Airway Management and Respiratory Care Techniques
1/194
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
195 Terms
Airway Management
Ensuring a clear airway for patient ventilation.
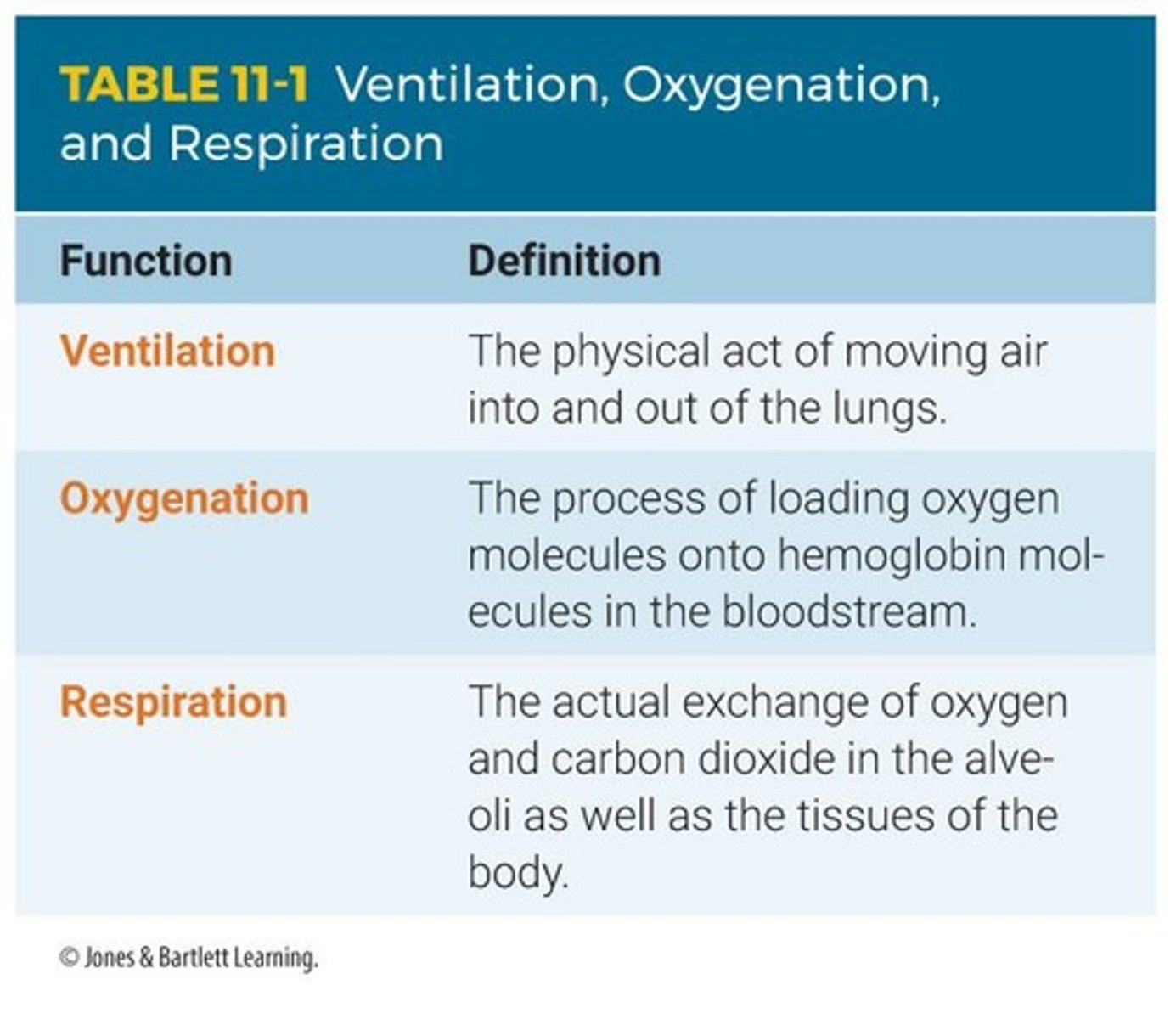
Respiration
Process of gas exchange in the body.
