Chloride & Calcium
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
CHLORIDE (Cl- )
• It is the major extracellular anion
• chief counter ion of Na in ECF
CHLORIDE (Cl- )
• ___ shifts secondarily to Na+ or HCO3-
• It is mainly involved in maintaining osmolality, blood volume, and electroneutrality
• Only known anion to serve as an enzyme activator (Amylase)
Urine & sweat
Excess Cl- is excreted in ___ & ____
aldosterone secretion
In chloride, Excessive sweating stimulates ___
glomerulus,, proximal tubules
How it maintains electroneutrality:
I. Cl- is filtered out by the ________ and passively reabsorbed in conjunction with Na+ by the ____
Chloride shift
REGULATION
II. ________________
— Uptake of Cl- in exchange of HCO3- in red blood cells.
Hyperchloremia
- Dehydration
- Hyperventilation (Respiratory Alkalosis)
- Renal Tubular Acidosis
- Metabolic Acidosis
- Diabetes Insipidus
-Salicylate Intoxication
- GI loss of HCO3- (severe/prolonged diarrhea)
Hypochloremia
- Prolonged Vomiting
- SevereBurns
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis
- Addison's Disease
- Salt-losing nephritis
- Metabolic Alkalosis
Serum or plasma
What specimen is used in Chloride?
Lithium Heparin
What is the anticoagulant used in Chloride?
Marked hemolysis, due to dilutional effect (false decrease)
What is the possible interference in Chloride and how can it affect the result?
Sweat and urine
What other body fluids can be used as a specimen in chloride?
24-hour collection (refrigerate)
What is the specimen/collection of choice for urine in Chloride?
- Ion selective electrode (ISE)
- Coulometric- Amperometric Titration
- Colorimetric methods
Laboratory Determination in Chloride:
- Schales & Schales Method (Mercuric nitrate Titration Method)
- Zall Color reaction (Whitehorn Titration Method)
Colorimetric methods used in chloride:
Ion Selective Electrode (ISE)
- Routine method in Chloride
- very sensitive & very specific
silver chloride- silver sulfide
Ion exchange membrane with Polycrystalline:
________________________ (Silver Polymeric Membrane)
Coulometric- Amperometric Titration
o Cotlove Chloridometer
o Coulometry: quantity of electricity (in coulombs) needed to convert an analyte to a different oxidation state
oAmperometry: measurement of the current flow produced by an oxidation-reduction reaction
Cotlove Chloridometer
What is the machine used in Coulometric- Amperometric Titration?
Coulometry
quantity of electricity (in coulombs) needed to convert an analyte to a different oxidation state
Amperometry
- measurement of the current flow produced by an oxidation-reduction reaction
- pair of silver electrodes serves as the indicator electrodes
Schales & Schales Method (Mercuric nitrate Titration Method)
Chloride:
- Indicator: Diphenylcarbazone
- Reagent: Mercuric nitrate
- Result/End product: Mercuric Chloride (HgCl2) Blue violet
Diphenylcarbazone
What is the indicator used in Schales & Schales Method (Mercuric nitrate Titration Method)?
Mercuric nitrate
What is the reagent used in Schales & Schales Method (Mercuric nitrate Titration Method)?
Result: Mercuric Chloride (HgCl2)
End product: Blue violet
What is the result/end product used in Schales & Schales Method (Mercuric nitrate Titration Method)?
Zall Color reaction (Whitehorn Titration Method)
- Reagent: Mercuric Thiocyanate
- Result/End product: Reddish complex
Mercuric Thiocyanate
What is the reagent of Zall Color reaction (Whitehorn Titration Method)?
End product: Reddish Ferric thiocyanate
End color: Reddish complex
What is the result/end product of Zall Color reaction (Whitehorn Titration Method)?
