Lab
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
1
New cards
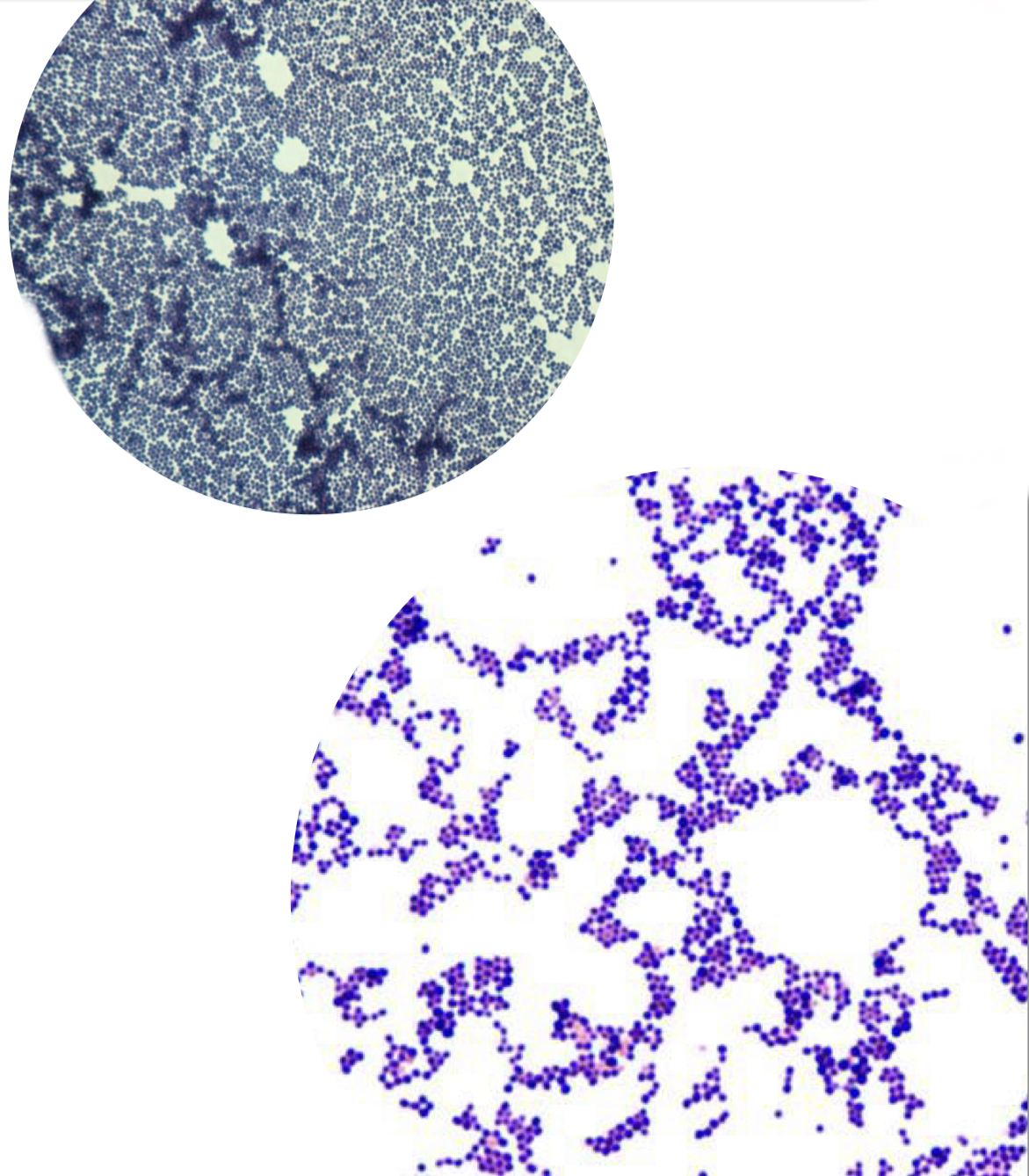
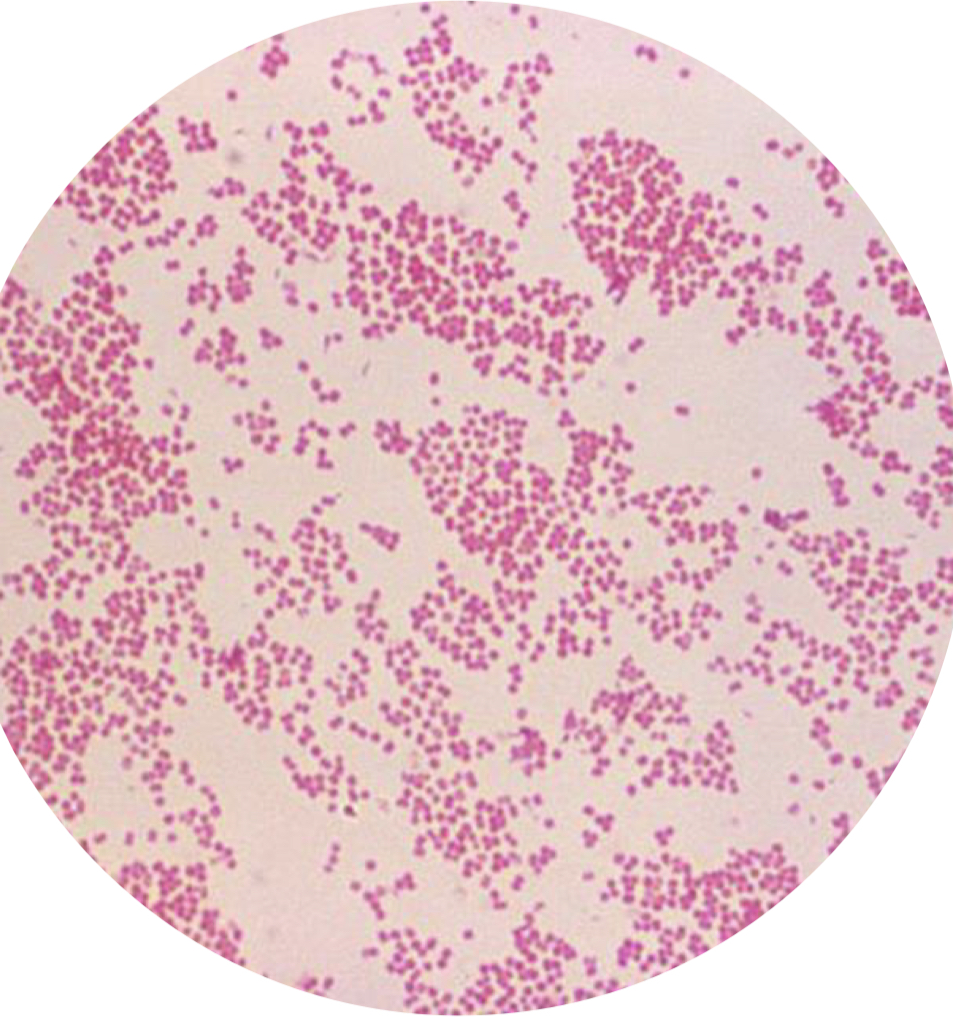
Gram positive, spherical-shaped shaped bacteria, arranged in clusters
Staphylococcus spp.
