Anatomy of the Skin: Epidermis, Dermis, and Hypodermis | Quizlet
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
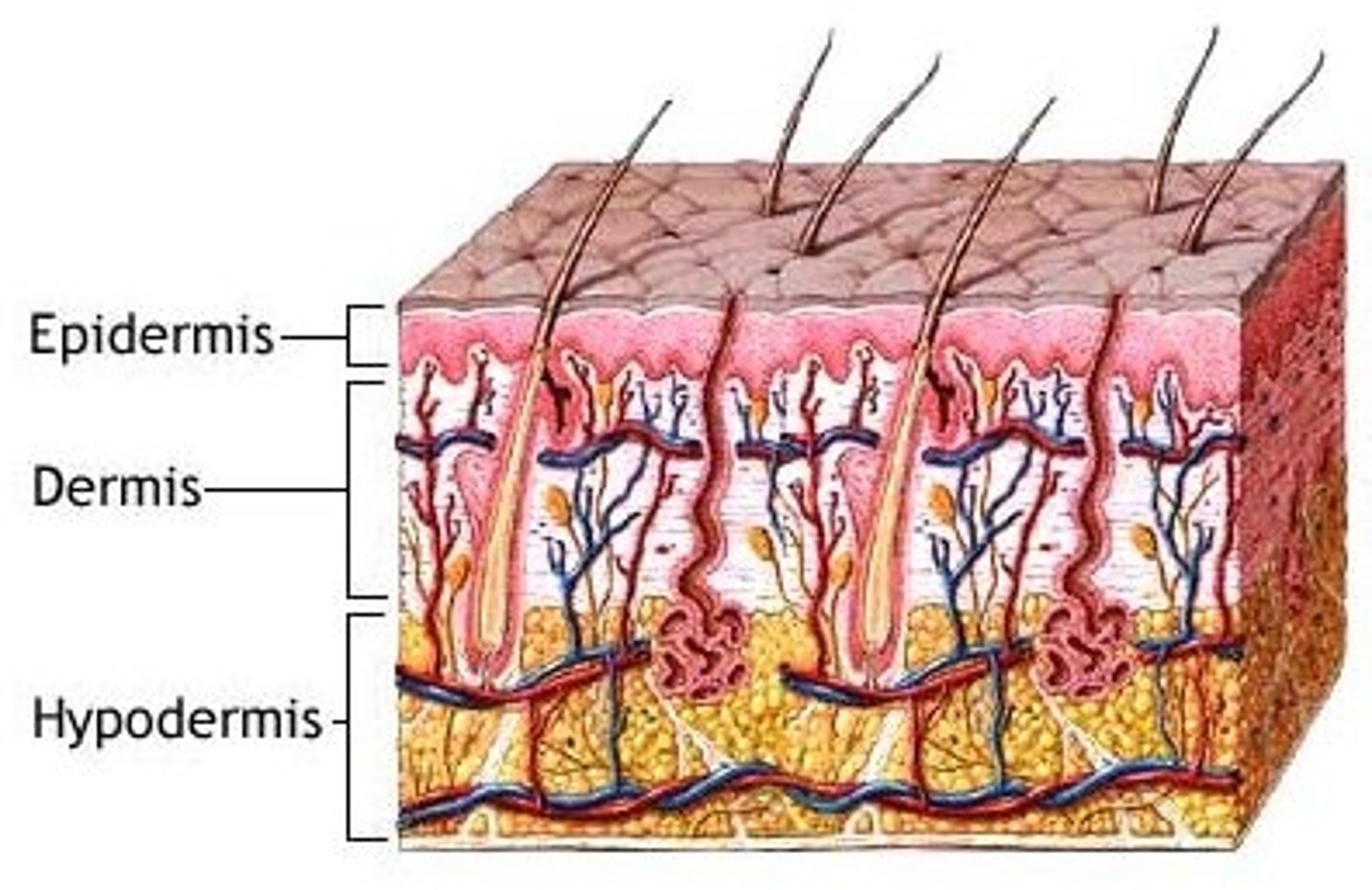
Epidermis
The outermost layer of the skin, made of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. It is avascular, meaning it lacks blood vessels and relies on the dermis for nutrients.
Functions of the Epidermis
Protects against pathogens, water loss, UV radiation, and provides sensation.
Keratin
A tough, fibrous protein that strengthens and waterproofs the skin.
Avascular
The epidermis has no blood vessels, so it depends on diffusion from the dermis for nutrients.
Mitosis in the Epidermis
Occurs in the stratum basale and lower stratum spinosum. Mitosis slows with age.
Keratinocytes
The most abundant cells in the epidermis. They produce keratin, which provides strength and protection.
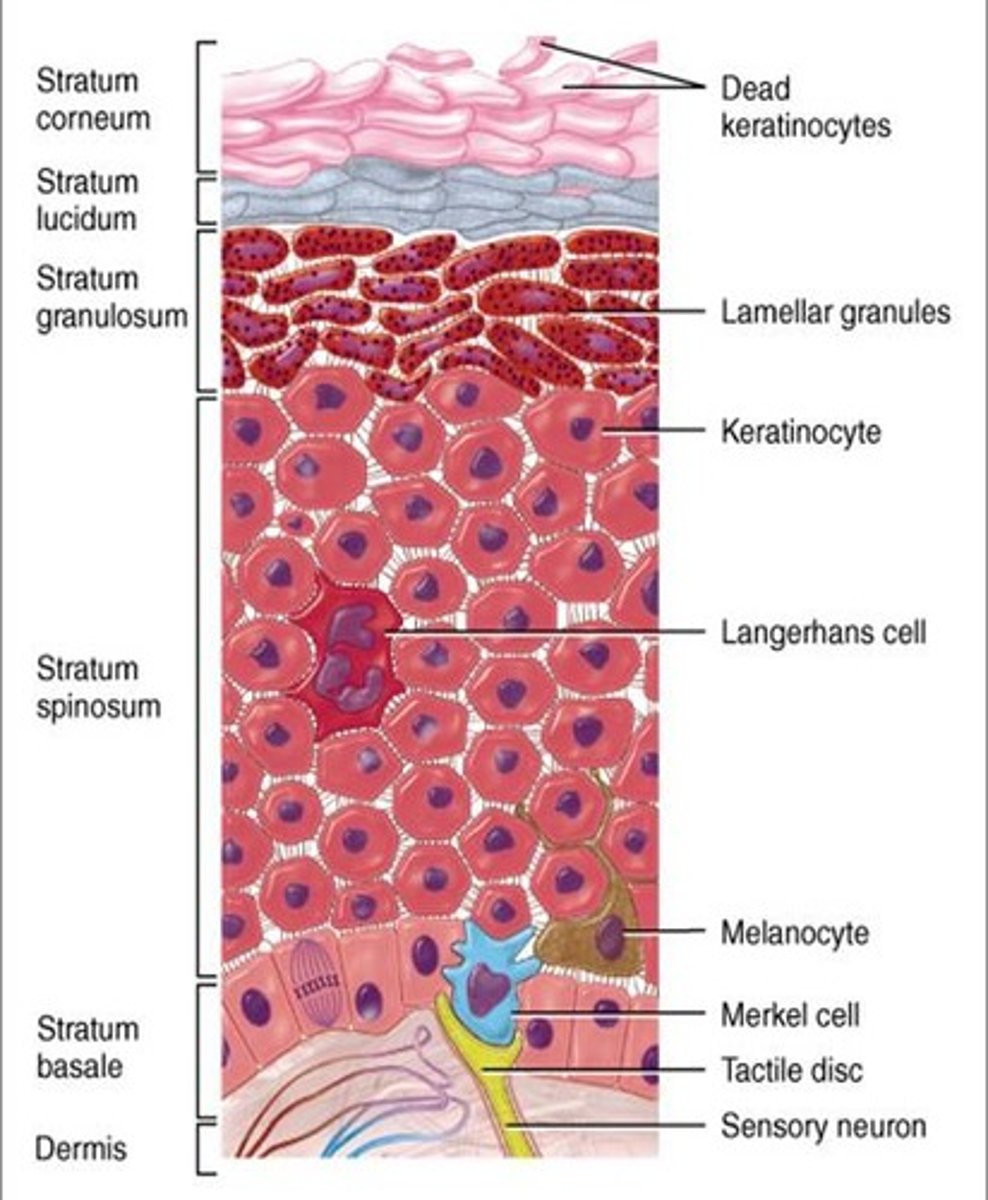
Stem Cells
Undifferentiated cells found in the stratum basale that divide to form new keratinocytes.
