b1- cell level systems (copy)
1/100
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
whats a eukaryote
cells which have a nucleus (e.g. all animals and plants)
whats a prokaryote
cells which dont have a nucleus (e.g. bacteria)
state the 5 parts of an animal cell
nucleus
cytoplasm
mitochondria
ribosomes
cell membrane
what are the 3 organelles only found in plant cells
cell wall
permanent vacuole
chloroplasts
what is the nucleus
contains dna in the form of chromosomes that controls the cells activities
whats the cytoplasm
gel- like substance where most of the chemical reactions take place
whats the mitochondria
carry out aerobic respiration so provide energy (in form of ATP) for cells to use in chemical reactions
what are ribosomes
where proteins are made in the cell (protein synthesis)
whats the cell membrane
protective barrier around outside of cell
controls which substances pass in and out of the cell
whats the function of the cell wall and whats it made of
it provides strength and support for the plant cell
is made of cellulose
whats the permanent vacuole and what does it contain
it supports the cell to help keep it turgid
contains cell sap ( solution of sugar and salts)
what are chloroplasts
where photosynthesis takes place so they make glucose for the cell
contain a green substance called chlorophyll
whats chlorophyll
green pigment within the chloroplasts which absorbs sunlight for photosynthesis
is chlorophyll which makes the plants green
what are the 5 structures inside a prokaryotic cell
chromosomal DNA
plasmids
ribosomes
cell membrane
cell wall
whats chromosomal dna in prokrayotic cell
its one long circular chromosome which controls the cells activities. It floats free in the cytoplasm
whats are plasmids in a prokaryotic cell
small rings of dna that arent part of the nucleoid
whats magnification
how much larger a displayed image is compared with the original object
whats resolution
how well a microscope can distinguish between two points that are close together
whats the magnifying power of a light microscope
x 2, 000
