a specific location in a cell?
Scaffold protein
When egg white is heated, it hardens. This cooking process cannot be reversed, but hard-boiled egg white can be dissolved by heating it in a solution containing a strong detergent (such as sodium dodecyl sulfate) together with a reducing agent (like 2-mercaptoethanol, HS–CH2–CH2–OH). Neither reagent alone has any effect.
Why does it require both a detergent and a reducing agent to dissolve the hard-boiled egg white?
The detergent overcomes the interchain noncovalent bonds, and the reducing agent breaks the covalent disulfide bonds.
What is the term for the nucleotide sequence in DNA to which RNA polymerase binds to begin transcription?
Promoter
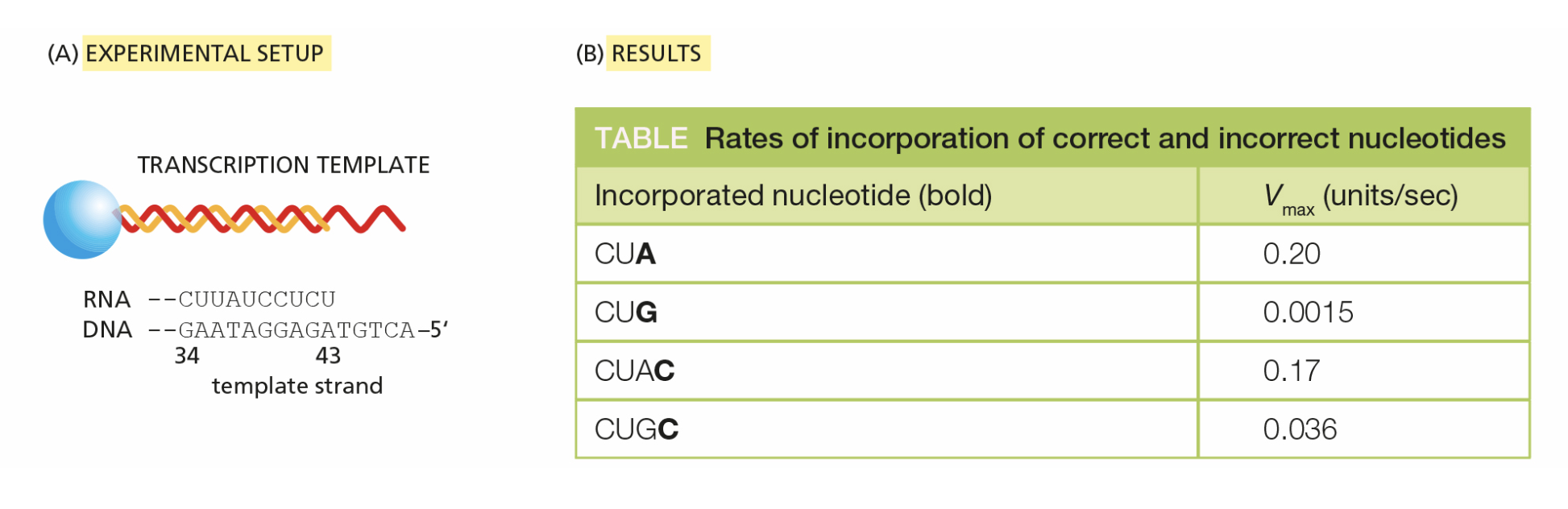
To test whether RNA polymerase slows its rate of synthesis after adding an incorrect nucleotide, to allow time to proofread its product, scientists devised a clever technique to measure the rate of nucleotide incorporation. As shown in the figure Part A, they covalently attached a DNA template (red strand) for an RNA transcript (orange strand) to agarose beads (blue). The beads allowed the complex, including the RNA polymerase, to be removed from solution and washed.
By using a series of solutions containing just one or a couple of nucleotides, the RNA polymerase was “walked” along the template to the site shown in the figure. At that point, the RNA polymerase and the template were resuspended in a solution containing one nucleotide, and the rate of incorporation of that nucleotide was measured. The rates of incorporation of A and G at position +44 in the RNA strand are shown in the table, along with the measured rate of incorporation of the following C at position +45 after A or G was incorporated at position +44.
Does the presence of an incorrect nucleotide at position +44 influence the rate of addition of the next nucleotide at position +45? How can you tell?
Yes, after an incorrect nucleotide, the correct nucleotide is incorporated at a slower rate.