98-107 mmol/L
Reference range of chloride in plasma/ serum:
110-250 mmol/d, varies with diet
Reference range of chloride in Urine (24h):
CALCIUM (Ca2+ )
• divalent cation with structural and metabolic roles
• 99% bone, 1% is mostly in the blood and other ECF
45
In calcium, ___% circulates as free Ca 2+ ions (ionized calcium/ ical)
40
In calcium, __% is bound to protein, mostly albumin
15
In calcium, __% is bound to anions (citrate, lactate, phosphate, etc.)
CALCIUM (Ca2+ )
an activator of intracellular signal transduction processes and is essential for DNA and RNA biosynthesis
duodenum and upper jejunum
Calcium is absorbed in the _______and ____ via an active transport process
Ionized calcium
• mean concentration in humans of about 1.18 mmol/L
• a more sensitive and specific marker for Ca 2+ disorders
• decrease in concentration
• cannot be reliably calculated from total Ca 2+ especially in acutely ill individuals
1.18 mmol/L
Ionized calcium have a mean concentration in humans of about ___
myocardial function
decrease in concentration of ionized calcium impairs ___
Tenany
decrease in concentration of ionized calcium can cause neuromuscular irritability, which may become clinically apparent as __________ (irregular muscle spasms)
Ionized calcium
• binds to negatively charged sites on the protein molecules
• binding is pH dependent
pH dependent
Binding in ionized calcium is ___
Alkalosis
____________ promotes increased protein binding: decreases ionized calcium
Acidosis
____________ decreases protein binding: increases ionized calcium
Parathyroid hormone
• stimulated by a decrease in ionized Ca 2+
• Bone: bone resorption
• Kidneys: increasing tubular reabsorption of Ca 2+ ions, stimulates renal production of active vitamin D
Vitamin D3
• 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol (1,25-[OH]2 -D3) biologically active form
• increases Ca 2+ absorption in the intestine and enhances the effect of PTH on bone resorption
1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol (1,25-[OH]2 -D3)
biologically active form in Vitamin D3
Calcitonin
• originates in the medullary cells of the thyroid gland
• decrease calcium levels by inhibiting the actions of both PTH and vitamin D
• secreted only in response to a hypercalcemic stimulus
9.0-10.1 mg/dL (2.24-2.53 mmol/L)
Reference range of Total calcium (adults), serum/plasma:
4.6-5.3 mg/dL (1.15-1.33 mmol/L)
Reference range of Ionized (free) calcium, serum:
4.6-5.1 mg/dL (1.15-1.27 mmol/L)
Reference range of Ionized (free) calcium, WB:
Hypocalcemia
decreased calcium level in the blood
Hypocalcemia
- Primary hypoparathyroidismglandular aplasia, destruction, or removal
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Pseudohypoparathyroidism
- Hypomagnesemia
- Rhabdomyolysis
- Acute pancreatitis
- Renal disease
- Hypermagnesemia
Ionized calcium
This is requested for ICU patients or sepsis
Surgery and intensive care
Hypocalcemia occurs commonly in critically ill patients—that is, those with sepsis, thermal burns, renal failure, or cardiopulmonary insufficiency
Hypocalcemia
occurs commonly in critically ill patients—that is, those with sepsis, thermal burns, renal failure, or cardiopulmonary insufficiency
Neonates
• Ionized Ca 2+ concentrations are high at birth and rapidly decline by 10% to 20% after 1 to 3 days
• Child, <3 years old: 2.13-2.63 mmol/ L (8.5-10.5 mg/dL)
10% to 20%
Ionized Ca 2+concentrations are high at birth and rapidly decline by ___ to ___ after 1 to 3 days
2.13-2.63 mmol/L (8.5-10.5 mg/dL)
Ionized Ca 2+concentrations of Child, <3 years old
Chvostek and Trosseau sign
- happen when Ca2+ is decreased
• Neuromuscular irritability and cardiac irregularities
• Severe hypocalcemia, in which total Ca 2+ levels are below 1.88 mmol/L (7.5 mg/dL)
< 1.88 mmol/L (7.5 mg/dL)
In Chvostek and Trosseau sign the total Ca2+ levels are ___
Hypercalcemia
abnormal increase of calcium in the bloodstream
Hypercalcemia
- Primary hyperparathyroidism — adenoma or glandular hyperplasia
- Hyperthyroidism
- Increased vitamin D
- Benign familial hypocalciuria
- Malignancy
- Multiple myeloma
- Milk alkali syndrome
- Thiazide diuretics
- Prolonged immobilization
Primary hyperparathyroidism
- adenoma or glandular hyperplasia
- main cause of hypercalcemia
Malignancy
Second cause of hypercalcemia
Neurologic, GI, and renal symptoms
Symptoms when moderate or severe Ca 2+ elevations (2.62 to 3.00 mmol/L [10.5 to 12 mg/dL]) —> panic level/ critical level
2.62-3.00 mmol/L (10.5-12 mg/dL)
What is the range of the panic/ critical level in calcium (fatal to px)?
