2. classifications of fractures
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
what type of fracture is an avulsion fracture
chip fracture
where does an avulsion fracture typically occur
at the corners or in the areas of ST attachment of a long bone where the ligament inserts
avulsion fracture etiology
occurs when a portion of bone is torn away by a muscle or ligament at the point of attachment (due to forceful contraction on that bone)
avulsion fracture treatment
immobilization, surgical pinning may be required
avulsion fracture complications
fragment can impinge a nerve or blood vessel
what is a blowout fracture
fracture of the orbital floor
blowout fracture etiology
blunt force trauma to the face = increased pressure = orbital walls/floor fracture
what does a blowout fracture look like on a radiograph (ie how can we tell it has occurred)
blood pooling in the sinuses, fracture lines
blowout fracture treatment
surgery
blowout fracture complications
infection, double vision, scarring of the muscles in the eye
what is the medical term for double vision
diplopia
what is a comminuted fracture
fracture where the bone has been broken into multiple fragments
comminuted fracture etiology
trauma due to axial loading/a vertical force
comminuted fracture treatment
surgery
comminuted fracture complications
poor healing due to many fracture lines
what are comminuted T and Y fractures + where do they occur in the body
intercondylar fractures of the distal humerus and distal femur
etiology of comminuted T and Y fractures
trauma by high energy forces or direct blows (MVA, falling)
describe the appearance of comminuted T and Y fractures
the bone breaks longitudinally and horizontally forming a line, occurs at joints and the fracture line communicates with the joint
comminuted T and Y fractures treatment
surgery
comminuted T and Y fractures complications