Melanocytes
Found in the stratum basale; they produce melanin, which protects the skin from UV radiation.
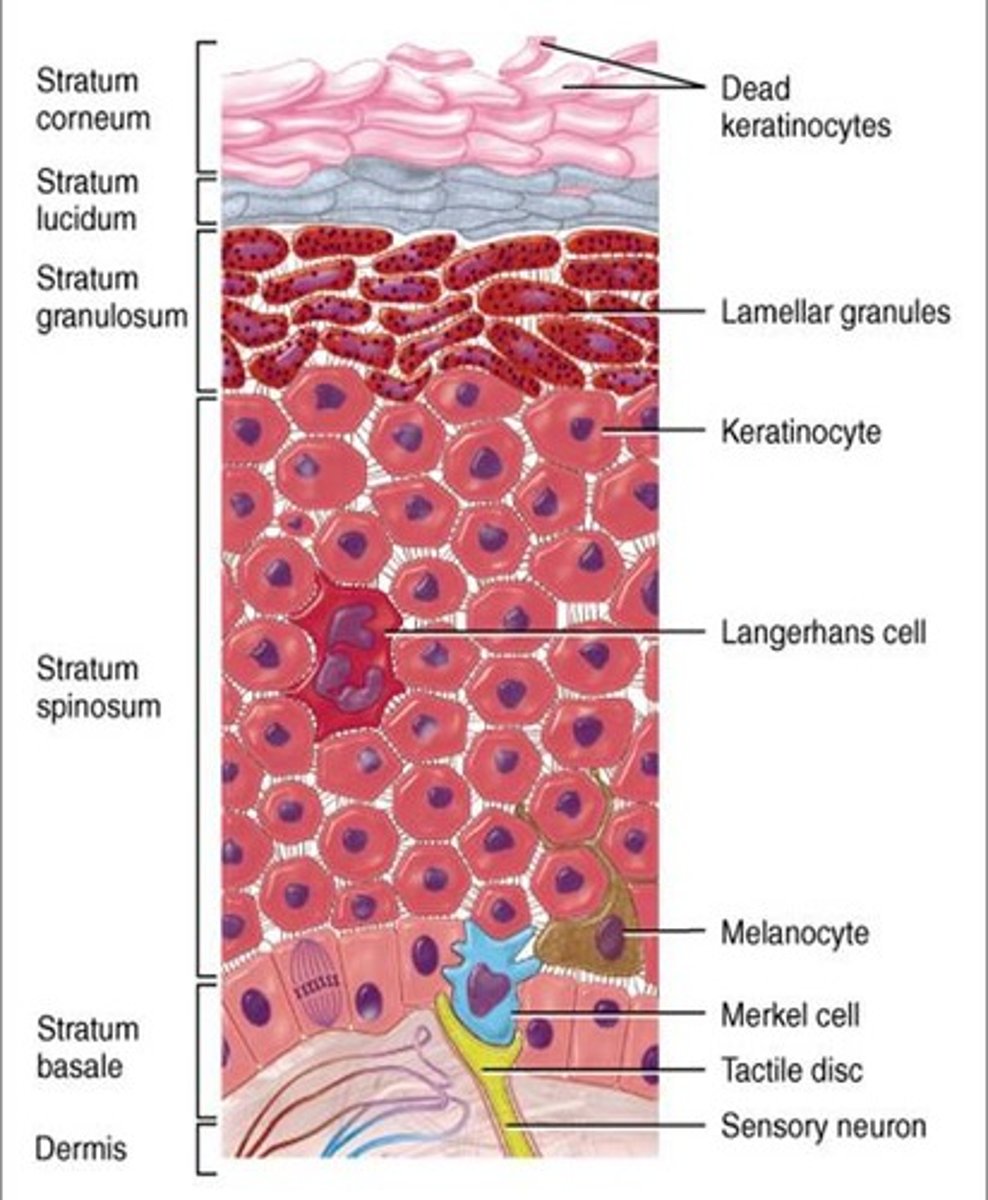
Tactile (Merkel) Cells
Sensory receptors for touch found in the stratum basale. They are connected to nerve endings.
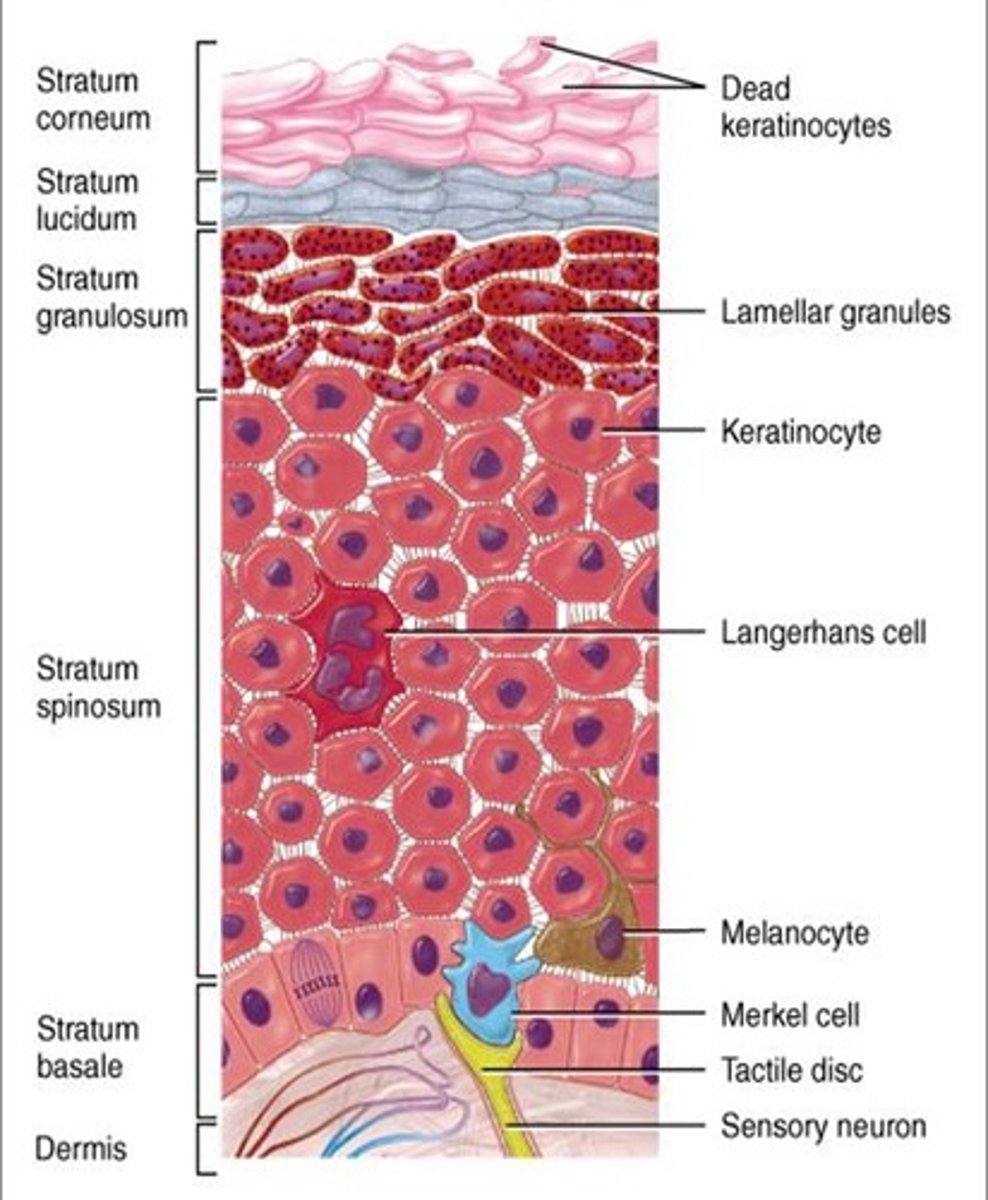
Dendritic (Langerhans) Cells
Immune cells found in the stratum spinosum and granulosum. They protect the skin by detecting pathogens and foreign invaders.
