Oxidative phosphorylation
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What happens when no ADP is present when mitochondria are placed in a buffer solution?
respire slowly to compensate for leakage of protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane
What happens when ADP is present when mitochondria are placed in a buffer solution?
respiration increases
mitochondria allow protons to flow across the mitochondrial membrane
What substances promote proton re-entry and what do they do?
ionophores & 2,4-dinitrophenol
short-circuit the proton motive force
oxygen can be consumed when no ATP is produced.
What are the parts of the electron transport chain?
Complex I, complex II, complex III, complex IV, complex V
Describe the movement of electrons through the electron transport chain.
QH2 passes electrons to complex III
complex III passes to cytochrome c
cytochrome c transfers to complex IV
complex IV transfers to oxygen
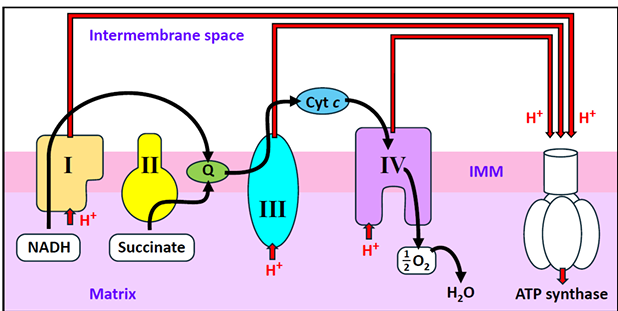
What oxidising prosthetic groups are used by complex 1 & complex 2 respectively?
complex 1 - FMN
complex 2 - FAD
*NB - immobile prosthetic groups that must be recycle
What complexes have iron-sulfur clusters?
1, 2 & 3
*NB - they transfer single electrons despite variable numbers of Fe atoms.
How is Q reduced to QH2?
Transports electrons from complex I & complex II to complex III
Also enables complex III to pump protons via the ‘Q cycle’
How & as what are cytochromes categorised?
a,b or c depending on the wavelength of light they absorb
What cytochromes are found in complex III?
b & c1
What cytochromes are found in complex IV?
a & a3
Where is cytochrome c found?
ferries electrons from complex III to complex IV
What is the structure & function of complex I?
uses NADH to reduce ubiquinone
NADH reduces FMN, electrons pass through FeS centres & reduce Q to QH2
What is the structure & function of complex II?
FAD reduced by succinate to FADH2
FeS centres pass electrons to Q to make QH2
What is the structure & function of complex III?
FeS centre passes electrons to cytochrome c1
cytochromes c1 transfers electrons to cytochrome c
What is the structure & function of complex IV?
cytochrome C reduces O2 to water
What are the 2 subunits of ATP synthase?
Fo & F1
F1 function
hydrolyses ATP (using water if detached from Fo)
Describe the function of the Fo complex.
forms a channel so the protons can return to the mitochondrial matrix
torque generated by flow of protons rotates the gamma subunit (stalk)
*NB - channel blocked by oligomycin.
What is the function of the gamma subunit (stalk)?
drives the binding change mechanism
3 protons translocated for every ATP produced.
Describe the structure of the F0 complex.
8c subunits
What are the 3 types of site in ATP synthase?
O (open) - low affinity for ADP & P
L (loose) - binds ADP & P loosely
T (tight) - tight binding required to squeeze out water
What is step 1 in the use of ATP synthase?
ADP & P binds to L site
What is step 2 in the use of ATP synthase?
energy in to convert L to T
ADP + Pi —→ ATP + H2O
What is step 3 in the use of ATP synthase?
energy in to convert T to O
ATP is released
What is the difference in how ATP & ADP and phosphate transport into and out of the mitochondria?
ATP & ADP exchange due to the charge difference
Phosphate enters due to the pH difference
How are partially reduced ubiquinone radicals produced?
rate of electron entry into chain is greater than the rate of electron transfer through the chain
What do ubiquinone radicals do?
donate an electron to oxygen to form superoxide
What does superoxide do?
Acts on citric acid enzyme aconitase to release Fe2+
Leads to the formation of OH free radical
Donor & acceptor of complex I
donor - NADH
acceptor - ubiquinone
Donor & acceptor of complex II
donor - succinate
acceptor - ubiquinone
Donor & acceptor of complex III
donor - reduced Q
acceptor - cytochrome C
Donor & acceptor of complex IV
donor - reduced cytochrome C
acceptor - O2