3.10 Technology of model cast FPD
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What is first step in preparing model cast FPD?
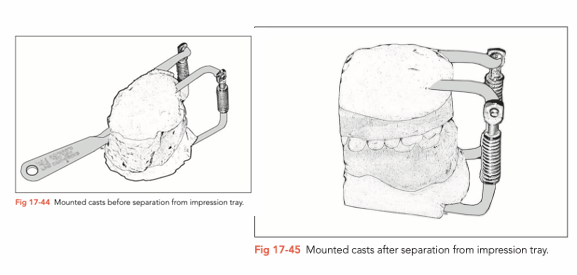
Pour dental stone model and fix it onto a articulater
Cut circumferentially around the abutment teeth with blade, teeth walls are almost visible
What is second step in preparing model cast FPD?
High melting point wax is added to several locations:
Over dies, shaped like smaller version of crown which stays at approx. 0.5 mm away from opposing teeth
Wax not added 1-1.5mm above cervical line
On crest of alveolar ridge at edentulous area to ensure minimal amount of space between pontic and gingiva
Any retentive areas of model ensuring an easier cast duplication
When doing the second step (PREPAIRING THE MODEL FOR DUPLICATION) of preparing model cast FPD what does the thickness of wax determine?
Thickness of wax layer determines the thickness of layer of cement after fixation
why is preemptive modelling used in preparing model cast FPD (2nd step of the preparation)?
Used to create distance between the dies’ walls and the cap, as well as the pontic and the gingiva
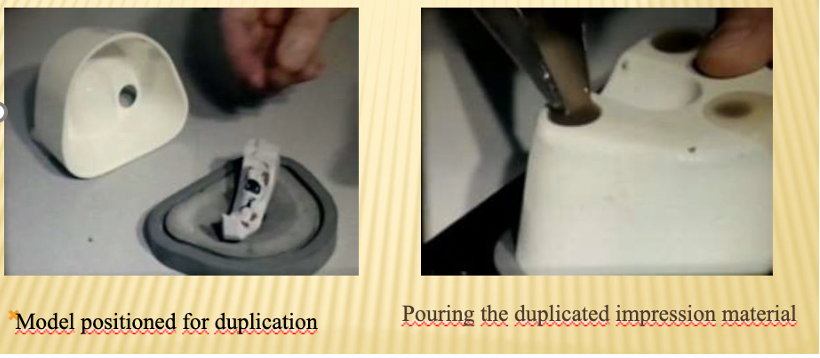
What is the 3rd step (MASTER CAST DUPLICATION) of preparing model cast FPD?
Reversible hydrocolloid (laboratory silicone) is used. Impression material turns from sol to gel which enables it to be poured into special flask
Investment material prepared and poured into impression. It is very fragile and brittle
Duplicate model is same but very precise
Model is hardened through dipping it in heated wax (colophony mixture)
Result is a protective layer of colophony mixture which gives the model a specific light brown colour
Compare impression silicones and laboratory silicones (used in Model duplication - step 3)
Laboratory silicones recreate fine details better
After polymerisation, laboratory silicones have hardness of 10-35 on shore scale
After polymerisation, impression silicones have hardness of 65-85 on shore scale
Both have very high elasticity - 99.92 - 99.98%, ensure no permanent elastic deformation and allows for repeated casting

What is the 4th step of preparing a model cast FPD?