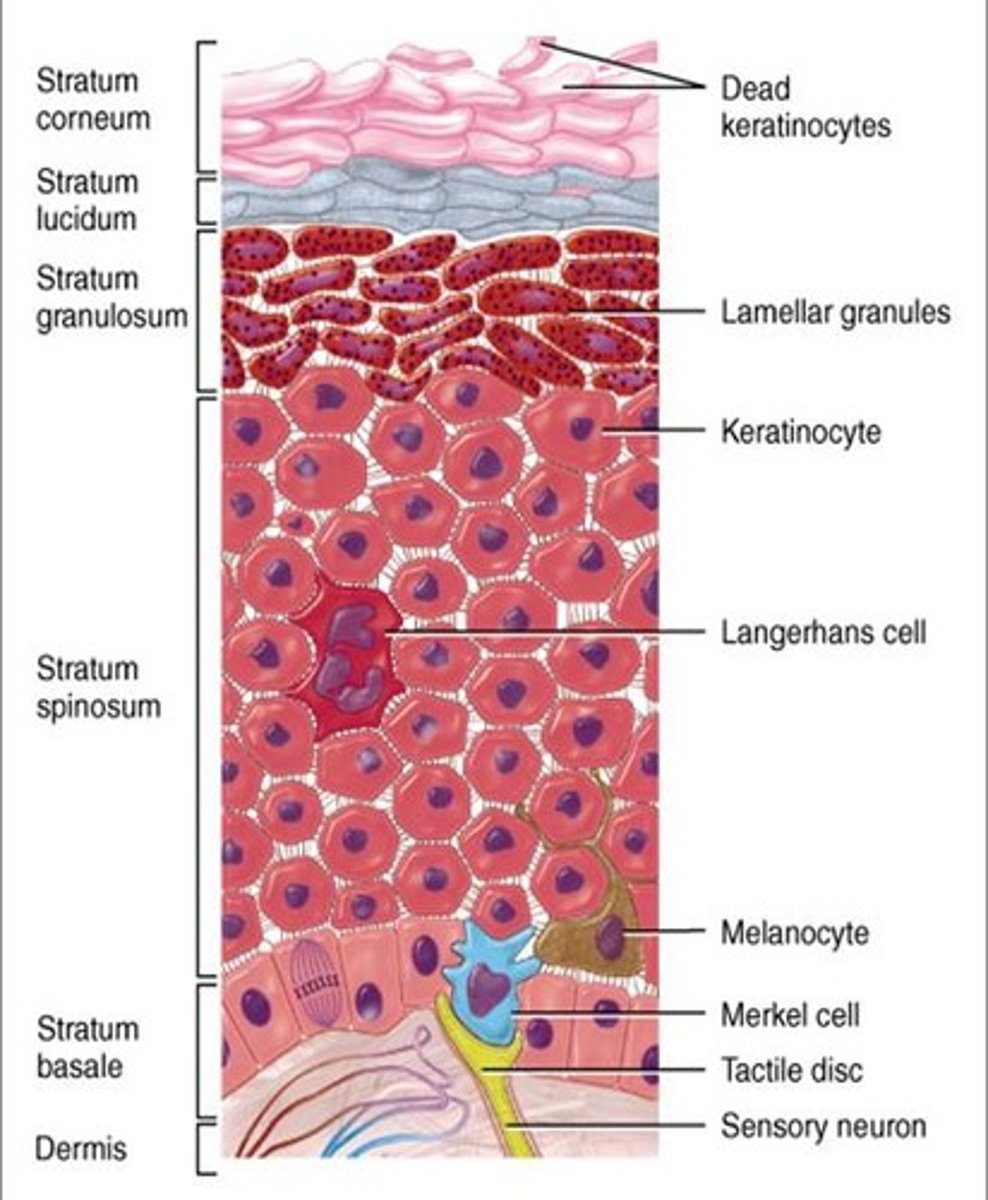
Stratum corneum
The outermost layer, made of dead, keratinized cells that continuously shed to protect the skin.
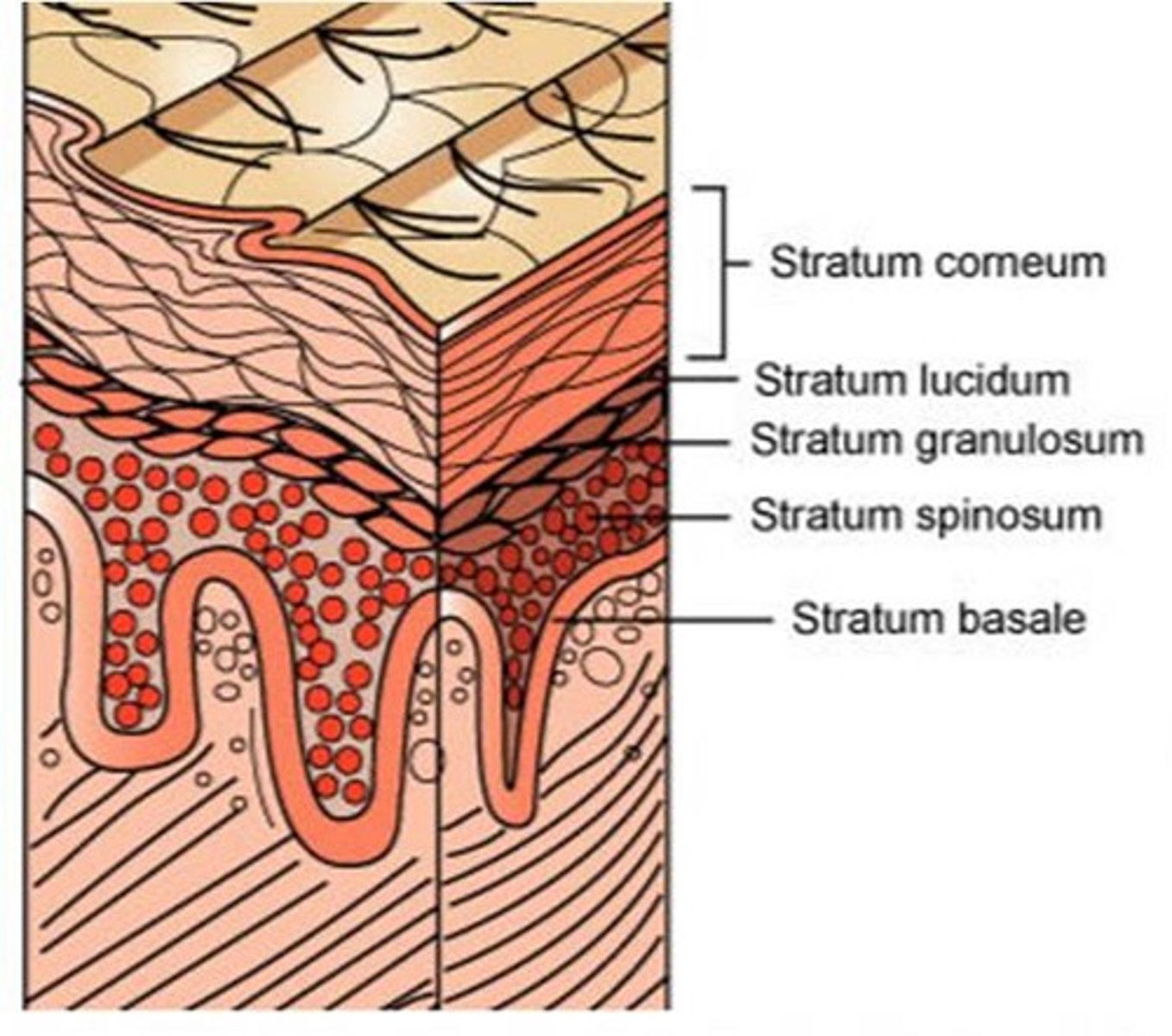
Stratum lucidum
Found only in thick skin (palms, soles). It is a clear, featureless layer of densely packed keratinocytes.
