Principles of Economics Chapter 30 Government Budgets & Fiscal Policy
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Savings
is the money that individuals put away.
Consumption
is the money individuals spend on goods and services.
Disposable income
is considered take home pay
Consumption Schedule
John Maynard Keynes provided two assumptions when it comes to consumption: People base their consumption on their disposable income, and when people get an additional income, they do not spend it all. These two assumptions explain the consumption schedule. The consumption schedule shows each level of consumption at various levels of disposable income.
Nonincome Determinants of Consumption and Savings
Wealth: Wealth is the value of household assets. If a consumer's wealth increases, that consumer will spend more money and save less money.
Expectations: Today the price of gas is $3.75 a gallon. If consumers know that the price of gas will increase to $4.25 tomorrow, they will spend more money today on gas and save less.
Real Interest Rates: Real interest rates is the interest rate on borrowed money. If consumers know that the interest rate is going to fall, they will borrow more which increases consumption and decreases savings.
Household Debt: If consumers experience an increase in their household debt, they tend to borrow more money. When consumers borrow more money, it causes them to spend more money which increases consumption and decreases savings.
second basic macroeconomic relationship
The second basic macroeconomic relationship looks at the perspective of the producer. The producer wants to make investments. The investments that the producer makes are in capital goods. As you can recall from chapter 1, capital goods are property and equipment. When the producers purchase capital goods, it is often done on credit. So, the real interest rate and the expected rate of return must be considered. The real interest rate is the interest rate paid on the equipment. The expected rate of return is the percentage of profits that the producer expects to generate through the use of the new equipment. The interest-rate-investment relationship is inverse. If the interest rates are increasing, then the producer will hold off on purchasing any equipment. But if the interest rates are decreasing, the producer will purchase more property and equipment. This inverse relationship between the interest rate and investment shows the investment demand curve to be downward sloping. Since the relationship has been explained, let's turn our attention to the things that cause the investment demand curve to shift.
Shifts in Investment Demand Curve
Acquisition, Maintenance, and Operating Costs: If the initial costs of capital goods is high, it has a negative effect on expected rate of return. A higher cost will decrease the expected rate of return, which decreases investment demand.
Business Taxes: If the producer receives an increase in his business taxes, then the expected rate of return decreases, which decreases investment demand.
Technological Change: If new technology is available which will help the producer produce goods more efficiently, it will cause an increase in investment demand.
Stock of Capital Goods on Hand: If a producer has an overstock of goods on hand, it deters the producer away from purchasing any more capital goods, which decreases investment demand.
Expectations: If the producer expects to generate higher returns from the investment of capital goods, it will cause an increase in investment demand.
Government Spending
Budget deficit: Government spends more than it receives in taxes
Budget surplus: Government receives more in taxes than it receives
Balanced budget: Government spending=taxation received
Federal Taxes
Main categories:
Personal income taxes
Payroll taxes
Corporate income taxes
Excise taxes
Personal Income Tax
Largest Single Source of federal government revenue
Due Apr 15
Considered a progressive tax: Tax rate increases as household income increases
Payroll Tax
Second Largest source of federal revenue
A tax based on the pay received from employers
Provides funds for Social Security and Medicare
Proportional Tax: flat percentage of all wages earned (Ex Social Security)
Regressive Tax: Individuals with higher incomes pay a smaller share of income in taxes
Corporate Income Tax
Third largest source of federal tax revenue
A tax imposed on corporate profits
Excise Tax
a tax on a particular good
gas, alcohol, tobacco
estate and gift tax: a tax on people who pass assets to the next generation - during death or during life in the form of a gift
Federal Deficit
National Debt: the total amount that the government borrowed over time
Budget deficit: how much was borrowed in a particular year
Fiscal Policy
Uses government spending or taxation to correct the economy
Discretionary: Initiated by acts of Council of Economic Advisors (CEA)
Non discretionary (Automatic): Triggered by the state of the economy
Fiscal policy is one of two policy tools for fine tuning the economy (the other is monetary policy). While monetary policy is made by policymakers at the Federal Reserve, fiscal policy is made by Congress and the President.