WAXING THE BRIDGE CONSTRUCTION

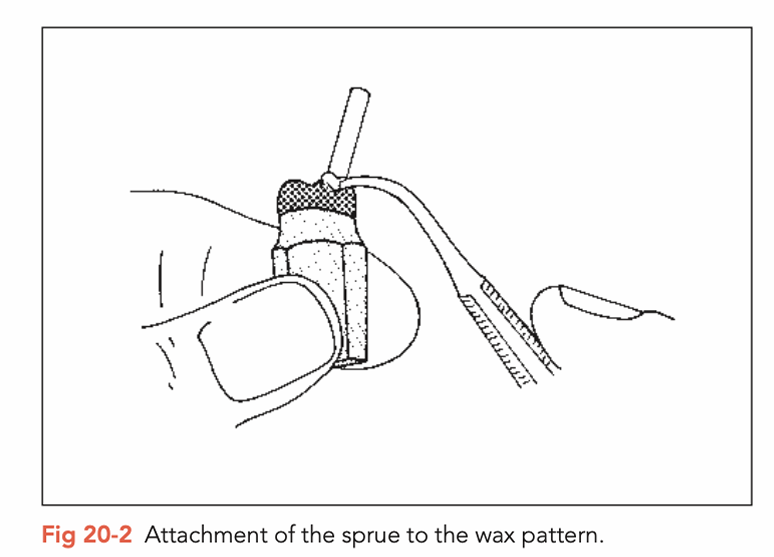
What is the 5th step of preparing a model cast FPD?
Selection of casting mould, spruce placement depends on construction size, retainer number and pontic profile
Duplicated model, cast from same substance as investment material
Mould filled with investment material and heated gradually tp specific alloy temperature (burnout)
Spruces and wax melt and vaporise, leaving space for casting channels and the casting pattern in the same negative impression of the finished wax up
Manufacturers provide instruction for heating duration and heating intervals for mould
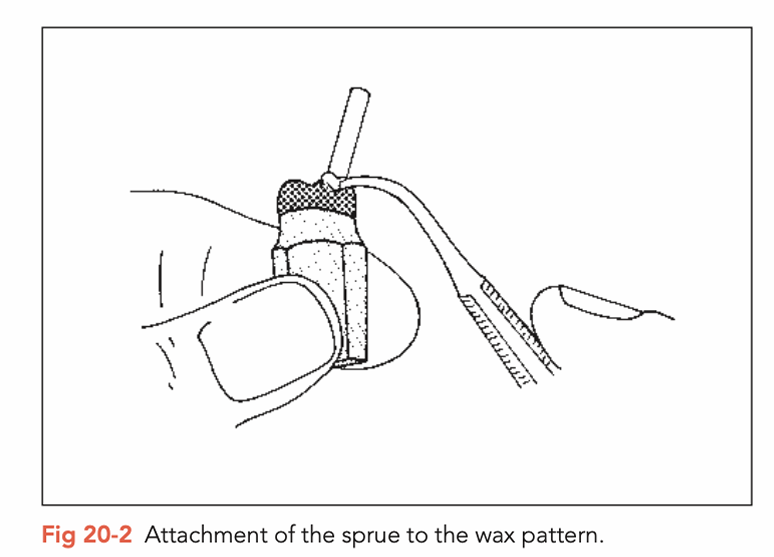
in the 5th step of preparing model cast FPD, what does the selection of casting mould and spruce placement depend on?
on construction size, retainer number and pontic profile
what is step 6 of preparing model cast FPD?
CASTING, FINISHING AND POLISHING
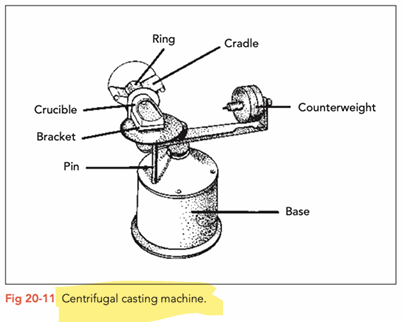
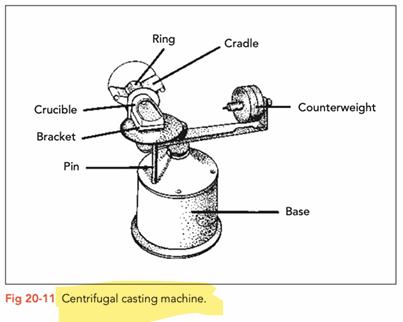
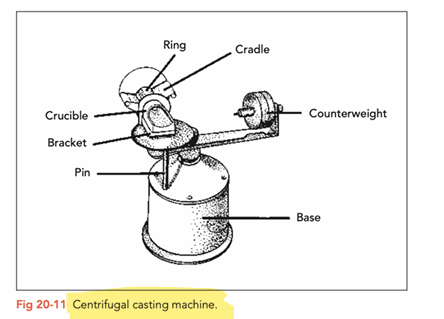
Mould is fixed horizontally on one end of centrifugal casting machine while a counterweight is fixed on the opposite side
Alloy melted in a flame-resistant melting pot through a high frequency induction current, outside of the crucible. Since these machines do not use an open flame, oxidisation is brought to a minimum and so no need to use flux (flux is used in soldering to remove oxide layers)
After alloy has been melted the centrifuge activates and automatically starts spinning. Through centrifugal force the melted alloy flows from the crucible through the casting channels and almost fills the casting form (pattern)
NA - cool to room temp post-casting
CCMA - colour change (red to gray-black) then submerge mold in cold water then cast is freed from investment material
FINAL CLEANING - sandblasting, spruce removal, electro-chemical treatment, polishing as per metal surface rules
What is a time sensitive factors to remember in step 6 of the preparation of model cast FPD?