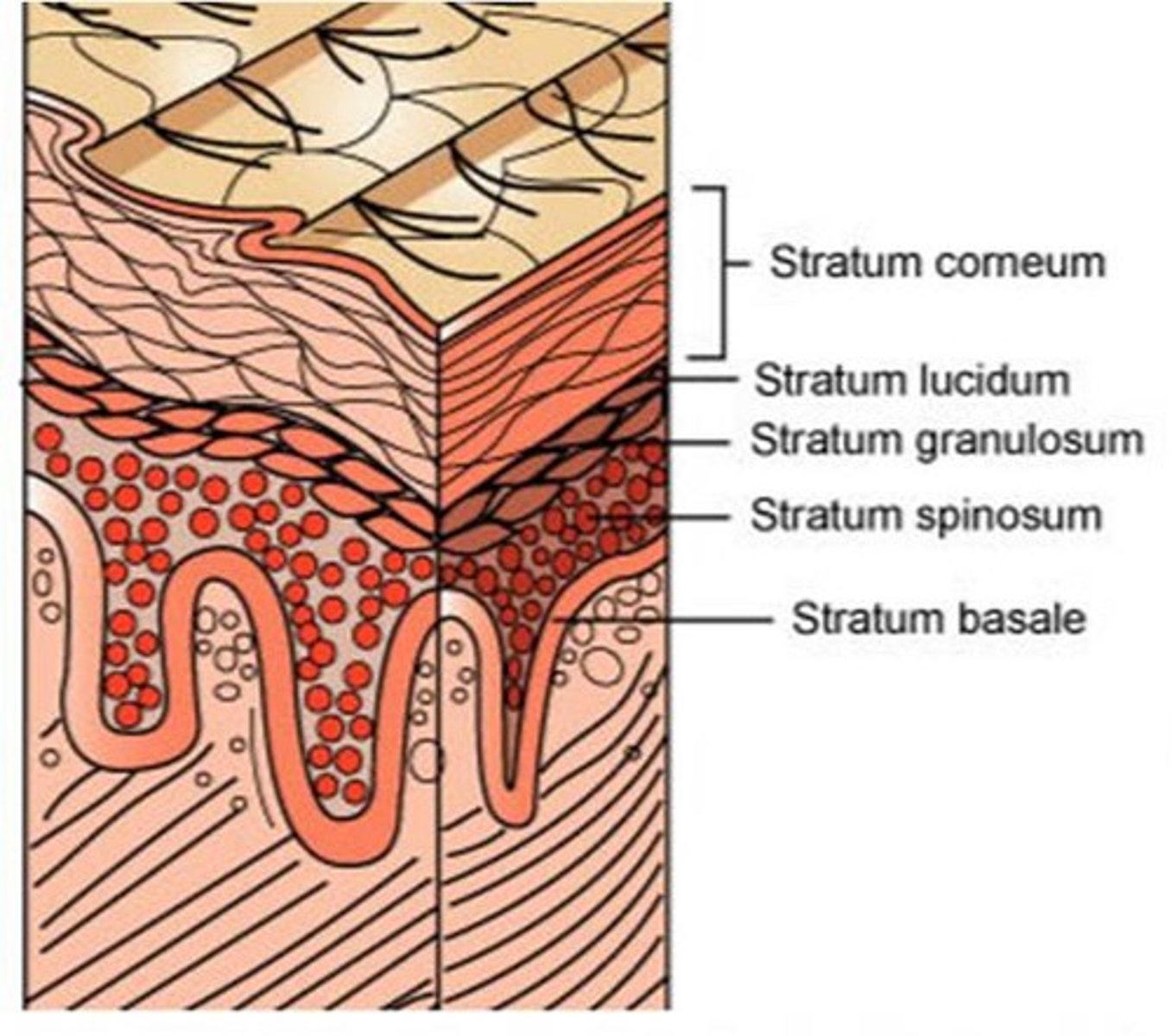
Stratum granulosum
Contains 2 to 5 layers of keratinocytes with keratohyalin granules that help with waterproofing.
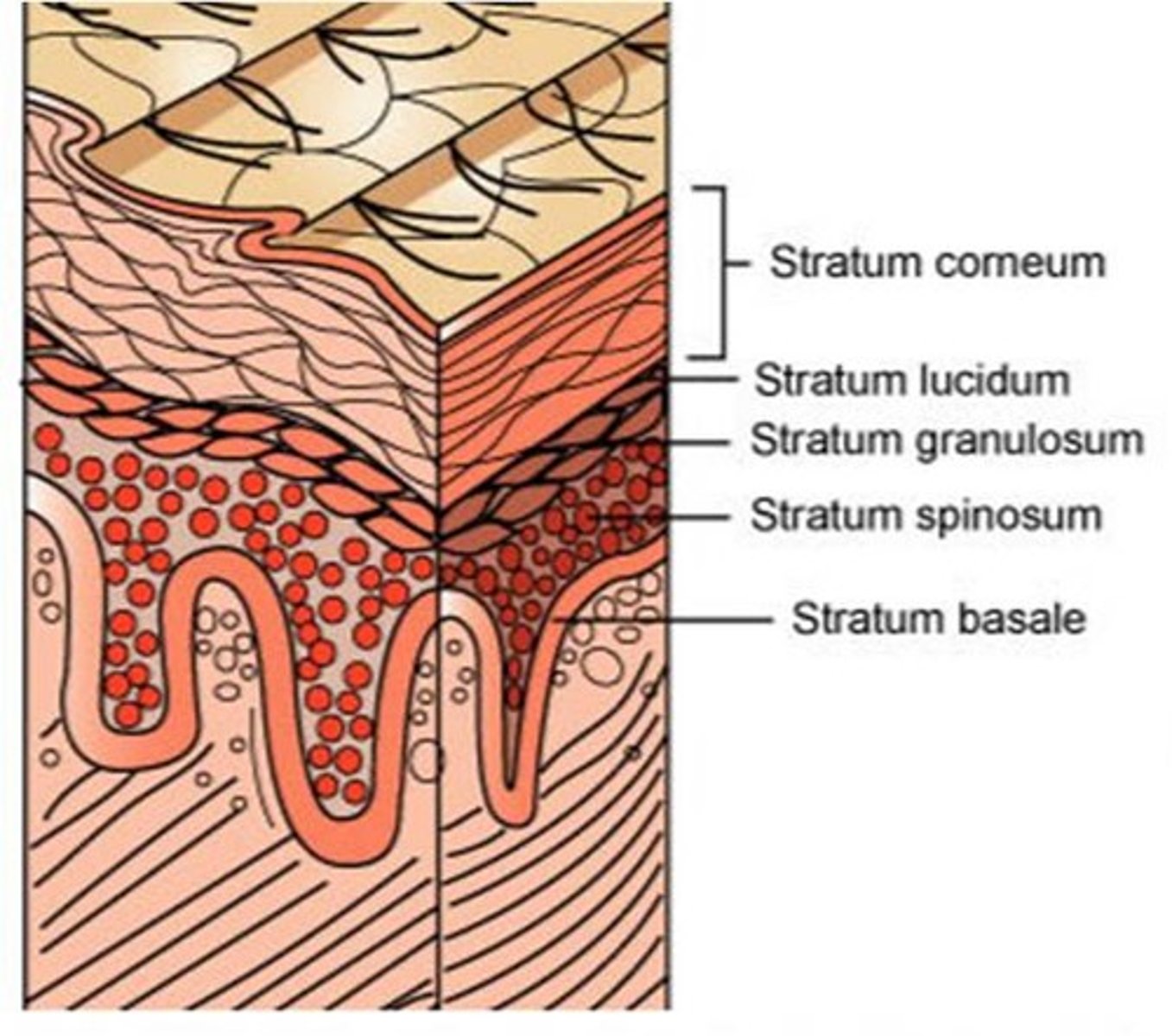
Stratum spinosum
Several layers of keratinocytes connected by desmosomes, giving them a spiny appearance. Contains dendritic cells for immune protection.
