Ch 32 Human Diversity
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
02/07 lecture
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
animalis
to have breath
animal characteristics
1) multicellularity
2) heterotrophs
3) eukaryotes
4) have tissues that develop from embryonic germ layers
5) breathe (need oxygen)
what do animals have instead of a cell wall?
extracellular matrix
what is the most prevalent structural protein in the body? what does it do?
collagen, makes up 50%; holds the body together
what kinds of special tissues do animals have?
nervous and muscle tissue
zygote
single-celled embryo
true or false: animals ONLY reproduce sexually
false
ligament
connects bone to bone
tendon
connects muscle to bone
what are HOX genes?
regulate the development of body form, produce transcription factors, and are important for body segmentation
early embryonic development
formation of embryonic tissue layers
zygote → blastula → gastrula
cleavage
a form of mitosis in early animal development where there is rapid cell division without cell growth
embryo stays the same size, but the cells get smaller
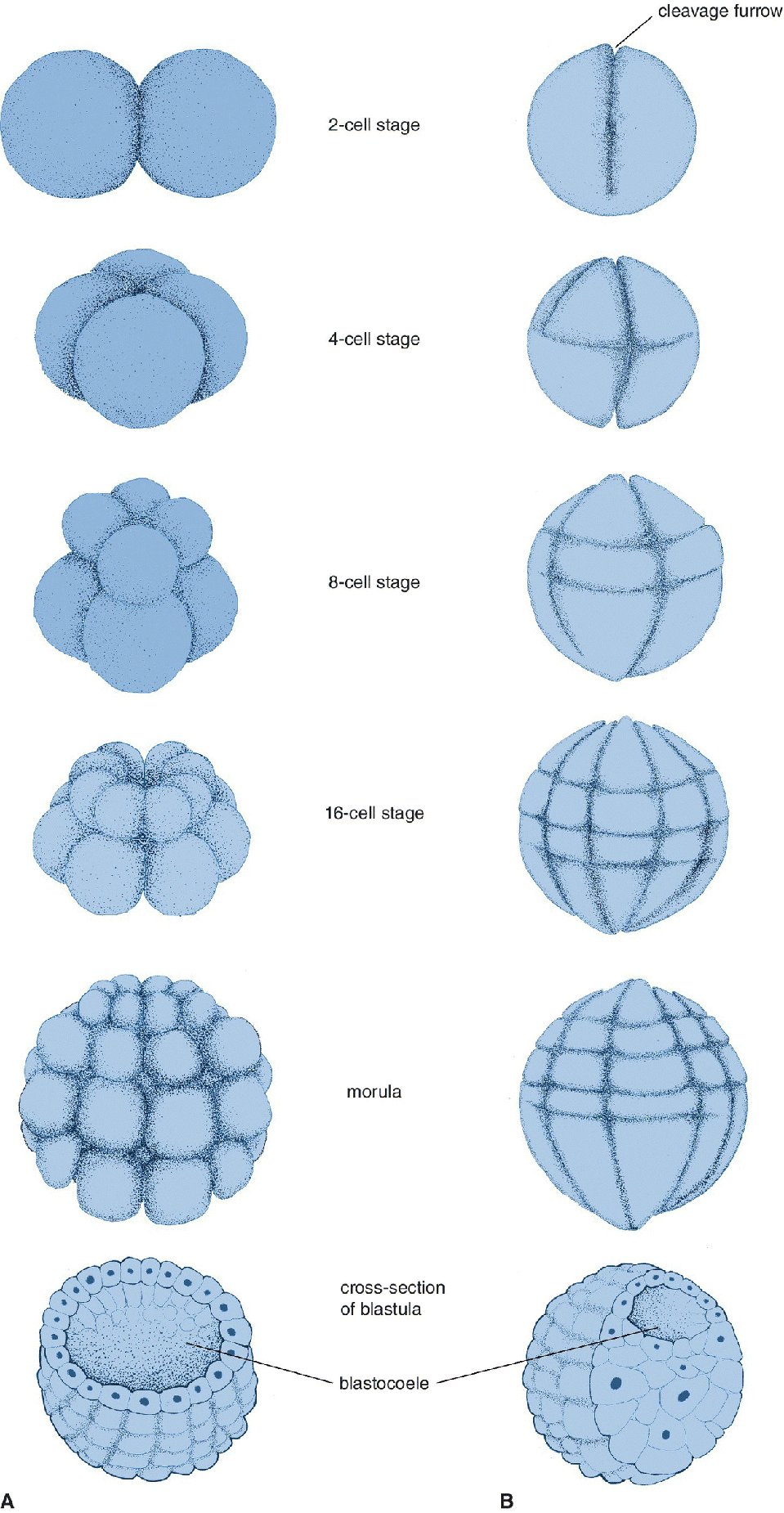
morula
a solid ball of cells resulting from cell division
blastula
embryonic stage with lots of cells and there is a cavity inside of the embryo
blastocoel
fluid filled cavity in the center of the blastula
“coel”
cavity
gastrula
An embryonic stage in animal development encompassing the formation of three layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
blastospore
pore in the blastula that cells can use to move into the cavity
it becomes either the anus or the mouth
Cells start to differentiate
archenteron
old gut
The endoderm lined cavity, formed during gastrulation, that develops into the digestive tract of an animal
Totipotent cells
“total potential” cells that can become any cell type and can become a separate organism when taken out of the embryo (how twins are formed)