Expansionary Fiscal Policy
Used during times of recession
Increases government spending
decreases personal taxes
Uses a combo of government spending and personal taxes
Expansionary fiscal policy creates a budget deficit: Tax expenditures exceed tax receipts
Expansionary Fiscal Policy
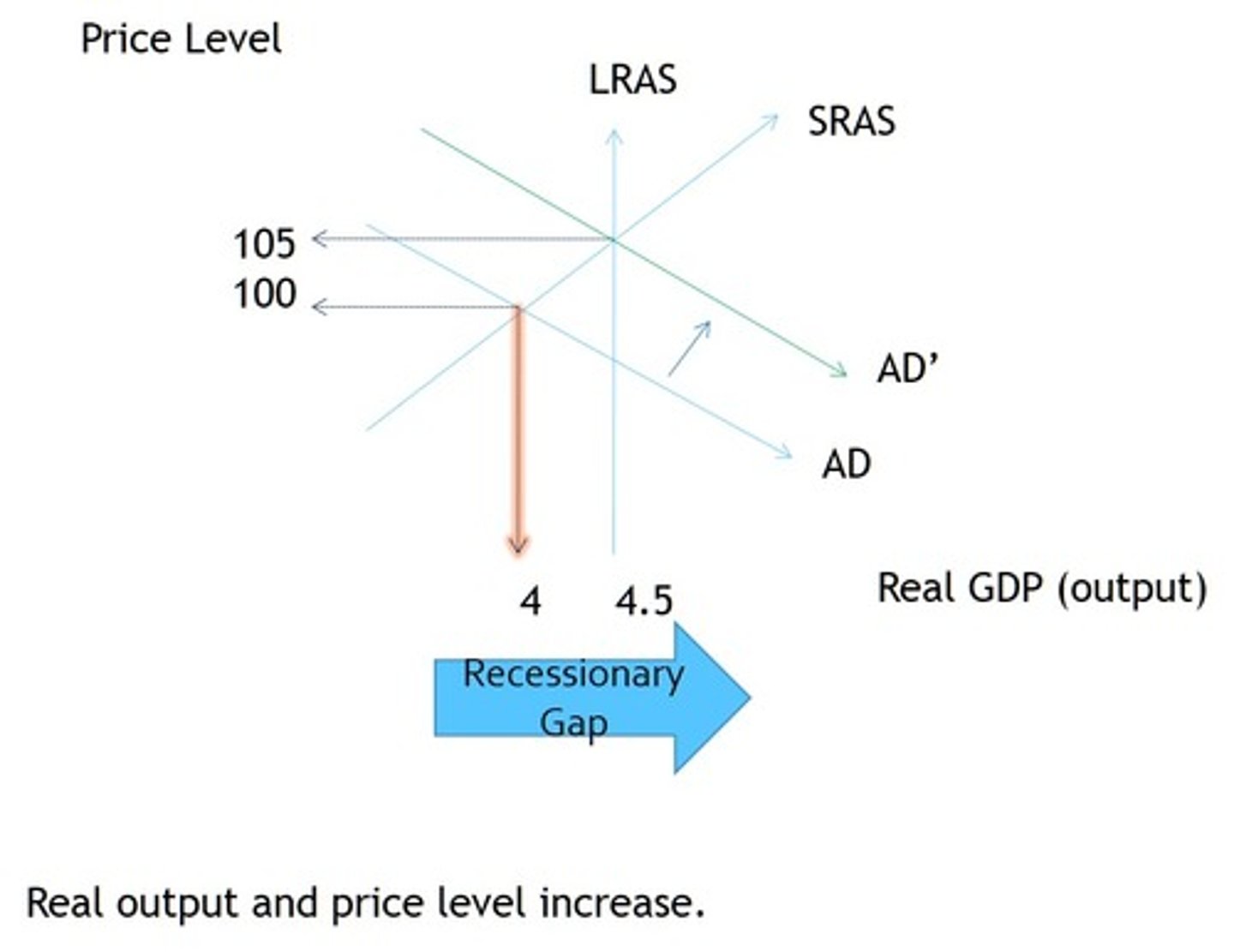
Increase Government Spending
At full employment, real GDP is $510; however, the economy has experienced a decrease in real GDP to $490. The government decides to increase by $5B. The MPC is .75. What would be the full increase in real GDP from the change in government spending?
M=increase real GDP/change in investment spending
M=1/1-mpc (1/1-.75)=4
4=x/5
Increase real GDP=$20 Billion
Decrease Personal Taxes
Suppose the government decided to decrease taxes by$6.67 billion. Will that close the recessionary gap of $20 billion?
MPC=.75
.75*6.67=5
5*4(multiplier)=$20 billion
Yes
If the Government decided to increase spending by $1.25 billion, while decreasing taxes by 5 billion, will that work?
