El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards about ENSO
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
ENSO
Largest pattern of climate variability on the planet;
prime example of ocean and atmosphere interaction
leading to near global alterations to rainfall, winds, pressure, and temperature in tropics and beyond.
Vallis, 2011
Climate variability
A feature of complex systems that can be unforced, arising through interactions within the system without external forcing.
does not require external forcing
Vallis, 2011
Tropical Pacific Mean State
Characterised by higher SSTs in the western Pacific near Australia and lower SSTs in the eastern Pacific near the Americas, with a gradient between them.
Vallis, 2011
West Pacific Warm Pool
The region of warm temperatures in the western Pacific.
Vallis, 2011
Subtropical Anticyclones
Air spinning clockwise in the northern hemisphere and anti-clockwise in the southern hemisphere near surface trade winds that converge in the Intertropical Convergence Zone.
Baede et al., 2018
Walker Circulation
Linked to the gradient in SST across the Pacific, contributing to high rainfall, especially near the Maritime continent.
rising air in the west, sinking in the east
Baede et al., 2018
Thermocline
The transition zone below the surface separating mixed warm ocean water with cold deep ocean
deeper in the west and shallower in the east
associated with upwelling of cold ocean water.
Baede et al., 2018
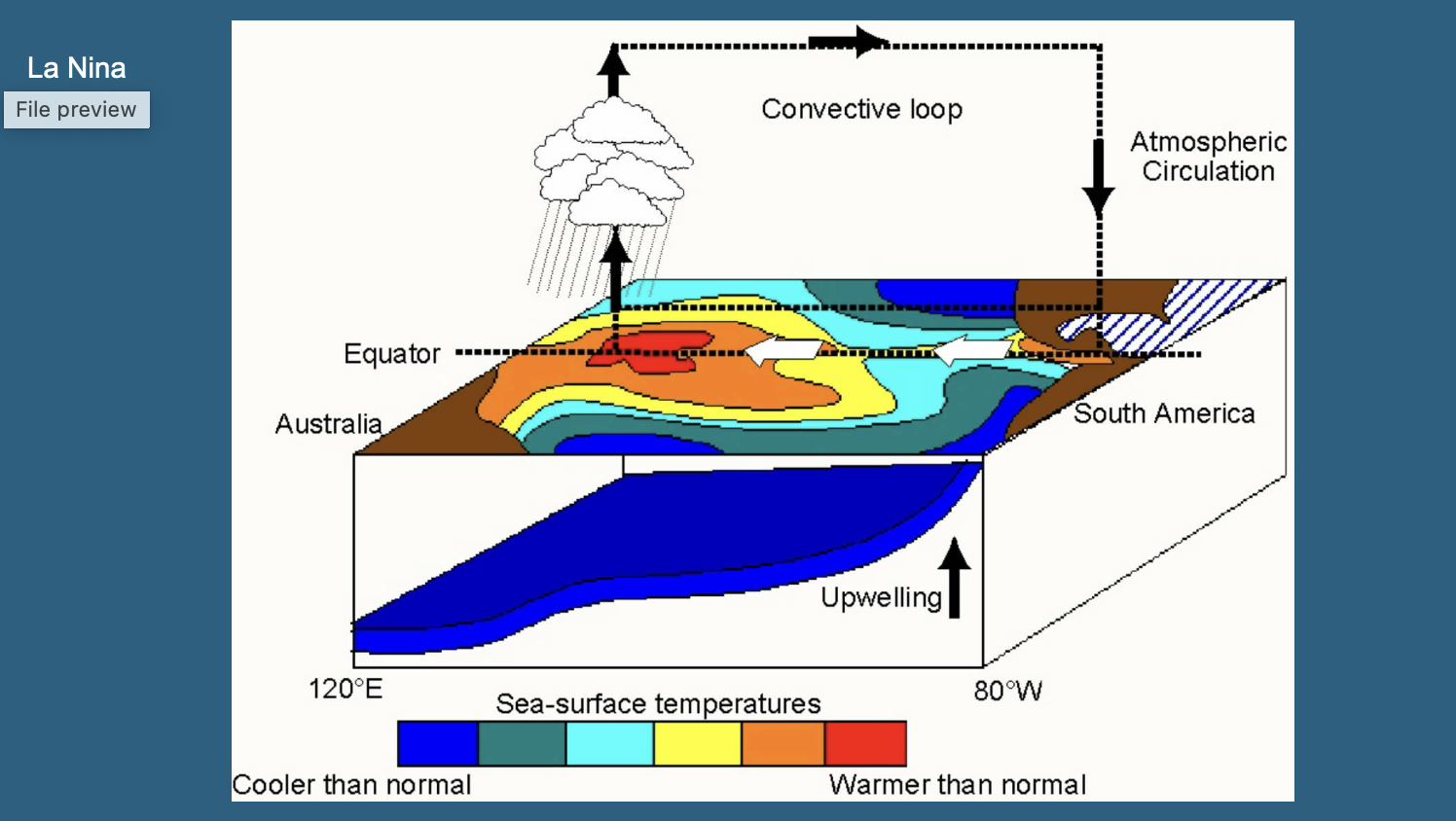
La Nina
An exacerbation of normal conditions over the Pacific, with the western Pacific getting warmer and the eastern Pacific getting colder, linked to a stronger Walker circulation.