no more than 30 seconds should be allowed to elapse between time the ring is removed from oven and molten alloy is centrifuged into the mold.
Any undue delay causes heat loss and resultant mold contraction
what are the machines used in step 6 of preparing mold cast FPD?
Model casting is always done with high frequency casting devices
These machines are mechanical centrifuges that work through high frequency centrifugal casting
in step 6 of preparing mold cast FPD how are noble alloys treated after centrifuging and how are chrome cobalt molybdenum alloys treated?
Nobel Alloy - mould cools to room temperature post-casting
Chrome, cobalt, molybdenum alloys - monitor colour change (red to gray-black). Immediately after that, mould is submerged in cold water and then the cast is freed from the investment material
Who suggested the idea of three occlusal stops for incisors and molars and two for premolars?
Julius Mathe 1948
what is main disadvantage of Julius Mathe’s idea?
Nowadays it is modified and known as Dann-A-Tube crown
main disadvantage of these crowns is that the acrylic resin within two years is worn out and the occlusal stops are prominent
Which material causes natural teeth occlusal surfaces to abrade quicker than metal?
ceramics
where are occlusal stops placed and what are they?
Occlusal stops are specific points of contact between the upper and lower teeth that help maintain proper bite alignment and stability. They play a crucial role in preventing excessive movement and ensuring that dental restorations, such as crowns or dentures, function correctly.
placed in strongest contact area
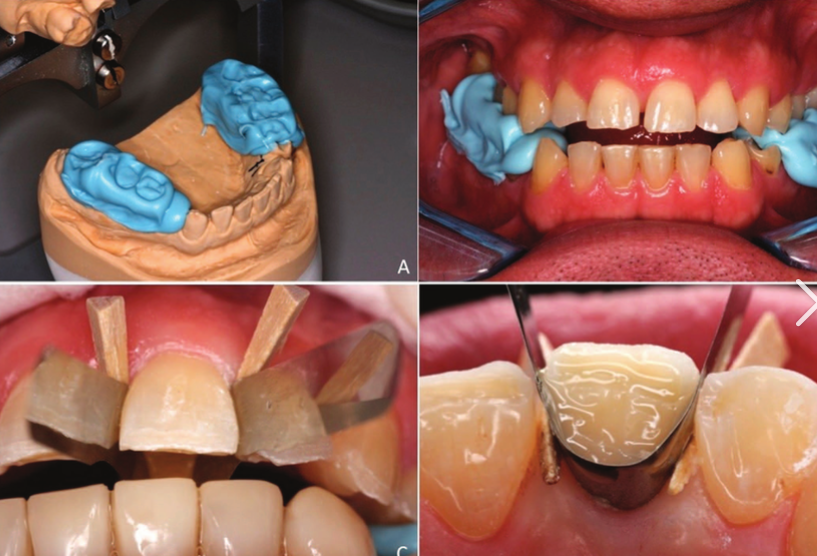
why is metal ceramic crowns preferred?
