Semester 2-Sports med Final
1/160
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
161 Terms
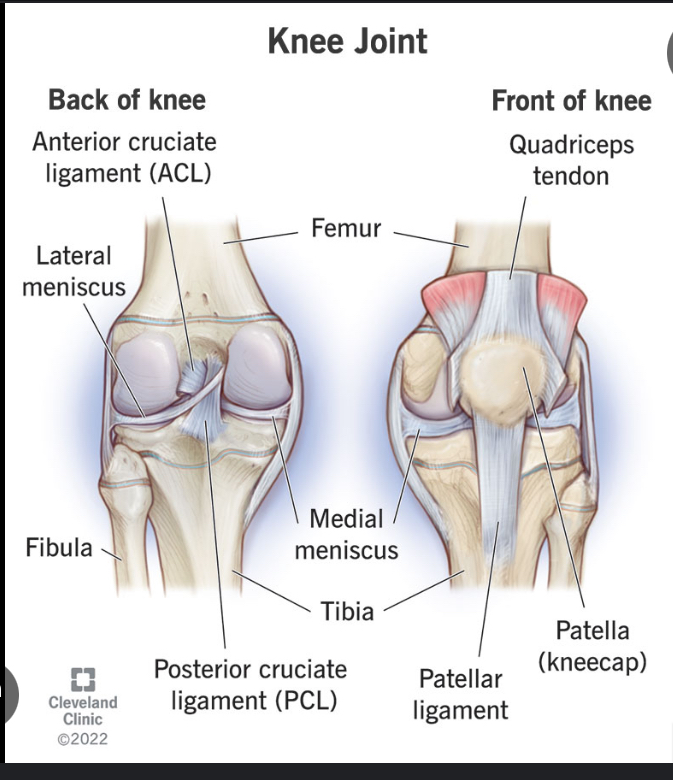
What does PCL stand for?
Posterior Cruciate Ligament
What are the functions of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament?
Stops anterior translation of the femur on the tibia in weight bearing
Stops posterior translation of the tibia on the femur in non weight bearing
Resists internal rotation
Resists hyperextension of the knee
What tendons make up the pes anserine?
joint tendon for the gracilis, sartorius, and semitendinosus muscle
What is the Infrapatellar fat pad?
Seperates the patellar tendon from rubbing on Tibia
What is the largest fat pad in the body?
Infrapatellar fat pad
What is normal flexion for the knee?
120-150 degrees
What is normal extension for the knee?
0 degrees
Overextension
Recurvatum-anywhere from 50-20 degrees
Tibia Internal Rotation
10 degrees
External Rotation
30-40 degrees
What does MCL stand for?
Medial Collateral Ligament
What else is the Medial Collateral Ligament known as?
Tibial Collateral Ligament
Function of MCL
Prevent knee valgus forces
Prevent external rotation
What does LCL stand for?
Lateral Collateral Ligament
What else is the Lateral Collateral Ligament known as?
Fibular Collateral Ligament
Function of Lateral Collateral Ligament
to resist knee varus forces
ACL stand for
Anterior Cruciate Ligament
ACL tear symptoms
Experience pop with severe pain and disability
Positive anterior drawer and Lachman’s
Rapid swelling at the joint line
Other ACL tests may be positive
ACL tear mode of injury
tibia externally rotated and valgus force at the knee (occasionally the result of hyperextension from direct blow)
What does PCL stand for?
Posterior Cruciate Ligament
Posterior Cruciate Ligament Mode of injury
Fall on bent knee
What is a PCL injury also known as?
Dashboard injury
Posterior Cruciate ligament Signs and Symptoms
Feel a pop in the back of knee
Tenderness and relatively little swelling in the popliteal fossa
Laxity with posterior sage test
Cruciate
Cross match
Intracapsular ligament
…
Extra capsular ligaments
…
What is the strongest ligament in the knee?
Posterior Cruciate Ligament
What is the longest muscle in the body?
Sartorius
What is the strongest bone in the body?
Femur
What bones make up the knee joint?
Femur
Tibia
Patella
What artery is the major blood supplier to the knee?
Popliteal artery
How many types of cartilage around found in the knee?
2 types
What are the types of cartilage found in the knee?
- Articular Cartilage (hyaline cartilage)
- Meniscus-medial and lateral (fibro-cartilage)
Articular Cartilage is also known as…
Hyaline Cartilage
Meniscus Cartilage is also known as…
fibro-cartilage
How many zones are in the meniscus?
3 zones
Describe the different zone levels of the Meniscus
• Zone 1 - vascular and closest to joint capsule
• Zone 2- in the middle of each ring and has minimal blood supply
• Zone3-Closest to center and is avascular
What else Zone 1 known as?
Red-red zone
What else is Zone 2 known as?
Red-White Zone
What else is Zone 3 known as?
White white zone
What does pes anserine mean?
“goose’s foot”
Quadriceps means
Four heads
Biceps means
Two heads
What is the major veins that drains the knee?
Popliteal vein
What is a Bursa?
Fluid filled sac
What type of injury causes effusion in 2-6 hours?
…
What type of injury causes effusion in 48-72 hours?
Meniscal Lesions
What is unique about a grade III MCL Sprain?
Most severe and complete tear of ligament
Grade III MCL Sprain Signs and symptoms
Complete tear of supporting ligaments
Complete loss of medial stability
Minimum to moderate swelling
Immediate pain followed by ache
Loss of motion due to effusion and hamstring guarding
Positive valgus stress test
What are the functions of the meniscus
To deepen the articular facets on the tibia
Act as a shock absorber.
Provide space between the tibia and femur
Help with knee stabilization, specifically when flexed
Elbow Articulations
Humeroulnar joint
Humeroradial joint
Proximal Radioulnar joint
What type of joint is the Humeroulnar?
