Primates: Taxonomy, Traits, Behavior, and Ecology
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
What kingdom do primates belong to?
Kingdom Animalia
What are the three major groups of mammals?
Placental mammals, marsupials, and monotremes.
What is a defining feature of the order Primates?
Primates have a high degree of grasping ability in hands and feet, characterized by opposable thumbs and big toes.
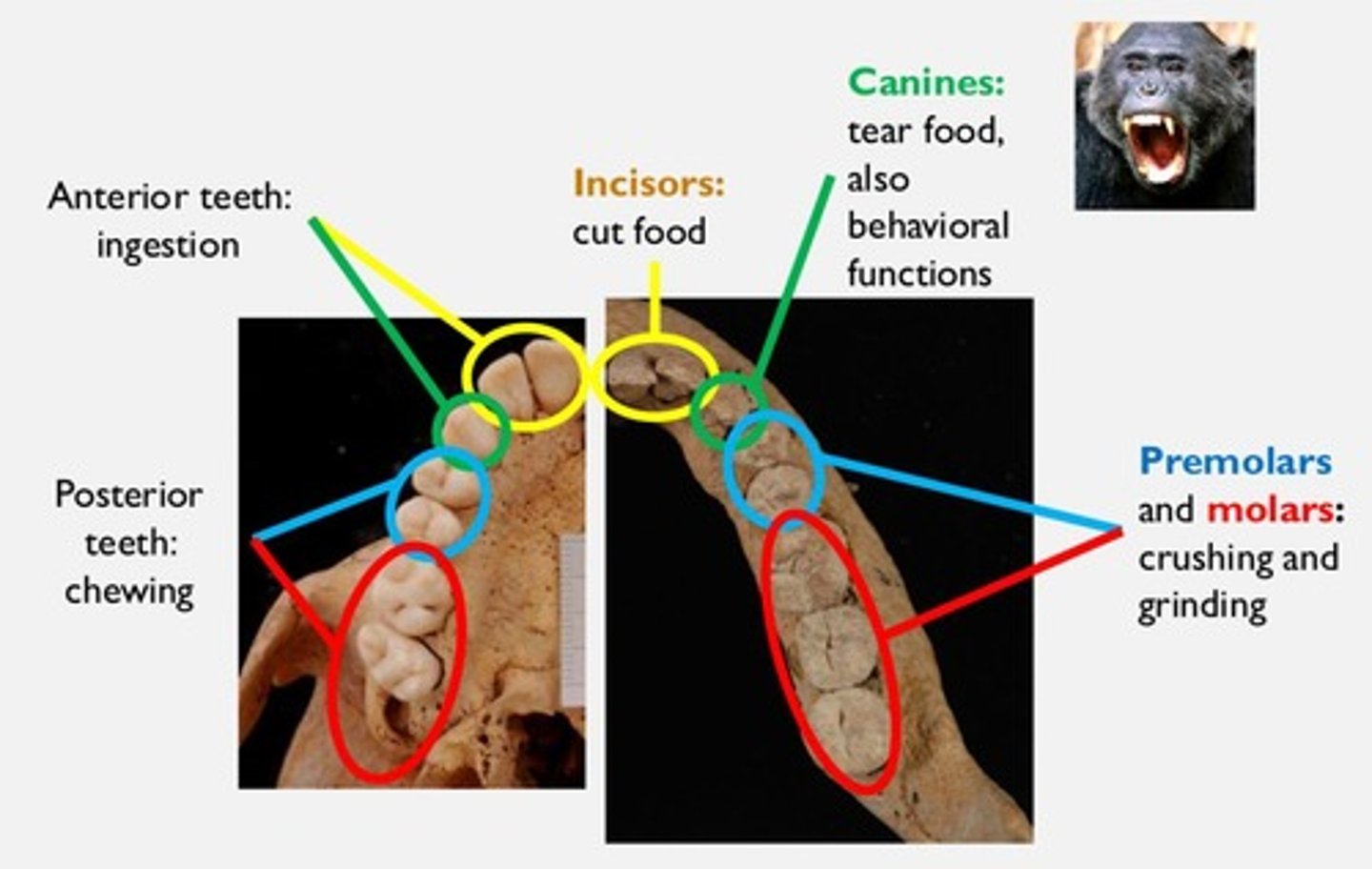
What are the three main types of teeth found in primates?
