Unit 2: Lecture 10: Neurophysiology Pt.1
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
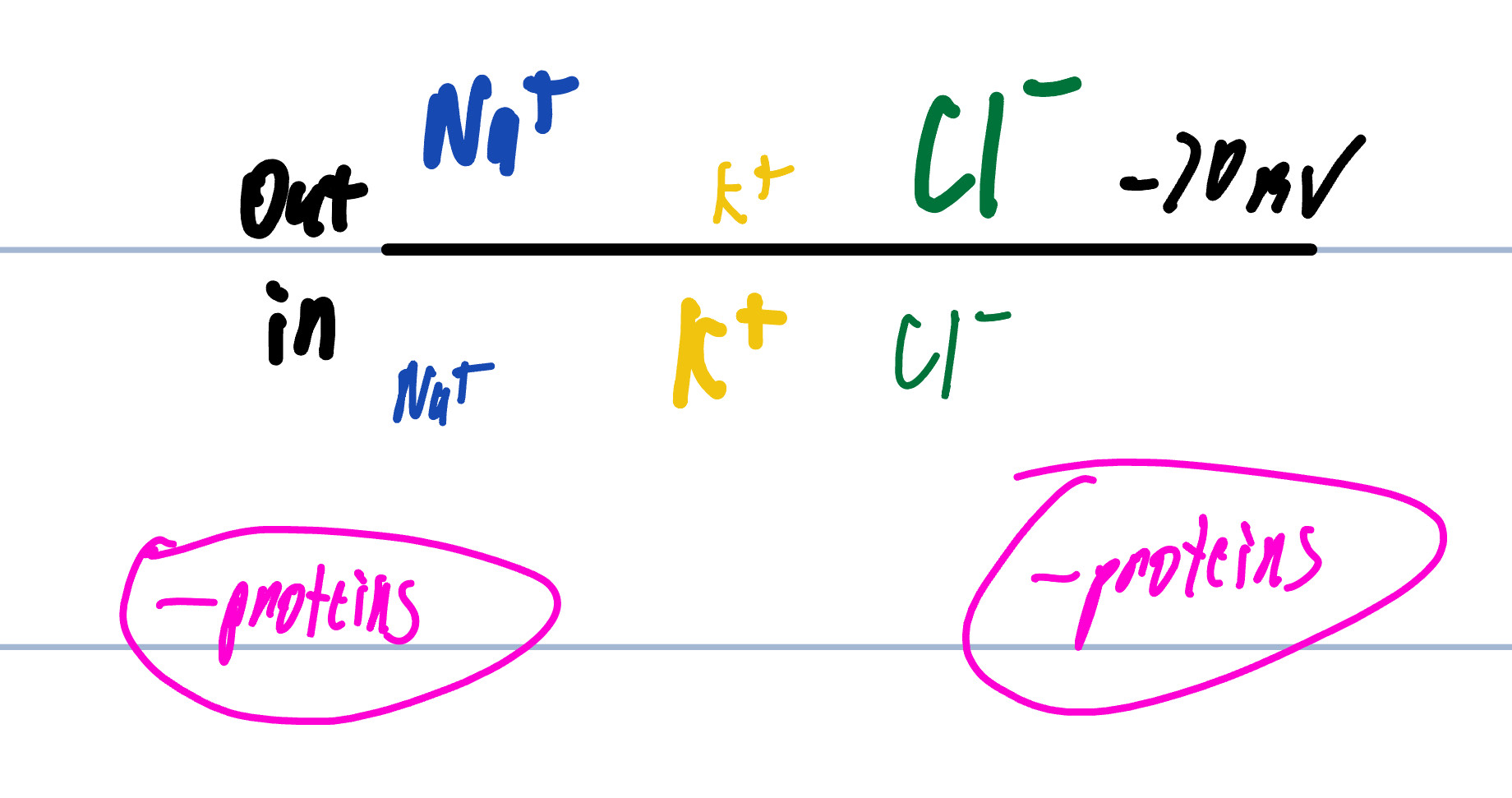
RMP(Resting Membrane Potential)
intracellular
approximately -70mv
Transmembrane potential of a neuron
inside cell= more (-)
Na+ is greater outside cell
K+ is greater inside cell
Cl- is greater outside cell
Charge Differential
Ions are distributed unequally
Negatively charged proteins inside the cell membrane
Selectively permeable
Membrane Channels
Passive/Leak Channels
