Kohlberg Piaget and Erikson's stages of development
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
3
How many levels?
6
How many stages?
3-7 yrs old
Ilang taon usually pag nasa preconventional morality?
Stage 1: Avoid punishment
Stage 2: What do I get out of this
Stages under Level 1 - Preconventional Morality
Stage 3: Good Boy/Girl
Stage 4: Obey the laws
Stages under Level 2 - Conventional Morality (8-13 yrs old)
Stage 5: Social contract & individual rights
Stage 6: Universal ethical principles
Stages under Level 3 - Postconventional Morality (13 and above)
The reason
What aspect did Kohlberg focus on?
Cosmic Stage
People consider the effect of their actions not only on other people but on the universe as a whole
T
(T/F) Just because a person is capable of moral reasoning does not necessarily mean the person actually engages in moral reasoning
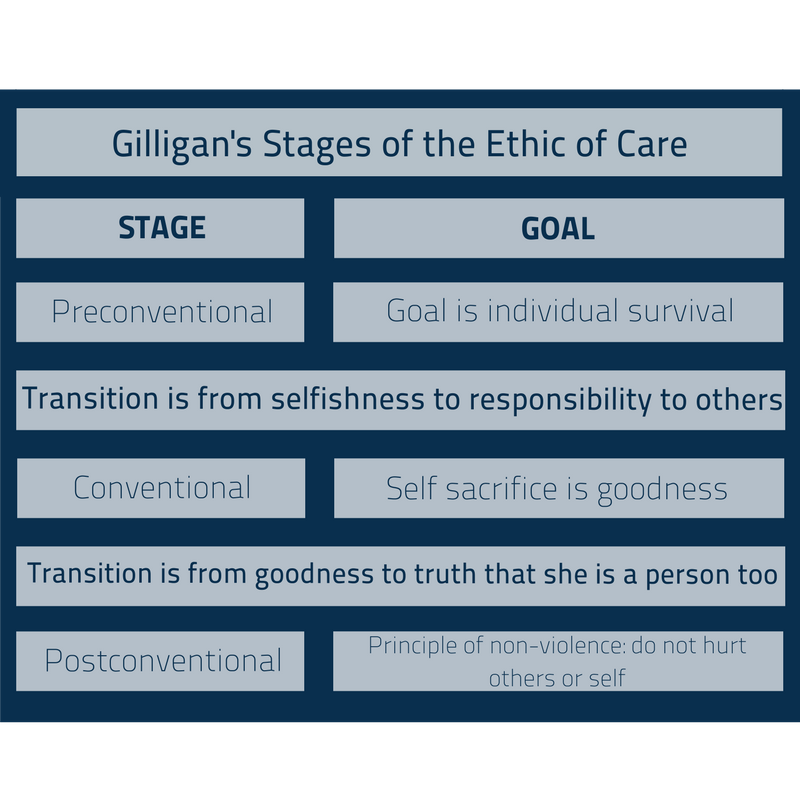
Carol Gilligan’s Stages of Ethic of Care
Heteronomous Morality (moral realism)
Piaget
Morality where the focus is on the outcomes/consequences
4-7 yrs old
Autonomous Morality (moral relativism)
Piaget
Moral reasoning where intent is the focus
10 yrs and older
Stage 1
Trust vs. Mistrust (Infancy):Infants develop a sense of trust if caregivers consistently meet their needs, leading to a belief that the world is safe and predictable.
Stage 2
Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt (Toddlerhood): Children learn to assert their independence and control over their bodies and environment, developing a sense of autonomy or experiencing shame and doubt if they are overly restricted.
Stage 3
3. Initiative vs. Guilt (Preschool):
Children begin to initiate activities, develop a sense of purpose, and gain confidence in their abilities, or they may experience guilt and self-doubt if they are discouraged.
Stage 4
Industry vs. Inferiority (School Age)
Children develop a sense of competence and self-worth through schoolwork, hobbies, and social interactions, or they may experience feelings of inferiority and inadequacy if they fail to meet expectations.
Stage 5
Identity vs. Role Confusion (Adolescence): Adolescents explore different identities and roles, seeking to determine who they are and what they want to do, or they may experience role confusion and a lack of direction.
Stage 6
Intimacy vs. Isolation (Young Adulthood): Individuals develop intimate relationships, including romantic partnerships and friendships, or they may experience isolation and loneliness.
Stage 7
Generativity vs. Stagnation (Middle Adulthood):
Adults focus on contributing to society and future generations, through parenting, mentoring, or creating a legacy, or they may experience stagnation and a lack of purpose.
Stage 8
8. Integrity vs. Despair (Late Adulthood):
Individuals reflect on their lives, accepting their accomplishments and failures with a sense of integrity, or they may experience despair and regret.