The RNA molecule synthesized during transcription remains fully hydrogen-bonded to the template DNA strand until transcription is terminated. True or False
False
In 1968, Cyrus Levinthal pointed out that because there are astronomical numbers of conformations open to a protein in the denatured state, it would take a very long time for a protein to search through all the possibilities to find the correct one, even if it tested each possible conformation exceedingly rapidly. Yet denatured proteins typically take less than a second to fold inside the cell or in a test tube. How do you suppose that proteins manage to fold so quickly?
Weak noncovalent interactions allow a protein to search a restricted subset of all possible conformations.
In allosteric enzymes, the active site and the regulatory site are independent of one another and do not communicate. True or False
False
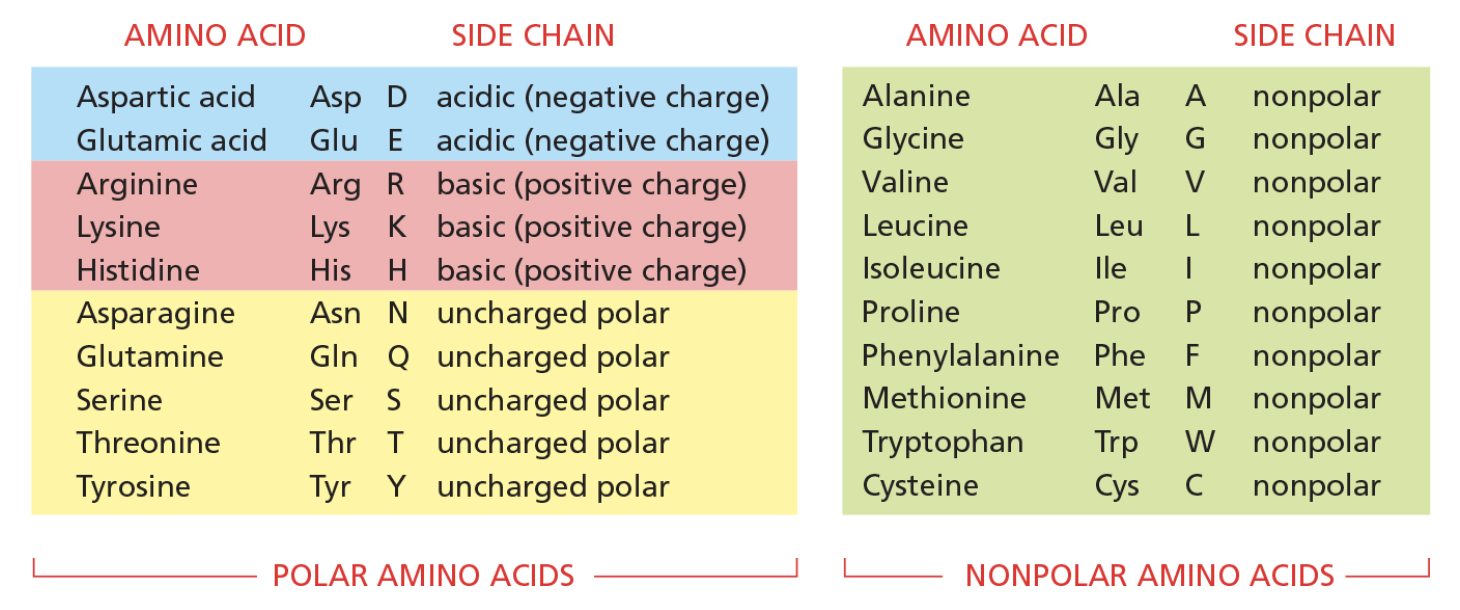
Like α helices, β sheets often have one side facing the surface of the protein and one side facing the interior, giving rise to an amphiphilic sheet with one nonpolar surface and one polar surface. A list of amino acids and their properties is shown in the figure.
Given the typical arrangement of side chains in a strand of a β sheet, which one of the sequences listed below could form a strand in an amphiphilic β sheet?
T L N I S F Q M E L D V
The uniform arrangement of the backbone carbonyl oxygens and amide nitrogens in an α helix gives the helix a net dipole, so that it carries a partial positive charge at the amino end and a partial negative charge at the carboxyl end.
Where would you expect the ends of α helices to be located in a protein?
Positive and negative ends of the helices would be located on the surface of the protein.