4=x/1.25
X=5
5*.75=3.75
3.75*4=15
15 for personal taxes +5 for government spending=20 for real GDP
Contractionary fiscal policy
used during inflation
reduced government spending
increase taxes
use a combo of government spending
Contractionary fiscal policy leads to a budget surplus: Tax expenditures exceed tax receipts
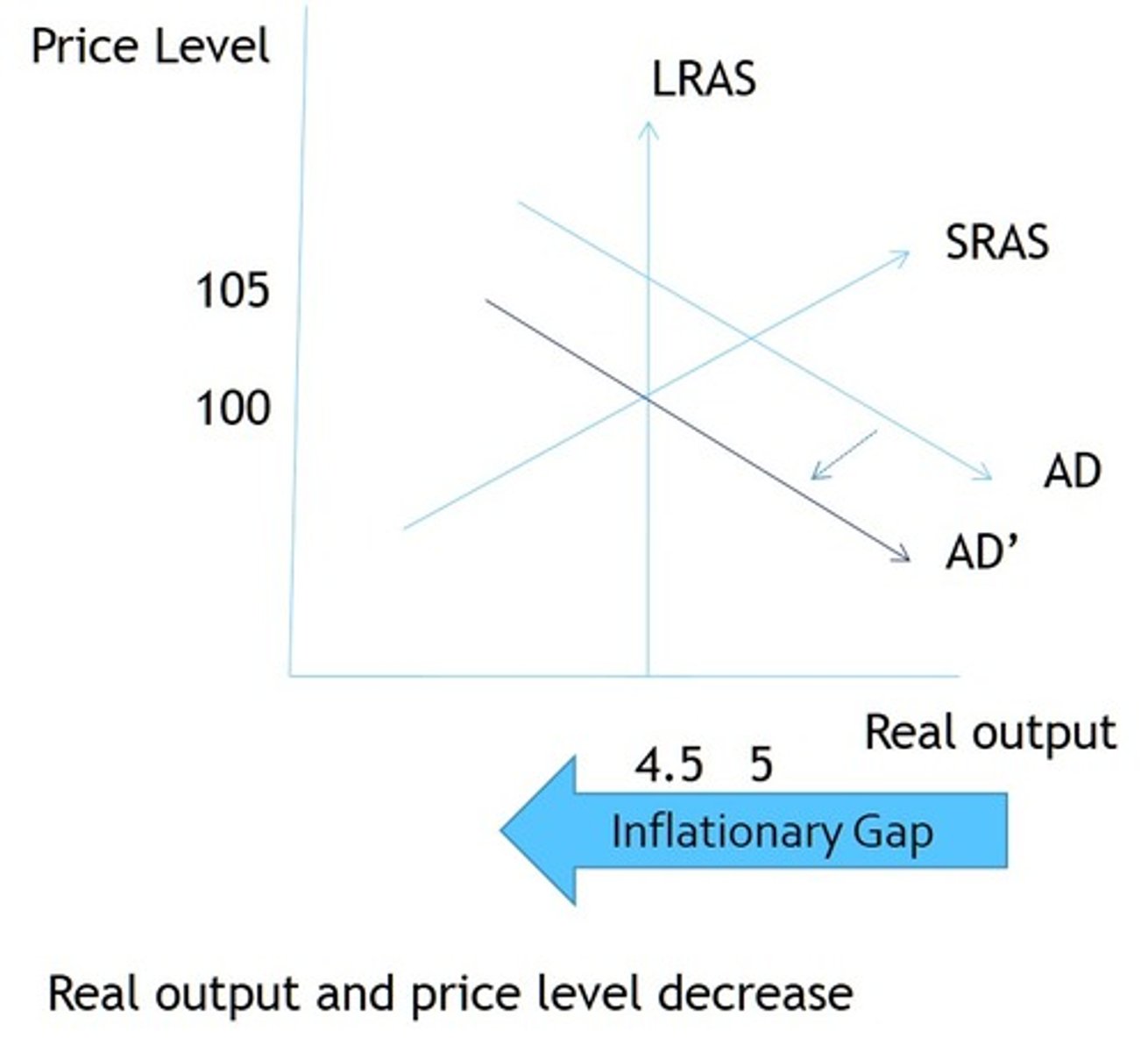
Decrease Government Spending
Suppose the economy experiences a shift in real output from 510 to 522 with the same price level. Multiplier is still 4 with MPC of .75
1. Inflation Occurs
2. What is the inflationary gap?
3. How do we reduce the gap?
2. 12
3. $12 billion gap/4 multiplier=$3 billion decrease in government spending
Increase personal taxes
Suppose the economy experiences a shift in real output from 510 to 522 with the same price level. Multiplier is still 4 with MPC of .75
Gap is $12 billion; multiplier is 4
12/4=3 billion needed for increase in personal taxes
3/.75=$4 increase in personal taxes (consumers will consume .75 of disposable income
Combo of the two
Suppose the government decides to decrease spending by $1.5 billion, how much should they increase personal taxes?