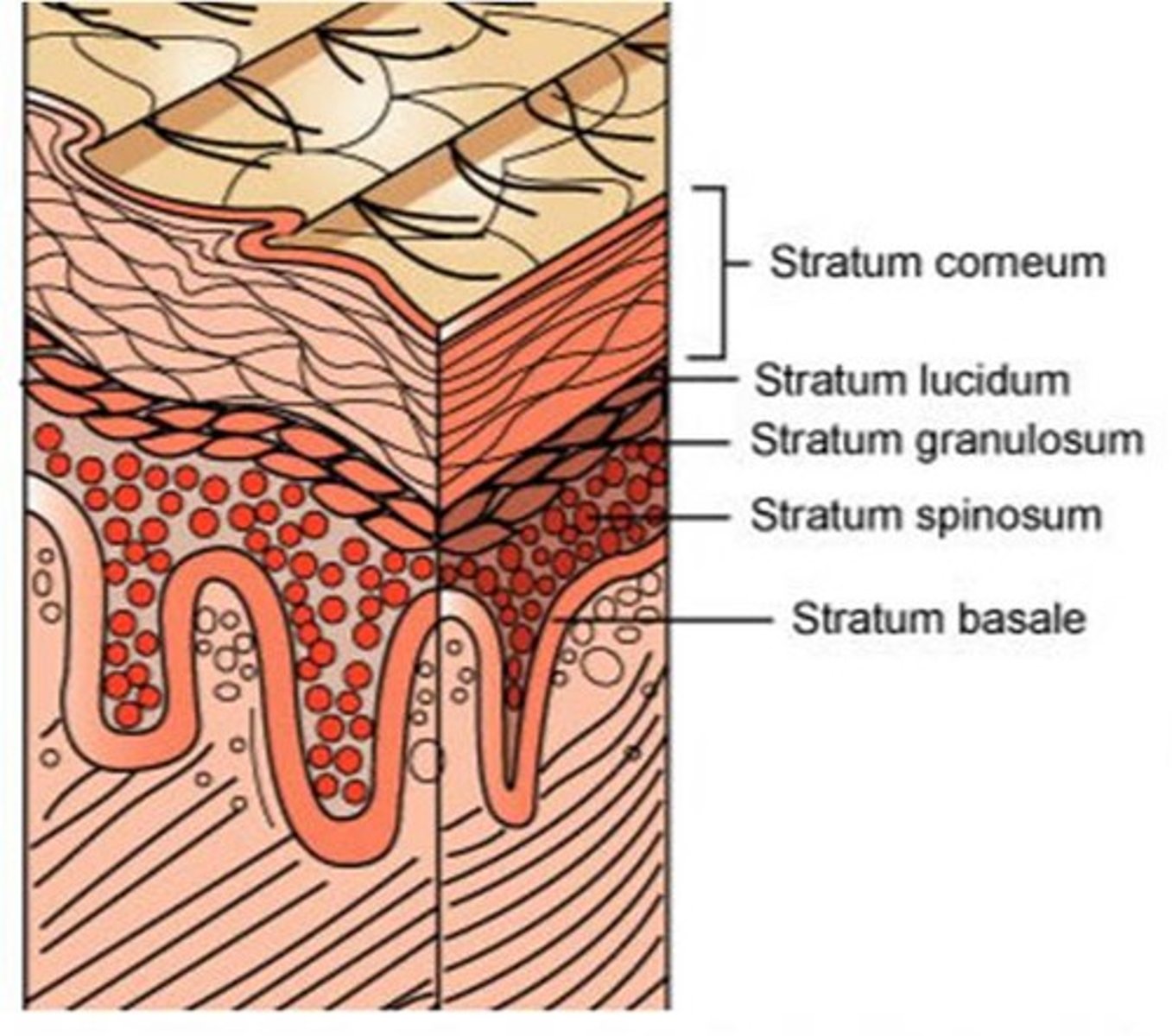
Stratum basale
The deepest layer of the epidermis. It contains stem cells, melanocytes, and tactile cells and is the site of mitosis (cell division).
Dermis
The connective tissue layer beneath the epidermis. It contains blood vessels, nerve endings, glands, hair follicles, and collagen fibers.