Staphylococcus spp.
2
New cards
To differentiate between staphylococcus and streptococcus
Catalase test
3
New cards
To differentiate between S. aureus and S. epidermidis
Coagulase test
4
New cards
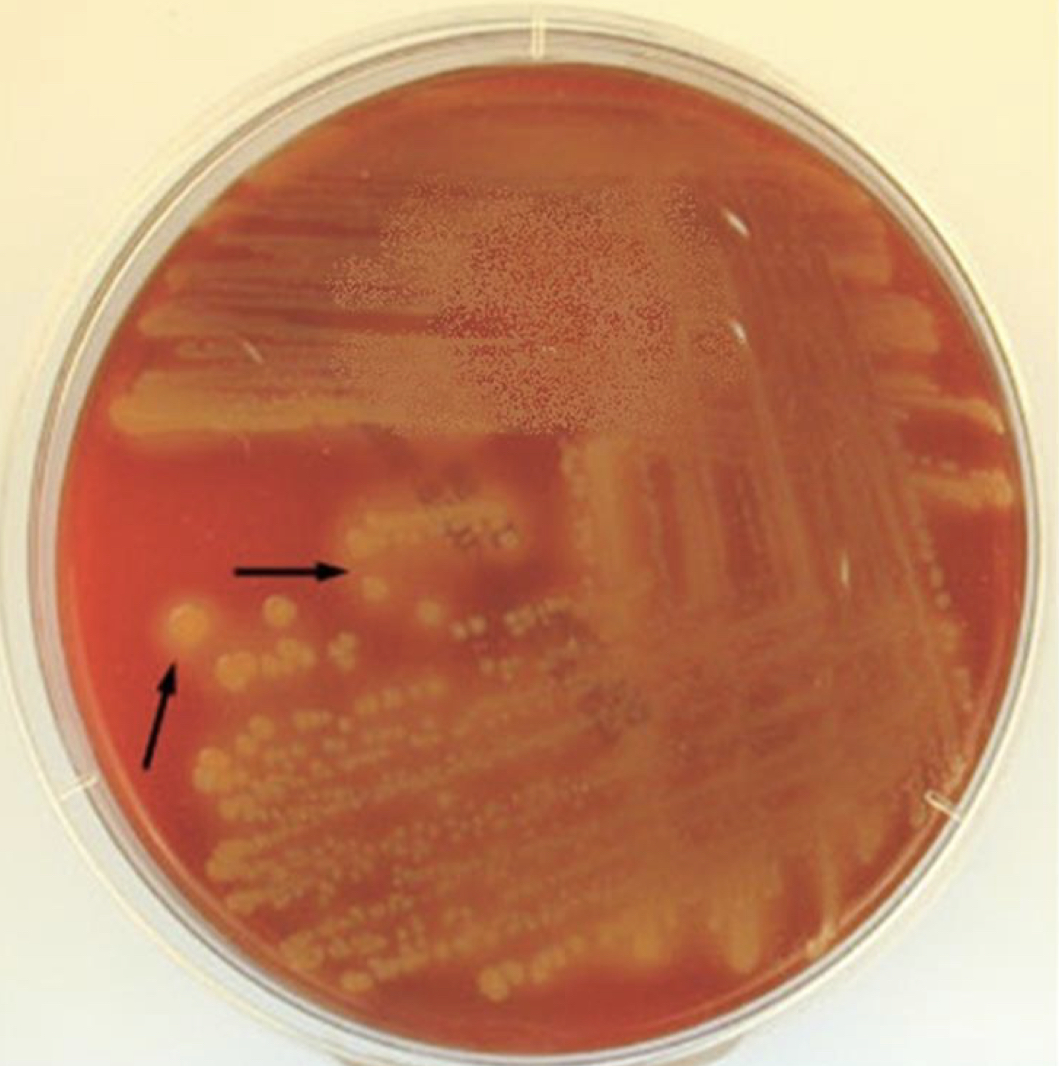
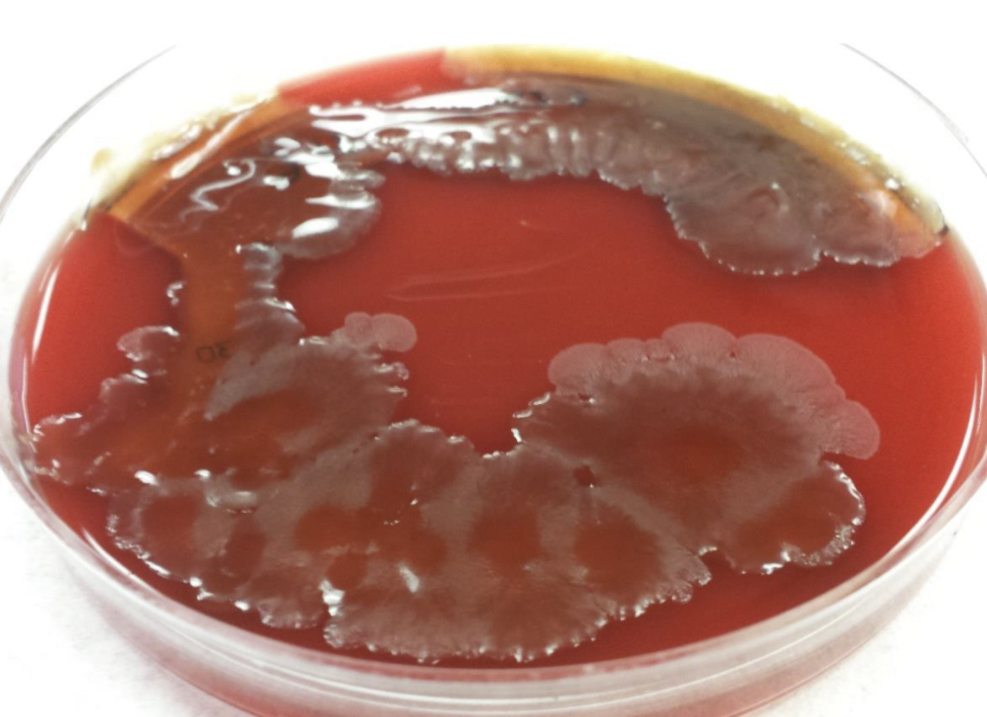
Staphylococcus aureus on blood agar
