Pt 2. Physics - Forces and Motion
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Term 2 - Physics - turning forces, formulae and machines
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Tell me about levers.
You can move heavy objects using a lever.
You can move light objects using a lever.
A lever is a long bar that tuns around a fulcrum.
The object on the other end of the bar is called the load.
When you push down on one side, you are applying an effort.
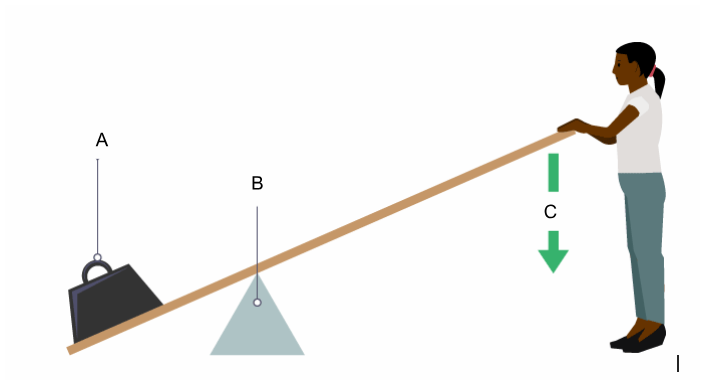
Label the diagram of Phoebe pushing down on a lever:
a = Load
b = Fulcrum/pivot
c = Effort
What is the pivot of a door?
The hinges
The longer the lever, the easier it is to move the load.
What else can be written in replace for the text in bold?
The further away from the pivot the effort/force is applied
What is a force multiplier (a) and what is a distance multiplier (b)?
a) a lever or other machine where the load is bigger than the effort.
b) a lever or other machine where the load moves further than the effort.
What is a moment?
The turning effect of a force.
What is the formula to work out the moment?
moment of a force = size of force × perpendicular distance from pivot
A spanner which is 0.2m long has a force of 20N applied to it. Calculate the moment of the turning force.
4 Nm
What is the pivot, machine and work done?
Pivot - the point around which movement occurs
Machine - anything that can help us to work with forces
Work done - energy transferred by a force when it makes something move
What is the benefit of using a ramp (an example of a simple machine)?
Less force is needed to push the object up the slope compared to lifting it directly.
Natalia is moving a box weighing 300N. She pulls it 3m along a sloping ramp using a force of 200N. Calculate the work Natalia does.
600 J
How do levers work?
Pivoting around a fulcrum so that a small force applied at a greater distance from the pivot can move a large load.
Why are ramps used?
Used to load heavy objects into trucks and to allow wheelchairs or cars to move up steps more easily.
What is the use of pulleys?
Used on cranes to lift heavy loads, on flagpoles to raise flags and on window blinds to move them up or down.
"A steeper slope requires a larger force to push an object up but over a shorter distance. A shallow slope requires a smaller force but over a longer distance."
True or false?
True
What is the formula for work done?
Work done = force × distance moved in direction of force
States three facts about pulleys.
Using multiple pulleys in a system increases the number of supporting ropes, spreading the weight of the object over several ropes.
More ropes = reduction of the force needed to lift the object (although the rope must be pulled a longer distance)
As energy is transferred by pulling the rope, it is transferred to the load/weight as a store of gravitational potential energy.
What is the difference between scalar and vector?
Scalar quantities have size (magnitude) only and no direction but vector quantities have both size and direction.
What is the difference between speed and velocity?
Speed is how fast something moves but velocity is speed with a direction.
How do you calculate a gradient (speed)?
change in distance ÷ change in time
What is the formula for acceleration (m/s²)?
change in velocity ÷ time taken (in seconds)
How is the area of a trapezium worked out?
0.5 x (a + b) x height
State the formula to work out the area of a triangle.
base x height x 0.5
How do you work out the are of a square or rectangle?
length x width
How do you work out the distance from a velocity-time graph?
Work out the area under the graph (the shape under the lines)
On a distance-time graph, what does a straight, horizontal line represent?
Motionless and no more distance is covered.
On a distance-time graph, what does the gradient tell us?
It tells us the speed.
On a distance-time graph, what does a steeper line indicate?
There is a higher speed.
yo
bro stop disturbing me
On a distance-time graph, what does a diagonal line going downwards indicate?
The object is returning to its starting point at a constant speed.
A fairy flutters in the air. She accelerates from 10 to 20 m/s with an acceleration of 2 m/s. How long did this take the fairy?
5 seconds