Lecture 28: Respiratory gas exchange and transport
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
vasoconstriction
When there is decreased O2 in the pulmonary arterioles, it leads to vasoconstriction/vasodilation
vasodilation
what there is decreased O2 in the systemic arterioles, it leads to vasoconstriction/vasodilation
vasodilation
When there is increased O2 in the pulmonary arterioles, it leads to vasoconstriction/vasodilation
vasoconstriction
what there is increased O2 in the systemic arterioles, it leads to vasoconstriction/vasodilation
gas exchange
pulmonary circulation makes ____ _____ efficient
metabolic
systemic circulation matches blood supply to local ____ needs
V/Q ratio
A measurement that examines how much gas is being moved effectively and how much blood is gaining access to the alveoli.
V
rate of airflow is represented by the letter
Q
rate of capillary blood flow to the alveoli is represented by the letter
0.8
the normal V/Q ratio is this
V/Q mismatch
in this, the rate of airflow is not similar to that of blood flow, usually under pathological conditions
Alveolar ventilation, shunting
A low V/Q ratio is produced by the block of _______________ ______________, which cuases the _____________ of blood flow
Dead space
High V/Q ratio is produced by the alveolar blood perfusion being blocked, which causes a ________ ____________ in the airways
Partial pressure
this is the pressure exerted by each gas in a mixture as if the other ones were not there
Henry's law
this states that the amount of dissolved gas is proprotional to its partial pressure in the gaseous phase
simple passive diffusion
gas exchange involves ____ _____ ____ of O2 and CO2 down their own partial pressure gradients
Bigger, lungs, capillaries
In the lungs, the partial pressure of oxygen is __________(bigger/smaller) than the partial pressure of oxygen in the pulmonary capillaries, therefore oxygen flows from the _______ to the _____________
Smaller, capillaries, lungs
In the lungs, the partial pressure of CO2 is ___________(bigger/smaller) than the partial pressure of CO2 in the pulmonary capillaries, therefore the CO2 flows form the _____________ to the _________
Bigger, capillaries, tissues
At the tissue levels, the partial pressure of O2 is __________(bigger/smaller) in the capillaries than in the tissues, which means that the O2 flows from the __________ to the ___________
Smaller, tissues, capillaries
At the tissue levels, the partial pressure of CO2 is ____________(bigger/smaller) in the capillaries than in the tissues, which means that CO2 flows from the ___________ to the ____________
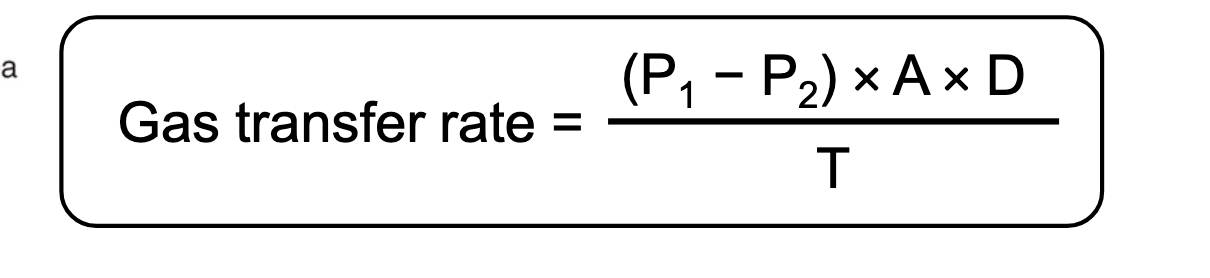
Ficks law of gas diffusion
this is gas transfer rate = (P1-P2) x (surface area) x (diffusion constant)/thickness of the membrane
Pressure gradient
What is the major determinant of the rate of transfer for most gases?