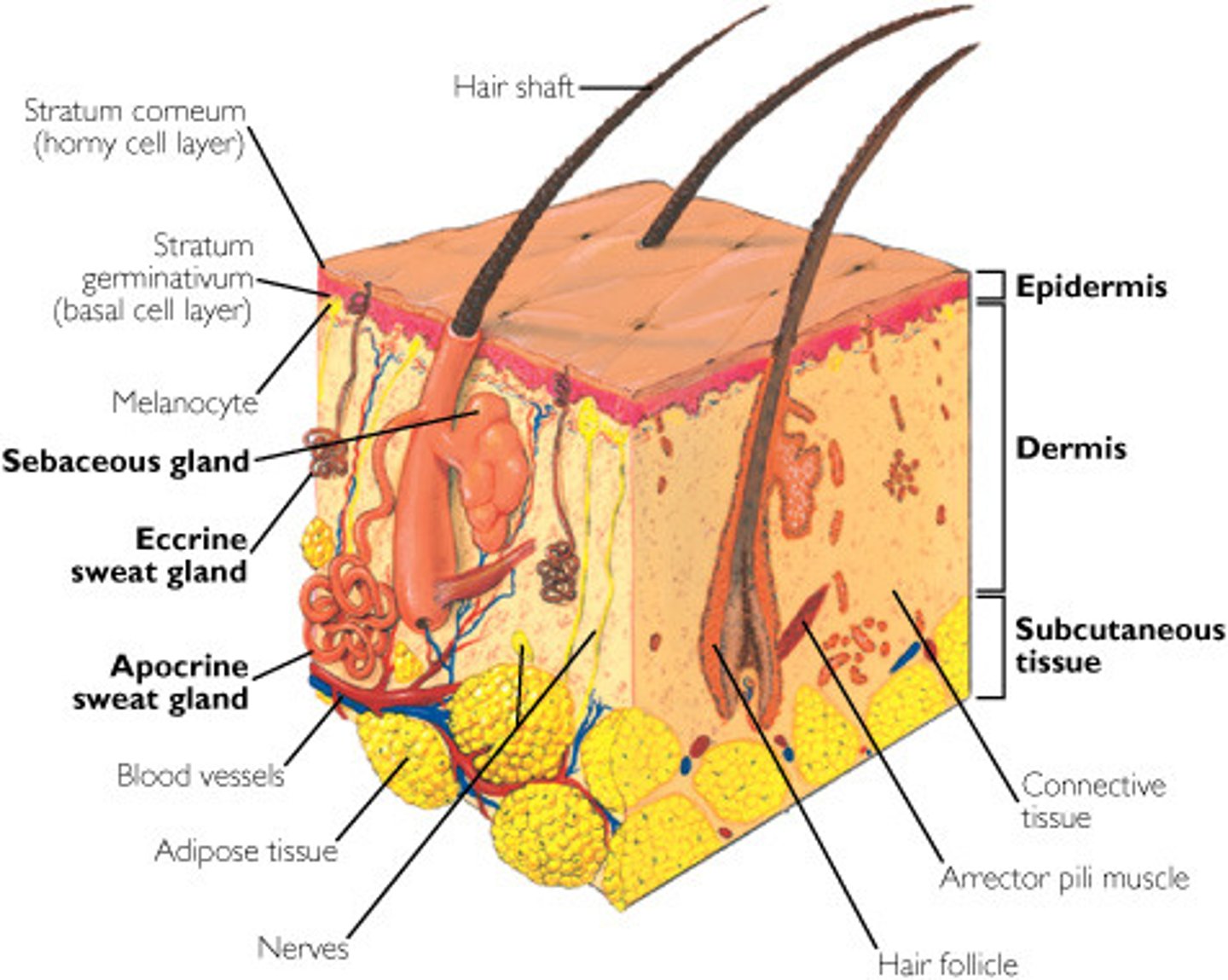
Composition of the Dermis
Made up of collagen, elastic fibers, reticular fibers, and fibroblasts.
Function of the Dermis
Provides strength, flexibility, blood supply, and sensory reception to the skin.
Hair Follicles & Nail Roots
Both are embedded in the dermis.
Facial Expressions
The skeletal muscles attach to dermal collagen fibers, allowing movement such as smiling, frowning, and raising eyebrows.
Dermal Papillae
The upward projections of the dermis into the epidermis. These interlock with the epidermis to prevent slipping and form fingerprints.
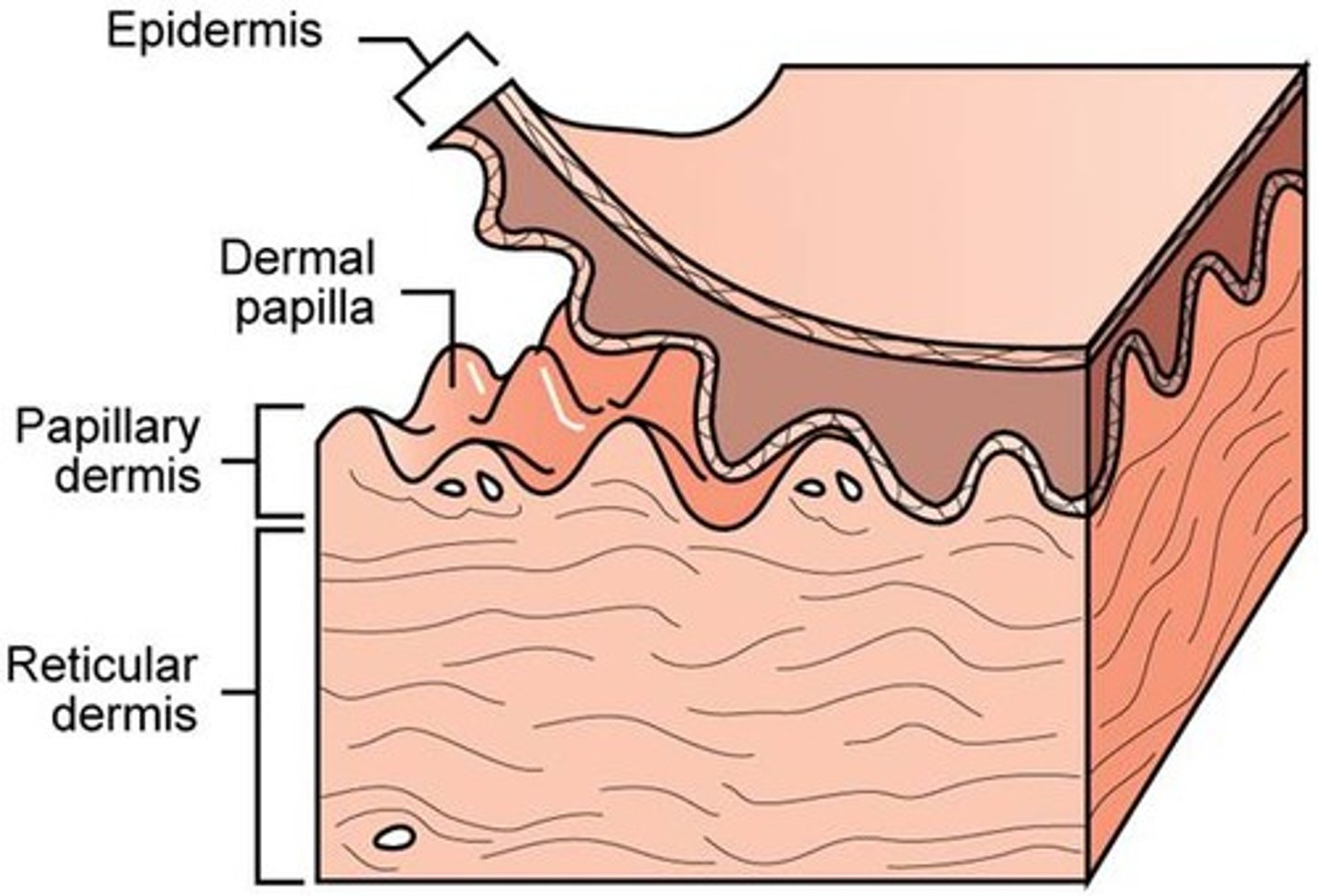
Papillary Layer
The superficial (top) layer of the dermis. It consists of loose areolar connective tissue and contains capillaries and immune cells. It extends upward into the epidermis as dermal papillae.
Reticular Layer
The deeper, thicker layer of the dermis. It consists of dense irregular connective tissue with thick collagen fibers that provide strength and elasticity.
