ECON 2020 EXAM 3
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study guide
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What is a Monopoly?
A monopoly is a market that produces a good or service for which NO close substitutes exists in which there is ONE supplier that is protected from competition by a barrier preventing the entry of new firms.
If a good has a close substitute, then
the firm effectively faces competition form the PRODUCERS of the SUBSTITUTE.
A constraint that protects a firm from potential competitor’s is called ________. What are the three different types?
barrier to entry; natural, ownership, legal
What is a natural monopoly?
is a market in which economics of scale enable one firm to supply the entire market at the lowest possible cost.
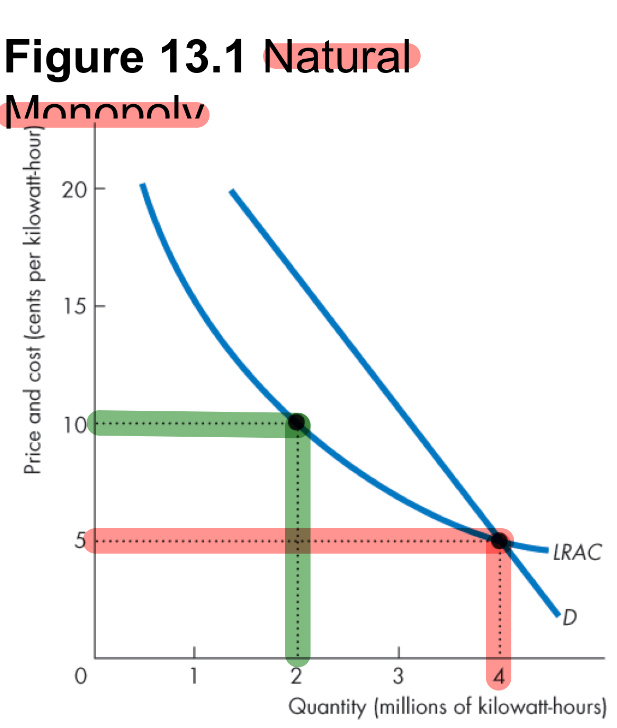
A LARGER production scale …
LOWERS average cost and is therefore inefficient to spread production over multiple firms. (may occur when there is a LARGER fix cost compared to marginal cost like in power production).
When does ownership barrier to entry occur?
If ONE firm owns a significant portion of a key resource.
Legal barriers to entry creates a __________.
Legal monopoly
What is a legal monopoly?
Is a market in which COMPETITION and ENTRY is restricted by the granting of a public franchise (like U.S. postal service), a government license, or a patent/ copyright.
For a monopoly firm to determine the quantity it sells, it must choose the appropriate price. What are the TWO types of monopoly price-setting strategies?
a single-price monopoly is a firm that must sell each unit of its output for the same price to all its customers.
price discrimination is the practice of selling different units of a good or service for different prices. (many firms price discriminate, but not all are monopolies)
what is total revenue?; what is marginal revenue?
(TR) is the price (P) multiplied by the quantity sold (Q).
Marginal revenue (MR) is the change in total revenue that results form a one-point