Lower Limb pt. 1 (Femur)
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
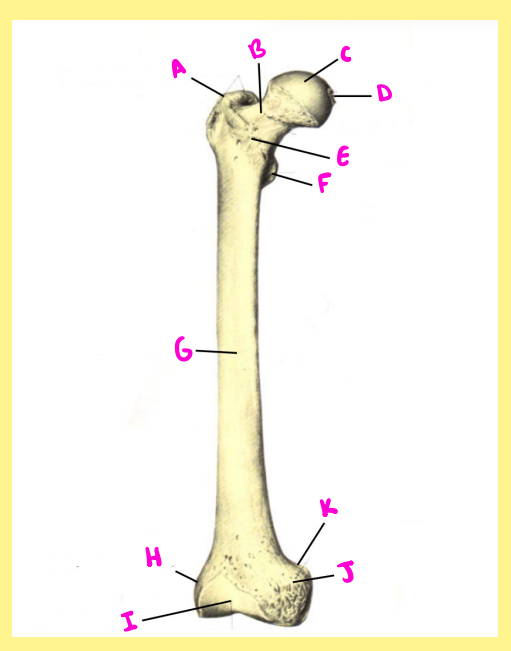
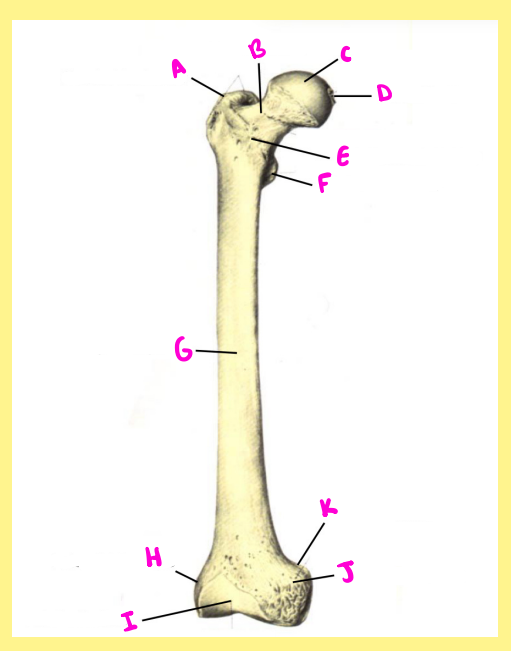
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
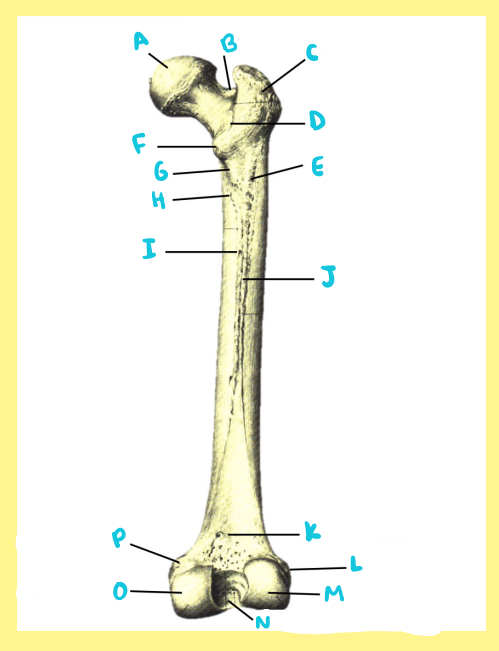
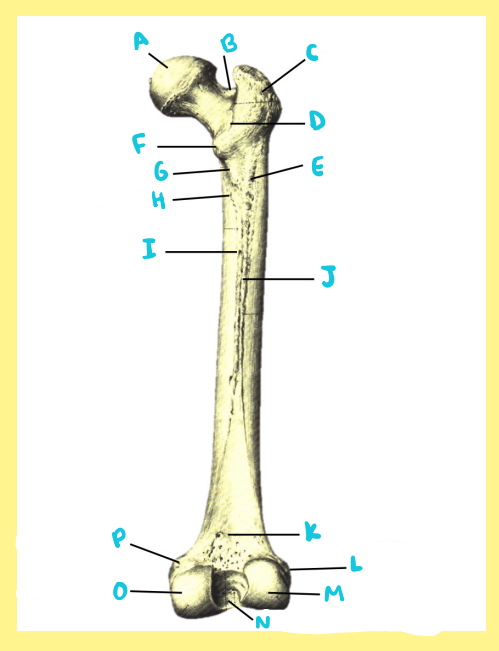
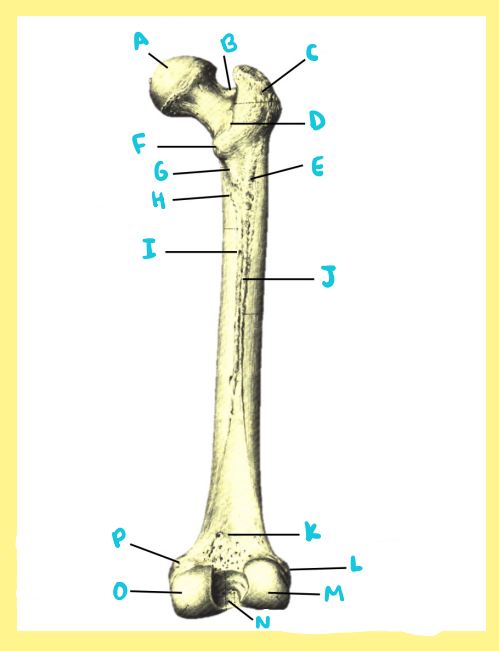
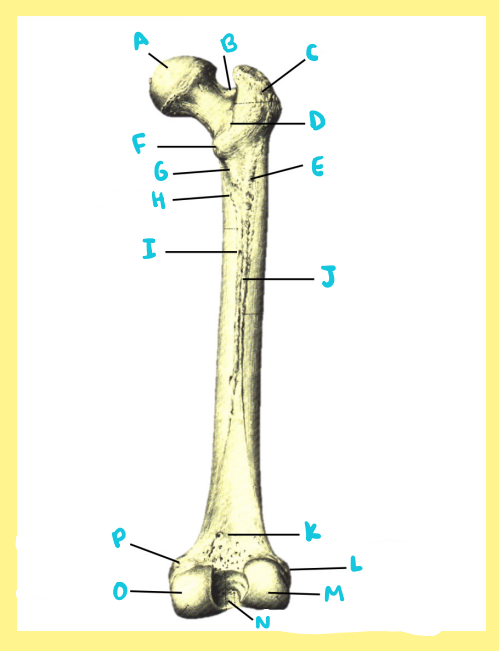
A?
