School Age Child (Peds Test 3)
4.0(4)
Card Sorting
1/60
Earn XP
Last updated 7:39 PM on 3/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
1
New cards
What age is considered a school age child?
6-12 years
2
New cards
Enlarged spleen
Splenomegaly
3
New cards
Eriksons stage (for school age)
Industry vs inferiority
* child is a worker and producer and wants to accomplish tasks
* competitiveness is common
* child is a worker and producer and wants to accomplish tasks
* competitiveness is common
4
New cards
Piaget stage (for school age)
* child thinks and reasons in __**concrete terms**__
* conservation (ability to recognize two equal quantities regardless of form)
* reversibility: ability to think in either direction (dog is an animal, animal is a dog)
* conservation (ability to recognize two equal quantities regardless of form)
* reversibility: ability to think in either direction (dog is an animal, animal is a dog)
5
New cards
6 year old vocab and sleep/physical development
2500 words
* need 11-13 hours of sleep per night
* set limits on activities, they will become overtired
* loss of temporary teeth
* need 11-13 hours of sleep per night
* set limits on activities, they will become overtired
* loss of temporary teeth
6
New cards
6-7 year old behavioral development
* still have magical thinking (santa!)
* can lie to escape punishment
* group activities important
* slightly more cautious
* can lie to escape punishment
* group activities important
* slightly more cautious
7
New cards
8 year old behavioral development
* group activities such as girl scouts are important
* same gender friends are prefered
* poor losers, but competitive sports are enjoyed
* same gender friends are prefered
* poor losers, but competitive sports are enjoyed
8
New cards
9 year old behavioral development
* worries such as (step on a crack breaks your mothers back)
* 10 hours of sleep are needed
* multiply and do simple division
* table manners
* more responsibility
* 10 hours of sleep are needed
* multiply and do simple division
* table manners
* more responsibility
9
New cards
11-12 year old development
* 24-26 permanent teeth
* table manners go away a bit
* ability to concentrate decreases
* do not want parents help
* 9 hours of sleep needed
* table manners go away a bit
* ability to concentrate decreases
* do not want parents help
* 9 hours of sleep needed
10
New cards
Nutrition for school age child
Increase in calorie needs
* higher for boys (usually 400 more than regular requirements for females)
* higher for boys (usually 400 more than regular requirements for females)
11
New cards
Vaccines for school age children
* Booster for Tdap (11 yrs)
* Meningococcal (MCV) (11 yrs)
* HPV (11 yrs)
By 6 years:
* DTaP
* polio
* MMR
* Varicella
* Meningococcal (MCV) (11 yrs)
* HPV (11 yrs)
By 6 years:
* DTaP
* polio
* MMR
* Varicella
12
New cards
Health maintenance for school age children
* WCC every year
* scoliosis checks
* dentist 2x per year
* minimum of 10 hours of sleep per night
* scoliosis checks
* dentist 2x per year
* minimum of 10 hours of sleep per night
13
New cards
Hospitalized school age child
* better understanding of what is going on
* concerned about looking different
* privacy
* concerned about looking different
* privacy
14
New cards
ADHD/ADD in boys vs girls
* more common in boys
* increased incidence in family (suggests genetics)
* boys exhibit more behavioral problems
* girls exhibit more academic underachievement
* increased incidence in family (suggests genetics)
* boys exhibit more behavioral problems
* girls exhibit more academic underachievement
15
New cards
Management of ADHD/ADD
Behavioral and medication approach most effective
(no medications for preschoolers 4-6)
* SNRIs (selective norepi re-uptake inhibitors)
* Alpha 2 agonists
* TCAs (tricylic antidepressants)
* Stimulants
(no medications for preschoolers 4-6)
* SNRIs (selective norepi re-uptake inhibitors)
* Alpha 2 agonists
* TCAs (tricylic antidepressants)
* Stimulants
16
New cards
Diagnosis of ADHD/ADD
* symptoms must be present for 6 mo
* manifestations are present between ages 4-18
* must be identified in more than one setting (home, school)
* must cause significant impairment to functioning: academic, social
* DSM-IV-TR criteria
* manifestations are present between ages 4-18
* must be identified in more than one setting (home, school)
* must cause significant impairment to functioning: academic, social
* DSM-IV-TR criteria
17
New cards
What causes ADHD/ADD
Not well understood
* most likely a lack of dopamine
* possibly an alteration in mid-brain causing reactions to every stimulus instead of selected ones
* genetic factors
* linked to fetal alcohol syndrome and lead toxicity
* most likely a lack of dopamine
* possibly an alteration in mid-brain causing reactions to every stimulus instead of selected ones
* genetic factors
* linked to fetal alcohol syndrome and lead toxicity
18
New cards
What type of resp. disease is asthma
Obstructive lung disease
19
New cards
Asthma meds
* Fluticasone (inhaled corticosteriods)
* salometrol (long acting B2 agonists)
