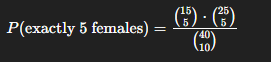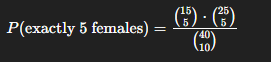Statistics Formula's 2025
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Basic Probability Rules
Possible values for probabilities range from 0 to 1
The sum of all the probabilities for all possible outcomes is equal to 1
Addition rule - the probability that one or both events occur
Multiplication rule - the probability that both events occur together
Conditional probability - the probability of an event happening given that another event has already happend
Addition rule - the probability that one or both events occur
Mutually exclusive events: P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B)
Not mutually exclusive events: P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A and B)
Mutuplication Rule - the probability that both events occur together
Independent events: P(A and B) = P(A) * P(B)
Dependent Events: P(A and B) = P(A) * P(B|A)
Conditional Probability - the probability of an event happening given that another event has already happened
P(A|B) = P(A and B) / P(B)
Bayes Theorem
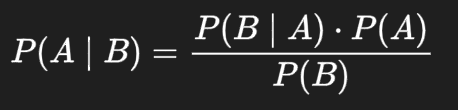
Covariance formula
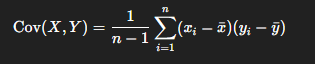
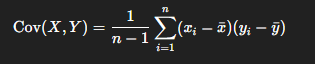
Correlation Formula’s
Formula 1:
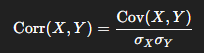
Formula 2:
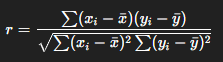
Skewness formula + interpretation
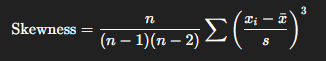
If Skewness > 0, it is a positive skew or right skew; tail is longer on the right side
If Skewness < 0, it is a negative skew or left skew; tail is longer on the left side
Hypergeometric Formula Probability
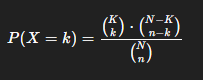
Use when calculating groups:
Committee of 40 people
15 Females, 25 Males
Calculate committee of 5 females and 5 males