femur, right, anterior, greater trochanter
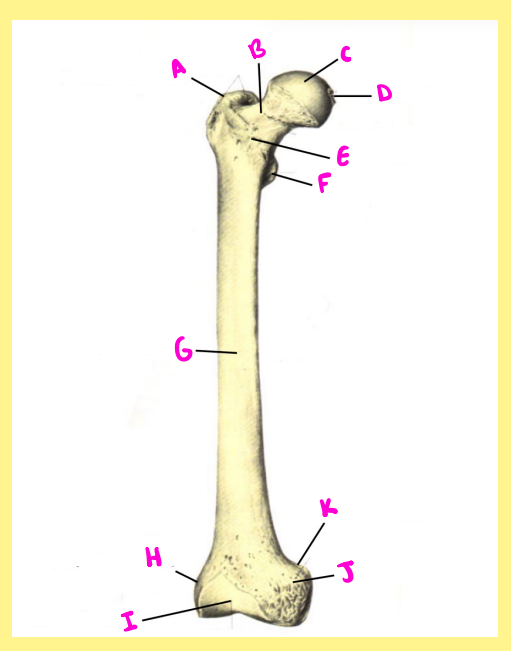
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
B?
femur, right, anterior, femoral neck
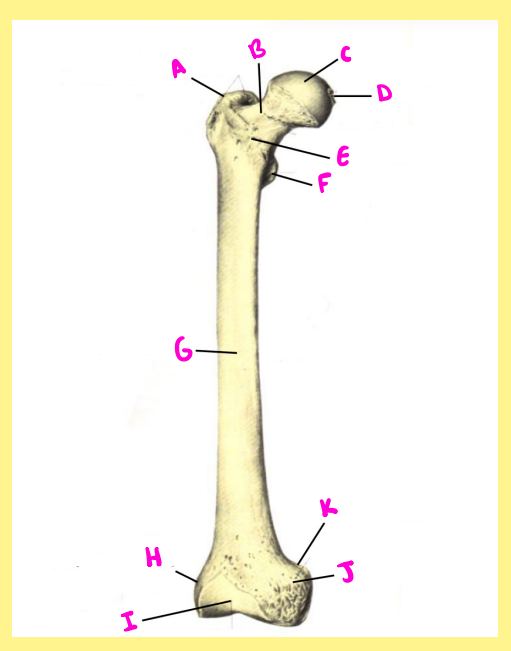
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
C?
femur, right, anterior, femoral head
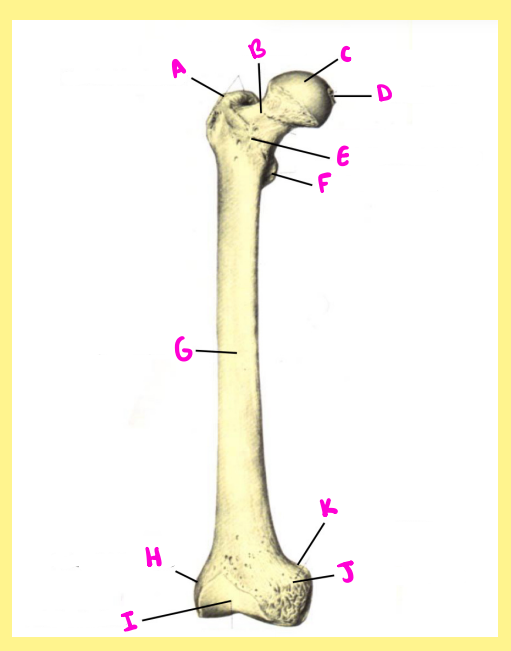
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
D?