* Budesonide (inhaled corticosteriods)
* formoterol (long acting B2 agonists)
* formoterol (long acting B2 agonists)
* Albuterol (**short acting B2 agonist**/rescue med)
* methylprednisolone, prednisolone, prednisone (oral corticosterioids)
* salometrol (long acting B2 agonists)
* Budesonide (inhaled corticosteriods)
* formoterol (long acting B2 agonists)
* formoterol (long acting B2 agonists)
* Albuterol (**short acting B2 agonist**/rescue med)
* methylprednisolone, prednisolone, prednisone (oral corticosterioids)
20
New cards
Peak flow procedure
Stand
Take the deepest breath possible
Blow out hard
Repeat 3 times
Record the highest of 3 measurements (wait 30 seconds in between attempts)
Take the deepest breath possible
Blow out hard
Repeat 3 times
Record the highest of 3 measurements (wait 30 seconds in between attempts)
21
New cards
Types of asthma medications
* inhaled corticosteroids
* systemic corticosteroids (oral)
* anti-inflammatory agents
* leukotriene receptor antagonist (decrease airway resistance)
* long acting B2 antagonists (long term)
* Short acting B2 antagonists (albuterol) (acute attack)
* anticholinergics
* systemic corticosteroids (oral)
* anti-inflammatory agents
* leukotriene receptor antagonist (decrease airway resistance)
* long acting B2 antagonists (long term)
* Short acting B2 antagonists (albuterol) (acute attack)
* anticholinergics
22
New cards
Diabetes S/S
Symptoms appear quickly in kids
* Polydipsia (extreme thirst r/t frequent urination )
* Polyuria (urination often, glucose in urine. High glucose body is trying to remove, leading to increased urination)
* Polyphagia (eating more but still losing weight due to brain tearing down fat)
* Wt. loss
* Lethargy
* Polydipsia (extreme thirst r/t frequent urination )
* Polyuria (urination often, glucose in urine. High glucose body is trying to remove, leading to increased urination)
* Polyphagia (eating more but still losing weight due to brain tearing down fat)
* Wt. loss
* Lethargy
23
New cards
Diabetic kedoacidosis
* extremely low levels of insulin
* CBG of >300
* Carbs not turned into fuel for energy
* Fat are used but can’t be completely broken down w/o insulin
* Ketones build up and excreted in urine
* causes - acidosis
* CBG of >300
* Carbs not turned into fuel for energy
* Fat are used but can’t be completely broken down w/o insulin
* Ketones build up and excreted in urine
* causes - acidosis
24
New cards
Insulin
**Rapid**
* lispro
* aspart
* glulisine
**Short acting**
* Regular (usually mixed with NPH)
**Intermediate acting**
* NPH (cloudy)
**Long acting**
* glargine
* detemir
* lispro
* aspart
* glulisine
**Short acting**
* Regular (usually mixed with NPH)
**Intermediate acting**
* NPH (cloudy)
**Long acting**
* glargine
* detemir
25
New cards
Hypoglycemia
Blood glucose below 60
* give juice, candy, if blood sugar goes back up, have child eat a small amount of protein or starch to prevent relapse
* glucagon if severe
* give juice, candy, if blood sugar goes back up, have child eat a small amount of protein or starch to prevent relapse
* glucagon if severe
26
New cards
Acute Rheumatic Fever
* caused by untreated step (throat or skin) (not common anymore)
* starts 2-6 weeks post strep infection
* body develops immune response to strep
* major cause of permanent heart damage, dysfunction of heart valves
* starts 2-6 weeks post strep infection
* body develops immune response to strep
* major cause of permanent heart damage, dysfunction of heart valves
27
New cards
S/S of Acute Rheumatic Fever
Onset slow and subtle
* FEVER
* Subcutaneous nodules
* Abdominal pain
* Weight loss
* Polyarthritis (red, hot joints, edema, elevated ESR \[inflammation test\])
* low hemoglobin
* macular rash on trunk
* cyanosis
* Chorea: CNS involvement with involuntary movement of muscles, stumbling, spilling things, grimace, laugh, cry RARE
* FEVER
* Subcutaneous nodules
* Abdominal pain
* Weight loss
* Polyarthritis (red, hot joints, edema, elevated ESR \[inflammation test\])
* low hemoglobin
* macular rash on trunk
* cyanosis
* Chorea: CNS involvement with involuntary movement of muscles, stumbling, spilling things, grimace, laugh, cry RARE
28
New cards
Diagnosis for Rheumatic Fever
Jones Criteria
* Two major manifestations (carditis, subcut nodules, polyarthritis, rash, chorea)
OR
* One major and two minor manifestations (minor = fever, arthralgia AKA joint stiffness)
With evidence of recent strep infection
* Two major manifestations (carditis, subcut nodules, polyarthritis, rash, chorea)
OR
* One major and two minor manifestations (minor = fever, arthralgia AKA joint stiffness)
With evidence of recent strep infection
29
New cards
Treatment for ARF
* prevent heart damage
* supportive care
* bed-rest
* antibiotics for strep
* steroids for severe carditis or CHF
* supportive care
* bed-rest
* antibiotics for strep
* steroids for severe carditis or CHF
30
New cards
What virus causes varicella (chicken pox)
Zoster (like a rooster because its chickenpox)
* herpes zoster
* herpes zoster
31
New cards
Which rash shows up after a high fever goes away?
