Module 3 quiz
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
What is opposite of non-parenteral?
Parenteral route
Parenteral Route
Injection can be into
Vein (IV)
Muscle (IM)
Subcutaneous (Sub-Q)
Intradermal
Others: epidural, intra arterial, intraperitoneal, etc. (outside of nursing scope)
Non-parenteral routes
Oral
Inhalation
Topical
Suppositories
Oral route
By mouth (pills)
Sublingual (nitro)
Buccal (liquid fentanyl)
Most convenient & most used
Absorbed into the system through the digestive tract
Slower onset of action by, but has more prolonged effect
Quick acting sublingual and buccal
Malabsorption, vomiting, NPO all affect absorption.
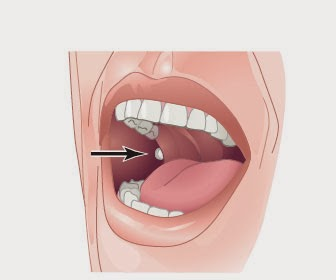
Buccal route of administration
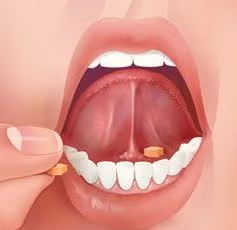
Sublingual route of administration
Topical
Skin (ointment, powder, duragesic)
Eyes (drops, ointments)
Ears (drops)
Medication placed on skin or mucous membranes
Absorbed into the skin and then the blood stream
Slowest onset
Avoid with open wounds and signs of trauma
Suppositories
Vaginal (miconazole)
Rectal (bisacodyl)
Typically quick acting
Absorbed through the membranes into the blood stream
Medication administration
AN essential part of nursing practice
Complex and time consuming
Multiple health care members and factors involved in the process
Much potential for error
Chief responsibility falls to the nurse; occupies 1/3 of our nursing time
Under appreciated how much time is put on medication administration→ very complex and multiple time that an error can occur
Usually, error of the nurse as we are the last line of defense but truly system issues
Participants in Medication Administration
Drug manufacturer→ name and label the drug
Prescriber→ provider
Pharmacist→ supply the medication
System process→ pyxis machine, scan ban, verify name & DOB, scanning medication
Nurse→ Knowing the medication
Patient→ should be encouraged to know what they are taking and why.
AC
Before meals
PC
After meals
HS
Hours of sleep
Avoid q2hr PRN
Instead Every 2 hours prn
Daily
Avoid QD
Three times daily
Avoid TID
Every 8 hours
Avoid Q8H
Why is it important to write things out?
Helps avoid miscommunication
Types of orders in acute care agencies
Standing or Routine
PRN
Single one-time
STAT
Now
Prescriptions
Standing or Routine order
Administered until the dosage is changed or another medication is prescribed (ex: multivitamin)
PRN order
Given when the patient requires it ALWAYS will need a frequency and reason (ex: stool softener)
Single one-time order
Given one time only for a specific reason (ex: vaccine)
STAT order
Given immediately in an emergency (ex: epinephrin in a code situation)
Now order
When a medication is needed right away, but not STAT; can be looked at as urgent, but not emergent
Prescription orders
Medication to be taken outside of the hospital
Verbal orders (in person or telephone)
Avoid if possible→ cannot be performed by a student nurse
If you must take→ write on patients chart ASAP
Always do a “read back”
Don’t use abbreviations
State numbers individually
Ask prescriber to spell drug names that are unfamiliar or sound like another drug name
Similar names/labels
Ex:
Hydroxyzine is an antihistamine
Hydralazine lower blood pressure
Nurse’s Role
Medication administration requires knowledge and skill set unique to a nurse and “critical thinking” at each step of the way.
Medication knowledge
Patient assessment skills
Critical thinking regarding medication→ given patient diagnosis, exam, lab findings
Skill to correctly administer medication→ the “how to”
Knowledge to monitor the effects of the medication
Ability to evaluate/educate patient and family
Medication Knowledge
Any drug you give→ you are always expected to know what the drug is for, how it works, why its being given, what the usual does is, and the anticipated outcome.
