Microbiology Lab
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Selective Media
specialized medium that contains ingredients that inhibit the growth of some microbes and encourage the growth of others.
Ex.Eosin methylene blue (EMB) contains methylene blue - toxic to Gram-positive bacteria, allowing only the growth of Gram-negative bacteria.
Differential Medium
A culture medium with an ingredient that certain microorganisms change in a recognizable way(visual); used to differentiate microbes based on their metabolic traits
The observed changes in appearance, such as color changes and gas generation, allow us to infer the metabolic processes of the microbe.
Ex.Some media can be defined as both selective and differential. For example, Mannitol salt agar (MSA) is selective for halophiles because of it's high salt concentration and differential for mannitol fermentation
Differential test
uses differential media to make observations of these metabolic processes.
Biochemical Test
are used to identify species of microbes by differentiating them on the basis of their biochemical activities.
Nutrient Utilization Tests
Highly defined media differentiates organisms on their ability to grow when an essential nutrient (carbon or nitrogen) is strictly limited
These tests involve differential media designed to differentiate organisms based on their ability to grow and utilize a particular nutrient. The by-products from the utilization of the nutrient will alter the appearance of the differential media allowing us to recognize that nutrient has been used.
For example, in the citrate utilization test when citrate is used by the microbe the media will change from a green color to a blue color.
Energy Metabolism Test
Heterotrophic bacteria obtain their energy by means of either cellular respiration or fermentation. Both convert the chemical energy of organic molecules to adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
In these types of tests, we can gather information on the organism's energy metabolism pathway by visualizing the change in the appearance of differential media caused by the products from the metabolic pathways.
Respiration Test
Cellular respiration involves three steps: glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain (ETC). Within cellular respiration, there are two types: aerobic and anaerobic. When the final electron acceptor at the end of the ETC is oxygen, the respiration type is aerobic.
When the final electron acceptor is a molecule other than oxygen (i.e., nitrate) respiration is anaerobic.
Fermentation Test
In contrast to cellular respiration, ________ only involves glycolysis to produce ATP and compounds of acids or alcohols, as well as, CO2. The specific by-products of fermentation depend on the specific organism and the substrate fermented.
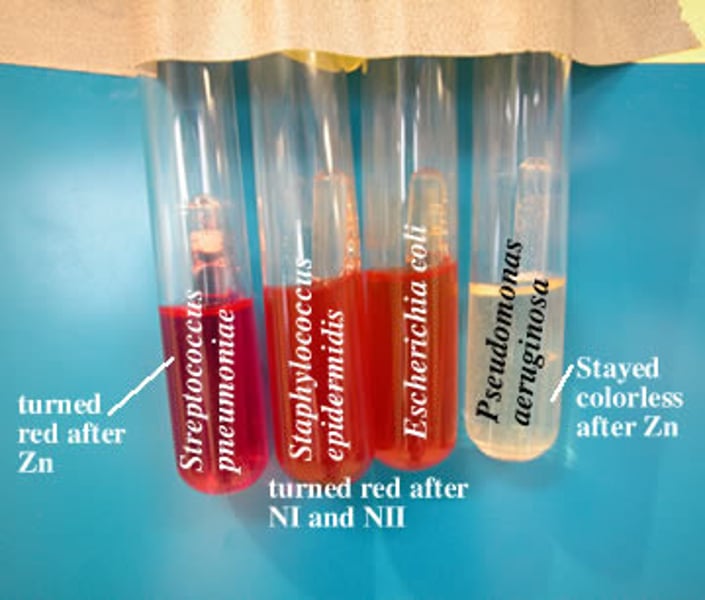
Nitrate Reduction Test
is a laboratory procedure used to determine if a bacterium can reduce nitrate to nitrite or other nitrogenous compounds, helping identify certain types of bacteria; it is a differential test because it distinguishes between bacteria based on their ability to perform this specific metabolic reaction.
