Energy Expenditure
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Total energy expenditure breakdown
Resting metabolic rate ~60-75%
Thermic effect of food ~10%
Physical activity ~15-30%
Direct measurement of energy expenditure
measures heat generated by metabolic reactions
Indirect measurement of energy expenditure
gas analysis, HR monitor
Heat production _____ with energy production
increases
can be measured in a calorimeter
Direct calorimeter
used for measurement of energy expenditure by an exercising human subject
heat generated by exercising body is transferred to air + walls of chamber — heat produced = measure of metabolic rate
Pros of direct calorimeter
accurate over time, good for resting metabolic measurement
Cons of direct calorimeter
expensive, slow, heat added by equipment, sweat creates measurement errors, not practical, and not accurate for exercise
Indirect calorimetry
estimates energy expenditure using O2 used and CO2 produced
measures respiratory gas concentrations
Why is indirect calorimetry only accurate for stead-state exercise?
Once anerobic metabolism kicks in, hard to look at the respiratory gas exchange
VO2
volume of O2 consumed per minute
VCO2
volume of CO2 produced
Ve
ventilations per minute
Respiratory exchange ratio
ratio between CO2 production and O2 usage (VCO2/VO2)
RER: O2 usage depends on type of fuel
glucose requires less O2 than lipid metabolism
start exercise using fat and transition to more carbs
1 glucose = ___ RER
1.0 RER
6 O2 + C6H12O6 —> 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + 32 ATP
6 CO2/6 O2 = 1.0 RER
1 fatty acid = ____ RER
0.70 RER
23 O2 + C6H12O6 —> 16 CO2 + 16 H2O + 129 ATP
16 CO2/23 O2 = 0.70 RER
limitations of indirect calorimetry
CO2 production may not = CO2 exhalation
RER is inaccurate for protein oxidation
RER near 1.0 may be inaccurate when lactate buildup increases CO2 exhalation
Gluconeogenesis produces RER <0.70
Increased psychological stress leads to…
higher RER and increased carb/glucose metabolism
Heart rate monitoring can be used to estimate…
VO2
linear relationship, considerable error rate (electronics)
used for estimation of submaximal exercise
Limitations of heart rate monitoring
only aerobic metabolism
complicated by body temp, upper body exercise, and fitness level
poor correlation for sedentary/low-intensity activity
Energy expenditure: Walk/Run
estimate: only during steady-state submaximal aerobic exercise; specific to body mass
Divide metabolic rate into…
resting = 3.5 mL/kg/min = 1 MET
+ energy cost for horizontal (0.1ml/kg/min)
+ energy cost for vertical movement (+1.8mL/kg/min)
+ much more (walking swing, height, etc.)
non-resting
Energy Expenditure: Cycle
looking for Watts
estimate: resistance/load (kg), distance (wheel size=m/rev), cadence (rev/min or RPM)
POWER (kg/m/min) = resistance (kg) x flywheel size (m/rev) x cadence (rev/min)
energy cost also includes external resistance, body weight, and bike weight
metabolic rate
rate of energy use by the body
based on whole-body O2 consumption
~2000 kcal/day
What is the average RER at rest?
0.80
Basal metabolic rate
energy expenditure at rest — minimum requirement for living
measured in supine position after 8 hr sleep & 12 hr fasting
related to fat-free mass and influenced by size, age, stress, hormones, and temp
resting metabolic rate (RMR)
like BMR (+5%/10%) — more realistic without fast
1200-1400 kcal/day
total daily metabolic activity includes
normal daily activity
1800-3000 kcal/day
Fick equation
tells how much oxygen is being delivered to and removed from the tissues
VO2=HR x SV (cardiac output) x a-vO2 difference
Cardiac output
quantity of blood pumped each contraction
cardiac output = stroke volume x heart rate
How many kcals used per liter of oxygen consumed?
5kcal
estimated over time
In submaximal aerobic exercise, metabolic rate ….
increases with exercise intensity
shared with oxygen use
At higher outputs, VO2 ______ & more type ____ fiber recruitments
continues to increase
more type II muscle fibers recruited (less efficient)
VO2 drift
upward drift observed even at low power outputs when person reaches a certain point
possibly due to ventilatory or hormone changes
VO2max
maximal O2 uptake
point at which O2 consumption does not increase with greater exercise intensity
more training allows athlete to compete at higher % of VO2max — adaptation plateaus after 8-12 weeks of chronic training
Best measurement of aerobic fitness?