femur, right, anterior, fovea capitis
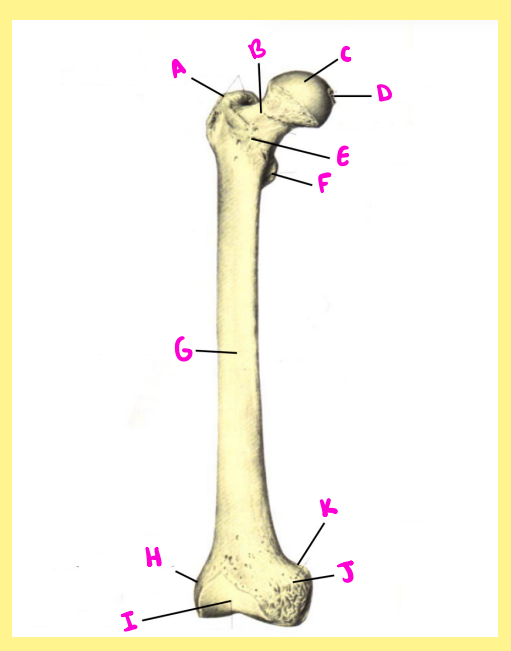
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
E?
femur, right, anterior, intertrochanteric line
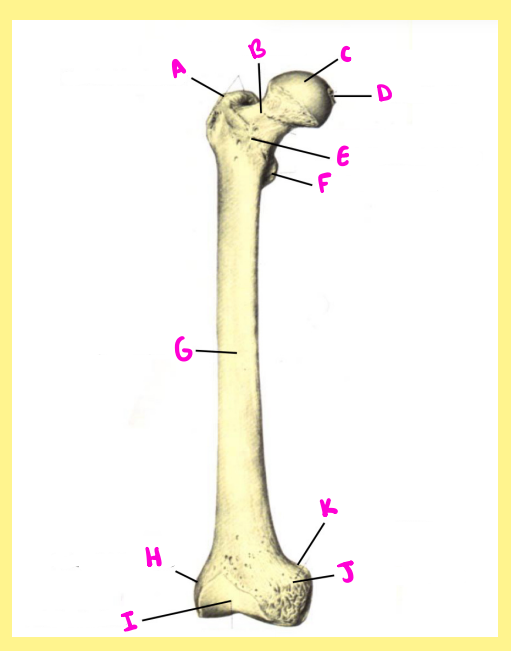
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
F?
femur, right, anterior, lesser trochanter
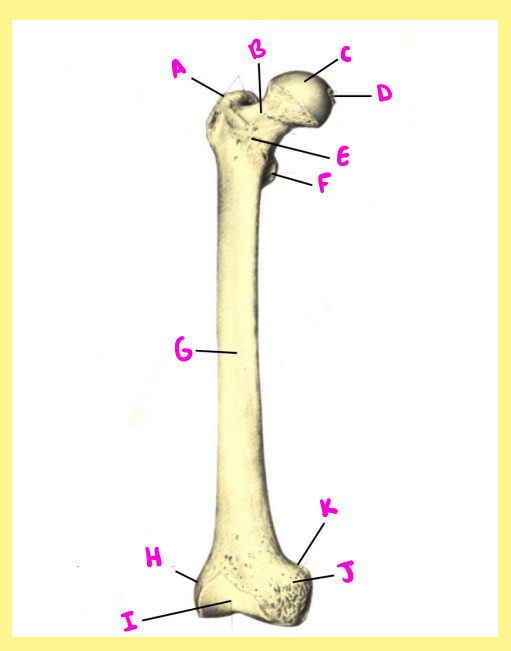
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
G?
femur, right, anterior, femoral shaft
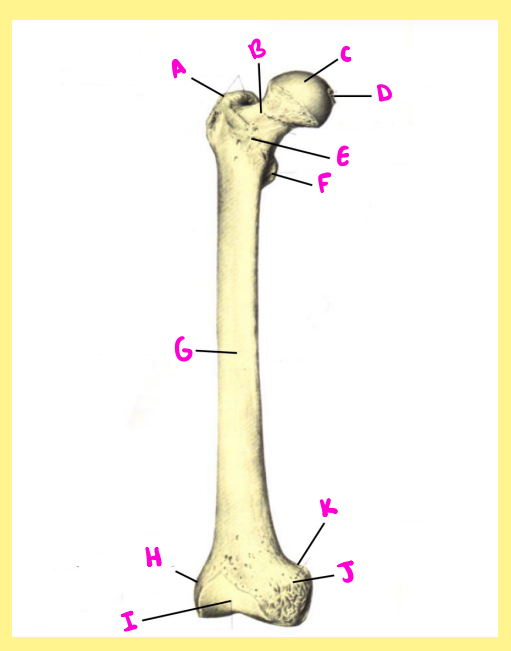
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
H?
femur, right, anterior, lateral epicondyle
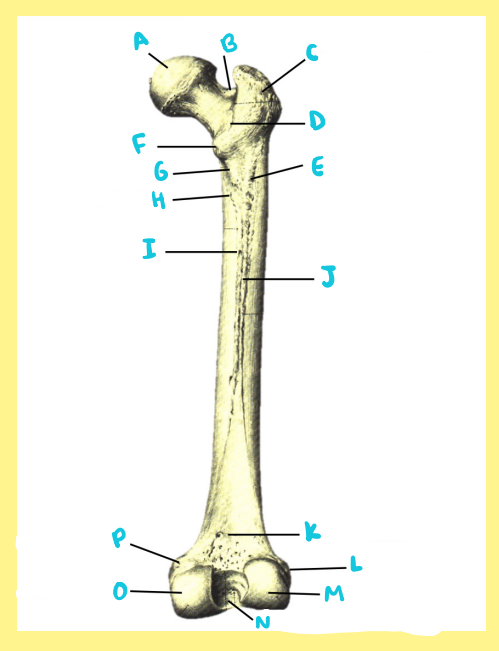
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
I?