the reagents ( are sulfanilic acid and naphthylamine)
Gas( Nonfermenter)= Dentritification- production of nitrogen gas )
Gas ( Fermeter)= Source of gas is unknown; requires the addition of reagents
Red Color ( after addition of reagents)= Nitrate to Nitrite (positive reagents)
No color change ( after addition of zinc)= Nitrate reduction to nongaseous nitrogenous compounds or Nitrate reduction occurred) (positive reagents)
Red color (after zinc)= No Nitrate reduction (negative result)
The enzyme is Nitrate Reductase

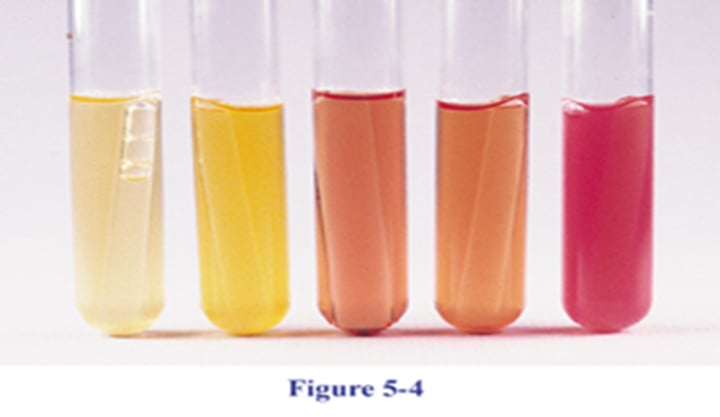
Phenol Red Broth
_____ _____ _____ is a liquid growth medium used to differentiate bacteria based on their ability to ferment carbohydrates, with phenol red serving as a pH indicator that changes color as the pH of the medium shifts due to fermentation; it is a differential medium as it helps identify organisms based on their fermentation patterns ( gases based on the Durham tubes)
Yellow Broth, bubble in tube= Fermentation with acid and gas end products
Yellow broth, no bubble in tube= Fermentation with acid end products; no gas produced
Red broth; no bubble in tube= No fermentation
Pink broth, no bubble in tube= Degradation/ Deamination of amino acids in peptone; alkaline end products
Yellow is below less than 6.8 pH
Pink to Magenta = greater than 7.4
Red is 6.8-7.4 ph
E. coli- Acid positve/ Gas positive
Bacillus subtilis- Acid positve/ Gas negative
A. faecalis- acid negative/ Gas negative
S. Saprophophticus- Acid positive/Gas negative

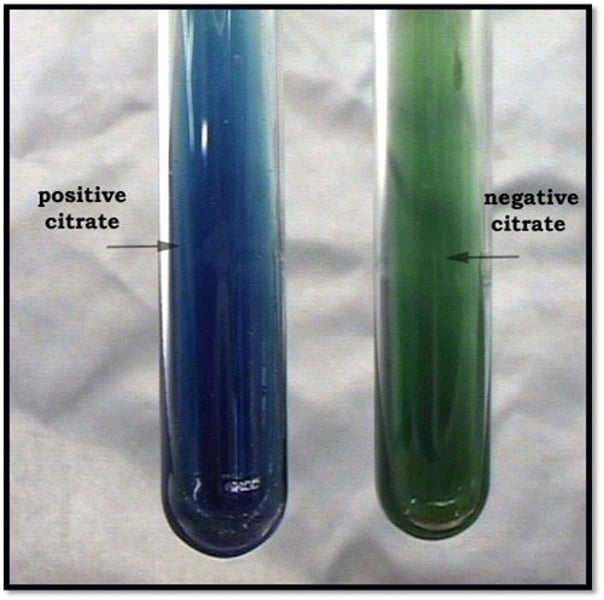
Simmons Citrate Agar
______ ______ ______is a type of bacterial growth medium used to test the ability of bacteria to utilize citrate as their sole carbon source;
it is both selective and differential, with its selectivity arising from the sole carbon source being citrate and its differential aspect based on the pH indicator bromothymol blue, which changes color in response to citrate utilization.
The enzyme( transport protein) is citrate permease which gets it into the cell and also allows for pyrvuate acid production and that's what changes the color
Green's pH=6.9
Blue's pH=7.6
Blue(even a small amount)= Citrate is utilized
No color change; no growth= Citrate is not utilized

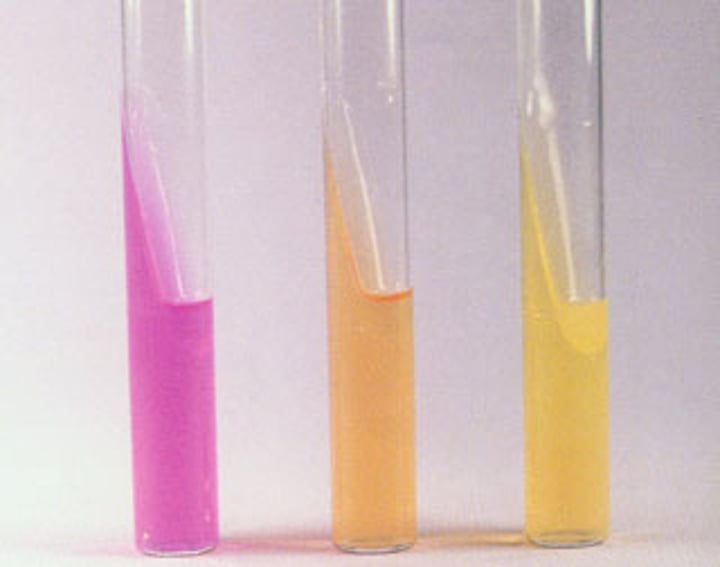
Urea Hydrolysis Test