whats the magnifying power of an electron microscope
x 2,000,000
what are the positives of light microscopes
easy to use
relatively cheap
small so easier to transport
produce colour images
can view live specimens
what are the negatives of light microscopes
light has longer wavelength than electrons = lower resolution
lower maximum magnification thats not good enough to study sub cellular structures (organelles)
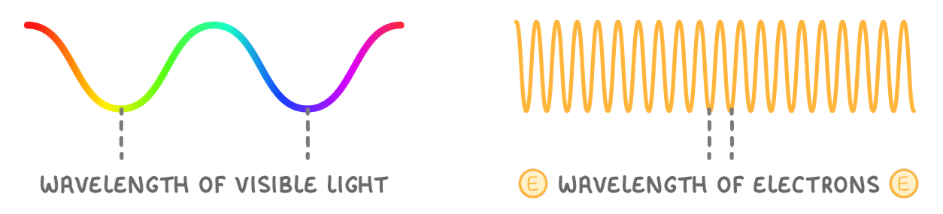
what are the positives of electron microscopes
have a greater magnification and resolution
can see details within sub- cellular structures
what are the negatives of electron microscopes
very expensive
hard to use - require specialist training
large - difficult to transport
black and white images
only view dead specimens
describe the image produced by an electron microscope
the image is black and white, in 2D or 3D and has a very high magnification and resolution
how has electron microscopy increased our understanding of sub cellular structures
electron microscopes can produce higher-resolution images than regular light microscopes. This allows us to see the sub cellular structures within the cell. for example they allow us to see the internal structures of mitochondria
why is staining used in light microscopes
some specimens are colourless
useful to highlight different structures
increases contrast
how do you prepare a specimen on a slide
pipette a drop of water onto a clean slide
use tweezers to place specimen on slide
add a drop of stain if needed
place a cover slip on the top and press down so there arent any air bubbles
how do you view a specimen on a light microscope
clip your slide onto the stage
select lowest powered objective lens
focus the specimen using the coarse and fine adjustment knob
if you need to see your specimen with greater magnification swap to a higher powered objective lens and refocus
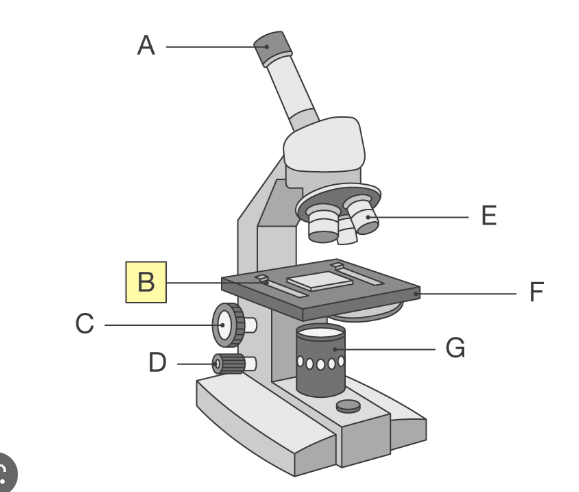
whats a on the light microscope
eyepeice lens which you look through to see the image
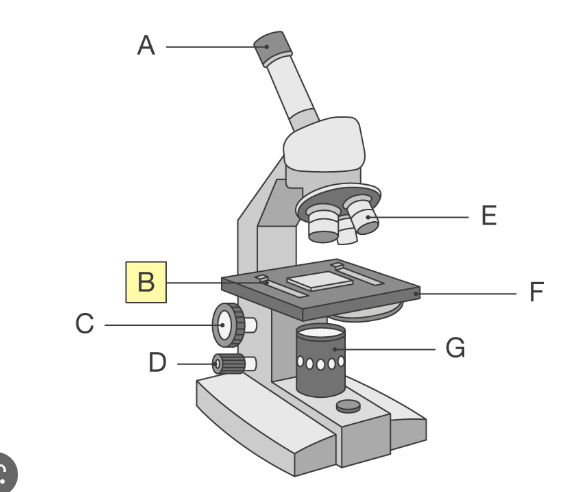
whats B on the light microscope
clips which hold the slides in place