femur, right, anterior, patellar surface
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
J?
femur, right, anterior, medial epicondyle
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
K?
femur, right, anterior, adductor tubercle
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
A?
femur, right, posterior, femoral head
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
B?
femur, right, posterior, trochanteric fossa
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
C?
femur, right, posterior, greater trochanter
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
D?
femur, right, posterior, intertrochanteric crest
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
E?
femur, right, posterior, gluteal tuberosity/line
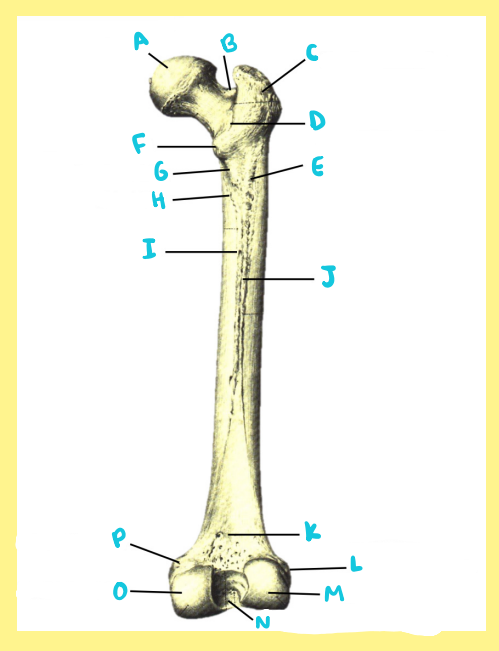
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
F?
femur, right, posterior, lesser trochanter
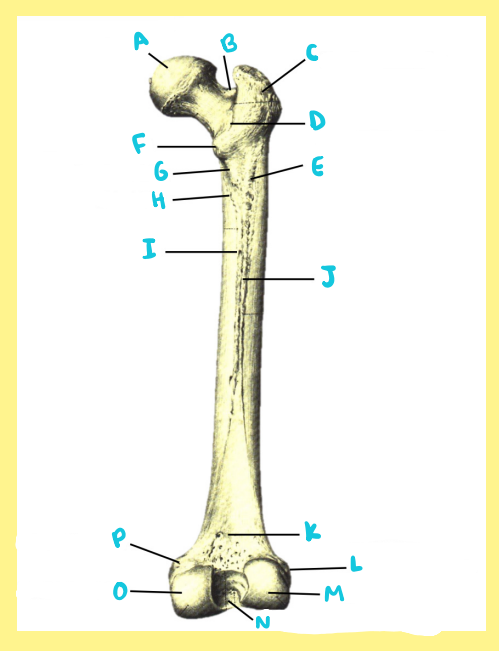
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
G?
femur, right, posterior, pectineal line
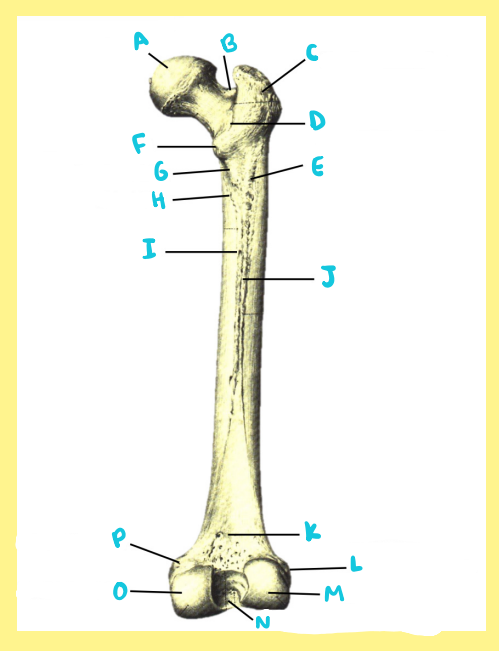
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
H?
femur, right, posterior, spiral line
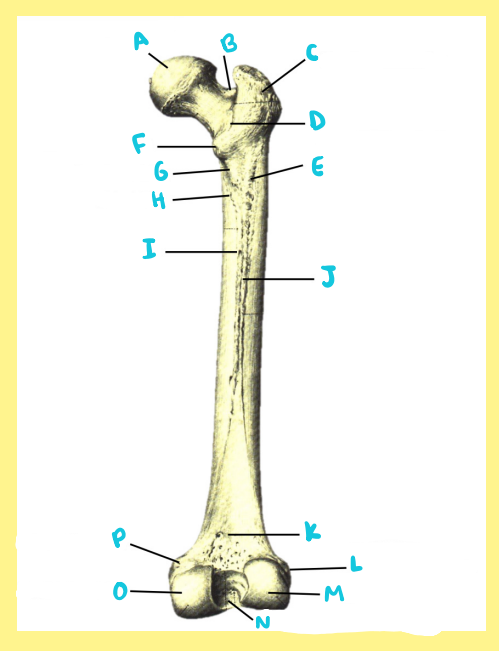
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
I?