Asymptomatic
Symptoms of mild hypercalcemia
Serum
What is the preferred specimen for Total calcium?
Citrate, oxalate, EDTA, hemolysis, icterus, lipemia, paraproteins, and magnesium
What are the interferences of calcium in colorimetric methods
serum or lithium heparin plasma
What is the preferred specimen for ionized calcium?
anaerobically,, 4C
In ionized calcium, Specimens should be collected ______________, transported on ice, and stored at ______ to prevent loss of carbon dioxide
Increase the pH
In ionized calcium, the loss of CO2 will ___ of the sample
Lower pH
In ionized calcium, tourniquet left on too long can __________
- Colorimetric method
- Atomic Absorption Spectrometry
Analytic methods of total calcium:
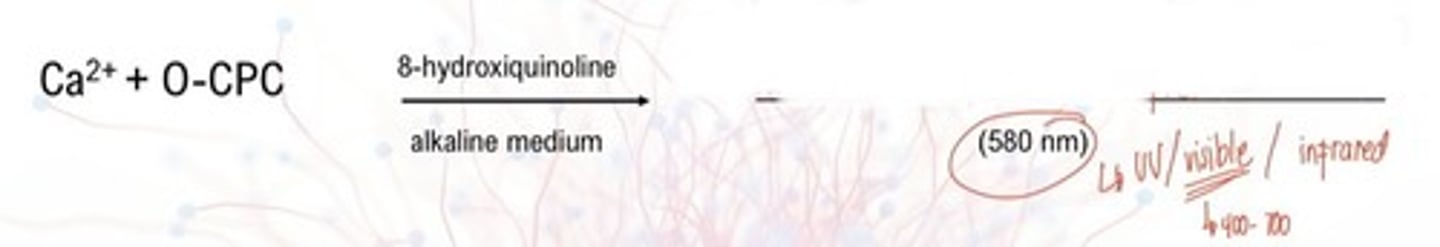
- Orthocresolpthalein complexone (O-CPC)
- use of Arsenazo III dye
Colorimetric methods of total calcium:
Calcium-Cresolphthalein Complex (purple color)
Purple color
What is the end color of Orthocresolphthalein complexone?
580 nm
What is the absorbance of Orthocresolphthalein complexone?
8-hydroxyquinoline
added to reduce interference by magnesium ions
Formula for Corrected Total Calcium
Corrected Total Ca (mg/dL) = measured total Ca2+ + [(normal albumin - px albumin) x0.8]
Arsenazo III dye
- metallochromic indicator
o Ca 2+ is released from its protein carrier and complexes by acidification of the sample
o high specificity for calcium at slightly acidic pH
Calcium-indicator complex

650 nm
Arsenazo dye method absorbance
Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (AAS)
• reference method for total Ca2+
• rarely used in the clinical setting
• technique is difficult for high-volume laboratories
ion-selective electrode (ISE)
Analytic method of Ionized calcium:
Ion Selective Electrode (ISE)
• membranes impregnated with special molecules that selectively, bind Ca 2+ ions
• electric potential develops across the membrane that is proportional to the ionized Ca 2+ concentration