Artificial Ventilation
Mechanical assistance for patient breathing.
Minute Ventilation
Volume of air breathed per minute.
Alveolar Ventilation
Air reaching alveoli for gas exchange.
Patent Airway
Open airway allowing unobstructed airflow.

Upper Airway
Includes nose, mouth, pharynx, and larynx.
Lower Airway
Includes trachea, bronchi, and lungs.
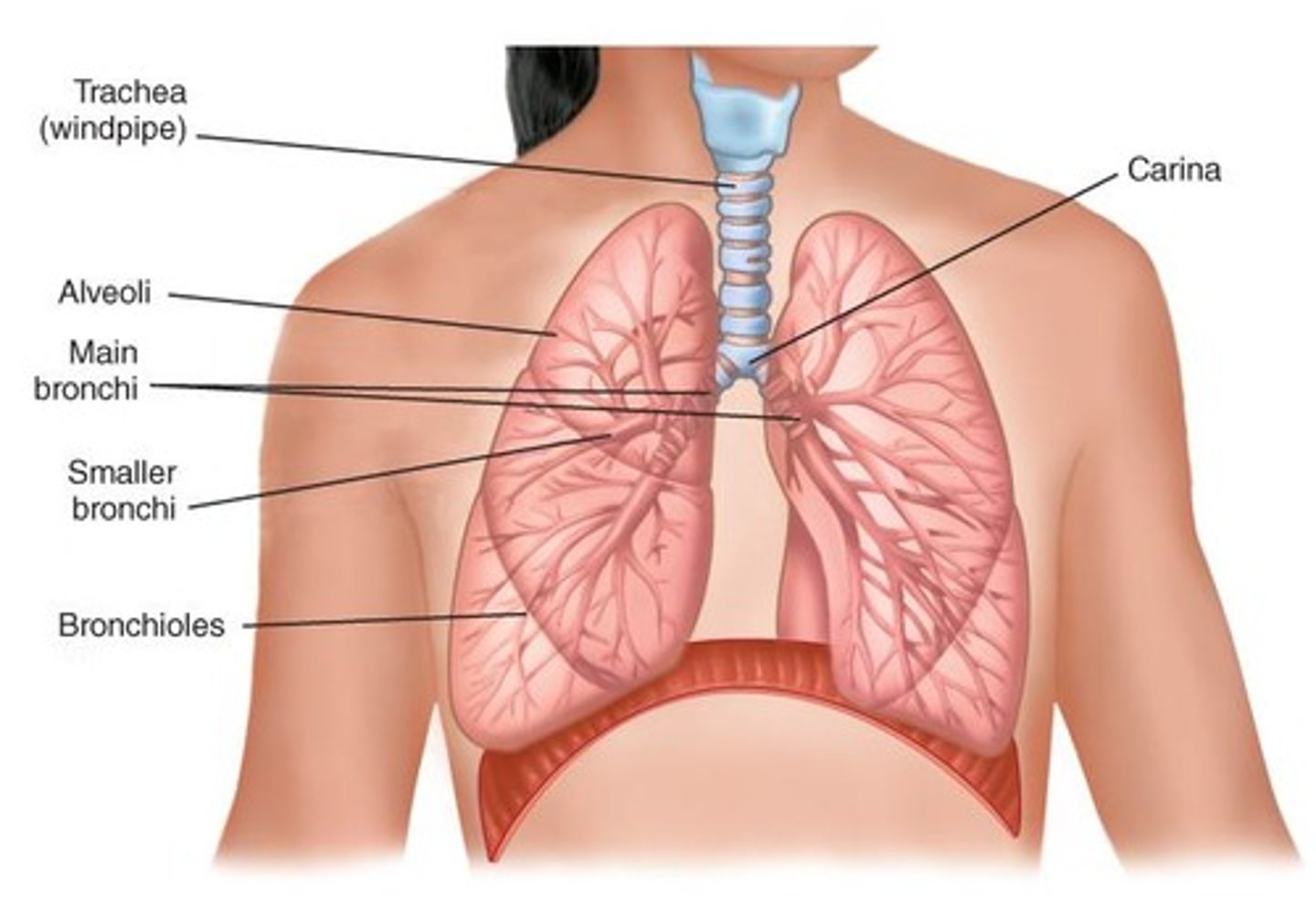
Trachea
Air passage connecting larynx to bronchi.