They offer aesthetic benefits along with prophylactic advantages, especially for patients with bruxism
what is SIGNUM?
next generation composite material
What are some features of SIGNUM?
absolute colour stability
can be applied layer by layer from 0.5 to 2 mm
Can reproduce in a perfect way the look of natural teeth
More elastic compared to ARTGLASS, more microfillers
Can be used for all indications, with or without metal framework
what are indications for SIGNUM?
non-metal crown (incl. molars)
FPD
veneers
model cast dentures (artificial teeth for dentures)
inlays, onlays
What are steps to using SIGNUM?
CONDITIONING - use sandblast equipment with 2-3 bar pressure, use AI203 with particle size of 110µm.
APPLYING OPAQUE LAYER - (first layer) 1-2 very thin layer of signum metalband II. Photopolymerise for 90 seconds using HiLite power. (second layer) 2 layer of signum opaque F. polymerise for 90 seconds with HiLite power. Standard application of signum composite
BUILDING STRUCTURE - (dentin) apply dentin core to give structure of mamelons, polymerise for 90 seconds using HiLite power. (enamel) very thin layer of signum composite enamel over upper incisal 1/3. Ensure the surface is soft with incisal paste. Polymerise with HiLite power for 180 seconds
FINISHING AND POLISHING - use signum toolkit for final finishing. Polishing pastes. Use HP paste and HP Diamond Paste for polishing
ADDITIONAL APPLICATION - apply signum cre-active as needed
what does signum ceramic represent?
glass-ceramic composite, designed for non-metal appliances
what are some properties of signum ceramics?
high content of microglass ceramic filler (73% vol)
resistance similar to natural teeth
tough and durable
radiopaque (material or substance that is opaque to X-rays or similar radiation. This means that it blocks or absorbs the passage of X-rays, appearing white or bright on radiographic images.)
offered in sets of 8 colours
16 dentin masses
what makes up signum ceramics?
non-organic filler - 73%
Size of particle - 0,7 µm
Types of filler - Silica (SiO2) (it is radioopaque) and Ba-AL-Si glass
multifunctional methacrylic aesther of organic glass (27%)
stabilizers
photo initiators
inorganic pigments
what two ceramics is signum ceramic an alternative of?
Tow types of materials for non-metalic restorations:
ceramic (zirconia, press-ceramics etc)
Composites (signum ceramics, Artglass ect)
what are advantages of signum ceramics?
fast and easy manufacturing of restoration
very high quality restoration
if needed, correction can be done in just 3 minutes
high modulus of elasticity
aesthetics
easy achieving of desired colours
what are some signum products?
signum composite - for restorations with metal substructure
signum metal bond - specially designed adhesive for metal
signum ceramics - for non-metal restorations
signum connector - for better connection to acrylic teeth
what is signum matrix?
nano-hybrid composite
62% inorganic filler
based on polyglass - microfiller technology
in compliance to the photodynamic concept of Hera Ceram Matrix
what is advantage of signum matrix?
individual way of work
fast polymerisation
perfect reproduction of transparency, translucency, opacity and fluorescence
what are advantages for dentist when using signum matrix?
direct polishing
usual luting technique
easy repairing using other composite materials such as Charisma, Venus
when and who introduced Vectris?
Ivoclar-Vivadent in 1990
what is Vectris?
combination of organic matrix (15-25%) and ceramic and glass-ceramic particles (fillers) - 75-85% respectively
what are benefits of vectris?
abrasion is closer to enamel
elasticity 1000 MPa (ceramic only 600MPa)
aesthetics - very nice natural transparency, translucency and fluorescence
what are the two types of ceromers (combination of polymer and ceramic)?
basic material - Vectris
Covering material - Targis
what are the three varieties of the base material (vectris) of ceromers?
discs serving as a basic cap of the future crown
bars - for the pontic
rectangular plates - cover the abutments and the pontic
what is the net structure of polymers in ceromers?
basic material -vectris
inorganic filler spreads all around the net fibers
how is the bond between Vectris and Targis material achieved?
with help of a special adhesive, Targis Link which forms bond to metal substructures
how does the base ceromers (vectris) polymerise?
in special device Vectris VS1 using -
light
heat
vacuum
how is the covering material of ceromers (targis) used and how it is polymerised?