deformity of the bone from poor apposition of the fragments, vascular and nerve damage
describe what multiple fractures are
when there’s more than one fracture separated by intact bone, and the fractures all result from the same injury
where in the body do multiple fractures typically occur
tib/fib, forearm
multiple fractures etiology
trauma
multiple fractures treatment
surgery
multiple fractures complications
poor healing due to many fracture lines
contrecoup fracture description
fracture at the opposite side to the point of initial injury/impact
where do contrecoup fractures usually happen
pelvis, tibia, skull, mandible
for contrecoup fractures, what is “coup”
the initial injury
contrecoup fracture treatment
surgery
contrecoup fracture complications
poor healing, bone deformity
displaced fracture description
fragments are not aligned; can occur minimally, slightly, or significantly
displaced fracture etiology
trauma
displaced fracture treatment
reduction to re-align fragments, immobilization, surgery may be needed
displaced fracture complications
bone deformity = shortening of the limb and decreased mobility
when do stress fractures occur
when there is repetitive strain on the bone
stress fracture etiology
result of microfractures caused by repetitive movements and applied force = small hairline fractures
where in the body do stress fractures occur
weight bearing bones
stress fracture treatment
reduction in the repetitive activity
stress fracture complications
ongoing pain, poor healing, early onset of arthritis
depressed fracture description
a piece of bone is pushed inward or indented
where in the body do depressed fractures occur
skull, tibial plateau
depressed fracture etiology
impaction injury
depressed fracture treatment
surgery
depressed fracture complications
fragments can affect nerves and blood vessels or cause ST damage