Golden-yellow colonies with beta-hemolysis on blood agar
Golden-yellow colonies with beta-hemolysis on blood agar
5
New cards
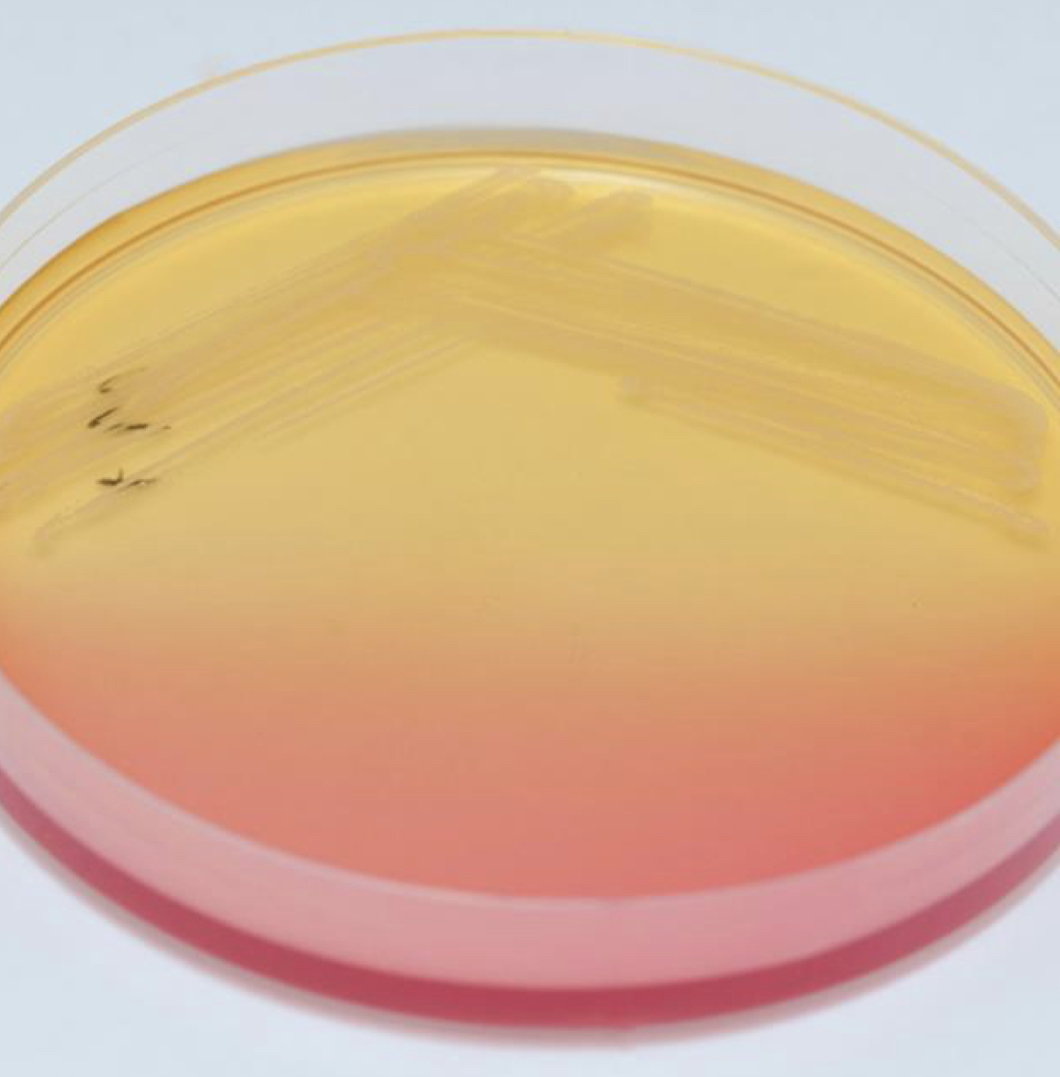
Differential media for:
Staphylococcus aureus, mannitol salt agar (MSA)
6
New cards
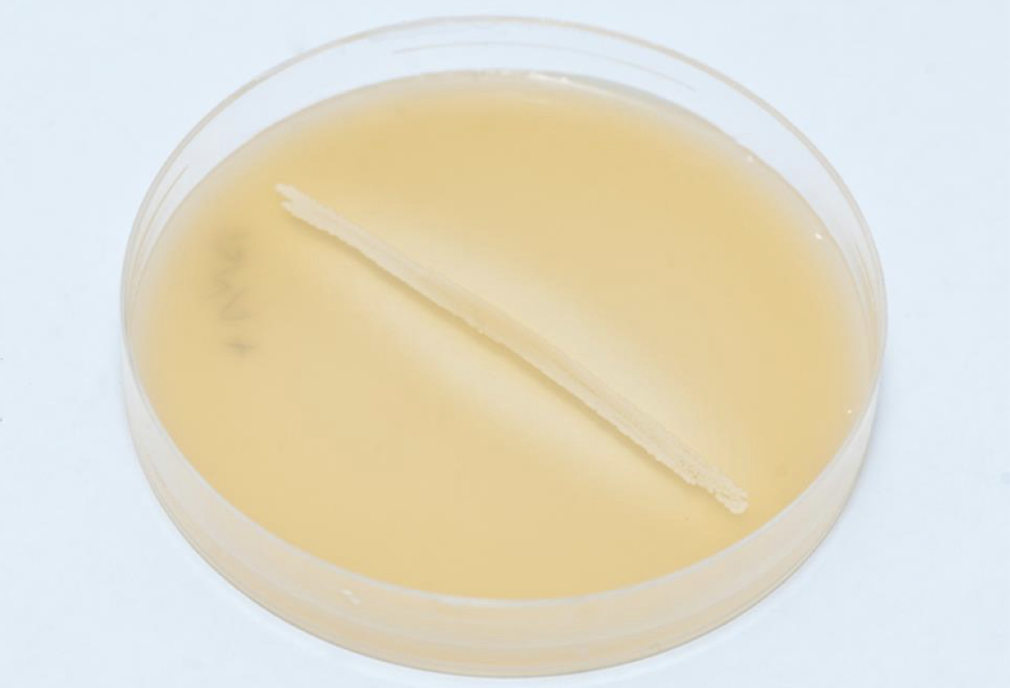
DNase test agar, used to identify S. aureus