Smaller, diffusion constant, bigger
The pressure gradient (difference) for CO2 is much ______________(bigger/smaller) than that of O2, however this is compensated because the _____________ _______________ for the rate of diffusion of CO2 is much ______________(bigger/smaller) than that of O2
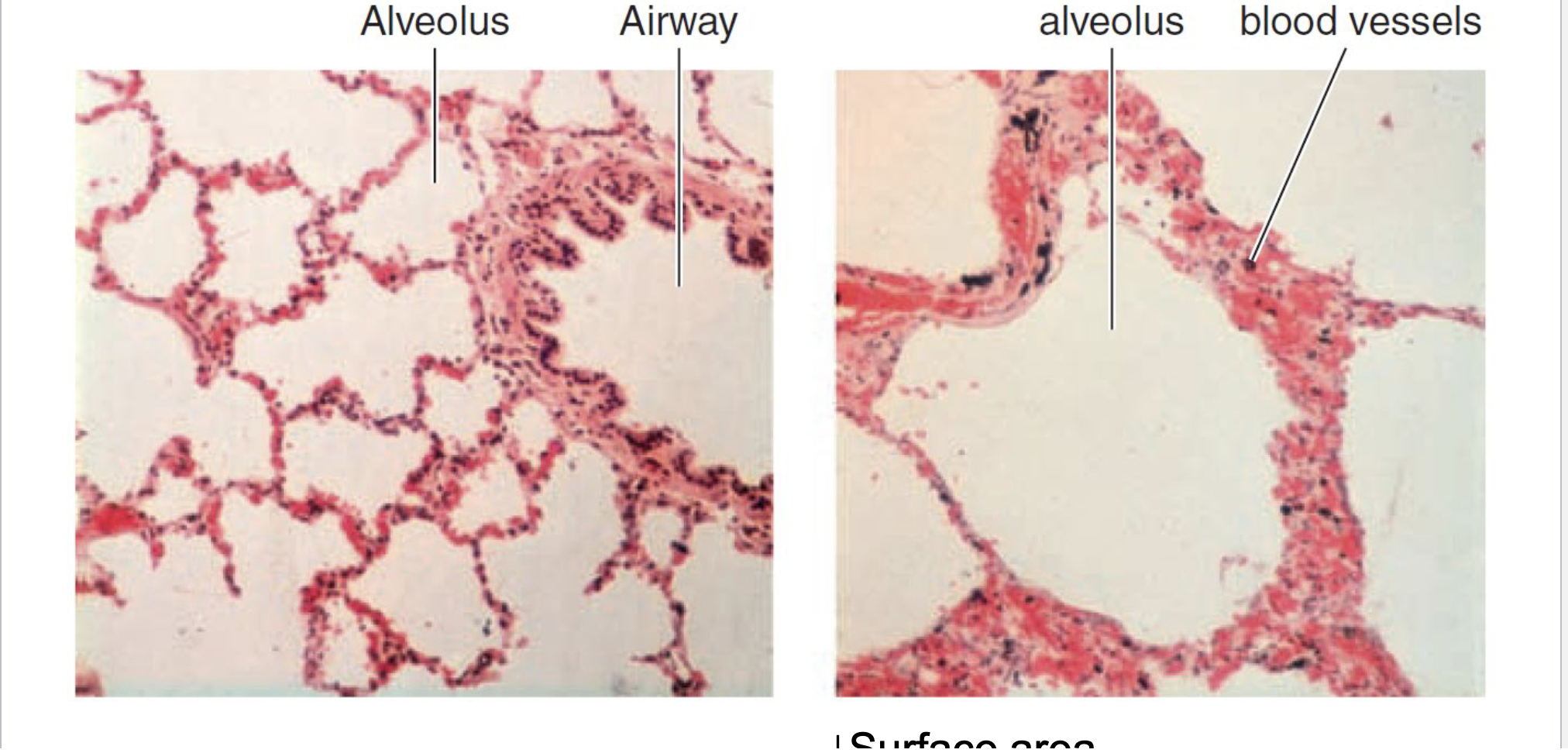
Emphysema
a condition in which the air sacs of the lungs are damaged and enlarged, causing breathlessness, due to decreased surface area and increased thickness of the membrane
Hemoglobin
Most of the Oxygen in the blood is bound to _________________
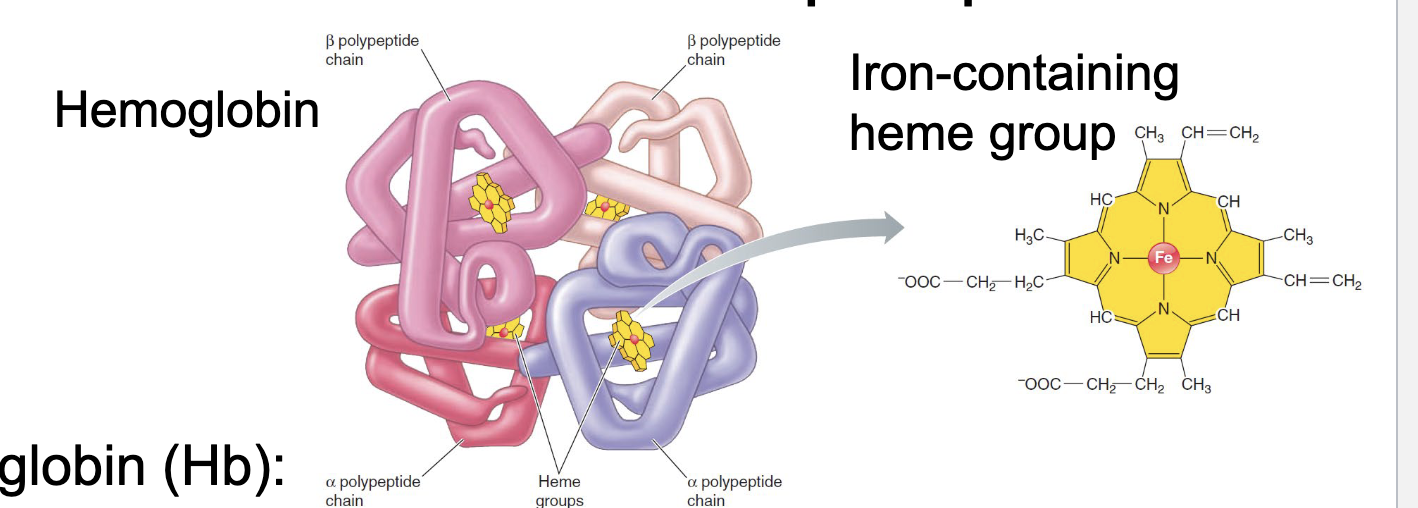
Hemoglobin
this is an iron containing molecule that has 4 heme molecules and can bind O2, each one binds 1 O2
True
True or false: the O2 bound to Hb does not contribute to Po2 of the blood
Oxyhemoglobin
this is hemoglobin bound to oxygen
PO2
what is a primary determinant of precent hemoglobin saturation with O2
Increases
The hemoglobin's affinity for O2 ___________(increases/decreases) as more O2 molecules become bound
does not