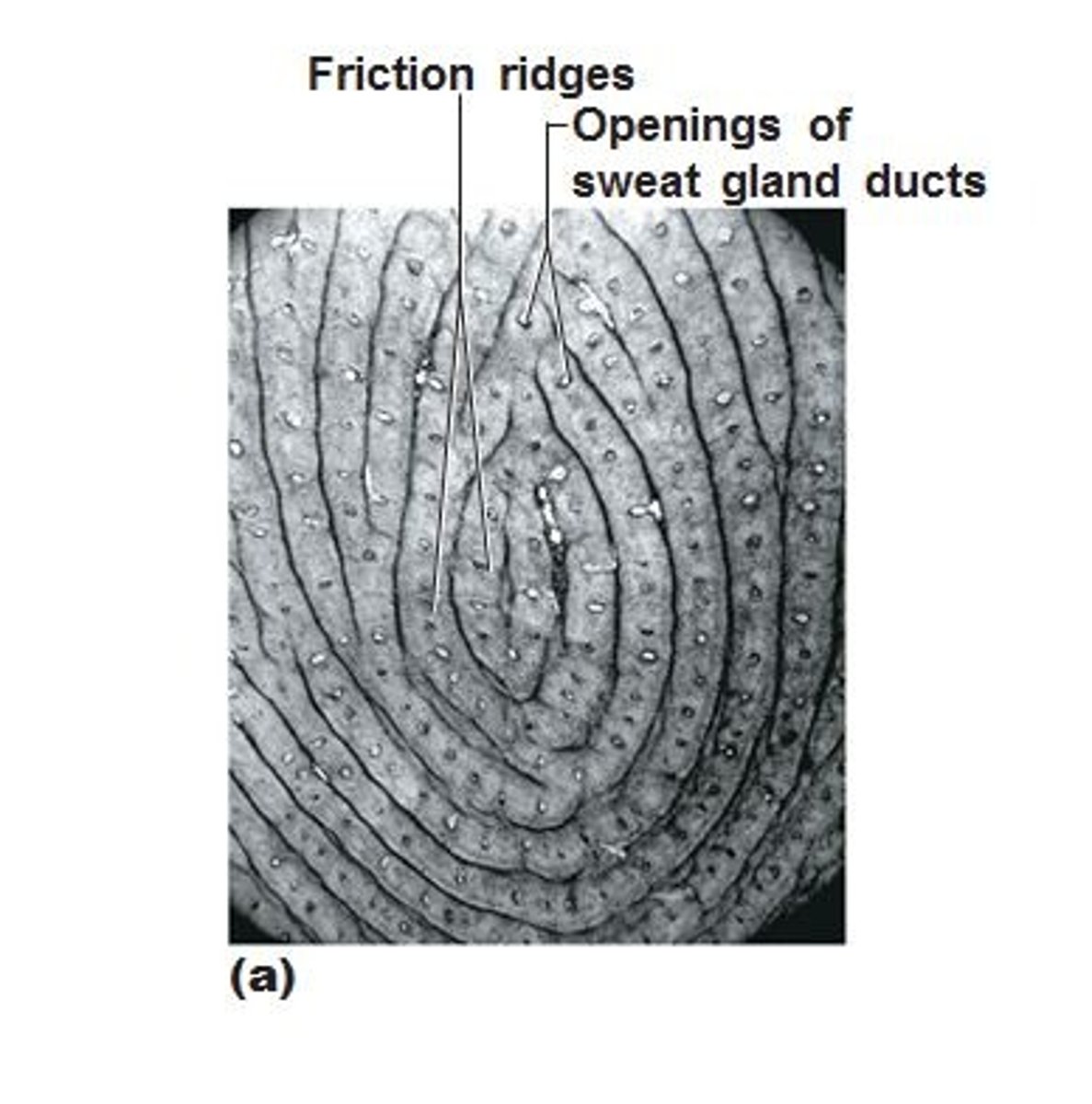
Friction Ridges
Form fingerprint patterns, caused by dermal papillae.
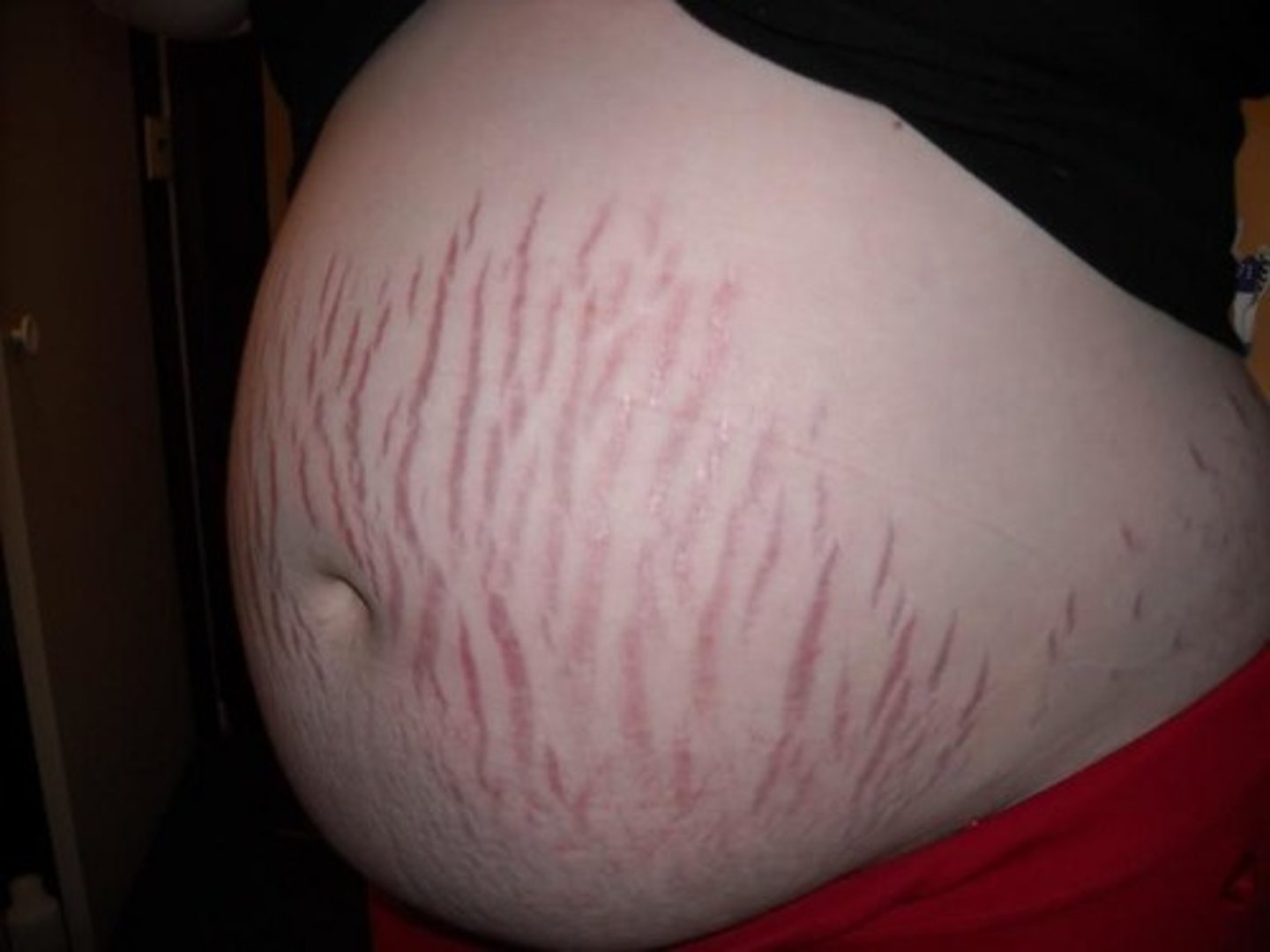
Stretch Marks (Striae)
Form when collagen fibers tear due to rapid skin stretching (e.g., pregnancy, obesity).