VO2max
Economy of movement is very important for…
aerobic athletes (think running form, swimmer’s technique, etc.)
How does gender affect VO2max?
testosterone & protein synthesis
increased testosterone —> males can synthesize more hemoglobin
also, males usually have slightly larger lungs and heart
Absolute measurement of VO2max
Not dependent on bodyweight
L of O2 / minute
Relative measurement of VO2max
Helps compare athletes of different weights
greater muscle mass involved = greater VO2
mL of O2 x min-1 x kg-1 = relative VO2max
Maximal aerobic exercise
nothing is 100% aerobic or anaerobic
Estimates of anaerobic effort involve…
Excess of postexercise O2 consumption (EPOC)
Lactate threshold (hard to quantify)
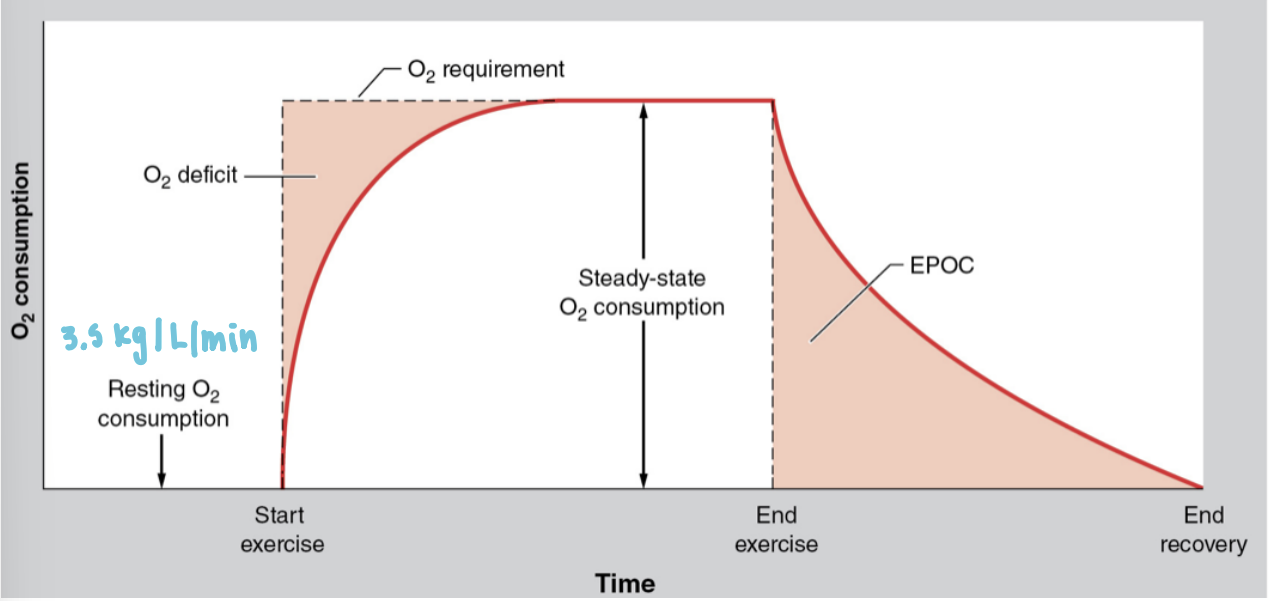
Early in exercise O2 demand is…
greater than O2 consumed
initial energy comes from anaerobic metabolism as aerobic takes awhile to ramp up
this builds an O2 deficit
Post-exercise O2 consumed is…
greater than O2 demand
EPOC: Excessive Postexercise O2 consumption
EPOC: Excessive Postexercise O2 consumption
replenishes ATP/PCr stores
converts lactate to glycogen
replenishes hemomyoglobin and clears CO2
Do we have lactate in the blood at rest?
Yes- some tissues have no mitochondria; RBCs push out lactate b/c they have no use for it (no aerobic metabolism)
Lactate Threshold (L1)
blood lactate accumulation increases markedly at this point (~2 mmol/L)
at this point, lactate production > lactate clearance (mix of aerobic and anaerobic systems)
usually expressed as a percentage of VO2max
Lactate threshold is a good indicator of potential for ______ exercise
endurance exercise
Economy of Effort
as athletes train, they use less energy at a similar pace
this is independent of VO2max
body learns this with practice
Economy increases with distance — multifactorial phenomenon
form: practice lends better economy of movement
varies with type of exercise (running, swimming)
Successful endurance athletes have…
high VO2max
high lactate threshold
high economy of effort
high % of Type I muscle fibers