7
New cards
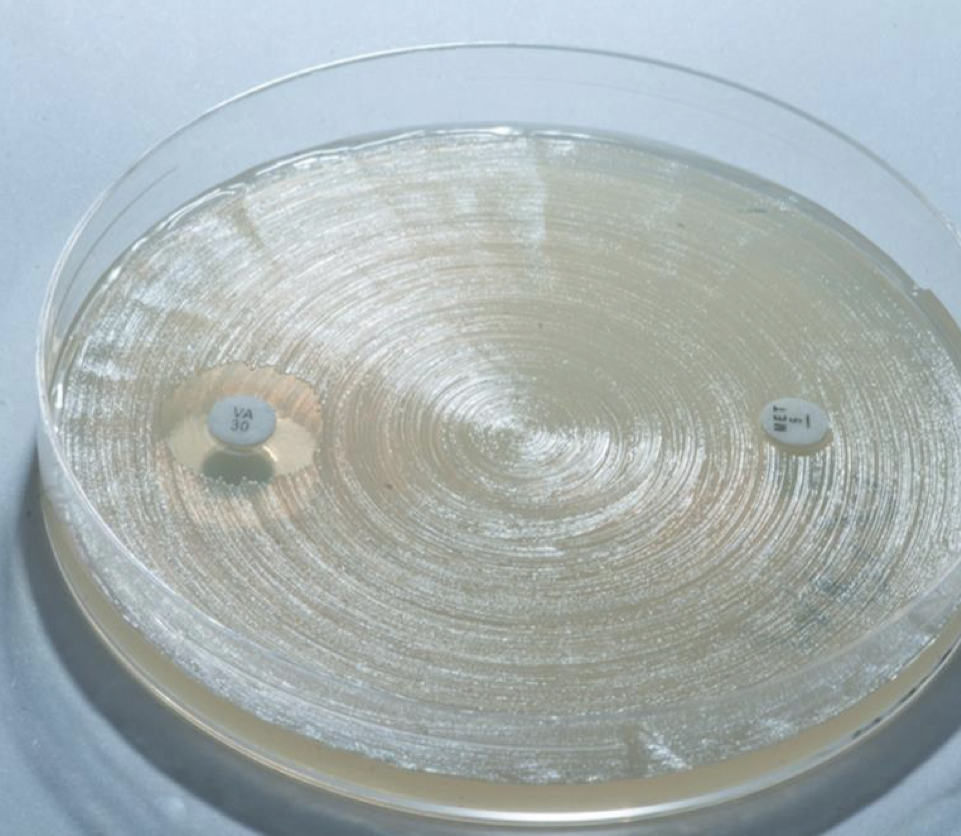
Müller-Hinton agar used for antibiotic susceptibility testing
8
New cards
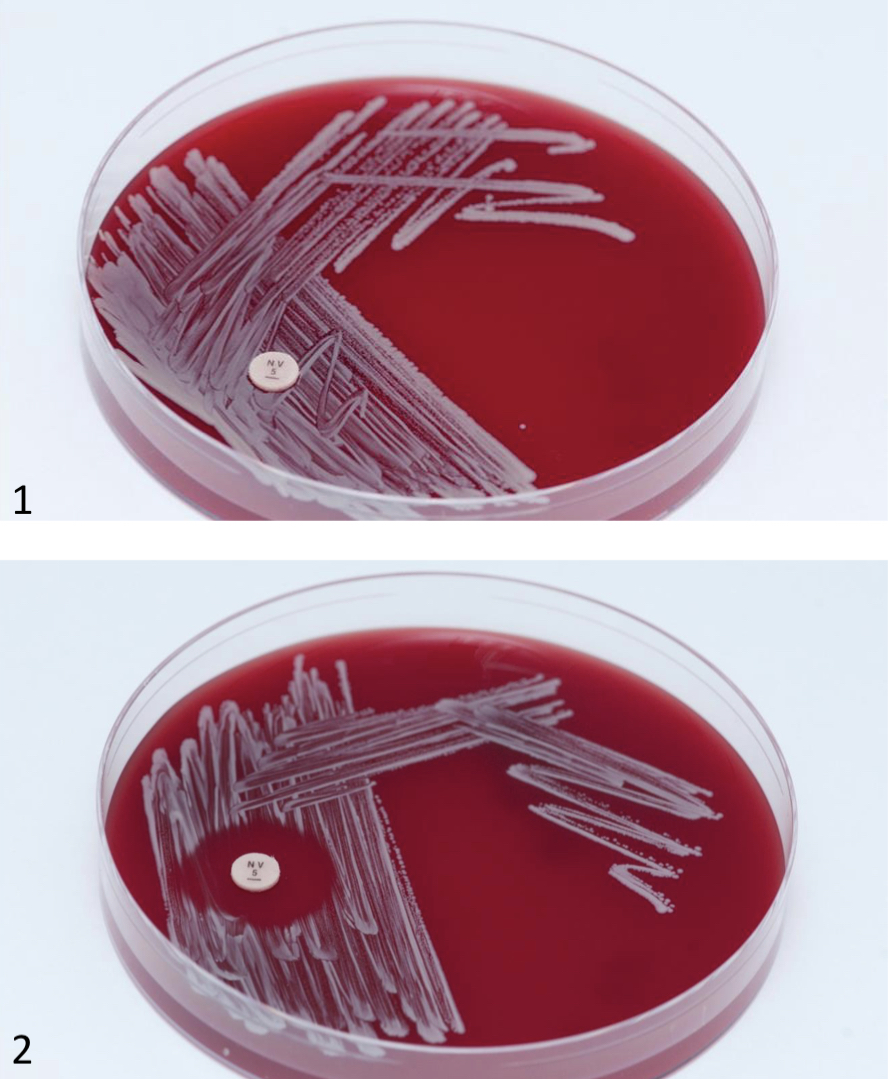
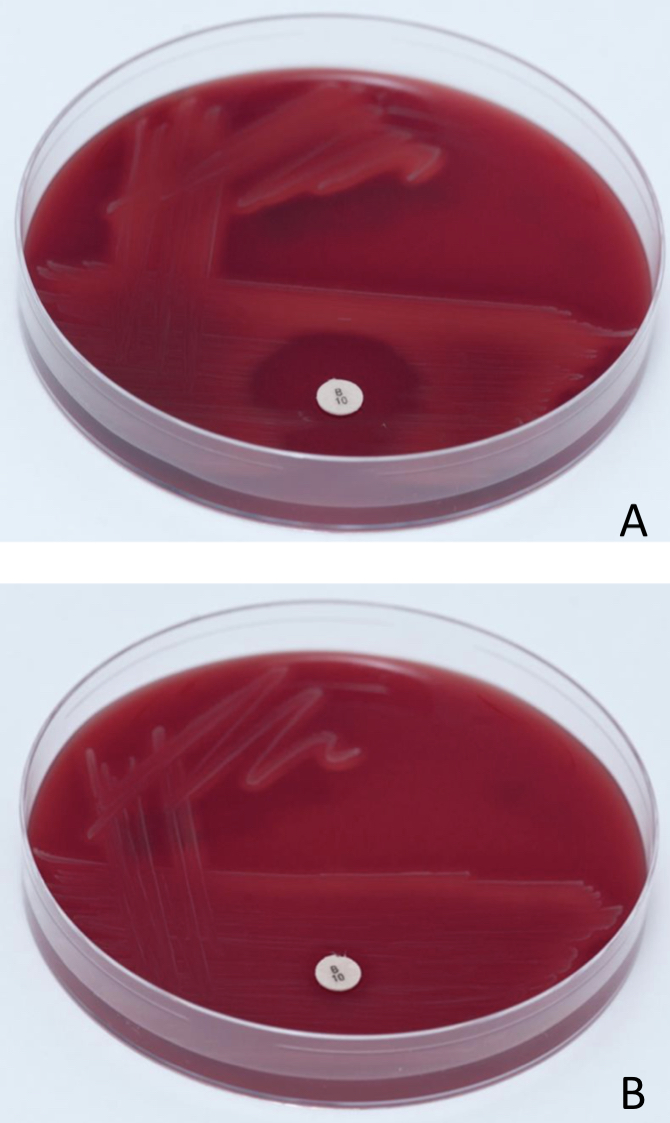
Differentiate between coagulase negative staphylococcus ( staphylococcus epidermidis and staphylococcus saprophyticus)