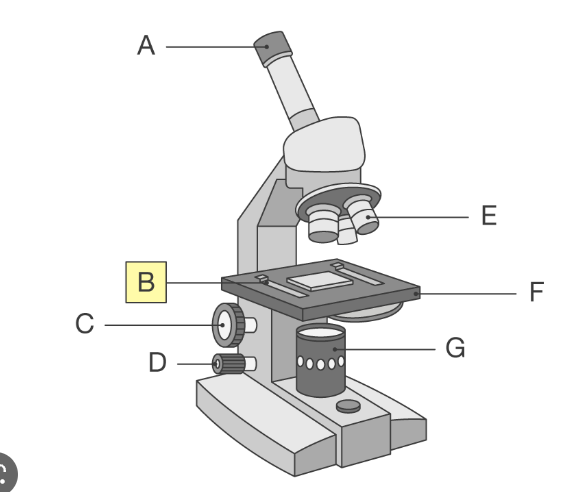
whats C on the light microscope
coarse adjustment knob
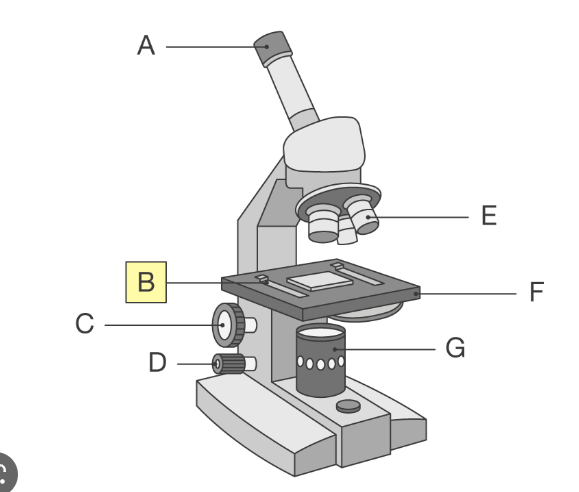
whats D on the light microscope
fine adjustment knob
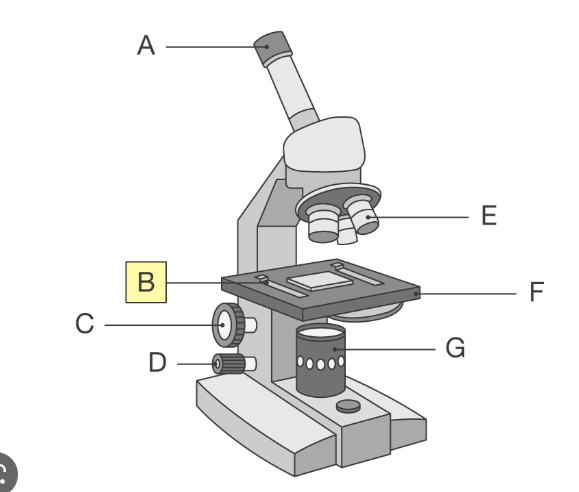
whats E on the light microscope
high and low power objective lenses which magnify the images
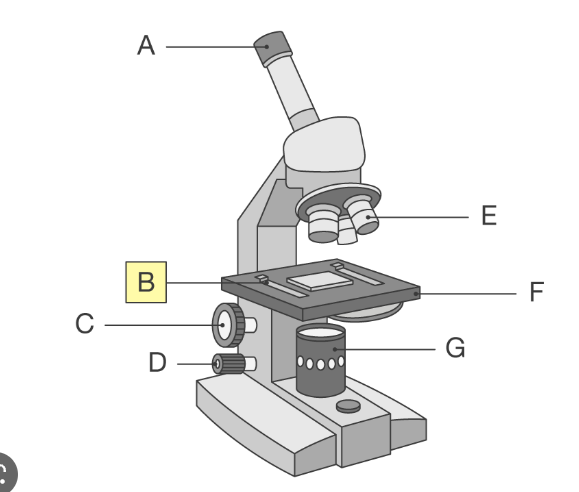
whats F on the light microscope
stage which supports the slide
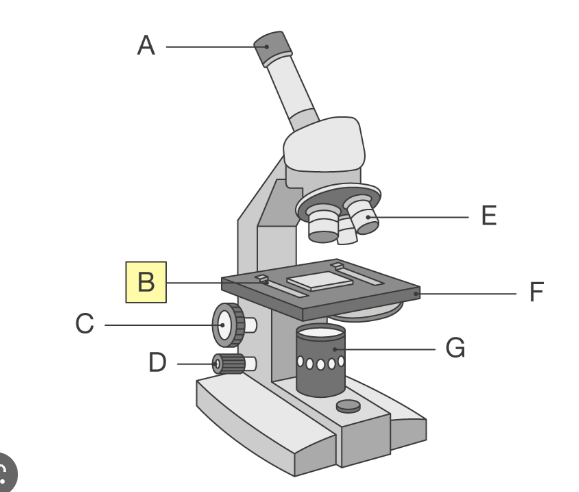
whats G on the light microscope
lamp which shines light through slide so images can be seen more clearly
how do you calculate the total magnification
total magnification = eyepiece magnification x objective lens magnification
whats the formula to calculate magnification from image size and actual size
image size = actual size x magnification
(I AM formula)
whats the structure of dna
is a polymer made up of two strands wrapped around each other to form a double helix
whats a polymer
large, complex molecules composed of long chains of monomers joined together
what are chromosomes
long molecules of coiled up dna which is divided into short sections called genes
whats a gene
a small section of DNA on a chromosome
each gene codes for a particular sequence of amino acids to make a specific protein
what does a nucleotide contain
a sugar, phosphate group and a base. The base is attached to the sugar
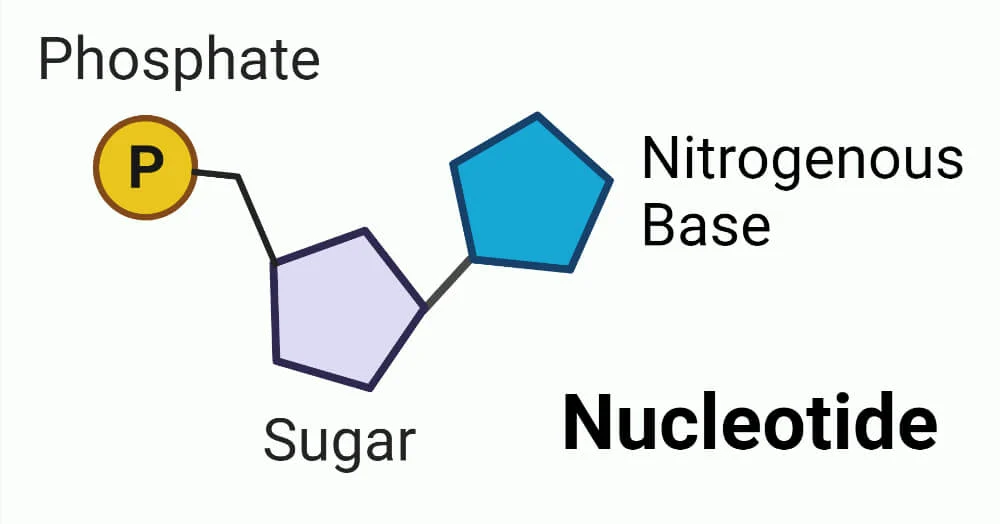
what are the 4 different bases in DNA and how do they pair up
a→t
c→ g
what are enzymes
biological catalysts that speed up the rate of metabolic reactions
what are catalyists
a substance that increases the speed of a chemical reaction without being used up in the process
whats the structure of enzymes
enzymes are proteins that contain an active sight that fits into a specific substrate
what do we call the complex that if formed when an enzyme binds to a substrate
enzyme substrate complex
when were discussing enzymes, what does complimentary mean
s substrate must be complementary to fit the active sight of the enzyme. This means it ‘fits’ the active sight.
