Chemistry - Chapter 2-2.3
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Types of bonds and their sturctures
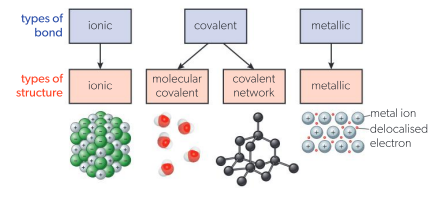
Chemical Bonds
Forces of attraction that hold atoms or ions together in a substance
Electronegativity
A measure of the ability of an atom to attract a pair of electrons.
Lattice Structure
Continuous, three dimensional networks of repeating units of positive and negative ions.
Lattice Enthaply
A measure of the energy required to break one mole of ionic bonds to form gaseous ions
Volatility
Refers to the tendency of a substance to vaporize
Electrical Conductivity
The ability to conduct electricity
Solubility
The amount of solute needed to form a saturated solution
Ionic compounds melting point
Ionic materials have very high melting points due to the strength of ionic bonds
Ionic compounds Electrical Conductivity
Electrical conductivity requires mobile charges. Therefore solid forms of ionic compounds are bad conductors, but liquid forms are good conductors.
Ionic Substances Soluability
Ionic substances are soluble in polar solvents and insoluble in non polar solvents
Ionic Materials Brittleness
Ionic materials are brittle due to the impact of forces which can displace a lattuce, leading to repulsion between charges ultimately breaking the lattuce.
Ionic Materials Volatility
Ionic materials tend to not evaporate due to the strength of bonds
Polarity
Related to the way electrons are distributed within bonds and molecules
Bond Polarity
Results in the difference in the electronegativities of the bonded atoms
Dipole Moment
The separation of charge between two non-identical bonded atoms
Malleability
The ability of a solid to be pressed or pounded into different shapes without breaking
Atomic radius
Half the distance between nuclei of atoms of the same element that are being bonded by a single covalent bond
Ionization energy
the energy needed to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of isolated gaseous atoms to form one mole of +1 gaseous ions
Electron Affinity
The energy change (in kJ/mol) when one mole of electrons is added to one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of gaseous negative ions