Modified hinge joint
What sets of motion does the Humeroulnar joint perform?
Only 1 set of motion-flexion/extension
What type of elf joint is the Humeroradial?
Modified hinge joint
What sets of motion does the Humeroradial perform?
2 sets of motion-Flexion/extension and Internal rotation/external rotation
What sets of motion does the Proximal Radioulnar joint perform?
1 set of motion-Flexion/extension
What is normal extension for the Elbow?
0 degrees
What is normal flexion for the Elbow?
150 degrees
What is the normal range of motion for Supination/Pronation in the Elbow?
80-90 degrees
What structure is very superficial and susceptible to injury?
Olecranon Bursa
What artery is the main supply in the Elbow?
Brachial artery
Arterial Supply of Elbow
Brachial artery main supply
Branches to radial and ulnar arteries to supply blood to the forearm
What are the four major veins of the Elbow?
Medial cubital
Basilic
Cephalic
Brachial vein
What do all of the four major veins of the elbow drain into?
Axillary Vein
What are the ligaments of the elbow?
Ulnar Collateral Ligament
Radial Collateral Ligament
Annular Ligament
What else is the Ulnar Collateral Ligament known as?
Medial Collateral Ligament
The Ulnar Collateral Ligament supports against the…
valgus force
What else is the Radial Collateral Ligament known as?
Lateral Collateral Ligament
The Radial Collateral Ligament resist against the…
varus stress
What movements does Annular Ligament help?
Internal rotation and External rotation of the radius/ulna
Annular Ligament Fibers
Anterior fibers are taut with supination
Posterior fibers are taut with hyperpronation
What is the normal carrying angle?
Elbow demonstrates a carrying angle due to distal projection of humerus
What is the normal carrying angle in females?
10-15 degrees
What is the normal carrying angle in males?
5 degrees
Who was the team physician that operate on Tommy John?
Dr. Frank Jobe
What is Tommy John Surgery?
Surgical procedure to repair the Ulnar Collateral Ligament in the elbow
What structure is temporarily moved during Tommy John Surgery?
The Ulnar Nerve
What structure is used for Tommy John Surgery?
Palmaris Longus
What are the nerves of the elbow?
Median Nerve
Radial Nerve
Ulnar Nerve
What arteries does the Brachial Artery branch off into?
Radial and Ulnar Arteries
Where is the Subcutaneous Olecranon Bursa located?
Between the skin and Olecranon
What is the role of the UCL in the forearm?
Holds together the Ulna and Humerus
Who was the second elbow surgeon to perform Tommy John Surgery?
Dr. James andrews
What percentage of all current major league pitchers have had Tommy John surgery?
33%
What is the success rate of Tommy John surgery?
Over 80%
Bennett’s Fracture
Etiology
Occurs at carpometacarpal joint of the thumb as a resul of an axial and abduction force to the thumb
Signs and symptoms
CMC may appear to be deformed-X ray will indicate fracture
Athlete will complain of pain and swelling over the base of the thumb
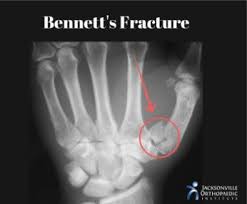
Bennetts Fracture Management
Structurally unstable and must be referred to an orthopedic surgeon
Surgery and immobilization-season ending
Bikers Palsy
Ulnar Nerve compression
Bikers Palsy Management
padding (Gloves), ICE, NSAIDs
Boutonniere Deformity
Rupture of extensor tendon dorsal to the middle phalanx-bone passes through central slip
Forces DIP joint into extensions and PIP Joint into flexion
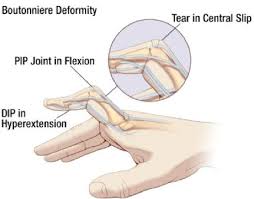
Boutonniere Deformity-Management
Cold application, followed by splinting in PIP extension and DIP flexion
Splinting must be continued for 5-8 weeks
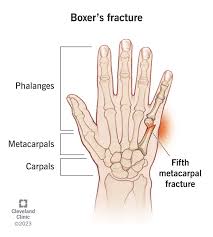
Boxer’s Fracture
Fractures of 5th metacarpal
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Compression of Median Nerve
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome-Special Tests
Tinel’s sign and Phalen’s
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome-Mangement
Conservative (PRICE, NSAIDs) and Surgical
deQuervain’s Disease
Stenosing(narrowing) tenosynovitis of the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus.
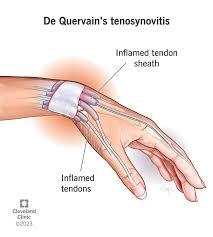
deQuervain’s Disease-Special Test
Finklestein’s test
deQuervains Disease-Management
RICE, NSAIDs
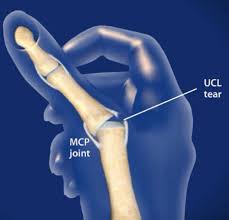
Gamekeepers Thumb
Etiology
Sprain of UCL of MCP joint of thumb
Mechanism is forceful abduction of proximal phalanx occasionally combined with hyperextension.
Signs and symptoms
Pain over UCL in addition to weak and painful pinch
Management
Immediate follow up must occur
Thumb splint should be applied for protection for 3 weeks
Splint should extend from wrist to end of thumb in natural position
Surgery may be required
Jersey Finger
Etiology
Rupture of flexor digitorum profundus tendon from insertion of distal phalanx
Often occurs with ring finger when athlete tries to grab a jersey
Signs and Symptoms
PIP can not be flexed, finger remains extended
Pain and point tenderness over distal phalanx
Management
Must be surgically repaired
Rehab requires 12 weeks and tehre is often poor gliding of tendon with possible of re-repture