what is the special region of the enzyme that binds to the substrate
active sight
whats the lock and key hypothesis for enzyme action
is a model that explains how enzymes are specific for their substrate.
It states that an enzyme is specific for its substrate like a key is for its lock.
substrate has to exactly match the shape of the enzymes active sight for a reaction to be catalysed
what are the 4 factors that affects enzyme function
temperature
pH
substrate concentration
enzyme concentration
how does changing the temperature affect an enzyme controlled reaction
a higher temperature increases the rate at first as the enzyme and substrate move around more so are more likely to meet up and react
but if it gets too hot the bonds holding the enzyme together start to break
the active sight starts to change shape
if it changes shape enough, the enzyme wont be able to bind to the substrate - at this point its been denatured
whats an enzymes optimum temperature
the temperature that gives the highest enzyme activity
whats the effect of the pH on an enzyme
if the pH is too high or low it interferes with the bonds holding the enzyme together which start to change the shape of the active sight (substrate can still fit but less well)
active shape changes so much that the substrate cant fit - denatured
whats an enzymes optimum pH
the pH the enzymes work best at
whats the effect of enzyme concentration on the rate of the reaction
the more enzyme molecules there are in a solution, the more likely a substrate molecule will meet up with it so the rate of reaction increases
if the amount of substrate is limited theres a point when all the substrates are dealt with so adding more enzyme has no further affect
whats the effect of substrate concentration on the rate of reaction
the higher the substrate concentration the more likely the enzyme will meet up and react with the substrate
however once all the active sights are full, adding more substrates makes no difference
whats cellular respiration
a universal chemical process that occurs in all living cells that breaks down glucose to release ATP, which may be used as energy to power many reactions throughout the body.
whats ATP
it stores the energy needed for many cell processes
what type of reaction is respiration
exothermic as cellular respiration is just releasing the energy from the glucose
give 3 examples of how cells use the energy from respiration
Chemical reactions to build larger molecules from smaller molecules
Muscle contraction to allow movement
Keeping warm (to maintain a constant temperature suitable for enzyme activity)
what are the 2 types of respiration
aerobic respiration
anaerobic respiration
whats aerobic respiration
the chemical reaction in cells that uses oxygen to break down nutrient molecules to release energy
complete breakdown of glucose to release a relatively large amount of energy for use in cell processes and reactions
Carbon dioxide and water are produced as waste products as well as releasing useful cellular energy
how much ATP does aerobic respiration produce
32 ATP
whats the word equation for aerobic respiration
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
whats the chemical equation for aerobic respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O → 6CO2 + 6H2O (opposite of photosynthesis)
whats anaerobic respiration
chemical reaction in cells that breaks down nutrient molecules to release energy without using oxygen
releases much less energy than aerobic respiration as it involves the incomplete breakdown of glucose
Different breakdown products are formed depending if the process is happening in animals or plants/fungi
how much ATP does anaerobic respiration produce
2ATP
where does anaerobic respiration take place in animals
muscle cells during vigorous exercise
When individuals exercise at high intensities, their muscles have a higher demand for energy
Bodies can only deliver so much oxygen to muscle cells for aerobic respiration
whats the word equatiopn for anerobic respiration in animals
glucose → lactic acid
when do plants need to use anaerobic respiration