Tests the ability of an organism to produce an exoenzyme, called urease, that hydrolyzes urea to ammonia and carbon dioxide
Testing for Urea production
it is primarily a differential test because it helps differentiate between urease-producing and non-urease-producing bacteria
All pink Rapid urea (24-48 hours) hydrolysis;= strong urease production
Begins turning pink( after a few days ) =Slow urea hydrolysis; weak urease production
Orange or yellow (After 72 hours )= No urea hydrolysis; urease is absent
yellow mean fermentation has happened
byproduct is ammonia

Handwashing Lab
We used Mannitol Salt Agar and Tryptic Soy Agar
Resident microbe is what consistently lives on the skin
Transient is was is easily taken off the skin
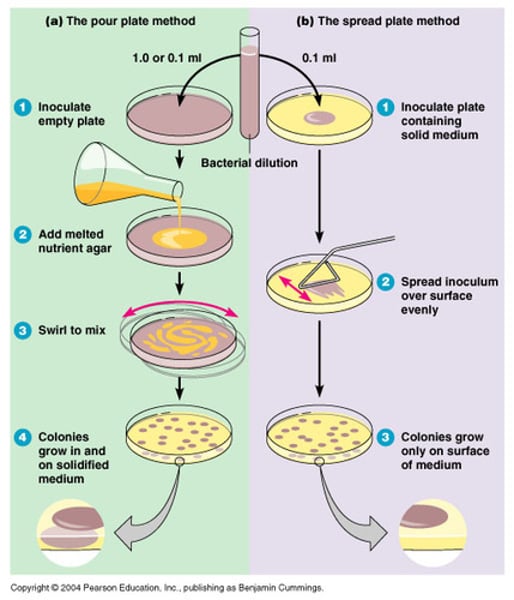
Mannitol Salt Agar Test
The ________ ______ _____ test is a microbiological test used to both select for and differentiate between bacterial species, particularly Staphylococcus aureus, based on their ability to ferment mannitol (a type of sugar) and their salt tolerance.
It is both selective ( means your gram-negative) and differential.
The ingredients that make it selective for halophiles, which inhibits the growth of many bacteria, and the differential ingredient is mannitol, which allows the differentiation of mannitol-fermenting and non-fermenting bacteria based on pH changes in the agar medium. ( meaning they are pathogenic)
Testing for pathogenic species
7.5 Sodium Chloride= only allows halophiles to grow
Mannitol- carbohydrate
Phenol Red- Ph indicator ( fermentation)
RESULTS:
Poor Growth or no growth; Organism is inhibited by NaCl; Not Staphylococcus
Good Growth; Organism is not inhibited by NaCl; Staphylococcus
Yellow growth or halo; Organism produced acid from mannitol fermentation; possible pathogenic Staphylococcus aureus
Red Growth ( no halo); Organism does not ferment mannitol. No reaction; Staphylococcus other than S. aureus
E.coli - no growth
S. aureus - yellow growth
S. epidermis is red growth
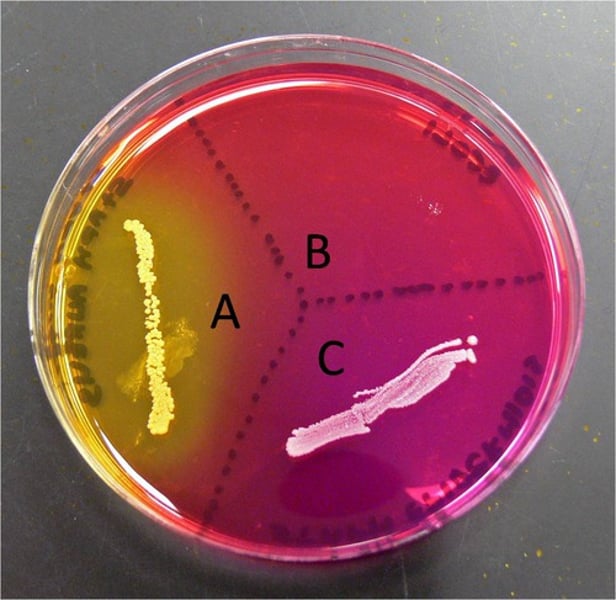
The Use- Dilution Test
a method of determining the effectiveness of a disinfectant using serial dilutions
You would want something that is clear and has no growth meaning that the it killed everything
it is not a selective or differential test but is designed to assess the disinfectant's general effectiveness in different dilutions.