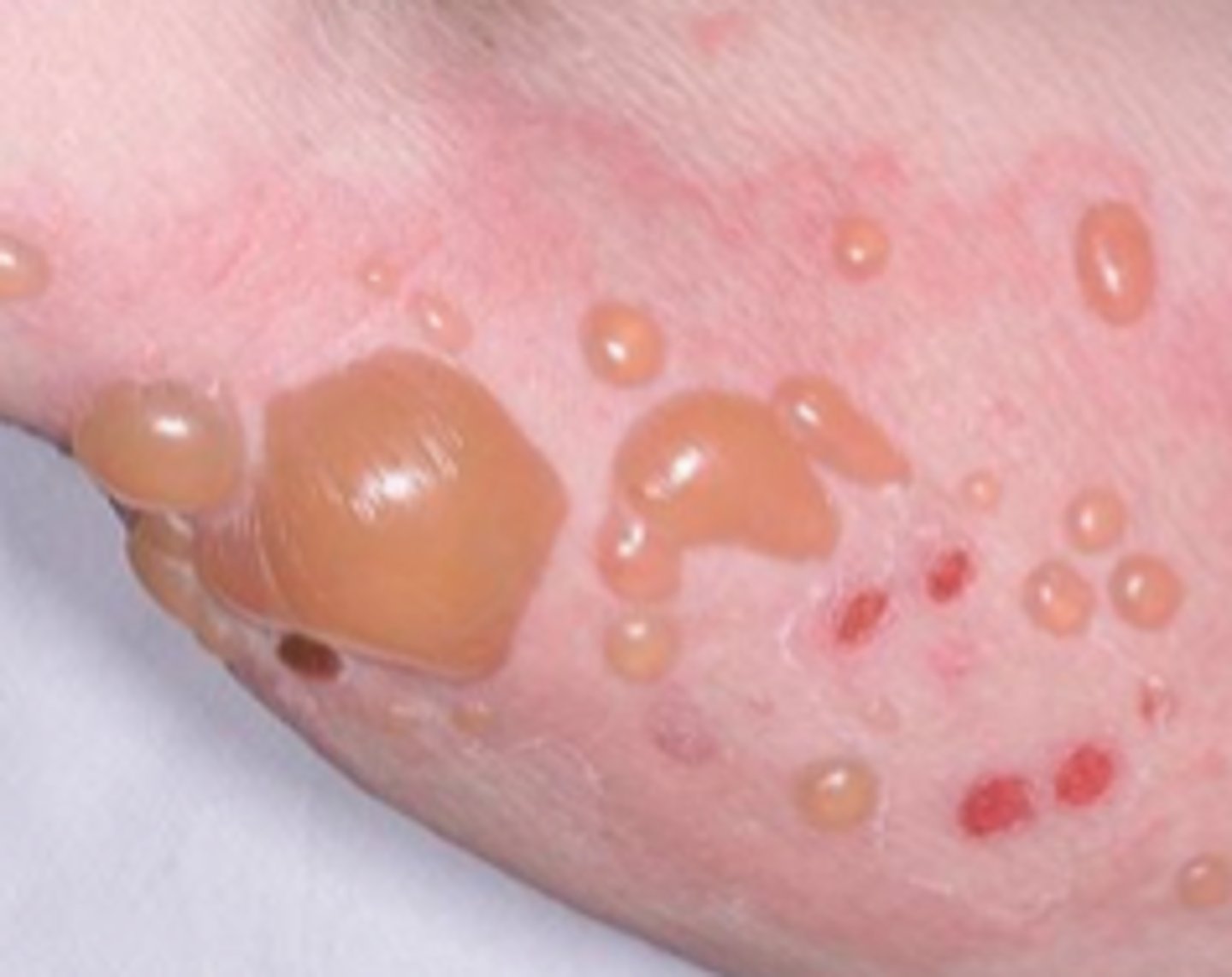
Blisters
Occur when fluid accumulates between the epidermis and dermis due to friction, burns, or pressure.
Hypodermis
The deepest layer of the skin, also called subcutaneous tissue. It consists of areolar and adipose tissue and connects the skin to muscles and bones.
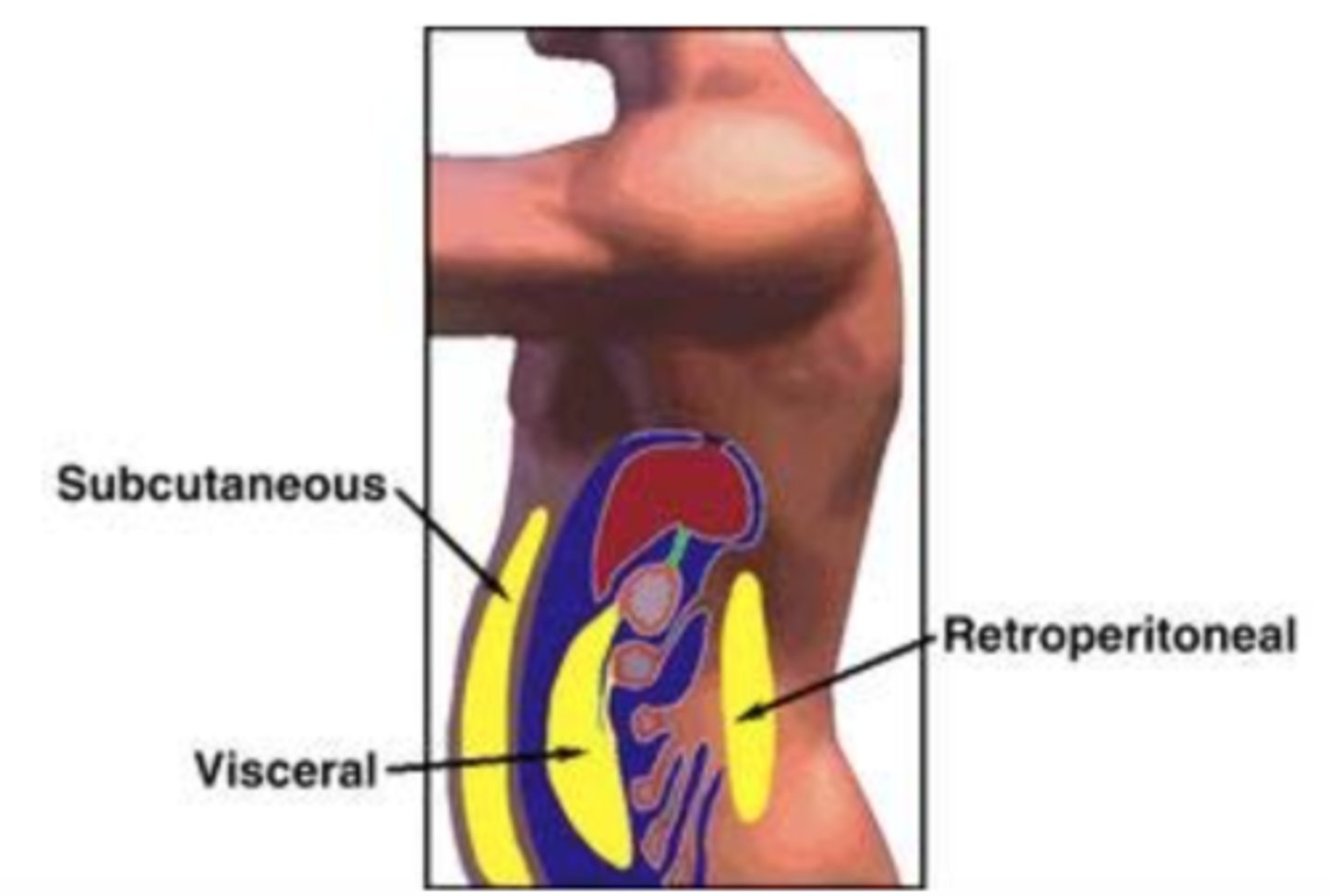
Functions of the Hypodermis
Acts as a shock absorber, energy storage site, and insulator to help regulate body temperature.
Subcutaneous Fat
A fat layer that provides padding and insulation. It is thicker in the abdomen, hips, thighs, and breasts.
Gender Differences in Subcutaneous Fat
Women have about 8% more subcutaneous fat than men.
Age-Related Changes
Infants and elderly people have less subcutaneous fat, making them more sensitive to cold.
Drug Absorption
The hypodermis is highly vascular, making it an ideal site for injections (e.g., insulin, vaccines).