leads to stronger upwelling in the eastern Pacific and deeper thermocline in the western pacific
Vallis, 2011
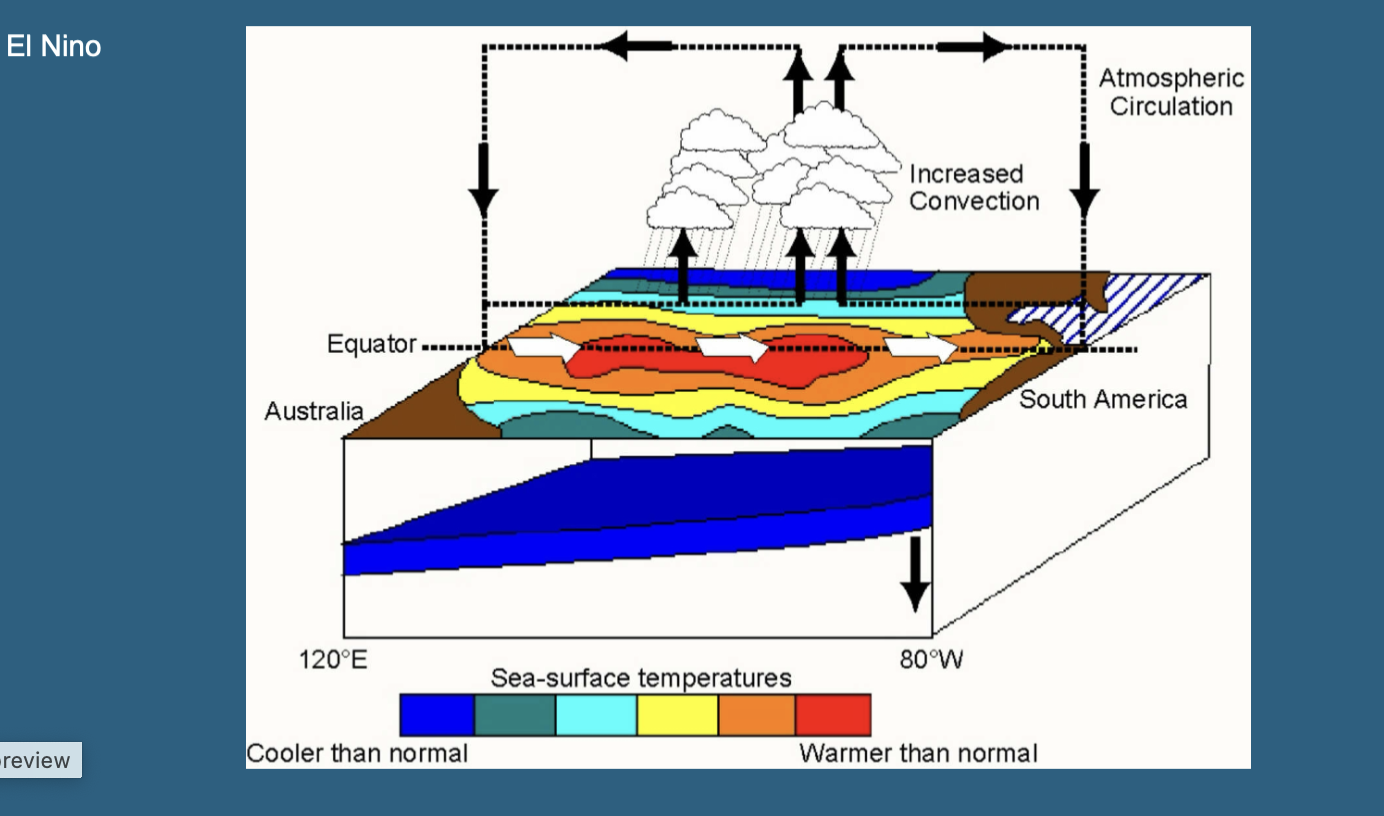
El Nino
A phase where warm water spreads out over the central Pacific, leading to cooler temperatures in the west and a more equalized thermocline across the Pacific.
warmth not concentrated in the west +thermocline no longer steep
Vallis, 2011
Sea Surface Temperature Anomalies
linked to big reduction in the upwelling in the Pacific
Vallis, 2011
Thermocline Depth Anomalies
Variations in the depth of the thermocline across the Pacific, with a shallower gradient during El Nino and a stronger gradient during La Nina.
Vallis, 2011
Pressure Anomalies
Weakened low-pressure region over the west Pacific (positive anomaly) during El Nino and negative anomalies in the eastern Pacific.
pressure gradient is what’s driving these winds
Vallis, 2011
Southern Oscillation Index (SOI)
A measure of the difference in surface pressure between Darwin and Tahiti used to track ENSO events
Positive SOI values tend towards La Nina, while negative values tend towards El Nino.
Wang et al., 2012
TAO/TRITON Array
A set of 70 moorings in the tropical Pacific that measure wind speed and direction, relative humidity, air temperature, and ocean temperatures at various depths to track the evolution of the tropical Pacific Ocean state.
Wang et al., 2012
Multivariate ENSO Index (MEI)
A more comprehensive measure of the atmospheric-oceanic alterations in the ENSO cycle
Determined based on six variables: SLP (sea level pressure, surface zonal winds, surface meridional winds, SSTs, surface air temperature, and cloudiness
Wang et al., 2012
Teleconnections
Remote impacts of ENSO, connecting climate anomalies in one place to another.
Vallis, 2011
Global impacts of ENSO
Tend to be higher in El Nino years/months and lower in La Nina years/months.
El Niño years temperatures tend to grow throughout the event and La Niña
less rain over Australia, More rainfall over South America
Vallis, 2011
Case study: ENSO
2003-4 severe monsoon for India predicted
but instead there was a drought
Kumar et al., 2006
ENSO and Walker Circulation
ENSO alters the east-west Walker circulation across the globe, controlling the strength and location of subsiding and rising air near the equator.
Vallis, 2011
ENSO and Hadley Circulation
Excess latent heating near the equator during El Nino can intensify uplift, resulting in a more vigorous Hadley circulation.
Vallis, 2011