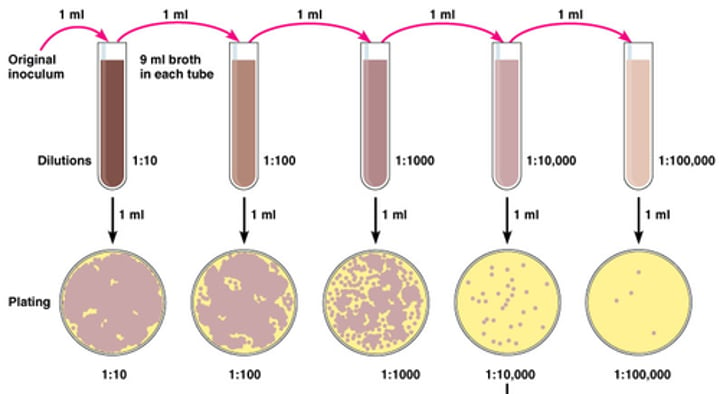
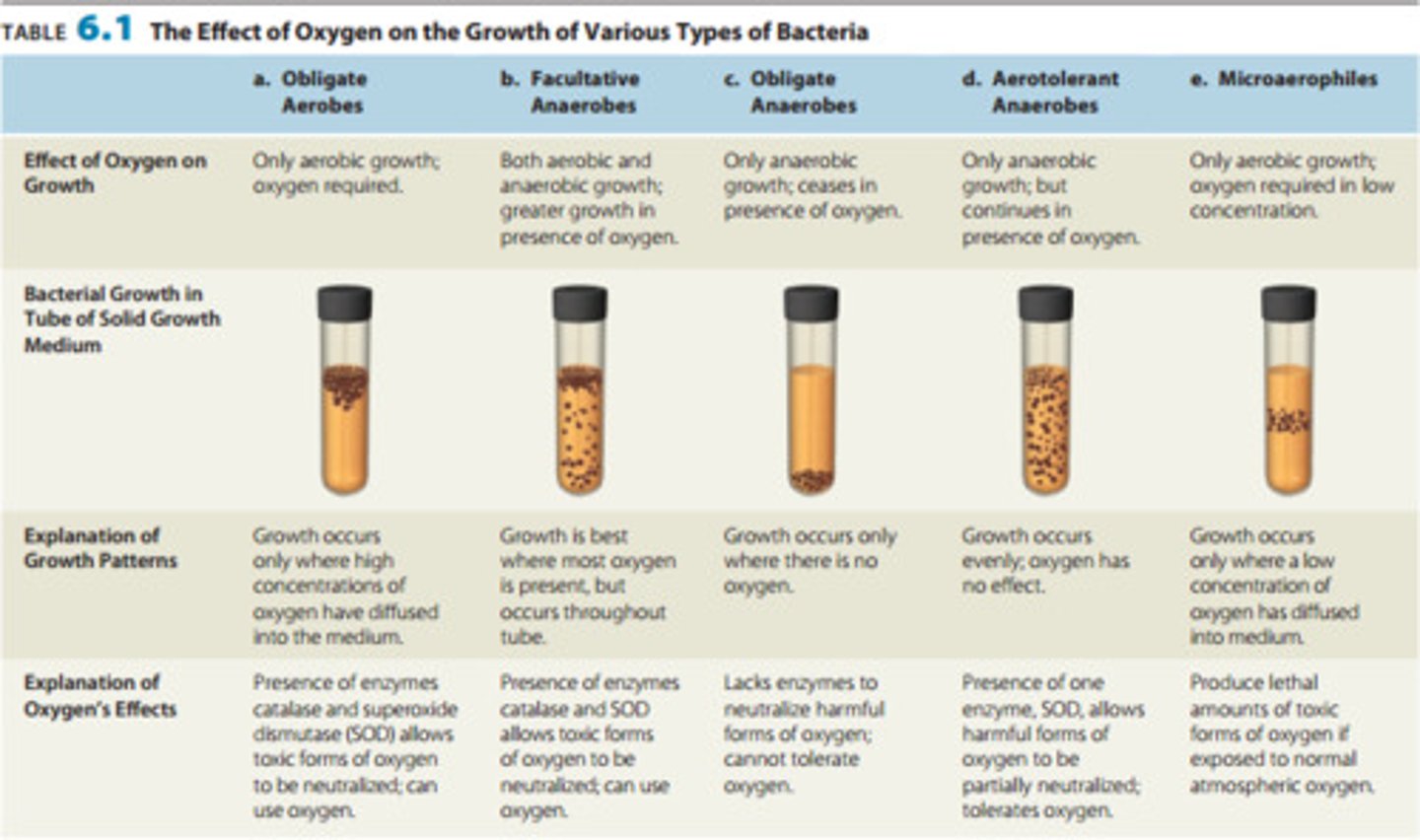
Different types of Aerobes
- *Aerotolerance:* Refers to an organism's ability to tolerate or thrive in the presence or absence of oxygen.