Bronchi
Branches from trachea into lungs.
Bronchioles
Smaller branches of bronchi leading to alveoli.
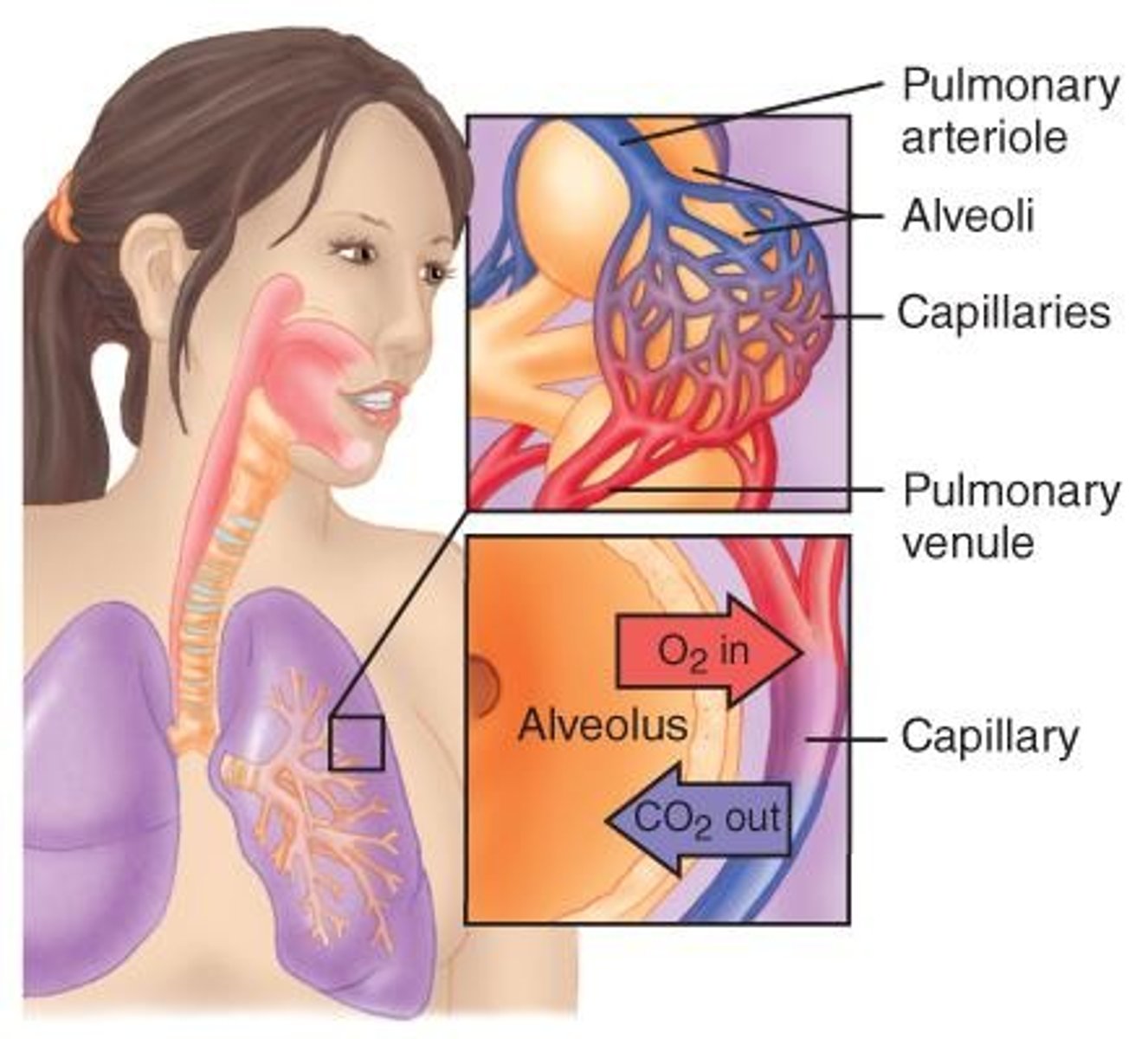
Alveoli
Tiny air sacs for gas exchange.