Chemically Regulated Channels/Ligand Channels
Mechanically Regulated Channels
Voltage Regulated Channels
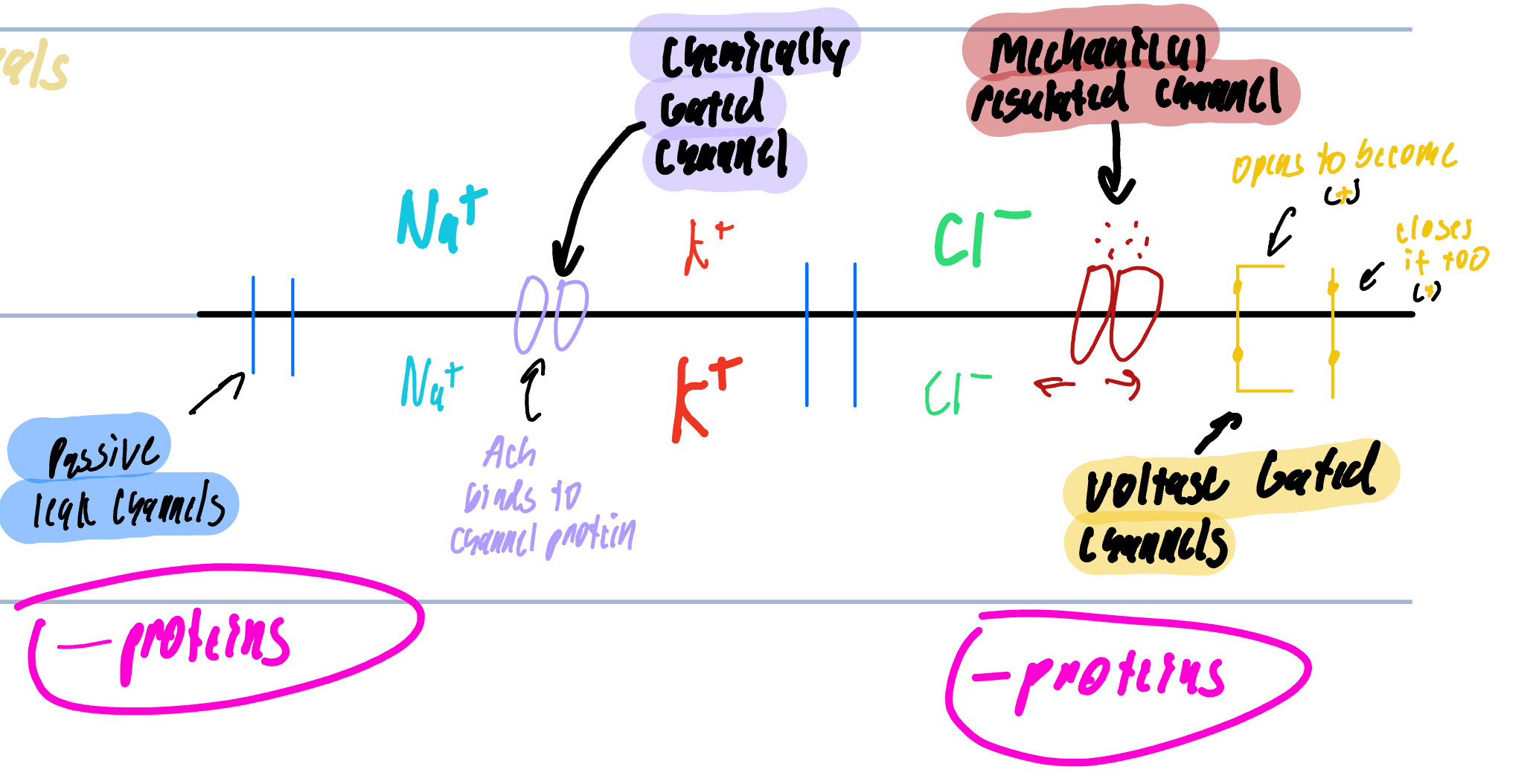
Passive/Leak channels
Always open
main cause for MP
found on the dendrites, axon, and terminals
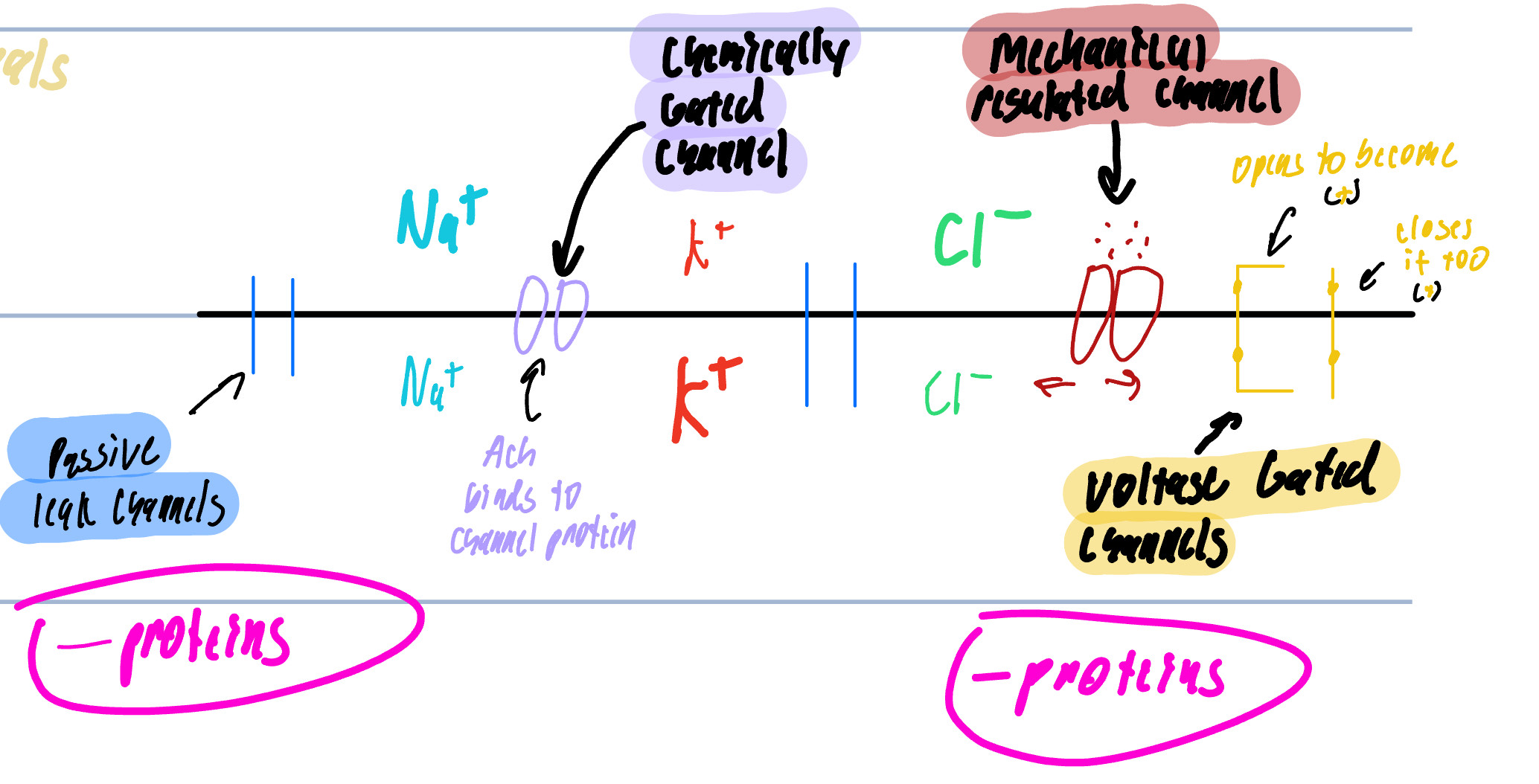
Chemically Regulated Channels/Ligand channels
Can be open or close in response to a specific chemical
NT opens the gate to allow ion movement
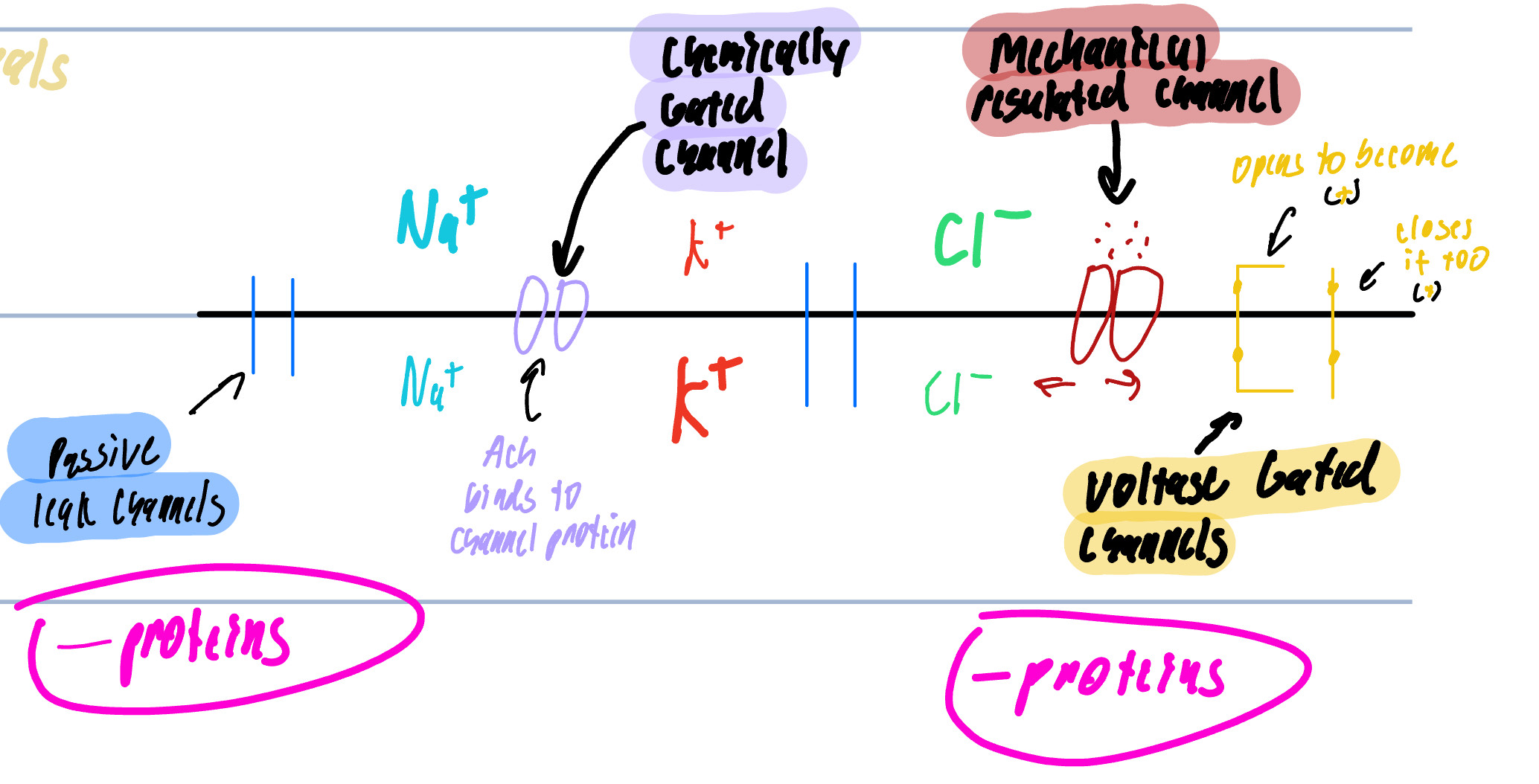
Mechanically Regulated Channels
