BCM6226 RNA Database
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
XIST
This is an example of a well characterized noncoding RNA gene located in the X inactivation center of the X chromosome and functions in X chromosome inactivation.
chromosome inactivation
XIST is expressed from the inactive X and binds to its chromatin, facilitating ________.
Rfam
This is a database of noncoding RNA families across the tree of life.
transfer RNA molecules (tRNA)
These RNA molecules carry a specific amino acid and match it to its corresponding codon on an mRNA during protein synthesis.
20 amino acid acceptor groups corresponding to the 20 amino acids specified in the genetic code.
tRNAs occur in how many amino acid acceptor groups?
cloverleaf
tRNA forms a structure consisting of about 70-90 nucleotides folded into what characteristic shape?
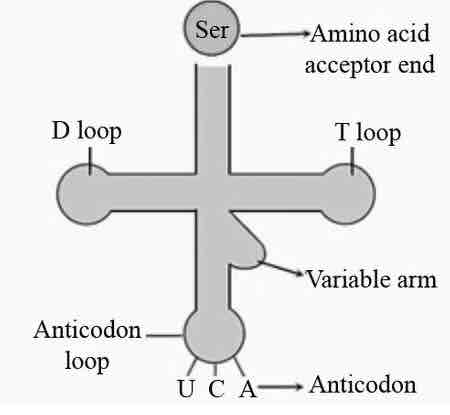
1. D-loop
2. anti-codon loop
3. T loop
4. 3'-end
4 key features of tRNA:
anti-codon loop
This key feature of tRNA is responsible for recognizing mRNA codons.
3'-end
This key feature of tRNA is where aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases attach the appropriate amino acid specific for each tRNA.
Vienna RNA package
A thermodynamic approach to tRNA prediction is implemented in programs such as the _________.
sequence position (x-axis)
entropy measurements (y-axis)
What is the x- and y-axis when plotting minimum free energy?
Ribosomal RNA molecules (rRNA)
These RNA molecules form structural and functional components of ribosomes, the subcellular units responsible for protein synthesis.
80-85%
rRNA consists approximately __% of the total RNA in a cell.
multicopy ribosomal DNA (rDNA)
rRNA derives from a __________ gene family. In humans, these families are localized to the p arms of the five acrocentric chromosomes (13, 14, 15, 21, and 22).
70S; 30S + 50S
What is the ribosomal unit of prokaryotes and what 2 subunits is it made of?
8)S; 40S + 60S
What is the ribosomal unit of eukaryotes and what 2 subunits is it made of?
smaller subunit; 30S (prokaryotes) and 40S (eukaryotes)
Which ribosomal subunit, in terms of size, is in charge of binding mRNA?
larger subunit; 50S (prokaryotes) and 60S (eukaryotes)
Which ribosomal subunit, in terms of size, is in charge of peptide bond formation?
small nuclear RNA (snRNA)
These RNA molecules are localized to the nucleus and consist of a family of RNAs that are responsible for functions such as RNA splicing and the maintenance of telomeres.
A group of noncoding RNAs that process and modify rRNA and small nuclear spliceosomal RNAs.
nucleolus
In eukaryotes, ribosome biogenesis occurs in what organelle?
Arabidopsis snoRNAs
What is the focus of the plant snoRNA database?
H/ACA and C/D box snoRNAs
What is the focus of the yeast snoRNA database?
human H/ACA and C/D box snoRNAs
What is the focus of SnoRNABase?
1. by region (e.g. brain vs. kidney)
2. in development (e.g. fetal vs. adult tissue)
3. in dynamic response to environmental signals (e.g. immediate-early response genes)
4. in disease states
5. by gene activity
Gene expression is content-dependent, and is regulated in several basic ways (5):
1. complementary DNA (cDNA) libraries
2. microarrays (e.g. using the Affymetrix platform)
3. RNA-seq
3 techniques for the study of mRNA:
Northern blots and PCR
Low throughput techniques such as ______ and/or __________ may seem laborious and able to provide only limited amounts of information. Yet they also serve as trusted "gold standards" and provide crucial validation of high throughput techniques.
location and quantity
The sequencing of cDNA libraries allows the ______ and ______ of RNA transcripts to be measured.
expressed sequence tags (ESTs)
cDNA inserts, called _______, are sequenced.
UniGene database
This database partitions ESTs into nonredundant clusters that generally correspond to expressed genes.
1 - ~50,000
Each EST cluster has some number of sequences associated with it, from ___-___.
64,000
About how many clusters have just 1 EST?
Digital Differential Display (DDD)
This is an online tool at NCBI to expolore gene expression; compares the content of ESTs in cDNA libraries from UniGene.explore
Fisher's 2x2 exact test
Probability values of DDD are given based on what test?
This test is used to test null hypothesis that a given gene is not differentially regulated in two pools.
FANTOM or Mammalian Gene Collection accessed via NCBI gene
There are many resources to purchase (or study) full-length cDNAs. 2 of them being:
Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project
This project catalogs tissue-specific gene expression across the human body; measures gene expression across the body.
BodyMap2
This measures gene expression across 16 tissues using RNA-seq.
True.
In stage 1 (experimental design), be sure to use enough biological replicates, typically n≥3 per group.
T or F?
1. RNA extraction
2. RNA conversion
3. RNA labeling
4. RNA hybridization
What 4 steps make up RNA preparation?
True.
In stage 2 (RNA preparation), be sure to create an appropriately balanced, randomized experimental design.
T or F?
Microarrays
In stage 3 (hybridization to DNA arrays), ________ typically consist of oligonucleotides (deposited by photolithography).
Samples are cRNA or cDNA with fluorescent tags.
1. Hypothesis testing
2. Clustering
3. Classification
In stage 4 (microarray data analysis), what are the 3 steps involved?
hypothesis-generating
Microarray experiments can be thought of as _______ experiments.
1. northern blots
2. RT-PCR
3. in situ hybridization
The differential up- or down-regulation of specific RNA transcripts can be measured using independent assays such as (3):
1. Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) at NCBI
2. ArrayExpress at the European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI)
There are 2 main microarray databases/respositories namely:
1. experimental design
2. microarray design
3. sample preparation
4. hybridization procedures
5. image analysis
6. controls for normalization
Minimum Information About a Microarray Experiment (MIAME) guidelines are followed to describe experiments (6):
Entrez
This provides access to GEO profiles and datasets.
positive
There appears to be only a weak (positive, negative) correlation between mRNA and protein levels.
considered
Correlation coefficients between mRNA and protein levels that were relatively high when highly abundant proteins were (excluded, considered).
excluded
Correlation coefficients between mRNA and protein levels that were relatively low when highly abundant proteins were (excluded, considered).
1. RNA structural effects
2. regulatory noncoding RNAs
3. codon bias
4. variable protein half-lives
5. experimental error
Weak correlations between mRNA and protein levels could be due to (5):
mRNA expression
This is a quantitative trait that can be described for a given cell type and physiological state in an organism.
Variants in genomic DNA may impact this.
Expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs)
These are genomic loci that control expression levels.
cis-eQTLs
This main type of control region are genomic loci that influence the expression of transcripts expressed from neighboring genes within some distance (such as 1 Mb or less), and may undergo allele-specific expression.
trans-eQTLs
This main type of control region act on transcripts expressed from genes that are farther away or on another chromosome.
True.
eQTLs could affect transcription directly or indirectly, for example by altering the sequence of a transcription factor binding site that controls a gene's expression proximally or distally.
T or F?