Patient assessment skills
Is the patient able to safely take medication the route it’s ordered? → Mental status, swallow, currently NPO, Allergy, etc.
Is your patient allergic to medications ordered?
Vital sign assessment, Symptom assessment (PRN medication?)
Does the medication ordered make since?
Going to be able to manage regimen in anticipated care setting→ dexterity, vision, mental activity?
Administration Skills/ Medication Rights
Right Medication
Right Does
Right Route
Right Time
Right Person
Right Documentation
What is the first medication right?
Right Medication
What is the second medication right?
Right Does
What is the third medication right?
Right Route
What is the fourth medication right?
Right Time
What is the fifth medication right?
Right Person
What is the sixth medication right?
Right Documentation
When preparing medications…
Compare the medication to the MAR THREE times!!!
When preparing a medication from a bottle or container compare with the MAR:
Before removing from the drawer or shelf
As you remove the amount from the container
Before returning the container to the drawer or shelf
When preparing a medication with unit does or are pre-packaged compare with the MAR:
When taking the medication out of the dispensing system
Check the MAR to the label again
Verify all medications at the bedside with the MAR
Right patient?
Two identifiers always
Name
ID arm band
Bar codes on patient armband
Birthdate
Medical ID number
Right Medication?
RN responsible for comparing the prescriber’s written order with the medication administration record (MAR)→ “transcribing orders” or reviewing prescribers computerized orders
Need to complete a medication reconciliation whenever patients transfer from one care setting to another (home to hospital, NH to hospital, unit to unit in hospital, vice versa)
this is a comparison of the most recent medication list against the orders
NO drugs can be administered without an order→ not even the OTC drugs people take by themselves when at home
Never-Ever: right medication?
Never give medications someone else has prepared
Never give a medication you are not familiar with
Never ignore when a patient questions a medication (may be an error)
Never “borrow” medication from another patients bin
Every time you give a medication you are EXPECTED to know what drug you are giving, the usual dose, and the anticipated outcome you expect from it.
Right Dose?
you are always expected to know the usual dose of any medication you are giving
Check dose carefully! “0” always leads, never follows→ 0.5 mg, never 5.0 mg; 100000 or 100,000
Only break tablets scored by manufacturer
Error increases when preparing medication from a larger volume or strength than needed→ unit dose tries to address this
Know med calculations and conversions
Ask another qualified nurse to check calculated doses
Use standard measuring devices
Right Route?
Oral, inhalation, topical, vaginal, or rectal?
If it is an injection: IM, IV, or SubQ?
Right Time?
This can also be viewed as “frequency” or “when”
Understand why medication is ordered for a certain time and whether can be altered? → 3 times daily medications vs. every 8 hours
Understand STAT, now, “on call”, ac, once, etc.
Each agency will have standards on how close to scheduled time a medication should be given, ex: give all medications within 60 minutes (or 30?) of scheduled time.
Critical thinking is needed!
Right Documentation
Record→ record medication as soon as it is given
Leave→ never leave medications unattended at the bedside→ observe patient taking (avoids hoarding, abuse, or misuse of medication)
Document→ document after medication is given (never before)
Document→ Document pertinent assessment prior to giving medication when indicated (heart rate prior to rate control medication)
Assess/document→ assess/document the effectiveness and any adverse response of medication you gave
Document→ document if patient refuses a medication or if medication is held and why
Medication Errors
Most common: wrong medication, wrong dose (or failing to administer a medication) wrong route.
Best is to prevent errors: report potential errors (an error waiting to happen) and near misses (errors that were caught before reaching the patient)
Identifying a Medication Error
Best person to report an error is whoever discovered or witnessed it (remember you’re not reporting a peer for an error→ you’re reporting the error itself).