femur, right, posterior, nutrient foramen
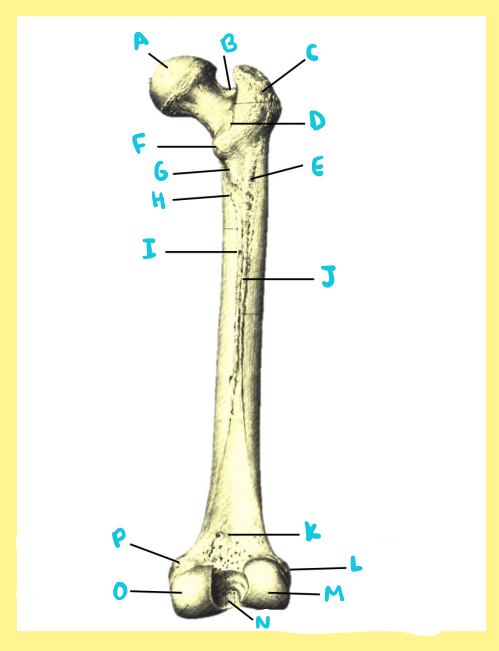
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
J?
femur, right, posterior, linea aspera
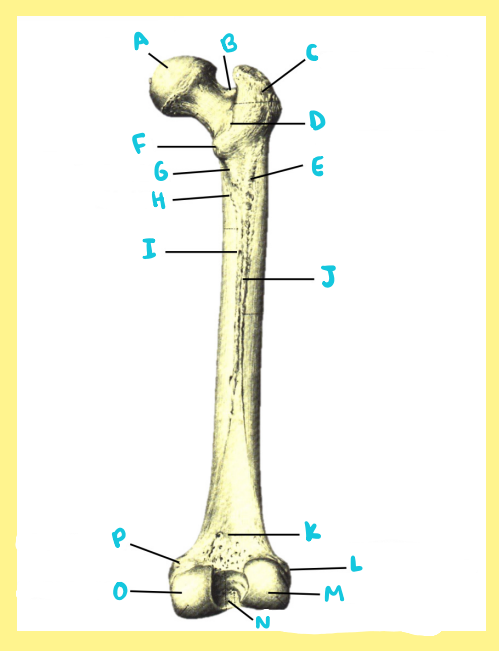
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
K?
femur, right, posterior, popliteal surface
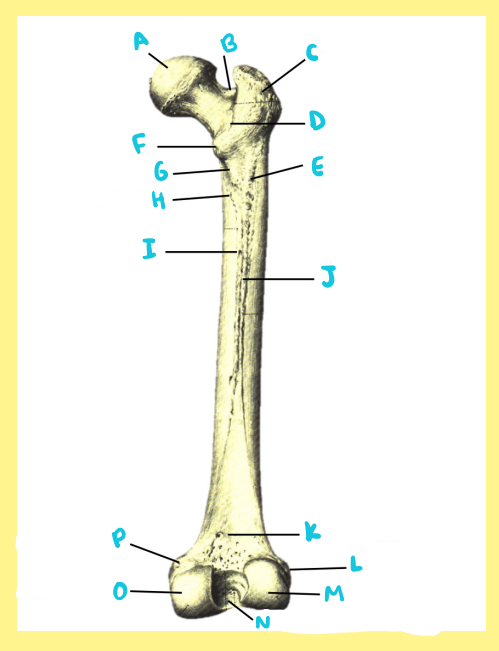
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
L?
femur, right, posterior, lateral epicondyle
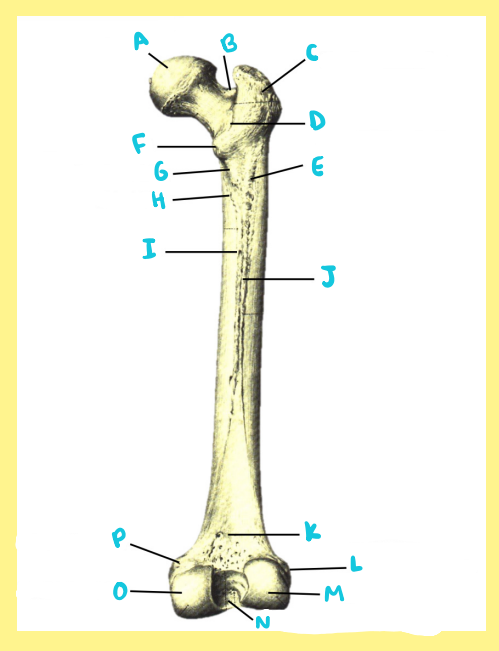
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
M?