The O2 bound to the Hb does/does not contribute to the PO2 of the blood
PO2
Hb acts as an O2 storage depot by keeping ____ low
O2
binding of O2 to Hb removes ___ from the blood
PO2
This binding of O2 to Hb reduces ___ and maintains the partial pressure gradient that drives O2 from alveoli into the blood
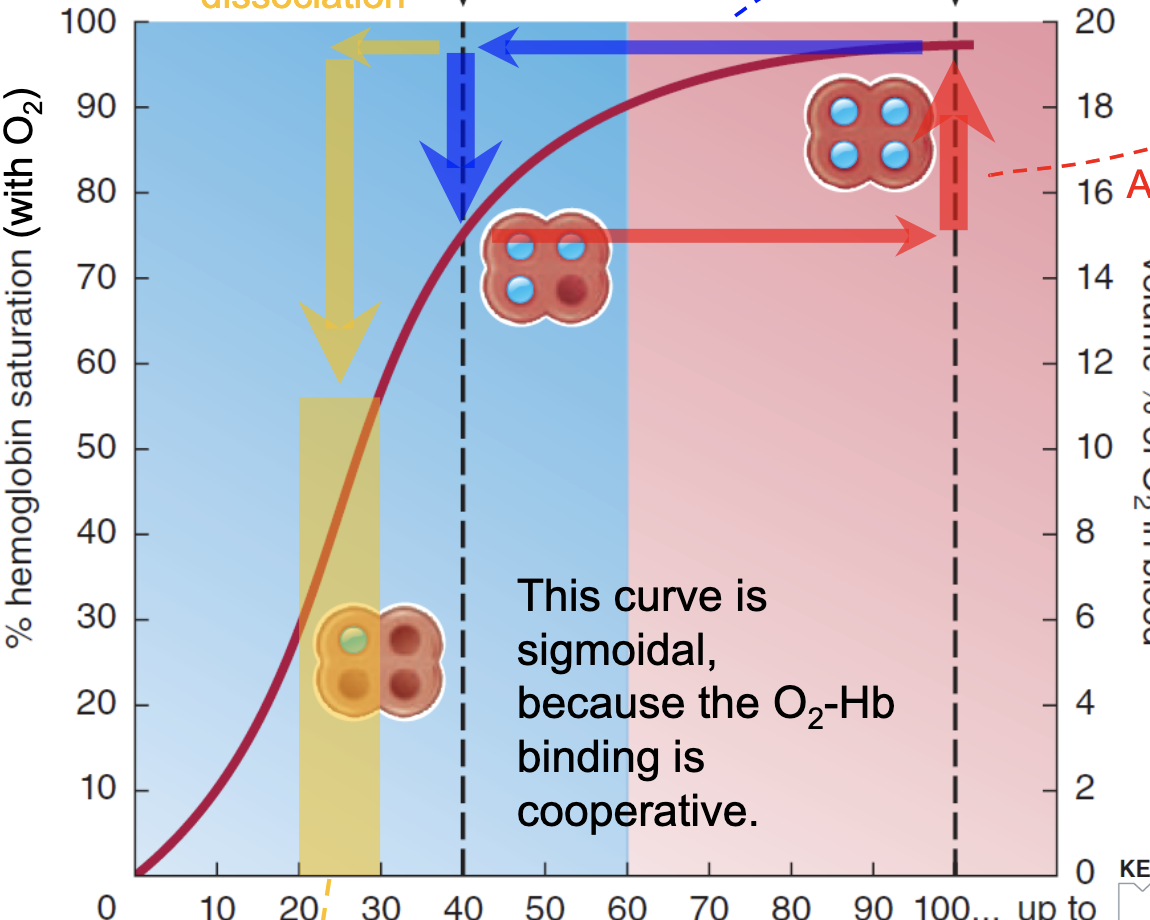
Increased CO2, increased acid, increased temperature, increased 2-3 BPG
What caues a rightward shift of the signmoidal O2 Hb saturation curve?
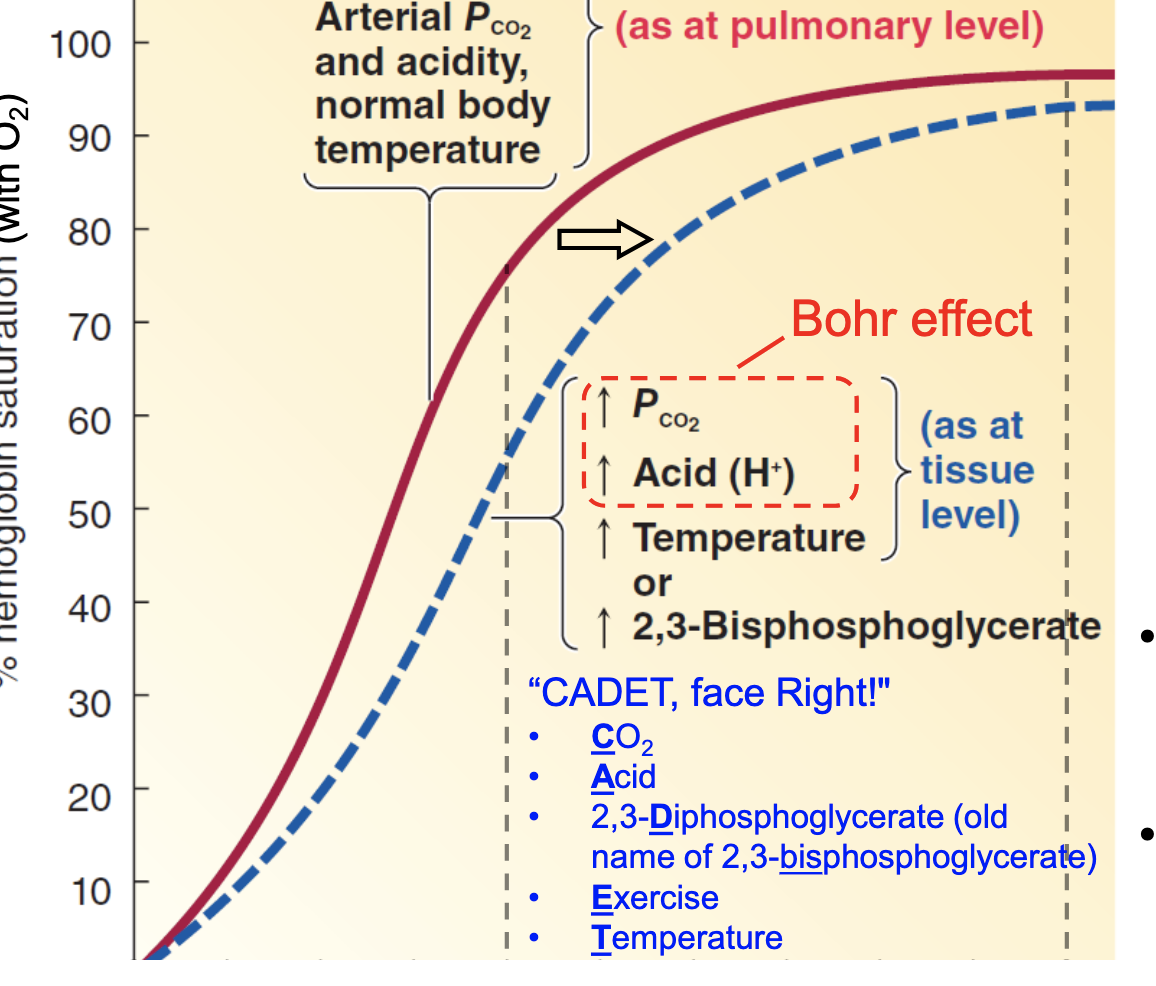
More, more
When there is a rightward shift of the Hb curve, __________(more/less) O2 is unloaded from Hb at the tissue levels, which causes _____(more/less) O2 being delivered to tissues
CADET - face right
CO2
Acid
2,3-Diphosphoglycerate
Exercise
Temperature
right (shift)
what is the pneumonic for right shift of the O2Hb curve
Bohr effect
a decrease in the amount of oxygen associated with hemoglobin and other respiratory compounds in response to a lowered blood pH resulting from an increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood.