Legally and ethically the right thing to do for the patient’s safety→ check patient safety first and then notify the patient and provider of the error that occurred
Agencies vary in how to report→ most use an “incident report” and not documented in the patients chart
Value of incident reporting is that it looks at how the system failed and allowed the error to reach the patient→ thereby rectifying the underlying causes and making the medication use process safer for patients
Establishing a climate of trust is necessary
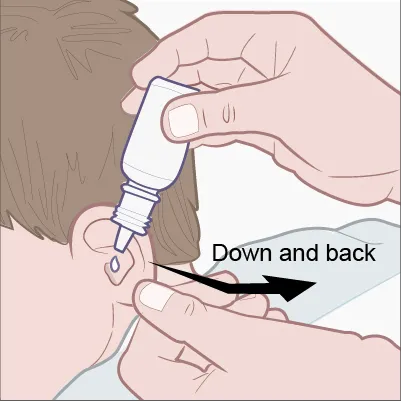
Instilling ear drops
Inserting a Rectal Suppository
Have the patient lie on their left side→ with their right leg pulled up towards their chest (maintain dignity)
APPLY GLOVES→ Remove suppository from package. Lubricate the tip of the suppository with either water or a water-based lubricant (ex: KY jelly)
Insert→ the lubricated tip of the suppository into the rectal opening
For adults, insert the suppository just past the internal rectal sphincter, which is about a finger length, and hold against the rectal wall for a few seconds (this will keep it in place)
What is missing from this order: Oxycodone 1 tab PO every 4 hours PRN
Dose and Indication
What is missing from this order: Ondansetron 4 mg tab for nausea or vomiting
Route and Frequency
Anatomy and Phys of Female breast
Extended vertically from second to sixth ribs; laterally from sternal margin to maxillary line. Normal to see some mild asymmetry.
Divided into 4 quadrants by vertical & horizontal lines intersecting at nipple.
Three types of breast tissue
Glandular tissue: Largest amount lies in outer quadrant of each breast→ could be why we see more breast cancers in this quadrant.
Where breastmilk is produced
Fibrous tissue
Subcutaneous & retromammary fat tissue
Tanner staging of breast development
Stages 1-5 of female breast development.
Tanner state 1
Preadolescent. Elevation of the papilla only.
Tanner stage 2
A small mount is formed by the elevation of the breast and papilla
Areolar diameter enlarges
Tanner stage 3
Further enlargement of breast and areola.
Tanner stage 4
Projection of the areola and papilla to form a secondary mound above the level of the breast.
Tanner stage 5
Mature breast
Areola recessed to the general contour of the breast
Anatomy and phys of Male breast
Male breast undergoes little development after birth; gland remains rudimentary
Consists of think layer of undeveloped tissue beneath nipple; areola small compared with that in female
During puberty, male breast may become slightly enlarged, producing temporary gynecomastia
Older men may also have gynecomastia (enlargement of male breast) secondary to decrease in testosterone.
Anatomy and phys Lymphatic system
Each breast contains extensive lymphatic network, which drains into lymph nodes:
More than 75% of lymph drainage is outward toward axillary lymph nodes, then upward to subclavicular and supraclavicular nodes.