Incisors, canines, premolars, and molars.
What is the significance of the neocortex in primates?
The expansion of the neocortex is associated with advanced cognitive functions, including language.
What is the typical reproductive strategy of primates?
Primates typically have long gestation periods followed by live births and often invest heavily in their young.
What are some adaptations of primates for locomotion?
Primates exhibit quadrupedalism, vertical clinging and leaping, and brachiation.
What is the dental formula for ancestral mammals?
3-1-4-3, indicating the number of each type of tooth.
What distinguishes the suborder Strepsirhini?
Strepsirhines have a well-developed sense of smell and retain a rhinarium.
What are some characteristics of Haplorhini?
Haplorhines lack a tapetum lucidum, have reduced olfactory senses, and possess forward-facing eyes.
What is the typical social structure of primates?
Primates are often social animals that learn from group mates and maintain close social bonds.
What is the significance of the postorbital bar in primates?
The postorbital bar provides structural support for the eye socket and is a characteristic feature of primates.
How do primates typically differ in their activity cycles?
Primates can be nocturnal or diurnal, depending on the species.
What adaptations do primates have for different diets?
Primates have specialized teeth for processing various foods, such as sharp crests for insectivory and low cusps for frugivory.

What is the relationship between primate brain size and body size?
Primates generally have relatively large brains for their body size, which supports complex behaviors.
What is the role of grooming in primate social behavior?
Grooming helps to strengthen social bonds and maintain group cohesion among primates.
What is the significance of the generalized body plan in primates?
A generalized body plan allows for a variety of locomotor adaptations and ecological niches.
What is the primary difference between New World monkeys and Old World monkeys?
New World monkeys often have prehensile tails, while Old World monkeys do not.
What is the typical lifespan and developmental period of primates?
Primates generally have longer lifespans and extended developmental periods compared to other mammals.
How do primates exhibit reduced reliance on olfaction?
Primates have reduced olfactory regions in the brain and lack a moist rhinarium.
What is the ecological significance of primate diversity?
Primate diversity reflects adaptations to various habitats and ecological niches, influencing their roles in ecosystems.
What is the primary diet of folivorous primates?
Folivorous primates primarily eat leaves and have adaptations for processing tough foliage.
What is a unique feature of tarsiers among primates?
Tarsiers are nocturnal and have large eyes adapted for night vision.
What are some examples of derived traits in anthropoids?
Anthropoids typically lack a tapetum lucidum, have increased social complexity, and possess fused lower jaws.
What are the two major groups of monkeys?
New World monkeys (found in the Americas) and Old World monkeys (found in Asia and Africa).
What is a key characteristic of the body plan of monkeys?
Both groups show similarity in their general body plan related to quadrupedalism, with hind limbs and forelimbs of nearly equal length.
What distinguishes New World monkeys from Old World monkeys in terms of nose structure?
New World monkeys have broad noses with outward-facing nostrils, while Old World monkeys have narrow noses with downward-facing nostrils.
What is the dental formula for New World monkeys?
2.1.3.3 in each quadrant.
What is a common trait of many New World monkeys?
Some have prehensile tails, while none of the Old World monkeys do.
What is the typical social structure of marmosets and tamarins?
They are usually monogamous with one breeding female and exhibit intense female-female competition.
What is a defining feature of the great apes?
They have lost their tails, relatively large brains, and adaptations for suspensory posture and locomotion.
What are the three living species of orangutans?
Bornean orangutan, Sumatran orangutan, and Tapanuli orangutan.
What type of locomotion do gibbons primarily use?
Brachiation, which involves swinging from the arms.
What is a significant behavioral trait of chimpanzees?
They engage in cooperative hunting and tool use, and they have complex social structures.
What distinguishes bonobos from chimpanzees in terms of social behavior?
Bonobos often use sexual behavior to avoid conflict and have strong female bonding.