Cabon Monoxide
What causes a leftward shift of the Hb curve?
Increased, decrease
Carbon monoxide causes a leftward shift by causing the affinity for O2 on hemoglobin to be ____________(increased/decreased) which makes the O2 transfer to tissues _____________(increase/decrease)
CO
Does O2 or carbon monoxide (CO) have a higher affinity for Hb
Asphyxiation
deprived of oxygen, however, the individual cannot tell that their cells are deprived of oxygen
Someone with CO poisoning would die of __________________
Normal
If someone has CO poisoning, their PO2 levels appear ____________(normal, irregular)
Bicarbonate
Most of the CO2 is transported in the blood via what molecule?
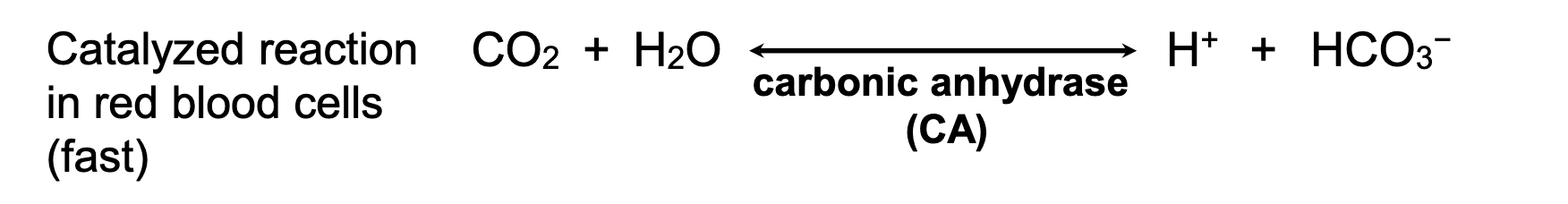
Carbonic anhydrase
this is the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of CO2 to H+ and bicarbonate (HCO3-)

switches through a H2CO3 intermediate
slow
how does the spontaneous conversion of CO2 and H2O to H+ and bicarbonate happen in the blood
Haldane effect
Deoxygenation of the blood increases its ability to carry carbon dioxide
More
At the tissues, the more dissolved CO2 in the plasma reacts with oxcygen to form H+ and bicarbonate, which allows for __________(more/less) transport of O2 in the tissues
Chloride shift
this is the transporter that is in the red blood cells that exchanges bicarb and chlorine
Peripheral chemoreceptors
these are in the carotid bodies and respond to the decrease in PO2, increased PCO2, or decrease in pH, which causes increased ventilation
pH, PCO2
the main stimulus of peripheral chemoreceptors are changes in ___, usually as a result of the increase in _______
Central chemoreceptors
these are in the medulla and respond to changes in the H+ concentration in the CSF, and in effect can increase ventilation
CO2
The reason why chemo receptors increase ventilation, is because this in effect lowers the partial pressure of ______ in the arteries
Chonic obstructive pulmonary disease
this is the chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed airflow from the lungs and breathing related problems, including emphysema and chronic bronchitis