Picture 1: staphylococcus saprophyticus (resistant)
Picture 2: staphylococcus epidermidis (sensitive)
Picture 2: staphylococcus epidermidis (sensitive)
9
New cards
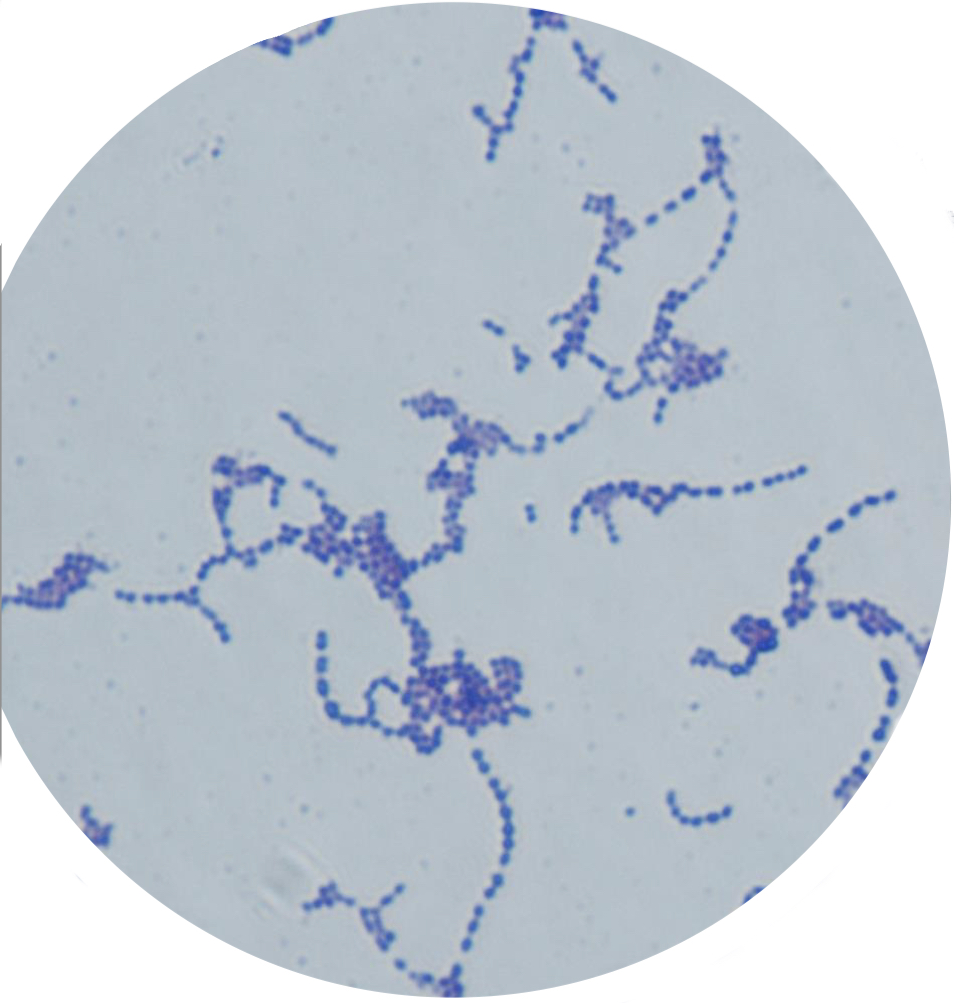
Gram positive, spherical-shaped bacteria, arranged in chain
Streptococcus spp.
Streptococcus spp.
