glaciation
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/72
Last updated 1:31 PM on 11/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
1
New cards
inputs
energy from the sun, precipitation, rock debris
2
New cards
outputs
meltwater, sediment deposition
3
New cards
transfers
erosion and transportation processes, which move ice and rock around the system
4
New cards
Steady-state equilibrium
changes in accumulation and ablation do not vary much from the long-term average conditions
5
New cards
metastable equilibrium
the glacier changes from one state of equilibrium to another due to an event causing a change in conditions
6
New cards
dynamic equilibrium
the state of equilibrium changes over a longer timescale than metastable equilibrium
7
New cards
positive feedback
increases the initial change: e.g
increase in snoww cover --> more solar energy, reflected, creating cooler temperatures --> more snow
increase in snoww cover --> more solar energy, reflected, creating cooler temperatures --> more snow
8
New cards
negative feedback
global warming increases evaporation and cloud cover --> more solar energy is reflected, creating cooler temperatures
9
New cards
eccentricity
elliptical orbit changes to more circular and back again over a 100,000 years, varying the amount of solar radiation reaching earth
10
New cards
axis tilt
varying from 21.8 to 24.4 over a period of 41,000 years, changing the amount of solar radiation at the poles
11
New cards
wobble
earth wobbles on its axis over a 20,000 year cycle, changing the time of year when it is closet to the sun
12
New cards
pleistocene (Quaternary period)
2.5 million - 11,500 years ago,
13
New cards
holocene (Quaternary period)
11,500 years ago to today, which is the present interglacial period
14
New cards
little ice age
glacial oscillation between 1350 and 1850
15
New cards
cold based glaciers
- occur in high latitudes
- ice temperature below pressure melting point
- basal ice is frozen to bedrock
- most movement by internal deformation
- little erosion due to lack of movement
- ice temperature below pressure melting point
- basal ice is frozen to bedrock
- most movement by internal deformation
- little erosion due to lack of movement
16
New cards
warm based glaciers
- occur in temperate regions
- temperature at base at pressure melting point
- heat from earth adds to melting
- meltwater assists movement of glacier
- actively eroding and transporting
- temperature at base at pressure melting point
- heat from earth adds to melting
- meltwater assists movement of glacier
- actively eroding and transporting
17
New cards
polythermal glaciers
cold-based in the upper region and warm-based lower down
18
New cards
shear stress
the downslope force due to gravity resulting from the build-up of an ice mass
19
New cards
internal deformation
intergranular flow - under pressure the ice crystals move relative to each other
laminar flow - ice crystals move along parallel layers within the glacier
laminar flow - ice crystals move along parallel layers within the glacier
20
New cards
basal sliding
enhanced basal creep - basal ice deforms around irregularities in the bedrock surface
regelation slip - basal ice deforms under pressure caused by obstacles; once past the obstacle the meltwater refreezes
regelation slip - basal ice deforms under pressure caused by obstacles; once past the obstacle the meltwater refreezes
21
New cards
subglacial bed deformation