Roseola (rosy has the rash)
32
New cards
In mumps, what is complication in adults?
Infertility
33
New cards
Causes of pneumonia
* aspiration
* virus
* drowning
* bacteria
* obstruction in lungs
* inhalation
* virus
* drowning
* bacteria
* obstruction in lungs
* inhalation
34
New cards
Patent Ductus Arteriosus
The passage between the pulmonary artery and aorta in fetus (ductus arteriosus), which should close in first 48 hours, __**is not closed**__
* blood continues to pass from aorta into pulmonary artery causing too much high pressure oxygenated blood in the lungs
* overburdens the pulmonary system, making heart work harder
Tx by ibuprofen to close shunts
* blood continues to pass from aorta into pulmonary artery causing too much high pressure oxygenated blood in the lungs
* overburdens the pulmonary system, making heart work harder
Tx by ibuprofen to close shunts
35
New cards
Erickson’s stage for adolescents (13+)
Identity formation vs role confusion
* determining who they are
* determining who they are
36
New cards
Piaget’s theory for adolescents (13+)
Formal Operations:
Early adolescents take things literally
Thinking in abstract terms by middle adolescence
Older adolescents see a situation from many viewpoints
Early adolescents take things literally
Thinking in abstract terms by middle adolescence
Older adolescents see a situation from many viewpoints
37
New cards
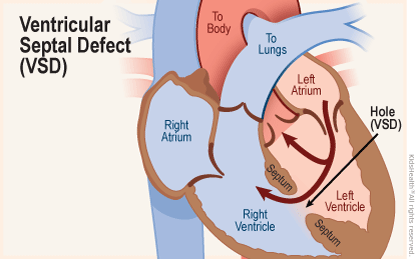
Ventricular septal defect
hole in between the right and left ventricle.
* Oxygenated blood gets pushed from the left ventricle to the right ventricle.
* loud murmur can be heard at left sternal border
* Oxygenated blood gets pushed from the left ventricle to the right ventricle.
* loud murmur can be heard at left sternal border
38
New cards
Coarctation of the aorta
Tightening/narrowing of the aorta
* high pulses in the upper extremities
* weak pulses in the lower extremities
* elevated BP in arms
* high pulses in the upper extremities
* weak pulses in the lower extremities
* elevated BP in arms
39
New cards
Tanner staging
Development of sexual maturation (breasts, public hair, gentiles)
\
\
40
New cards
Tanner Stages
1-5
1: preadolescent
2: Early puberty
3: Middle puberty
4: Late puberty
5: Adult
1: preadolescent
2: Early puberty
3: Middle puberty
4: Late puberty
5: Adult
41
New cards
Infectious mononucleosis
AKA Mono
* __***caused by Epstein-Barr virus***__
* causes flu like symptoms
* can cause enlarged spleen
* incubation 1-2 months
* transmitted by saliva
* __***caused by Epstein-Barr virus***__
* causes flu like symptoms
* can cause enlarged spleen
* incubation 1-2 months
* transmitted by saliva
42
New cards
When is puberty considered over
* onset of menses
* production of sperm
* production of sperm
43
New cards
S/S of mononucleosis (Mono)
* fever
* sore throat
* headache
* fatigue
* skin rash
* malaise
* enlarged lymph nodes
* sore throat
* headache
* fatigue
* skin rash
* malaise
* enlarged lymph nodes
44
New cards
Nursing findings for patient with appendicitis
* Absent or diminished BS
* rigidity of abdomen
* rebound tenderness (pressing down and releasing pressure fast causes pain)
* rigidity of abdomen
* rebound tenderness (pressing down and releasing pressure fast causes pain)
45
New cards
What can happen with untreated scoliosis
* back pain
* fatigue
* disability
* thoracic insufficiency syndrome (restriction of lung growth and function due to deformity )
* fatigue
* disability
* thoracic insufficiency syndrome (restriction of lung growth and function due to deformity )
46
New cards
S/S of glomerululnephritis
Usually caused by __**strep**__ of skin or throat
* Urine is brown and can be bloody
* hypertension
* swelling of the eyes may occur + general swelling
* abd pain and discomfort
* fatigue
* vomiting
* urinary output is decreased
* protein, RBC, WBC, in urine.