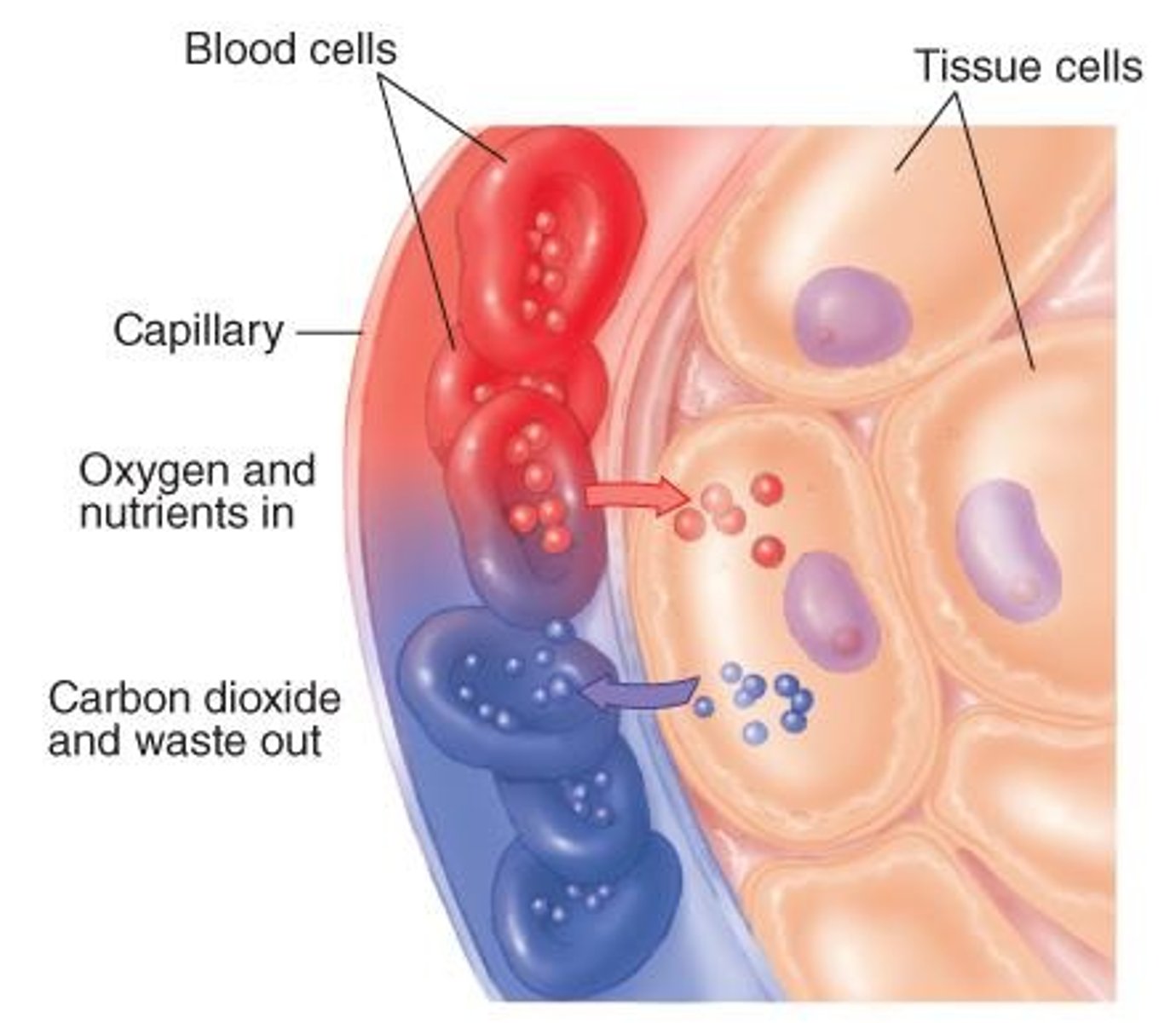
Oxygenation
Process of delivering oxygen to tissues.