10
New cards
A system of classification that classifies catalase-negative gram-positive cocci based on the carbohydrate composition of bacterial antigens found on their cell walls
Lancefield grouping
11
New cards
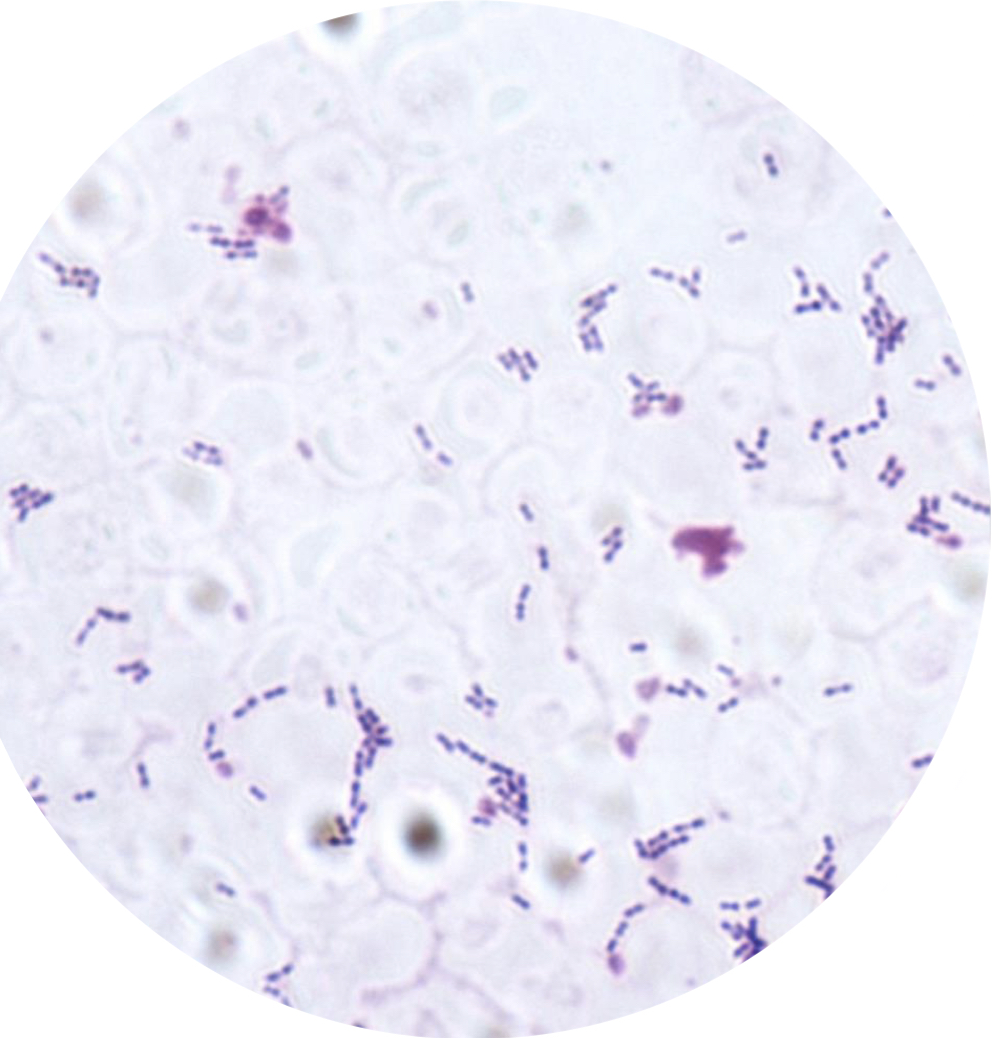
Gram-positive, spherical-shaped bacteria, arranged in pairs (diplococci)
Streptococcus Pneumoniae
Streptococcus Pneumoniae
12
New cards
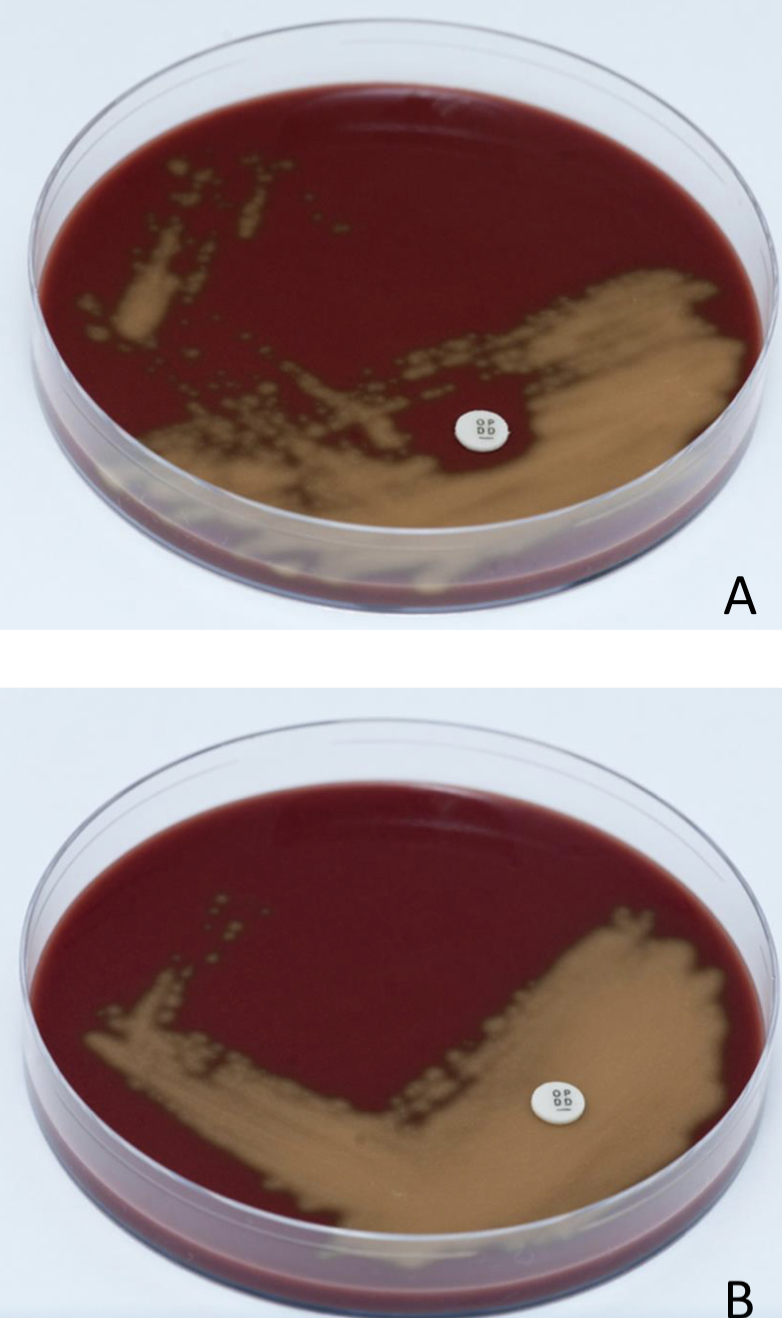
Bacitracin sensitivity test
Picture A: streptococcus pyogenes (Bacitracin sensitive)
Picture B: streptococcus agalactiae (Bacitracin resistant)
Picture B: streptococcus agalactiae (Bacitracin resistant)
13
New cards
Optochin sensitivity test
Picture A: streptococcus pneumoniae (optochin sensitive)
Picture B: streptococcus viridans group (optochin resistant)
Picture B: streptococcus viridans group (optochin resistant)
14
New cards
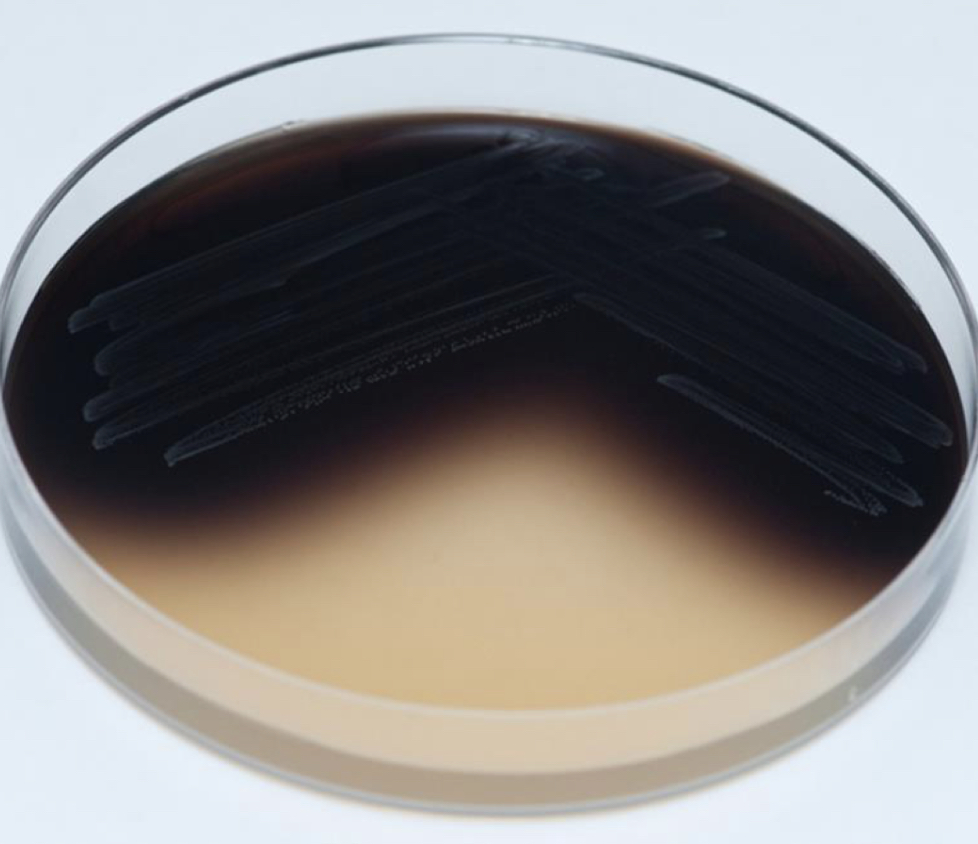
Selective and differential medium