- Found through out-
- *Obligate Aerobes:*
- Grow only in the presence of oxygen.
- Found near the top of a test tube where oxygen is abundant.
- *Obligate Anaerobes:*
- Thrive in the absence of oxygen.
- Found at the bottom of a test tube away from oxygen.
- *Facultative Anaerobes:*
- Can grow with or without oxygen.
- Distributed throughout the test tube, but often more concentrated at the top.
- *Microaerophiles:*
- Prefer low levels of oxygen.
- Typically found in the middle of the test tube where oxygen concentration is moderate.
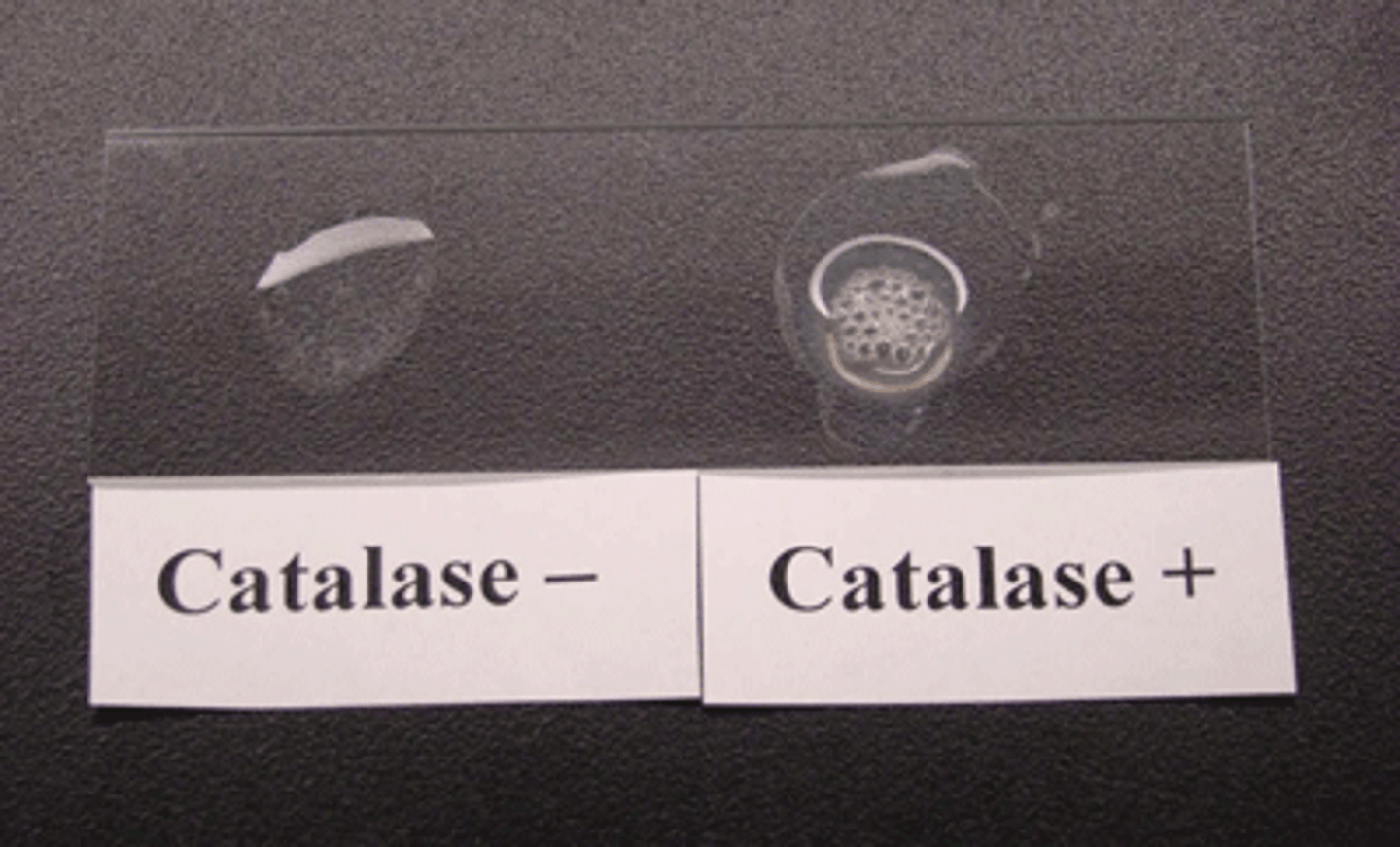
Catalase Test
-The _______ Test is a diagnostic laboratory test that determines the presence of the enzyme catalase in bacteria, helping differentiate between catalase-positive (enzyme present) and catalase-negative (enzyme absent) microorganisms;