impacted fracture description
one portion of bone is driven into its adjacent segment; can also be a compressed or depressed fracture
impacted fracture treatment
reduction, immobilization
impacted fracture complications
poor healing, deformity of the bone
linear fracture description
the fracture line is // to the LA of the bone
linear fracture etiology
trauma
linear fracture treatment
immobilization
linear fracture complications
poor healing
longitudinal fracture description
the fracture line runs along the shaft but is not // to the LA of the bone like a linear fracture is
longitudinal fracture etiology
trauma
longitudinal fracture treatment
immobilization
longitudinal fracture complications
poor healing
transverse fracture description
fracture line is at 90 degrees to the LA of the bone
transverse fracture etiology
trauma
transverse fracture treatment
immobilization
transverse fracture complications
poor healing
oblique fracture description
fracture line runs at an angle that is 25+ degrees from the transverse axis of the bone
oblique fracture etiology
trauma
oblique fracture treatment
immobilization
oblique fracture complications
poor healing
spiral fracture description
fracture line is helical around a long bone, and the edges are very sharp as it twists around
another name for a spiral fracture
torsion fracture
spiral fracture etiology
trauma caused by rotational force (ie skiing)
spiral fracture treatment
surgery to provide good apposition
spiral fracture complications
deformity of bone, fragments can cause further damage to nerves + vessels + ST
stellate fracture description
fracture lines radiate from a central point of impact
where are stellate fracture commonly seen
skull, patella
stellate fracture etiology
trauma, direct blow to the bone
stellate fracture treatment