Bile esculin agar, enterococci and group D streptococci
Enterococcus faecalis hydrolysis esculin in the presence of bile and turns more than half the medium into black
Enterococcus faecalis hydrolysis esculin in the presence of bile and turns more than half the medium into black
15
New cards
Gram negative, spherical-shaped bacteria arranged in pairs (diplococci)
Neisseria spp.
Neisseria spp.
16
New cards

Bacillus on a blood agar
Ground glass appearance
Ground glass appearance
17
New cards
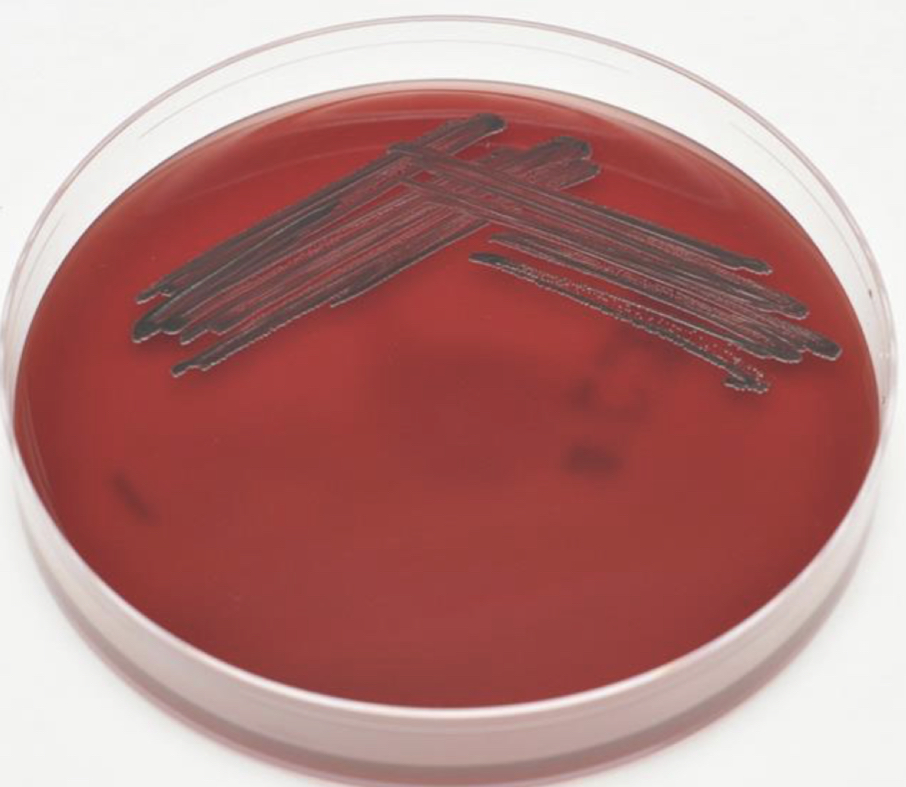
Tellurite blood agar selective media for Corynebacteria Diphtheriae
18
New cards
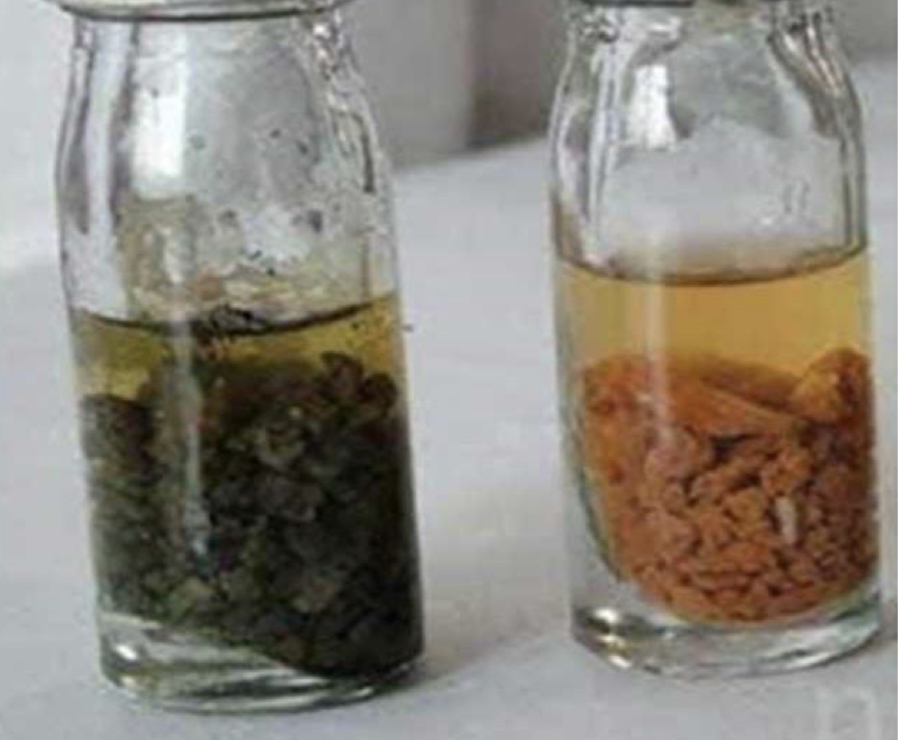

Robertson’s cooked meat
Clostridium perfringens: saccharolytic anaerobes (turn the color of meat pieces into red)
Clostridium tetani: proteolytic anaerobes (blacking of the meat)
Clostridium perfringens: saccharolytic anaerobes (turn the color of meat pieces into red)