Put layer by layer
polyerised (light and heat only) in device called Targis power (97 degrees for 25 minutes)
what is recommended for luting the ceromer crowns and bridges?
resin cement Variolink II (Ivoclar) is recommended
what is composition of Targis/Vectris?
77wt% (77% of total weight of material) filler - barium glass, silica
23wt% organc resin
What is Vectris suitable for because of its fibre reinforced framework?
for fabrication of FRC frameworks (fibre reinforced composite), it has natural fibre bonds making it capable of withstanding extreme stresses from natural surroudning
what does FRC materials consist of?
elastic fibres embedded in an organic matrix
what is Vectris seen as an alternative to?
alloys, ceramics and zirconia oxide
What does vectris allow dentistst to do?
treat clinical cases, such as missing posteriro teeth with tooth conserving solution
i.e - Vectris based inlay retained bridge that is cemented in place using adhesive cementation technique
Give the general structure of Vectris
several layers of fibre wafers and fibre bundles embedded in an organic polymer matrix
matrix assures a strong bond and homogenously distributes the masticatory forces exerted on the veneering material throughout the framework
what are some physical properties of vectris?
vectris framework has intimate stress-free fit and beneficial physical properties thanks to manufacturing process that combines pressure, light and vaccum
What does the newly developed working technique based on Transil matrix material facilitate with vectris?
facilitates fabrication of cusp-supporting frameworks
what are aesthetic properties of Vectris?
translucent, due to tooth coloured fibre wafer
Light can pass through restoration without being blocked by opaque areas of substructure
FRC framework is advantageous in areas where there is transition from pink tissue to white tooth colours
Grey margins seen in metal restorations not present in Vectris-based reconstructions
Cervical area exhibits a lifelike aesthetic appearance
can vectris be veneered with SR Adoro?
yes
what is SR Adoro?
microfilled light/heat curing veneering composite for fixed metal-supported and metal free dental reconstructions
what are advantages of SR Adoro over glass-filled and hybrid composite materials?
polish ability
handling
plaque ressistance
surface finish
High degree of translucency (light refraction index of matrix and microfillers are coordinated with eachother)
Aesthetic
what does the formulation of SR Adoro ensure?
smooth, non-sticky consistency
Excellent modelling properties
What is a advantageous feature of the foundation material of SR Adoro?
foundation material has opalescent characteristics, equal to those of natural tooth
How are SR Adoro and Vectris veneered?
with help of SR Adoro Liner
Give some features of Vectris VS1 (polymerises base material and bonds the base and covering material of ceromers)
high performance, fully automated framework former
designed for metal-free crown and bridge frameworks
formed under pressure
polymerised with light using a single program
What is SR Ivocron?
its a PMMA-based veneering material used mainly for temporary restorations and denture veneering
suitable for veneering metal-free long term temporaries
How is SR Ivocron processed?
cold curing
heat curing
pressure heat curing technique
what are examples of indirect veneering materials that are products of ivoclar vivadent?
SR Ivocran
SR Adoro
what are indications for use for adhesive cementation?
framework for anterior + posterior crowns
framework for 3-unit anterior + posterior bridges in conjunction with Transil
framework for 3-unit inlay-retained bridges in conjunction with Transil
what are contraindications for use of adhesive cementation?
fabrication of bridge frameworks without using Transil
Vectris frameworks for bridges consisting of 4 or more units
Vectris frameworks for inlay-retained bridges consisting of 4 + units
cantilever extension bridges
rehabilitation of quadrants with Vectris frameworks without sufficient support by the remaining tooth structure
conventional cementation of fixed Vectris restorations
metal-free temporary restorations intended for a period of wear longer than 12 months
patients with occlusal dysfunctions or parafunctions, such as bruxism
patients who practice insufficient oral hygiene
What is a Transil?
Transil is a light bodied, transparent and therefore light transmitting silicone suitable for use in dental laboratories. Adjusted to the flasking technique, it enables the fabrication of a counter model and therefore the detailed reproduction of the wax-up in the final composite restoration.