- the purpose is to identify bacterial species and aid in the diagnosis of infections, especially distinguishing between staphylococci and streptococci; it is a differential test, and the important information is whether bubbles form when hydrogen peroxide is added
The Catalase will be present if it is Aerobic or Facultative Aerobic
Negative test means it is anaerobic
the flavo protein- is the electron carrier
S.Saphrosyticus- will have the catalase (+)
S.mutans- will not have the catalase(-)
Bubbles= Catalase is present
No bubble- Catalase is absent
Byproduct is water and oxygen gas
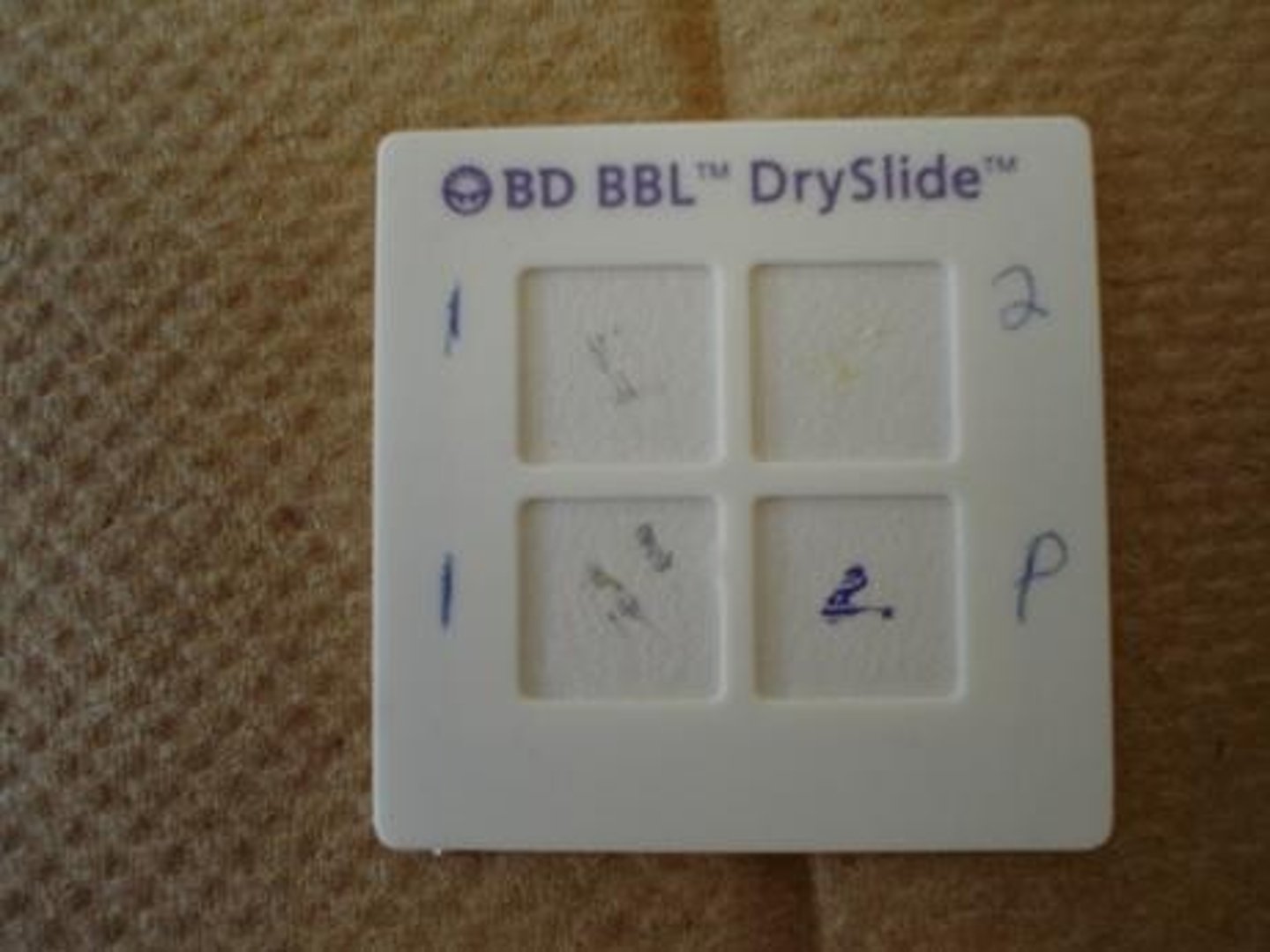
Oxidase Test
The _______ ______ is a laboratory technique used to determine the presence of cytochrome c oxidase ( the electron carrier) in bacteria, typically indicating the ability to respire aerobically; it involves applying a reagent to a bacterial sample, and the development of a purple color indicates a positive result.