femur, right, posterior, lateral condyle
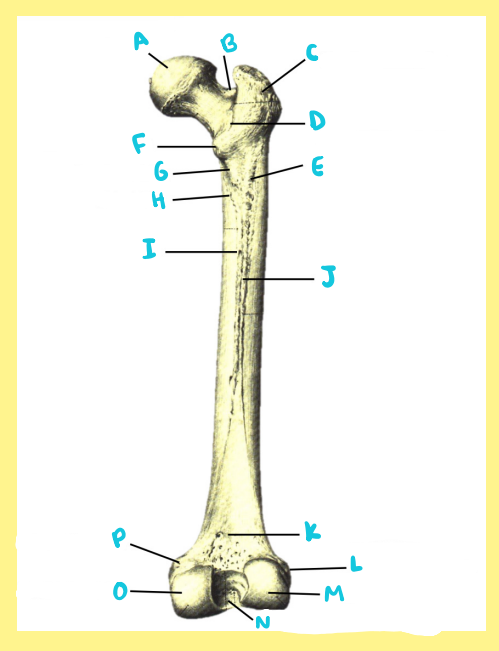
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
N?
femur, right, posterior, intercondylar fossa/notch
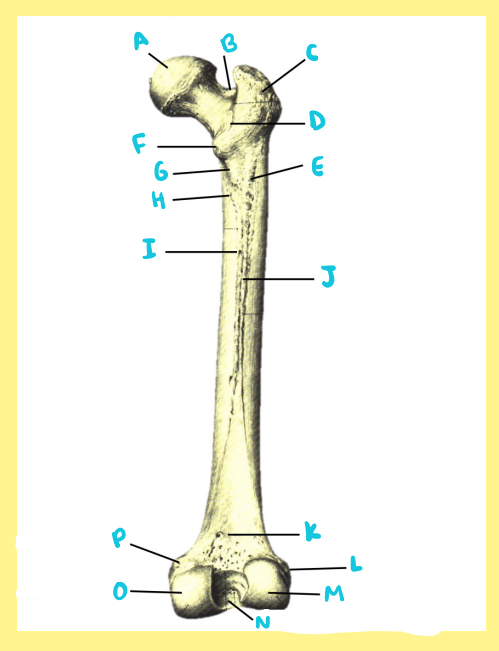
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
O?
femur, right, posterior, medial condyle
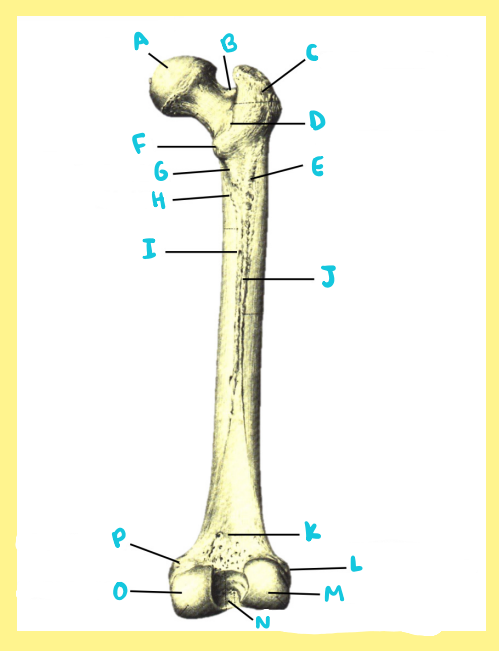
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
P?
femur, right, posterior, medial epicondyle
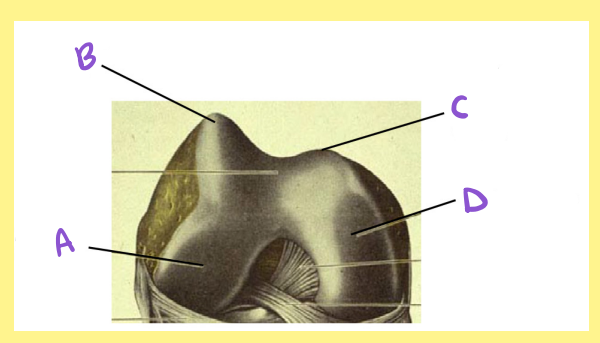
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
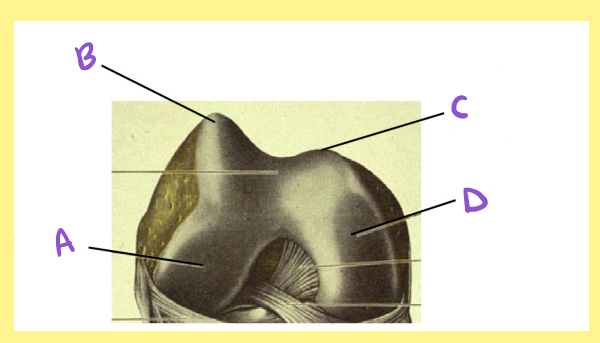
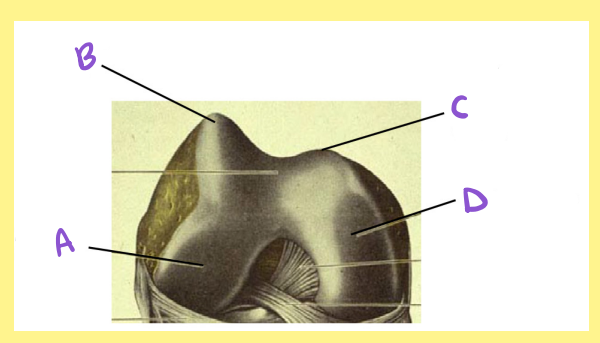
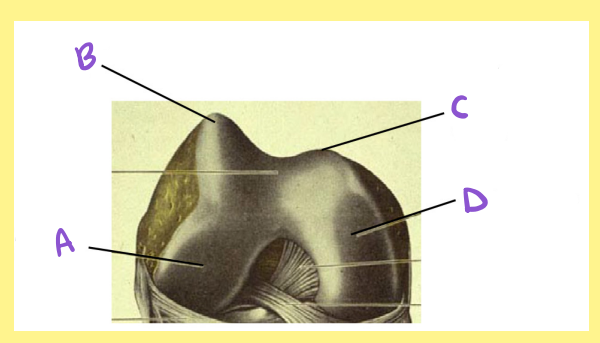
A?