Gap is $12 billion
Multiplier is 4
12/4=3 billion needed
3-1.5=$1.5
1.5/.75=$2 increase in personal taxes
An economy is in a recession and the government decides to increase spending by $4 billion. The MPC is .8. What would be the full increase in real GDP from the change in government spending?
The government will have to decrease taxes by what amount?
If the government decided to increase spending by $2 billion, what amount would they decrease personal taxes by?
Automatic Stabilizers
Passive or Automatic
Increases the budget deficit or reduces the budget surplus without action from the government
Ex: food stamps,
unemployment
Standardized Employment
What the budget deficit or surplus would be if the economy were producing at potential GDP
People find work in a reasonable time
Businesses make a normal profit
Workers and businesses earn more and pay more in taxes
Problems with Discretionary Fiscal Policy
Crowding Out: Government borrowing and spending results in higher interest rates which reduces business investment and household consumption
Recognition lag: The time it takes to determine that a recession has occurred
Legislative lag: The time it takes to get a fiscal policy bill passed
Implementation lag: The time it takes for the funds relating to fiscal policy to be dispersed the appropriate agencies to implement the programs
Federal Government Spending
In recent decades, the level of federal government spending and taxes, expressed as a share of GDP, has not changed much, typically fluctuating between about 18% to 22% of GDP.
State Spending
the level of state spending and taxes, as a share of GDP, has risen from about 12-13% to about 20% of GDP over the last four decades.
Four main areas of federal spending
national defense, Social Security, healthcare, and interest payments, which together account for about 70% of all federal spending.
When governments run budget deficits, how do they make up the differences between tax revenue and spending?
The government borrows funds by selling Treasury bonds, notes, and bills.
When governments run budget surpluses, what is done with the extra funds?
The funds can be used to pay down the national debt or else be refunded to the taxpayers.
Is it possible for a nation to run budget deficits and still have its debt/GDP ratio fall? Explain your answer. Is it possible for a nation to run budget surpluses and still have its debt/GDP ratio rise? Explain your answer.
Yes, a nation can run budget deficits and see its debt/GDP ratio fall. In fact, this is not uncommon. If the deficit is small in a given year, than the addition to debt in the numerator of the debt/GDP ratio will be relatively small, while the growth in GDP is larger, and so the debt/GDP ratio declines. This was the experience of the U.S. economy for the period from the end of World War II to about 1980. It is also theoretically possible, although not likely, for a nation to have a budget surplus and see its debt/GDP ratio rise. Imagine the case of a nation with a small surplus, but in a recession year when the economy shrinks. It is possible that the decline in the nation's debt, in the numerator of the debt/GDP ratio, would be proportionally less than the fall in the size of GDP, so the debt/GDP ratio would rise.
What are the two categories of taxes?
those collected by the federal government and those collected by state and local governments
Suppose that gifts were taxed at a rate of 10% for amounts up to $100,000 and 20% for anything over that amount. Would this tax be regressive or progressive?
Progressive. People who give larger gifts subject to the higher tax rate would typically have larger incomes as well.
If an individual owns a corporation for which he is the only employee, which different types of federal tax will he have to pay?
Corporate income tax on his profits, individual income tax on his salary, and payroll tax taken out of the wages he pays himself.
What taxes would an individual pay if he were self-employed and the business is not incorporated?
individual income taxes
The social security tax is 6.2% on employees' income earned below $113,000. Is this tax progressive, regressive or proportional?
The tax is regressive because wealthy income earners are not taxed at all on income above $113,000. As a percent of total income, the social security tax hits lower income earners harder than wealthier individuals.
Debt has a certain self-reinforcing quality to it. There is one category of government spending that automatically increases along with the federal debt. What is it?
As debt increases, interest payments also rise, so that the deficit grows even if we keep other government spending constant.
True or False:
Federal spending has grown substantially in recent decades.
As a share of GDP, this is false. In nominal dollars, it is true.
True or False:
By world standards, the U.S. government controls a relatively large share of the U.S. economy
False
True or False:
A majority of the federal government's revenue is collected through personal income taxes.
False
True or False:
Education spending is slightly larger at the federal level than at the state and local level.
False. Education spending is much higher at the state level.
True or False:
State and local government spending has not risen much in recent decades.
False. As a share of GDP, it is up about 50.
True or False:
Defense spending is higher now than ever.
As a share of GDP, this is false, and in real dollars, it is also false.
True or False:
he share of the economy going to federal taxes has increased substantially over time.
False
True or False:
Foreign aid is a large portion, although less than half, of federal spending.