A. faecalis- has a positive result
S. epidermis- has a negative result
The Oxidase Test is neither selective nor differential.
The slide has a chromogenic reducing agent which allows it to change color and donate electrons to cytochrome c
The media used for the Oxidase Test usually involves filter paper impregnated with the oxidase reagent.
Important info: A positive result in the Oxidase Test suggests the presence of cytochrome c oxidase, which is a key enzyme in the electron transport chain of aerobic respiration in bacteria.

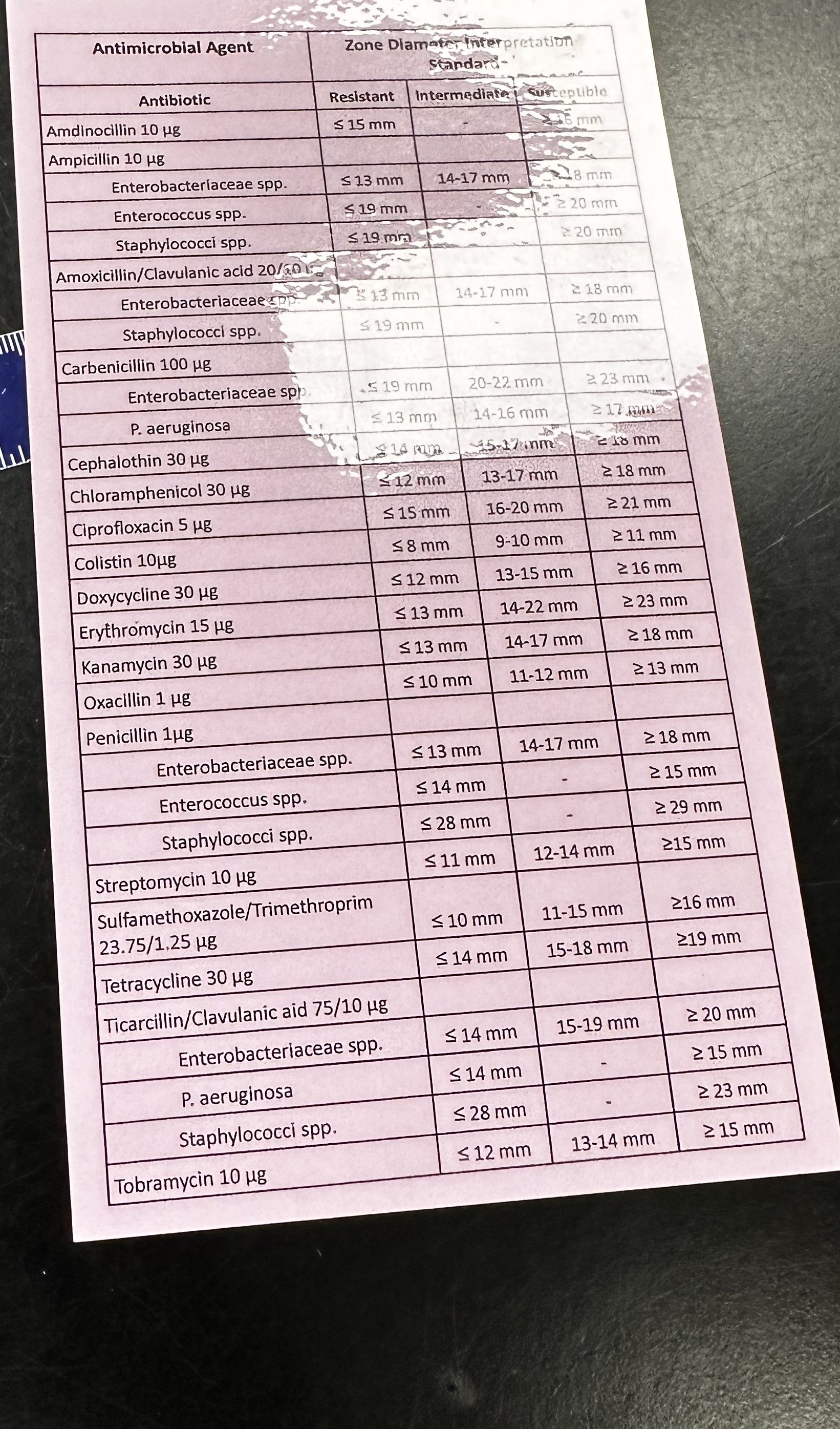
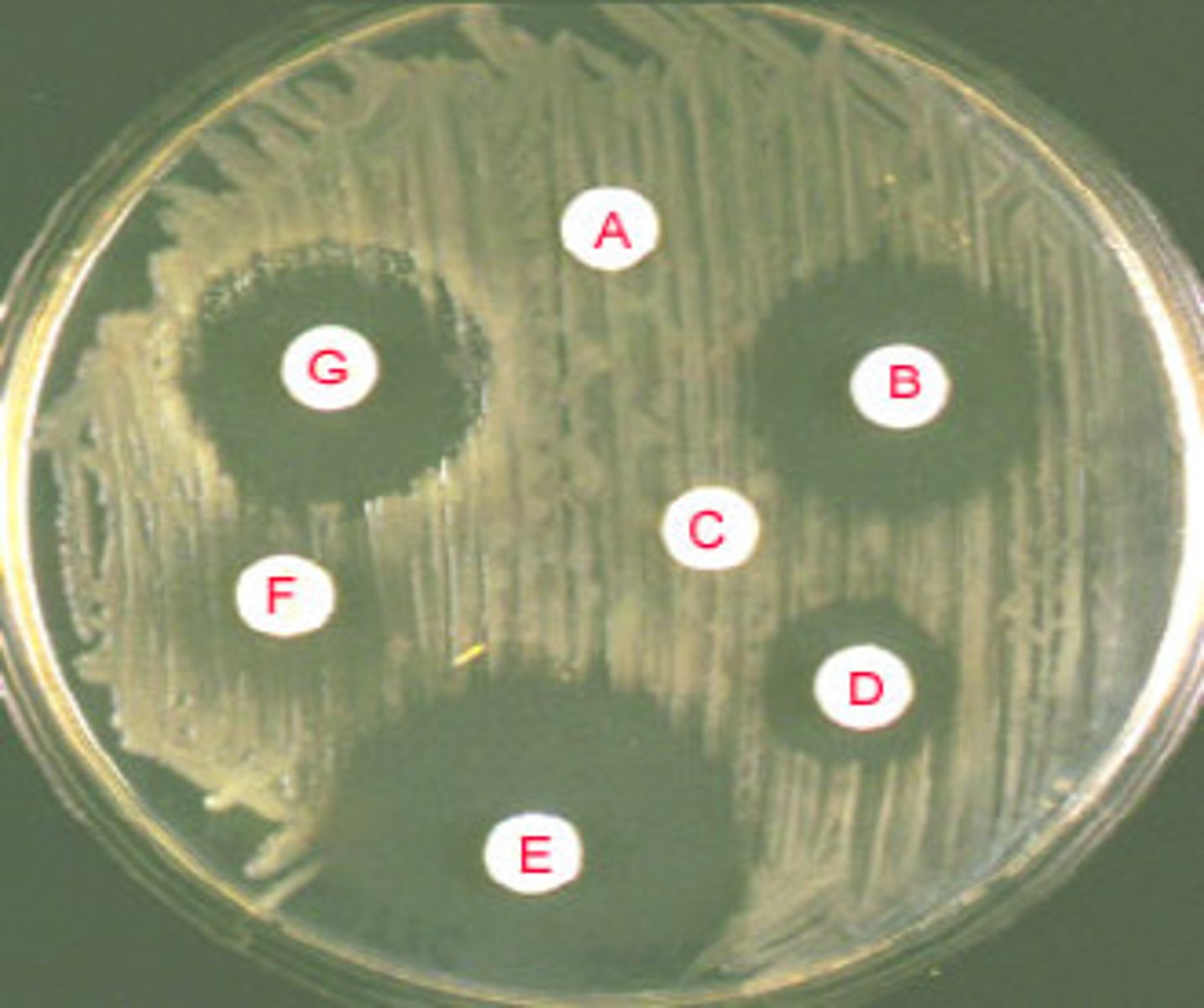
Kirby-Bauer Test
The _______ _______ test is a method used to determine the susceptibility of bacteria to different antibiotics by measuring the size of the zones of inhibition around antibiotic-impregnated disks on a nutrient agar plate; its purpose is to guide antibiotic selection for treatment, it is neither selective nor differential, and it contains no selective ingredients. Important information includes the specific antibiotics tested and the interpretation of zone sizes based on standardized guidelines.
Beta-Lactamase Test
penicillins and cephalosporins type of beta-lactam. The enzyme acts by breaking the beta-lactam ring, which is a common structural feature in these antibiotics.
What makes it stronger is the peptiodoglycan
Beta-Lactamase Test:
- Purpose: To detect the presence of beta-lactamase enzyme in bacterial isolates.
Interpretation of Results:
1. Positive Result (Pink Color): If the bacterial isolate produces beta-lactamase,
2. Negative Result (Yellow Color): If the bacterial isolate does not produce beta-lactamase, there will be no hydrolysis of the substrate, and the color remains yellow. YOU WANT IT TO BE NEGATIVE
Summary:
- Positive (Pink): Beta-lactamase production; the enzyme breaks down the substrate, leading to a color change.
- Negative (Yellow): No beta-lactamase production; no color change.