femur, right, distal/inferior, lateral condyle
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
B?
femur, right, distal/inferior, lateral lip of the patellar surface/groove
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
C?
femur, right, distal/inferior, medial lip of the patellar surface/groove
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
D?
femur, right, distal/inferior, medial condyle
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
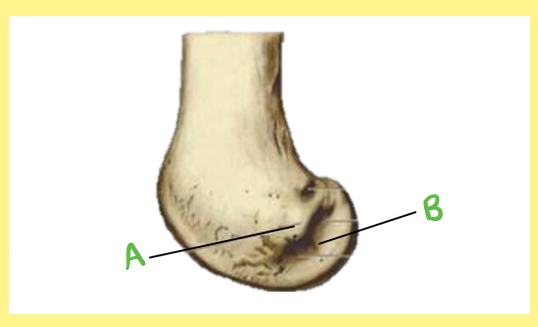
A?
femur, right, distal/lateral, lateral epicondyle
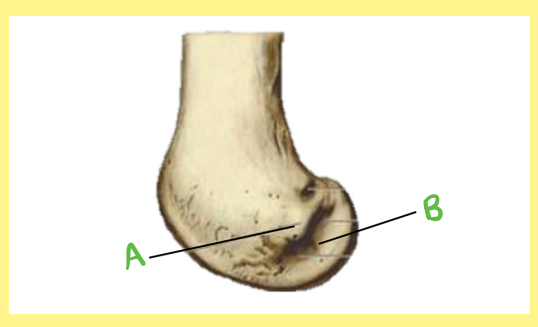
Name the following:
Bone?
Side?
View?
B?
femur, right, distal/lateral, popliteal groove
The longest, heaviest, and strongest bone in the human body
femur
Supports all our body weight when standing, walking, and running
femur
the plural of “femur”
femora
Femur Articulation
Proximally with the _____________ of the ______ → forms the ____ _____
Distally with the ________ (_____ ____) & proximal _______ → forms the _____ _____
acetabulum, pelvis, hip joint, patella, knee cap, tibia, knee joint
Which femur joint has the largest range of motion: hip or knee?
hip
Name the 6 types of movement the hip joint can do
Flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, medial rotation, lateral rotation
Name the 2 types of movement the knee joint can PRIMARILY do
flexion, extension
The femur starts ossifying _______ to ________
distal, proximal
Name the 4 main femur ossification sites
femoral head, greater trochanter, lesser trochanter, distal epiphysis
Femur Fusion & Growth
Femoral Head → males ___-___ years & females ___-___ years
14-19, 12-16
Femur Fusion & Growth
Greater Trochanter → males ___-___ years & females ___-___ years
16-18, 14-17
Femur Fusion & Growth
Lesser Trochanter → males ___-___ years & females ___-___ years
16-17, 16-17
Femur Fusion & Growth
Distal Epiphysis → males ___-___ years & females ___-___ years
16-20, 14-16
Which ossification site is one of the first areas in our femur to start appearing just before birth yet the last one to fuse (at least for males)
distal epiphysis
Proximal Femur
The proximal portion of the femur angles _________ in a downwards diagonal
laterally
Proximal Femur
Name the 2 features of the proximal femur that are seen both on the anterior side and posterior side
femoral head, greater trochanter
Proximal Femur
smooth, round ball structure at the proximal end; ball of the hip joint
femoral head
Proximal Femur
What does the femoral head articulate with?
acetabulum (lunate surface kind of encapsulates it)
Proximal Femur
Which portion of the femoral head is SMOOTHER: anterior or posterior?
anterior
Proximal Femur
Is the femoral head MEDIAL or LATERAL?
medial
Proximal Femur
small divot in the medial side of the femoral head (so not directly in the center but a little offset); attachment site for a ligament that helps the hip joint stabilize (keeps the femur in place)
fovea capitis
Proximal Femur
Is the fovea capitis more INFERIOR or SUPERIOR on the femoral head?
inferior
Proximal Femur
Is the fovea capitis more ANTERIOR or POSTERIOR on the femoral head?
posterior
Proximal Femur
Which feature can be used to distinguish the femoral head from the humeral head?