Other drainage routes flow through:
Anterior axillae (pectoral) nodes above breast
Internal mammary nodes in thorax
Sub-diaphragmatic nodes toward abdomen and cross-mammary pathways ti opposite breast
Heath history: Subjective
Breast
Axilla
Family history
Heath history: Subjective→ Breast
pain
Lump
Discharge
Rash
Swelling
Trauma
History of breast disease
Surgery
Self-care behaviors
Breast self-examination
Last mammogram
Heath history: Subjective→ Axilla
tenderness, lump or swelling
Rush
Heath history: Subjective→ Family history
breast disease
Gynecological cancer
Female breast examination: Objective
Inspect both breast: note size, shape, contour, and symmetry
Inspect skin for color pigmentation, vascularity, surface characteristics and lesions
Inspect areolae for color and surface characteristics
inspect nipples for position, symmetry, surface characteristics, lesions, bleeding, and discharge
Male breast examination: Objective
Inspect breasts and nipples
Palpate breast and nipples
Palpate axilla
If any lumps present, Note:
Location→ quadrant and clock
Size→ cm
Shape→ round, oval
Consistency→ hard, soft
Mobility→ fixed or mobile
Distinctness→ clear borders
Nipple retraction
Overlying skin→ edema, dimpling
Tenderness→ painful or not
Lymphadenopathy
Fibrocystic Changes to Breast
Age range→ 20-49
Occurrence→ usually bilateral
Number→ multiple or single
Shape→ rounded
Consistency→ soft to firm; tense
Mobility→ mobile
Skin or nipple retraction→ absent
Tenderness→ usually tender
Borders→ well delineated
Variations with menses→ yes
Fibroadenoma
Age range→ 15-55
Occurrence→ usually bilateral
Number→ single; may be multiple
Shape→ rounded or discoid
Consistency→ firm, rubbery
Mobility→ mobile
Skin or nipple retraction→ absent
Tenderness→ usually non-tender
Borders→ well delineated
Variations with menses→ no
Cancer
Age range→ 30-80
Occurrence→ usually unilateral
Number→ single
Shape→ irregular or stellate
Consistency→ hard, stone like
Mobility→ fixed
Skin or nipple retraction→ often present
Tenderness→ usually non-tender
Borders→ poorly delineated; irregular
Variations with menses→ no
Gynecomastia
Enlargement of male breast tissue
Occasional and temporary in adolescent males but very distressing.
May occur in adult men with obesity, liver cirrhosis, and numerous medications
When is it best to preform a self breast examination?
just following menstruation cycle (day 4-7)
if no menstruation, note on the same day each month
Identifying suspicious signs/lumps?
retraction
dimpling
nipple changes
nipple discharge
changes in skin/surface characteristics
Female reproductive system: external genitalia
Mons pubis
Labia majora
Labia minora
Clitoris
Vestibule
Mons pubis
Adipose tissue covered with hair
Labia majora
Tissue folds that extend downward from mons, surround vestibule, and meet at perineum
Labia minora
Lies inside majora, are darker, smoother, hairless folds, divided into medial & lateral aspects
Medial meet superior to clitoris and prepuce to form cliteroal hood
Lateral meet inferior to clitoris to form frenulum
Clitoris
Small, cylindric bud of erectile tissue that is primary center of sexual stimulation
Vestibule
Lies between labia minora & contains: urethral meatus, introitus, hymenal tissue, bartholins, & shenes glands
Female reproductive system: Puberty
Breast bud development is the first physical change of female puberty
Adolescents experience menarche approximately 2 years after breast development
Growth spurt occurs about the time of menarche
Pubic hair development precedes axillary hair by about 2 years
Tanner staging
no pubic hair, only body hair
Sparse growth of long, slightly dark, fine pubic hair, slightly curly and located along the labia (ages 11-12)
Pubic hair becomes darker, curlier, and spreads over the symphysis (ages 12-13)
Texture and curl of pubic hair is similar to that of an adult but not spread to thighs (ages 13-15)
Adult appearance in quality and quantity of pubic hair; growth is spread to inner aspect of thighs and abdomen
Female reproductive system: Menopause
Decreased hormonal function
Changes associated with aging & estrogen depletion
One full year with no menses
Ovulation usually ceases 1-2 years before menopause
Male reproductive system: external genitalia
a pouch covered with thin, darkly pigmented, rugous skin, divided by septum into 2 sacs
Contains a testis and epididymis, suspended by spermatic cord, network of nerves, blood vessels, & vas deferens
Testes are suspended outside body because sperm production a temperature lower than body temperature
With cold temperature, scrotal sac & its contents move close to body; conversely, with rising temperature, scrotal sac relaxes & testes drop downward
Male reproductive system: internal structures
Testes
Urethra
Prostate gland
Bulbourethral glands
Testes
Paired sex organs located within scrotum, oval shaped, with a smooth surface and rubbery texture
Primary function of testes is production of perm (spermatogenesis)
Each testicle contains series of coiled ducts (seminiferous tubules), where spermatogenesis occurs
As sperm cells are produced, they move toward center of testes, traveling into efferent tubules adjacent to epididymis
Urethra
Inner most tube of penis; 7-10 inches (18-20cm) from bladder to meatus.