What are some major threats to ape populations?
Habitat destruction, disease, hunting, political instability, and the illegal pet trade.
What are the four main dietary categories for primates?
Fruits, insects, gums, and leaves.
How does body size correlate with diet in primates?
Insectivores tend to be smaller in body size, while folivores tend to be larger due to the need for complex digestion of fibrous leaves.
What is a home range in primate behavior?
The area that a group or individual uses over a given period of time, often tracked by primatologists.
What factors can predict a primate's home range?
Patterns of food distribution and the energy needs of the group or individual.
What is the significance of ischial callosities in primates?
They are adaptations found in some primates that provide support when sitting.
What type of vision do most New World monkeys have?
Most have dichromatic vision, while some have trichromatic vision.
What is the dental adaptation for insectivory in primates?
Sharp crests for puncturing the outer skeleton of insects.
What is the dental adaptation for folivory in primates?
Well-developed shearing crests for cutting tough leafy material into small pieces.
What are the two subfamilies of Old World monkeys?
Cercopithecoidea (including macaques and baboons) and Colobinae (dietary specialists on mature leaves).
What is the significance of tool use in chimpanzees?
It demonstrates their cognitive abilities and cultural behaviors, as they create and use tools to obtain food.
What is a unique social structure observed in chimpanzees?
They form multi-male, multi-female groups with complex hierarchies and social bonds.
What is the role of males in marmoset and tamarin social groups?
Males are principal caregivers, often helping to raise the young.
What is the significance of food seasonality in primate ecology?
Food seasonality affects food availability, with leaves being more abundant and predictable than fruits.
What are the two main types of competition for resources among primates?
1. Scramble competition: resources cannot be monopolized and are accessed on a first-come, first-served basis. 2. Contest competition: some individuals can monopolize resources, excluding others.
What are the costs of sociality for primates?
Greater competition for resources and increased vulnerability to infections and diseases.
What are the two main benefits of sociality in primates?
Enhanced access to resources and reduced vulnerability to predation.
What is the Resource Defense Model?
This model suggests that primates live in groups because they are more successful in defending access to resources than individuals.
What conditions make joint defense of food resources profitable according to the Resource Defense Model?
1. Food items are relatively valuable. 2. Food sources are clumped in space and time. 3. There is enough food within defended patches to meet the needs of several individuals.
What is the Predator Defense Model?
This model posits that group living evolved as a defense against predators, reducing vulnerability to predation.
How does group size relate to predation risk in primates?
Terrestrial species tend to form larger groups than arboreal species, as larger groups may reduce the risk of predation.
What is biological fitness in the context of primate reproduction?
Biological fitness refers to an individual's ability to survive and reproduce, impacting their reproductive success.
How do female primates increase their reproductive success?
Females can increase reproductive success by investing more energy into offspring or by being selective about mating with high-quality males.
What factors influence male reproductive strategies in primates?
Male reproductive strategies are influenced by competition with other males for access to fertile females and the distribution of those females.
What cognitive abilities are required for primates to track resource seasonality?
Primates need to remember locations of food, recognize group members, and remember reputations among group members.
What is social learning in primates?
Social learning allows primates to learn from one another through observation, imitation, and communication, increasing flexibility and reducing risk.
What are some examples of cultural traditions in non-human primates?
1. Chimpanzees use tools for termite fishing and hunting. 2. Orangutans pass down nest-building techniques from mother to offspring. 3. Capuchins create and use stone tools for opening nuts.
How does resource distribution affect female primate behavior?
Resource distribution predicts female distribution, influencing their interactions and dominance rank in access to preferred resources.
What is the impact of dominance rank on reproductive success in primates?
Higher-ranking individuals may have priority access to preferred resources, increasing their reproductive success.
What is the relationship between group living and competition among primates?
While group living can enhance access to resources, it also increases competition among group members.
What challenges does the Resource Defense Model face in explaining group living among folivores?
The model does not fully explain why folivores live in large groups under different conditions.
What is the significance of cognitive requirements in primate ecology?
Cognitive requirements are crucial for adapting to changing environments and resource availability.