False, it is about 1%
True or False:
Federal deficits have been very large for the last two decades.
False. Although budget deficits were large in 2003 and 2004, and continued into the later 2000s, the federal government ran budget surpluses from 1998-2001.
True or False:
The accumulated federal debt as a share of GDP is near an all-time high.
False
What is the main reason for employing contractionary fiscal policy in a time of strong economic growth?
To keep prices from rising too much or too rapidly.
What is the main reason for employing expansionary fiscal policy during a recession?
To increase employment.
automatic stabilizers
which are taxing and spending mechanisms that, by their design, shift in response to economic events without any further legislation.
Standardized employment budget
the calculation of what the budget deficit or budget surplus would have been in a given year if the economy had been producing at its potential GDP in that year
In a recession, does the actual budget surplus or deficit fall above or below the standardized employment budget?
It falls below because less tax revenue than expected is collected.
What is the main advantage of automatic stabilizers over discretionary fiscal policy?
Automatic stabilizers take effect very quickly, whereas discretionary policy can take a long time to implement.
Explain how automatic stabilizers work, both on the taxation side and on the spending side, first in a situation where the economy is producing less than potential GDP and then in a situation where the economy is producing more than potential GDP.
In a recession, because of the decline in economic output, less income is earned, and so less in taxes is automatically collected. Many welfare and unemployment programs are designed so that those who fall into certain categories, like "unemployed" or "low income," are eligible for benefits. During a recession, more people fall into these categories and become eligible for benefits automatically. The combination of reduced taxes and higher spending is just what is needed for an economy in recession producing below potential GDP. With an economic boom, average income levels rise in the economy, so more in taxes is automatically collected. Fewer people meet the criteria for receiving government assistance to the unemployed or the needy, so government spending on unemployment assistance and welfare falls automatically. This combination of higher taxes and lower spending is just what is needed if an economy is producing above its potential GDP.
What would happen if expansionary fiscal policy was implemented in a recession but, due to lag, did not actually take effect until after the economy was back to potential GDP?
Prices would be pushed up as a result of too much spending.
What would happen if contractionary fiscal policy were implemented during an economic boom but, due to lag, it did not take effect until the economy slipped into recession?
Employment would suffer as a result of too little spending.
Do you think the typical time lag for fiscal policy is likely to be longer or shorter than the time lag for monetary policy? Explain your answer?
Monetary policy probably has shorter time lags than fiscal policy. Imagine that the data becomes fairly clear that an economy is in or near a recession. Expansionary monetary policy can be carried out through open market operations, which can be done fairly quickly, since the Federal Reserve's Open Market Committee meets six times a year. Also, monetary policy takes effect through interest rates, which can change fairly quickly. However, fiscal policy is carried out through acts of Congress that need to be signed into law by the president. Negotiating such laws often takes months, and even after the laws are negotiated, it takes more months for spending programs or tax cuts to have an effect on the macroeconomy.
Crowding Out
federal spending and borrowing causes interest rates to rise and business investment to fall
How would a balanced budget amendment affect a decision by Congress to grant a tax cut during a recession?
The government would have to make up the revenue either by raising taxes in a different area or cutting spending.
How would a balanced budget amendment change the effect of automatic stabilizer programs?
Programs where the amount of spending is not fixed, but rather determined by macroeconomic conditions, such as food stamps, would lose a great deal of flexibility if spending increases had to be met by corresponding tax increases or spending cuts.
If government tax policy requires Peter to pay $15,000 in tax on annual income of $200,000 and Paul tp pay $10,000 in tax on an annual income of $100,000, then the tax policy is:
Regressive
When the government passes a new law that explicitly changes overall tax or spending levels, it is enacting:
discretionary fiscal policy
_____________________ are a form of tax and spending rules that can affect aggregate demand in the economy without any additional change in legislation.
Automatic stabilizers
During a recession, if a government uses an expansionary fiscal policy to increase GDP, the:
aggregate demand curve will shift to the right
If the federal government collects $1.7 trillion in tax revenues in 2015 and total spending in the same year is $3.2 trillion the result will be a:
budget deficit
Which of the following terms is used to describe the set of policies that relate to government spending, taxation, and borrowing?
Fiscal Policies
The government can use ________________ in the form of ____________________ to increase the level of aggregrate demand in the economy.
an expansionary fiscal policy; an increase in government spending
A __________________________ policy will cause a greater share of income to be collected from those with high incomes than from those with lower incomes.
progressive tax
A ______________________ means that government spending and taxes are equal.
balanced budget
The federal government levies _____________________ on people who pass assets _______________________ either after death or during life.
an estate and gift tax; to the next generation