surgery, wire wrapped around the fragments to contain them, surgeon might remove patella
stellate fracture complications
fragments can impinge on nerves and vessels and cause further damage
pathological fracture description
fracture of a bone that’s already been affected by a pathological disease
pathological fracture etiology
trauma to an already weakened bone
pathological fracture treatment
surgery
pathological fracture complications
ongoing pain, decreased mobility, deformity of long bones
articular fracture description
fracture involving a joint, cartilage and ST may be involved too
articular fracture etiology
trauma
articular fracture treatment
reduction, immobilization
articular fracture complications
post-traumatic arthritis
supracondylar fracture description
involves the area between the condyles of the femur or humerus
femoral supracondylar fracture etiology
impact to a bent knee
humeral supracondylar fracture etiology
fall
supracondylar fracture treatment
surgery
supracondylar fracture complications
poor healing, deformity of the bone
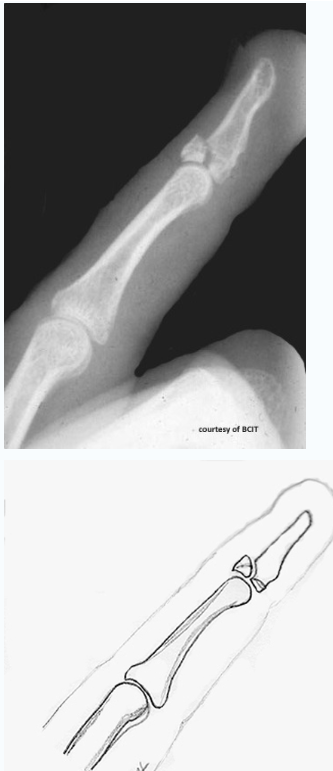
which type
avulsion
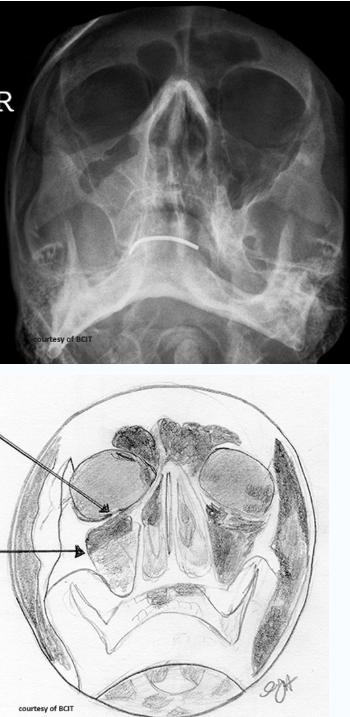
which type
blowout
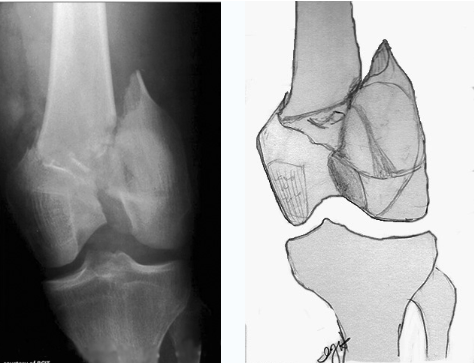
which type
comminuted T and Y
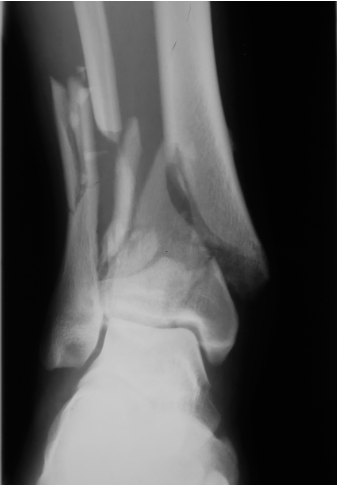
which type
multiple
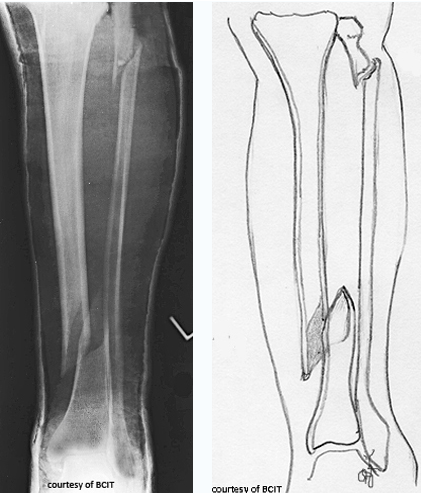
which type
contrecoup
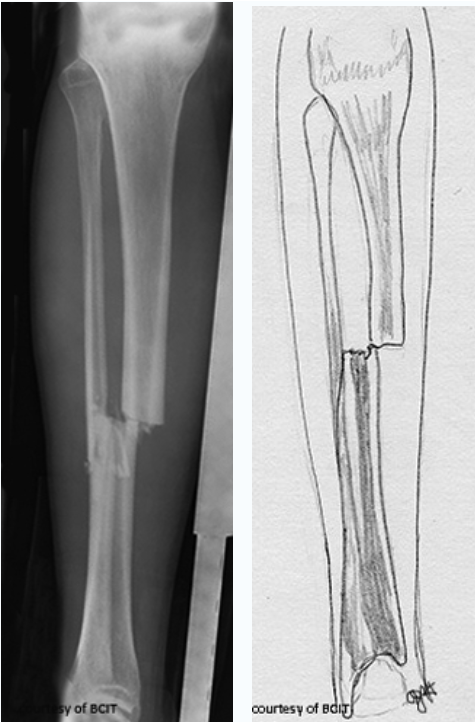
which type (2)
displaced, transverse
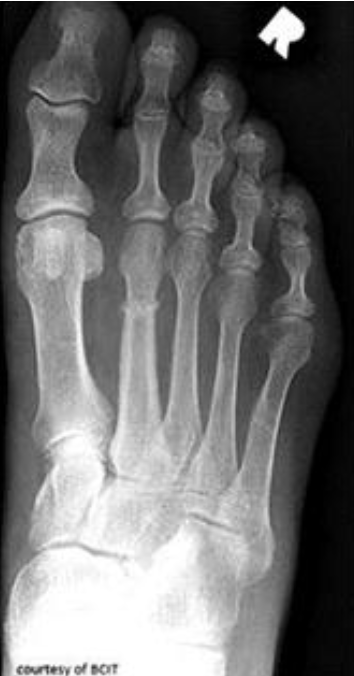
which type
stress
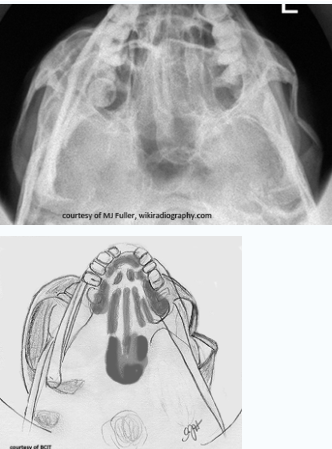
which type
depressed
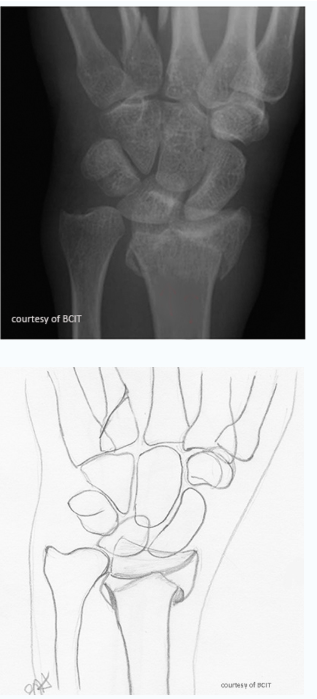
which type
impacted
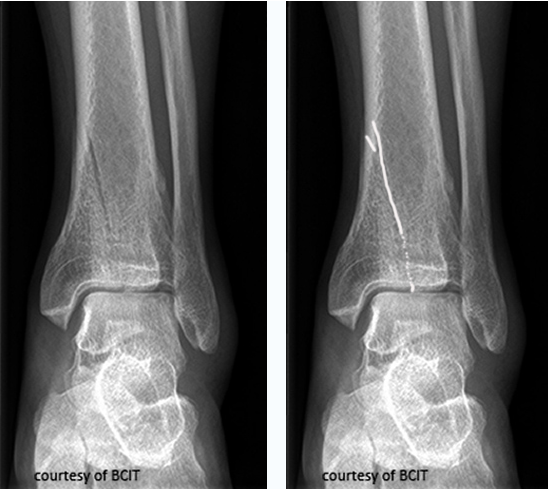
which type
linear
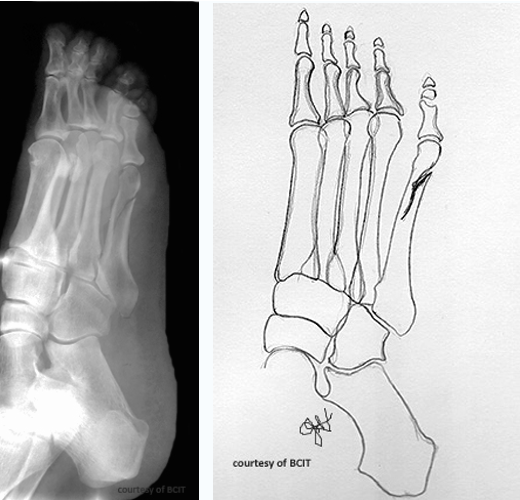
which type
longitudinal
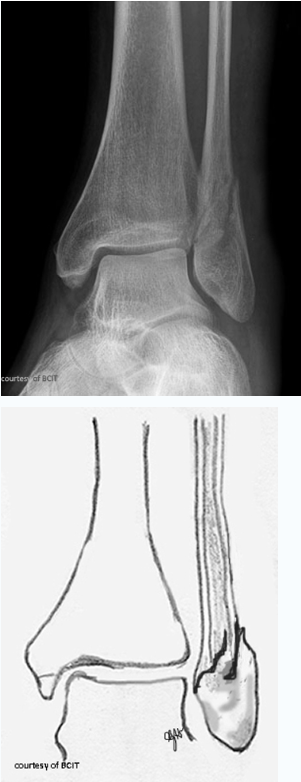
which type
oblique

which type
spiral
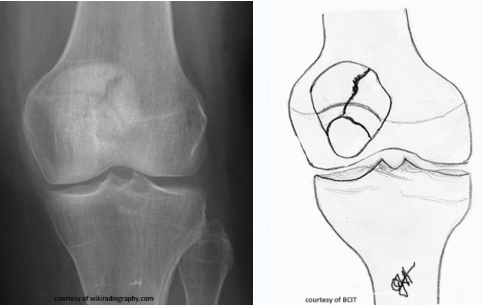
which type
stellate