if plants are in waterlogged soil, there is little or no oxygen available
The plant root cells will respire anaerobically
whats the word equation for anaerobic respiration in plants
glucose →ethanol + carbon dioxide
whats fermentation
Anaerobic respiration in yeast
is economically important in the manufacture of bread (where the carbon dioxide produced helps the dough to rise) and in brewing (where the ethanol produced makes beer)
what is oxygen debt
the extra oxygen that is needed to break down the lactic acid formed in anaerobic respiration
what are biological molecules
molecules found in living organisms and are produced by cells
what are nutrients
substances needed for growth, repair and metabolism
what type of molecules are carbohydrates and proteins
polymers
what are carbohydrates made up from
simple sugars e.g. glucose which are joined in long chains (polymers)to make complex carbohydrates e.g. starch
use the terms polymer and monomer to explain the difference between simple sugars and complex carbohydrates
complex carbohydrates are large molecules made up of lots of individual smaller molecules called simple sugars
complex carbohydrates are polymers whilst simple sugars are monomers
how are carbohydrates broken down
the polymer molecules are broken down back into sugars when the chemical bonds between the monomers are broken
what type of enzyme breaks down carbohydrates and where are they found
carbohydrases - found in mouth and small intestine
what are the monomers that make up protein
amino acids
what enzyme breaks down protein back into amino acids and where are they found
Protease - found in stomach and small inestine
what are lipids made up of
fatty acids and glycerol
true of false , lipids are polymers
FALSE - they are not polymers because they dont form a long chain of repeating units
what enzyme breaks down lipids and where are they found
lipase - found in small intestine
what are photosynthetic organisms
the main producers of food and therefore biomass for life on Earth
what type of reaction is photosynthesis
endothermic - energy is transferred from the environment during it
whats the purpose of photosynthesis
for photosynthetic organisms (e.g. green plants and algae) use energy from the sun to make glucose
whats the word equation for photosynthesis
carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
whats the chemical equation for photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
where does photosynthesis take place
in the chloroplasts
whats the process of phtosynthesis
energy transferred by light is used to split water into oxygen gas and hydrogen ions
carbon dioxide gas then combines with hydrogen ions to make glucose
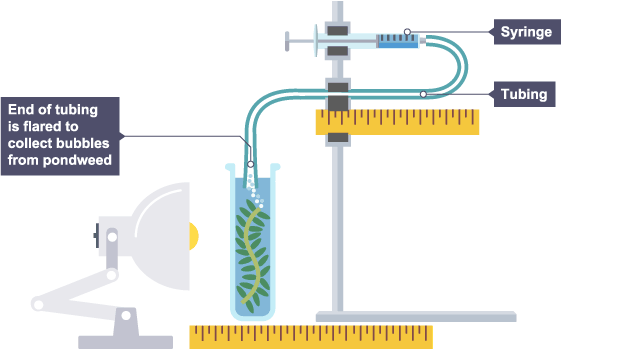
whats the experiment to calculate the rate of photosynthesis
pond weed is places in a test tube full of water
the top is sealed with bung
a lamp is placed at a measured distance from the test tube
count the number of oxygen bubbles coming out of the cut stem in 1 minute
repeat experiment and record results
calculate average number of bubbles produced per minute
whats the effect of temperature on photosynthesis
with an increase in temperature, the rate of photosynthesis also increases
because reaction is controlled by enzymes, this only continues up till a certain temperature and then the enzymes will denature and the rate of reaction will decrease
whats the effect of light intensity on photosynthesis
the higher the light intensity, the rate of photosynthesis increases
how is the relationship between the light source and the plant inversely proportional
because as the distance between the light source and the plant increases, the light intensity decreases
whats the effect of carbon dioxide concentration on photosynthesis
as carbon dioxide concentration increases, so does the rate of the reaction
what are the limiting factors in photosynthesis
carbon dioxide, light intensity and temoerature
in low levels these restrict any increase in the rate of photosynthesis
despite increases in other factors the rate of photosynthesis will not increase any more