* BUN is raised and so is creat.
* Urine is brown and can be bloody
* hypertension
* swelling of the eyes may occur + general swelling
* abd pain and discomfort
* fatigue
* vomiting
* urinary output is decreased
* protein, RBC, WBC, in urine.
* BUN is raised and so is creat.
47
New cards
Normal WBC count
4-11 ish
48
New cards
Leukemia
overproduction of immature WBC, so they are unable to do the usual WBC tasks such as fighting infection. Normal cells are crowded out (ie: less RBCs)
* CBC with differential to dx: to see numbers of different types of WBCs
* High white count common
* Chest x-ray shows lymph nodes that run along side of sternum
* CBC with differential to dx: to see numbers of different types of WBCs
* High white count common
* Chest x-ray shows lymph nodes that run along side of sternum
49
New cards
Osteosarcoma
Bone cancer
* found in long bones
Pain, limping, swelling
* found in long bones
Pain, limping, swelling
50
New cards
When do girls typically stop growing?
About 2 years after menarche
51
New cards
Annual health screening for adolescent
* scoliosis screening
* BMI calculation
* Hgb and Hct
* lipid screen
* STI screening
* BMI calculation
* Hgb and Hct
* lipid screen
* STI screening
52
New cards
what is the first manifestation of sexual maturation in boys?
testicular enlargement
53
New cards
Risk factors for development of asthma
* family hx of asthma
* family hx of allergies
* exposure to smoke
* low birth weight
* being overweight
* family hx of allergies
* exposure to smoke
* low birth weight
* being overweight
54
New cards
Varicella (chicken pox)
Incubation 14-16 days
* communicability 1-2 days before lesions appear and until they are crusted over
* **Droplet, contact with patient or contaminated objects**
* rash starting in center of trunk
* communicability 1-2 days before lesions appear and until they are crusted over
* **Droplet, contact with patient or contaminated objects**
* rash starting in center of trunk
55
New cards
Pertussis (Whooping cough)
Caused by bordetella
Incubation 6-20 days
* Communicability 4-6 weeks from onset
* **Contact with patient or objects, droplet**
Incubation 6-20 days
* Communicability 4-6 weeks from onset
* **Contact with patient or objects, droplet**
56
New cards
S/S of pertussis (whooping cough)
Coreza (dry cough)
* coughing with a whoop at the end
* vomiting (post coughing attack)
* coughing with a whoop at the end
* vomiting (post coughing attack)
57
New cards
Rubella/Mumps (paramyoxovius)
Incubation 14-21 days
* communicability 7 days before and 5 days after rash appears
**Direct contact (with patient) and droplet**
* swollen glands
* earache
* flu like symptoms
* communicability 7 days before and 5 days after rash appears
**Direct contact (with patient) and droplet**
* swollen glands
* earache
* flu like symptoms
58
New cards
rubeloa (measles)
Incubation 10-20 days
* communicability 4 days before and 5 days after rash occurs
**Direct contact (with patient), and droplet (airborne)**
* fever
* conjunctivitis
* flu symptoms
* White spots in mouth rubethat appear before rash
* rash starting on face and spreading downwards
* communicability 4 days before and 5 days after rash occurs
**Direct contact (with patient), and droplet (airborne)**
* fever
* conjunctivitis
* flu symptoms
* White spots in mouth rubethat appear before rash
* rash starting on face and spreading downwards
59
New cards
Conjunctivitis (AKA pink eye)
Incubation: depends
**Direct contact**
* pink color in sclera of eye
* yellow/green drainage from eye
* crusting of eyelids in the morning
**Direct contact**
* pink color in sclera of eye
* yellow/green drainage from eye
* crusting of eyelids in the morning
60
New cards
Fifths disease
Incubation: 4-14 days
communicability: onset of manifestation until rash appears
**Droplet, blood**
Rash on face and extremities
communicability: onset of manifestation until rash appears
**Droplet, blood**
Rash on face and extremities
61
New cards
Bulimia Nervosa
Binging (eating more than the average person in a 2 hour period) and then throwing it up
* At least once a week for 3 months
* At least once a week for 3 months