fovea capitis
Proximal Femur
large chunk of bone lateral to the femoral neck; kind of curves inwards like a hook; this is the part of the femur we can feel
greater trochanter
Proximal Femur
serves as a major muscle attachment site (gluteus medius & gluteus minimus)
greater trochanter
Proximal Femur
narrowed region connecting the femoral head to the shaft & Greater Trochanter; common site for hip fractures
femoral neck
Proximal Femur
The femoral neck is angled downwards __________ to withstand the forces of _________
laterally, walking
Proximal Femur
The femoral neck has a _________ & more _______ line on the underside of the femoral head & a more ________ lip on the superior edge of the head
smoother, gradual, defined
Proximal Femur
subtle ridge of bone connecting the Greater Trochanter & Lesser Trochanter on the anterior surface; site of attachment for a ligament that connects the pelvis to the leg
intertrochanteric line
Proximal Femur
The intertrochanteric line extends _______ to _______ in a downwards diagonal line kind of wrapping around to the __________ side
lateral, medial, posterior
Proximal Femur
Is the intertrochanteric line on the ANTERIOR or POSTERIOR surface?
anterior
Proximal Femur
smaller rounded medial projection of bone on the posterior face; insertion point of a muscle responsible for hip flexion
lesser trochanter
Proximal Femur
The lesser trochanter is _______ and ________ to the greater trochanter
inferior, medial
Proximal Femur
larger ridge of bone on the posterior surface connecting the tip of the Greater Trochanter & the Lesser Trochanter
intertrochanteric crest
Proximal Femur
The intertrochanteric crest extends _______ to _______ in a downwards diagonal line
lateral, medial
Proximal Femur
deep pit on the superior surface in between the Greater Trochanter & the Femoral Neck; attachment site for another muscle; the space underneath the hook of the Greater Trochanter
trochanteric fossa
Proximal Femur
line connecting the inferior end of the Intertrochanteric Line with the medial lip of the Linea Aspera, spiraling underneath the Lesser Trochanter
spiral line
Proximal Femur
The spiral line extends _______ to _______ in a downwards diagonal line
medial, lateral
Proximal Femur
short, curved line that passes inferior-laterally from the base of the Lesser Trochanter
pectineal line
Proximal Femur
rough ridge of bone extending from the base of the Greater Trochanter to the lateral lip of the Linea Aspera; varies in prominence
gluteal tuberosity/line
Proximal Femur
The gluteal tuberosity/line extends slightly _______ to _______ in a downwards diagonal line
lateral, medial
Proximal Femur
List the 3 posterior lines in order from most medial to most lateral before they converge into the linea aspera
spiral line, pectineal line, gluteal tuberosity/line
Proximal Femur
The femoral shaft is _______ & has more of a _________ shaped cross section than the humeral shaft
thicker, teardrop
Proximal Femur
rough line running down the middle of the posterior surface; point of convergence for the 3 posterior lines; major muscle attachment site
linea aspera
Proximal Femur
The linea aspera is _______ on the proximal portion and gets _______ as you go distally until it starts to _____
thicker, thinner, fork
Proximal Femur
line extending from the lateral fork of the distal Linea Aspera
lateral supracondylar line
Proximal Femur
line extending from the medial fork of the distal Linea Aspera
medial supracondylar line
Proximal Femur
Which line is more PRONOUNCED: lateral or medial supracondylar line?
lateral
Proximal Femur
holes on the posterior surface of the shaft; there is one on the proximal portion of the shaft adjacent to or on the linea aspera & one on about halfway down the shaft; opens up distally (but is variable so don’t rely on this as the singular diagnostic feature. LOGICALLY it should work like the humerus, but this is not always true.)
nutrient foramen
Distal Femur
The distal portion of the femur angles _________ in a downwards diagonal
medially
Distal Femur
roughened bulge of bone superior to the Lateral Condyle; serve as attachment sites for ligaments and muscles; extends down from the Lateral Supracondylar Line
lateral epicondyle
Distal Femur
small groove on the lateral side that runs right underneath the Lateral Epicondyle; helps you orient/side the femur; variable feature
popliteal groove
Distal Femur
roughened bulge of bone superior to the Medial Condyle; serve as attachment sites for ligaments and muscles; extends down from the Medial Supracondylar Line
medial epicondyle
Distal Femur
small bump of bone just above the medial epicondyle; insertion point for a thigh muscle
adductor tubercle
Distal Femur
if you run your finger down the medial side of the shaft, the first bump of bone you hit is the _________ _________, NOT the ________ ___________
adductor tubercle, medial epicondyle
Distal Femur
smooth surface/groove between the condyles on the anterior & distal surface
patellar surface
Distal Femur
where the patella sits and articulates with the knee
patellar surface
Distal Femur
Does the patellar surface cover more of the Lateral Condyle or the Medial Condyle?
lateral condyle
Distal Femur
raised ridge on the lateral side of the Patellar Surface; helps the patella stay in place and not dislocate
Lateral Lip of the Patellar Surface/Groove
Distal Femur
Which lip of the patellar groove/surface comes up higher on the anterior surface: MEDIAL or LATERAL?
lateral
Distal Femur
Which lip of the patellar groove/surface is more prominent: MEDIAL or LATERAL?
lateral
Distal Femur
raised ridge on the medial side of the Patellar Surface; helps the patella stay in place and not dislocate
medial lip of the patellar surface/groove
Distal Femur
smooth triangular surface right above the condyles between the 2 Supracondylar Lines on the posterior surface
popliteal surface
Distal Femur
rounded distal end on the lateral side
lateral condyle
Distal Femur
What does the lateral condyle articulate with?
tibia
Distal Femur
Which condyle extends more anteriorly: MEDIAL or LATERAL?
lateral