Any Distortion to the cell membrane
touch, pressure, vibration, that will pull or stretch the channel
Found only on the dendrites and soma
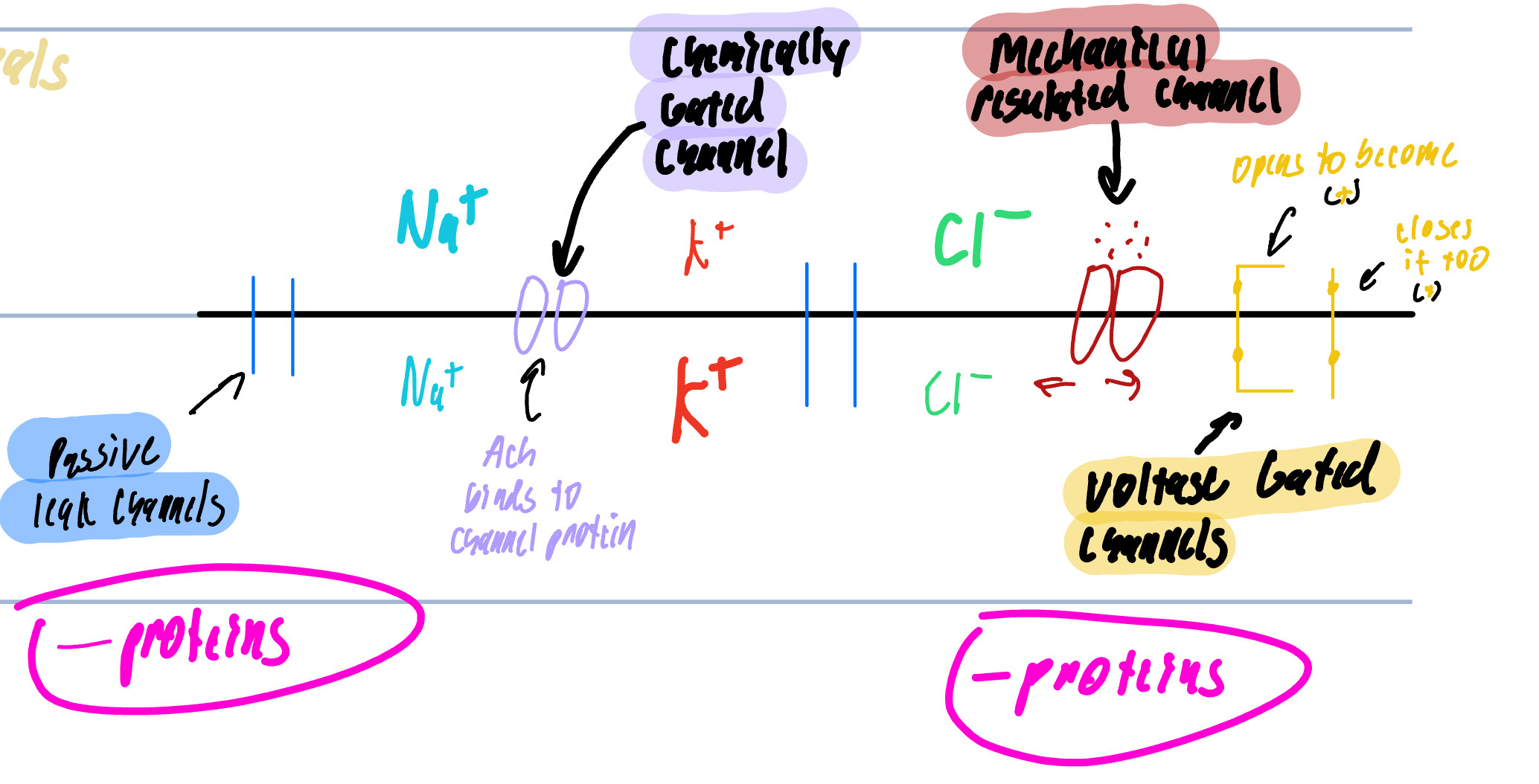
Voltage Regulated Gated Channels
Changes in the transmembrane potential
Found on the Axon and Terminals
Electrochemical Gradient
Potential Energy maintained by plasma membrane potential
Chemical Gradient
move high to low
higher force than electrical
K+ wants to move out of the cell
Na+ wants to move into the cell
Electrical Gradients
based on charge
opposites attract
K+ wants to stay attracted to negative
Na+ wants to stay attracted to negative
Net Gradient
K+ partially in favor moving out of the cell
Na+ Strongly in favor of moving into the cell
Electrochemical Gradient: K+
RMP= -70 mv
wants to move out
become more (-)
Equillibrium = -90 mv
Electrochemical Gradient: Na+
RMP= -70mv
wants to move in
become more (+)
Equilibrium= +66 mv
Na+/K+ ATPase Pump
Maintains RMP
Return Cells to RMP after changes to the MP
Exchanges 3 Na+ for 2 K+ in the cell
Requires ATP (energy)
Moves against the concentration Gradient
Returning AP levels of ions
Step 1 of the Na+/K+ pump
3 Na+ outside MP
K+ inside
Step 2 of the Na+/K+ pump
ATP will phosphorylate the membrane pump
ADP+Pi
covalent bond PE converted to KE when broken
Step 3 of Na+/K+ Pump
3 Na+ released out of cell
Step 4 of Na+/K+ Pump
2 K+ binds to inside of MP
Step 5 of Na+/K+ Pump
Phosphate detaches from MP
Closes the MP
Step 6 of Na+/K+ Pump
Releases K+ into the cell