have 1-8 of them
pluripotent cells
potential to be any cell types but not a separate organism
have 1-64
multipotent cells
potential to be multiple cell types, but not every cell type
have 1-a lot of them
Ex: hemopoietic stem cells, endo/ecto/mesoderm cells
how many animals that once lived have gone extinct?
99%
protist most closely related to animals?
choanoflagellates
what is a grade?
a group of organisms that are categorized together basd on body complexity; not monophyletic
ex: bugs, evergreens, etc
body plan
how animals are grouped toghether; based on morphological and developmental traits
animal categorization
symmetry
tissues
body cavities
embryonic development
radial symmetry
symmetry radiates from the middle out
ex: sea anemone
bilateral symmetry
separates us into lateral halves
ex: humans
tissues?
collections of similar, specialized cells isolated form other tissues by membranous layers
carry out specific functions
derived from embryonic ectoderm, endroderm, and mesoderm layers
what are diploblastic organisms?
animals w/ two germ layers (lack mesoderm)
triploblastic organisms
animals that have three germ layers
most form coelums (body cavity) layers
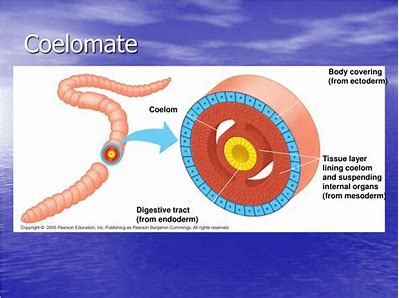
coeleum
a body cavity; space between body wall and digestive tract
can be air or fluid filled
coelomates
animals with a body cavity completely lined by tissue derived from mesoderm
hemocoels
animals with body cavities that are only partially lined with mesoderm derived tissue
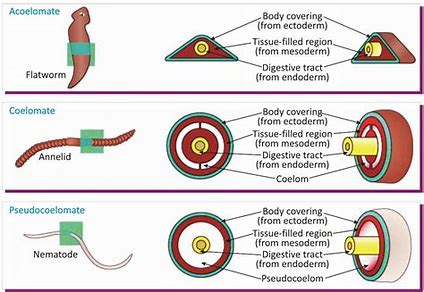
acoelomate
animals without body cavties
protostome
animals who's first opening becomes the mouth
have determinate cleavage
schizocoelous
deuterostome
animal whose 2nd opening becomes the mouth
first opening become the anus
indeterminate cleavage
enterocoelous
gastrulation
blastula embryo folds inward, producing a three-layered embryo, the gastrula