softer rock and unconsolidated sediments are not strong, so the weight of the ice in a glacier can cause the sediments to deform. As the sediments change shape, the ice on top moves with them
22
New cards
compressional flow
a reduction in gradient results in a slowing of movement. The ice thickens, crevasses close and thrust faults develop in the ice
23
New cards
extensional flow
an increase in gradient results in accelerated movement. The ice thins and crevasses form
24
New cards
ice sheet
an ice dome, several kilometres thick, submerging the topography beneath
25
New cards
ice shelf
a large area of floating glacier ice extending from the coast
26
New cards
ice cap
a smaller version of an ice sheet covering an upland area
27
New cards
ice field
ice covering an upland area, but not burying topography
28
New cards
valley glacier
a glacier confined between valley sides
29
New cards
Piedmont glacier
a valley glacier that fans out over a flatter area at the end of the valley
30
New cards
cirque glacier
a small glacier filling a hollow on the side of a mountain
31
New cards
distribution of ice cover
today - 10% of earth's land area
85% of all glaciers are in Antarctica
85% of all glaciers are in Antarctica
32
New cards
freeze-thaw
repeated freezing and thawing of water, expanding cracks in rocks and eventually causing fragments to break off and fall on to the glacier
33
New cards
abrasion
debris embedded in the glacier base scrapes the bedrock as it moves
34
New cards
plucking
ice freezing on to valley sides, floor and bedrock pulls away rocks as it moves
35
New cards
subglacial fluvial erosion
meltwater flowing at the base of a glacier erodes rock the same way as surface streams. Pressure causes streams to flow faster, increasing erosion potential
36
New cards
factors affecting glacial erosion
- basal thermal regime
- ice velocity
- ice thickness
- bedrock permeability
- bedrock jointing
- debris characteristics
- ice velocity
- ice thickness
- bedrock permeability
- bedrock jointing
- debris characteristics
37
New cards
supra glacial
debris from weathering falls from valley sides onto the glacier
38
New cards
englacial
debris falls into crevasses and is moved within the glacier
39
New cards
subglacial
basal ice freezes around material and drags it along by traction. Englacial material moving to the base and plucking adds to the amount
40
New cards
ablation till
unsorted, angular material deposited by melting ice. Stones show no preferred orientation
41
New cards
lodgement till
rounded, subglacial material deposited by a moving glacier. The long axis of stones is orientated in the direction of movement
42
New cards
deformation till
weak bedrock is deformed by ice movement
43
New cards
terminal moraine
a high ridge across a valley deposited as a glacier retreats from the furthest point reached
44
New cards
recessional moraine
a series of ridges across a valley behind a terminal moraine, marking a stationary period in ice retreat
45
New cards
lateral moraine
weathered material falls on to a glacier from valley sides. When the ice melts it deposits a ridge parallel to the valley sides
46
New cards
medial moraine
two lateral moraines combine along the centre of glacier surface when valley glaciers merge. As ice melts it is deposited along the middle of the valley
47
New cards
push moraine
when glaciers begin advancing again, the debris at the snout is pushed into a ridge
48
New cards
erosion - fluvioglacial processes