Extends out base of bladder, through prostate gland urethral orifice is small slit at tip of glands, into pelvic floor and through penile shaft
Terminal passageway for urine and sperm
During ejaculation, sperm travel away from ejaculatory duct, through urethra, & out of the body
Prostate gland
Lies beneath urinary bladder & surrounds upper portion of urethra
Posterior surface of prostate lies adjacent to anterior rectall wall & two of three lobes are palpable through rectum
Bulbourethral glands
On each side of urethra, just below prostate, empty directly into urethra
Health history questions: Male
Frequency, urgency, and nocturia
Dysuria
Hesitancy and straining
urine color
Past genitourinary history
Penis→ pain, lesion, discharge
Scrotum, self-care behaviors, lump
Impotence
Premature ejaculation
TSE
Prostate screening
Male reproductive system: puberty
First sign is enlargement of testes
Next, pubic hair appears, then penis size increases
Complete change in development takes around 3 years
Male tanner stage of development
Prepubertal, with no pubic hair
Scrotum and testes have enlarged and have more textured scrotal skin. growth of slightly pigmented downy hair is sparse
The penis has grown, especially in length. hair is darker and curlier
Further penile growth, in length and breadth, has occurred. Glans is larger and broader, and hair is adult in typer
The testes and scrotum are adult in size. Pubic hair is adult in quantity and pattern and present along the inner borders of the thighs
Male reproductive system: Aging
No definite end of fertility
Production of sperm decreases about age 40, but continues into 80’s and 90’s
After age 55 to 60 years, testosterone production declines
Prostates normally enlarges with aging
Rectum and anus: anatomy and physiology
Anal canal extends from anorectal junction to the anus and is lined with mucous membranes arranged in longitudinal folds called rectal columns containing network of arteries and veins, frequently referred to as internal hemorrhoidal plexus
Anus is terminal portion of rectum, located on perineum
Hairless, with moist mucosal tissue surrounded by hyper pigmented perianal skin, is normally closed except during defecation
Internal and external sphincter, two concentric rings of muscles, surround anal canal.
Internal sphincter consists of smooth muscle and is under involuntary control
External sphincter, consisting of skeletal muscle, under voluntary control, allows for control of delectation
bowels Health history: subjective
Describe bowel habits (frequency, appearance of stool). Pain or difficulty with defecation; excessive flatus, change in stools (color, consistency); problems with diarrhea or constipation; presence of blood in stool; hemorrhoids; use of digestive or evacuation aids (stool softner, laxatives, enemas)
Health promotion: use of dietary fiber supplements; colon cancer screening
Rectal examination
Tell the patient the advanced provider is going to perform rectal examination and that is may be uncomfortable.
Patient may feel pressure like a bowel movement
They will glove, then lubricate first two fingers of hand
Place their middle finger, palm side up, over anus
Ask patient to bear down
Gently insert middle finger into rectum
Insert index finger into vagina to locate cervix
Patient should assume either the left lateral position with hips and knees flexed, a knee-chest position, or standing position with hips flexed and patient bending over examination table.
The patient reports tenderness to the right breast-what should the nurse do next?
Perform OLD CARTS assessment
Patient reports a lump in the left breast- OLD CARTS completed amd no pain or change in size reported. upon palpation, feels rubbery. patient more than likely has.
Fibroadenoma