Clostridium tetani: proteolytic anaerobes (blacking of the meat)
19
New cards
Oxidase test and sugar fermentation on Neisseria spp.
Both N. gonorrhoeae and N. meningitidis are oxidase positive
N. meningitidis: glucose (+), maltose (+), sucrose (-)
N. gonorrhoeae: glucose (+), maltose (-), sucrose (-)
N. meningitidis: glucose (+), maltose (+), sucrose (-)
N. gonorrhoeae: glucose (+), maltose (-), sucrose (-)
20
New cards
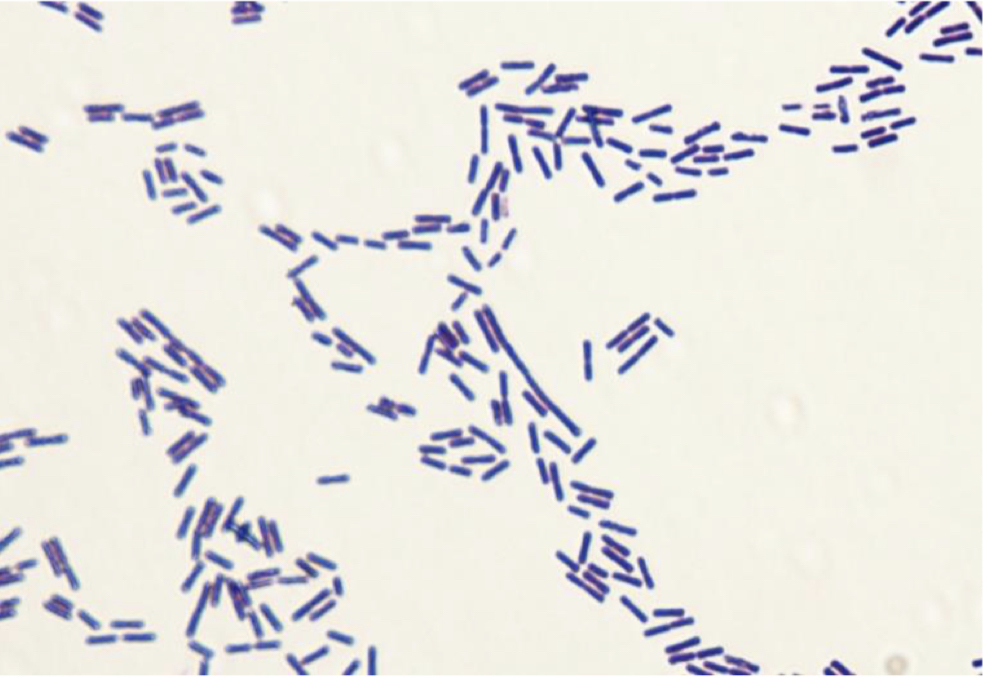
Gram positive, rode shaped bacteria
Aerobic or anaerobic (under some conditions)
Most strains of Bacillus are not pathogenic for humans unlike ==Bacillus anthracis==
B. cereus sometimes causes spoilage in canned foods and food poisoning
Aerobic or anaerobic (under some conditions)
Most strains of Bacillus are not pathogenic for humans unlike ==Bacillus anthracis==
B. cereus sometimes causes spoilage in canned foods and food poisoning