subglacial streams are under pressure and fast flowing, eroding bedrock especially by abrasion
49
New cards
transportation - fluvioglacial processes
high-energy meltwater streams have the capacity to transport large sediment loads
50
New cards
deposition - fluvioglacial processes
when I loses energy it deposits material; rounder than glacial deposits, sorted by size, distinct layers
51
New cards
periglacial
the edges of glacial areas, where repeated freezing and thawing modify the landscape
52
New cards
permafrost
soil and rock that is below O degrees celsius for at least 2 years
53
New cards
continuous permafrost
a.layer of frozen ground that can be hundreds of metres deep
54
New cards
discontinuous permafrost
a thinner, fragmented layer of frozen ground
55
New cards
sporadic permafrost
an isolated mass of permafrost in unfrozen ground
56
New cards
active layer
the surface layer up to 3m deep, which thaws in summer and refreezes during the winter
57
New cards
pingos
a dome-shaped mound of earth up to 70m high and 500m in diameter, with an ice core
58
New cards
mass movement
the downward movement of materials due to gravity
59
New cards
rapid mass movement
rockfalls and landslides change the profile fo a glacial valley
60
New cards
rapid glacier melt
volcanic activity causes large-scale melting, resulting in flooding and rapid mudflows
61
New cards
Arête example
Helvellyn range
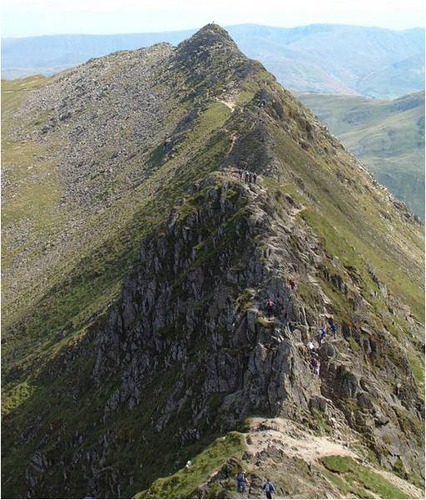

62
New cards
corrie/tarn example
red tarn

63
New cards
U shaped valley example
Ullswater valley
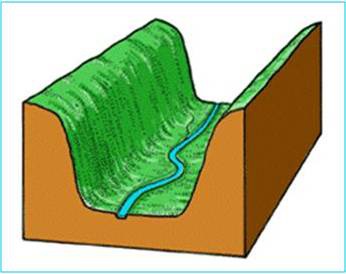
64
New cards
Ribbon lake example
Ullswater
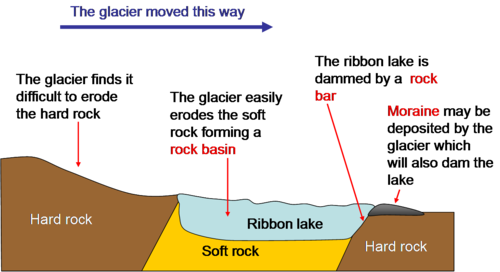
65
New cards
Roché mountonnée example
Norfolk island
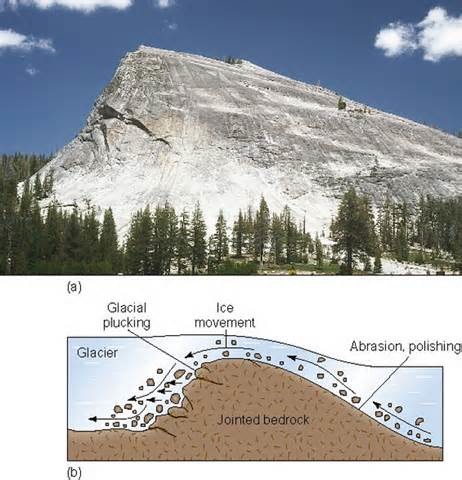
66
New cards
Truncated spur example
Walla crag
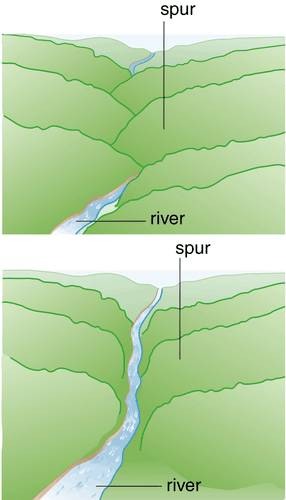
67
New cards
What countries were in the alpine convention 1995
8 countries
- France
- Switzerland
- Liechtenstein
- Italy
- Slovenia
- Austria
- Germany
- Monaco
- France
- Switzerland
- Liechtenstein
- Italy
- Slovenia
- Austria
- Germany
- Monaco
68
New cards
what are the 8 protocols of the Alpine convention
- mountain farming
- energy
- mountain forests
- conservation of nature + countryside
- Transport
- Tourism
- soil conservation
- spacial planning and sustainable development
- energy
- mountain forests
- conservation of nature + countryside
- Transport
- Tourism
- soil conservation
- spacial planning and sustainable development
69
New cards
Hohe Tauern - Austria
- largest protected area in alps
- Grossglockner glacier --> 3000m
- 4000 types of fungi
- 20,000 animal species
- Grossglockner glacier --> 3000m
- 4000 types of fungi
- 20,000 animal species
70
New cards
What is done to make Hohe Tauern sustainable
- donation of land use
footpaths well maintained
- Gardonna Mountain Resort --> eco hotel
- public transport = free
- protection of ski areas --> cow's graze in summer
footpaths well maintained
- Gardonna Mountain Resort --> eco hotel
- public transport = free
- protection of ski areas --> cow's graze in summer
71
New cards
GLOF
glacial lake outburst flood
72
New cards
impacts of GLOF's
affects fresh water, agriculture, livelihood
73
New cards
GLOF case study = Dig Tsho (Butan - 1994)
- increase in depth due to melting ice caused moraine dam to break
- village flooded 7 hours after dam break
- 2m deep, 200km away from source
- village flooded 7 hours after dam break
- 2m deep, 200km away from source