Pulmonary Ventilation
Movement of air in and out of lungs.
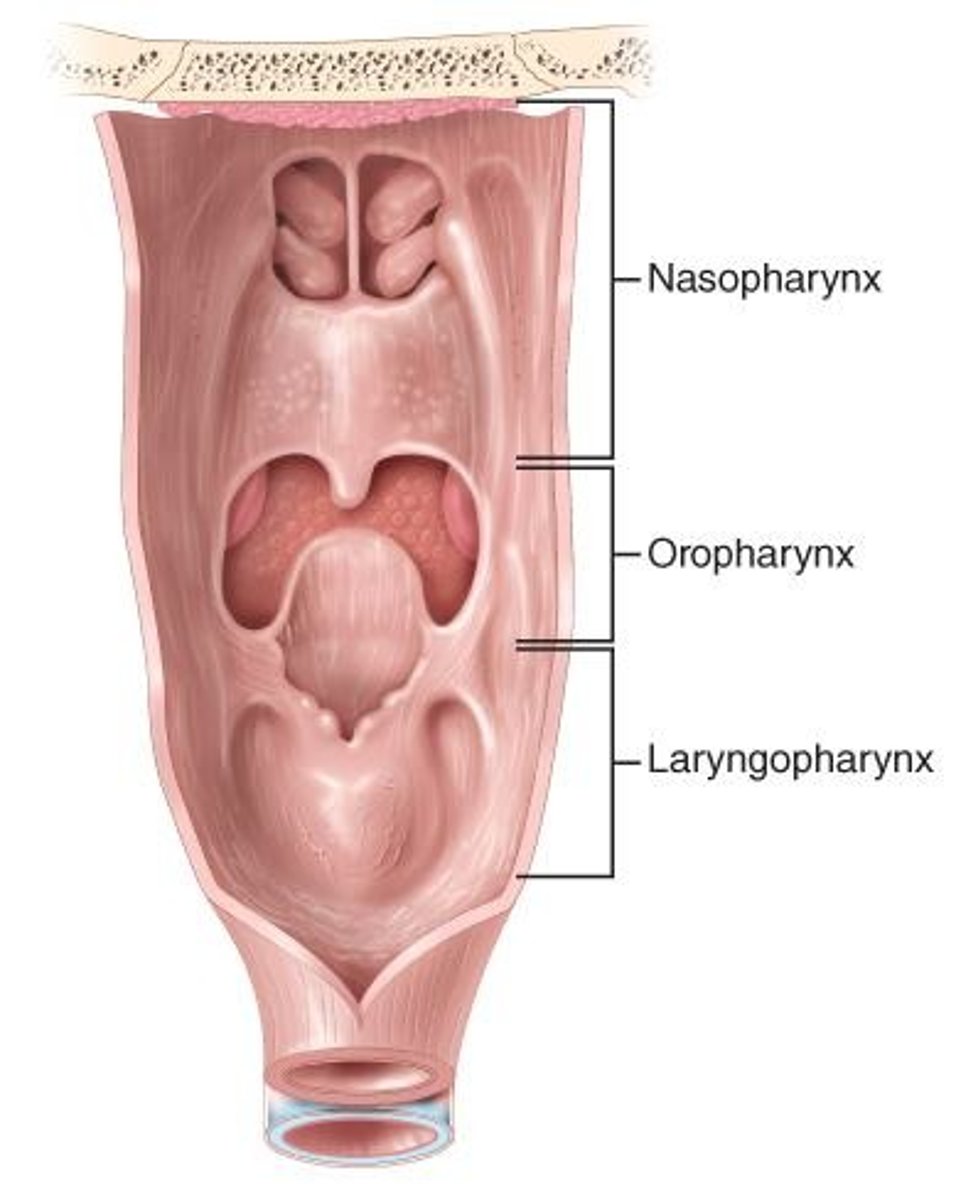
Nasopharynx
Upper part of the pharynx behind the nose.
Oropharynx
Part of pharynx behind the oral cavity.
Laryngopharynx
Lower part of the pharynx leading to esophagus.
Epiglottis
Flap preventing food from entering airway.
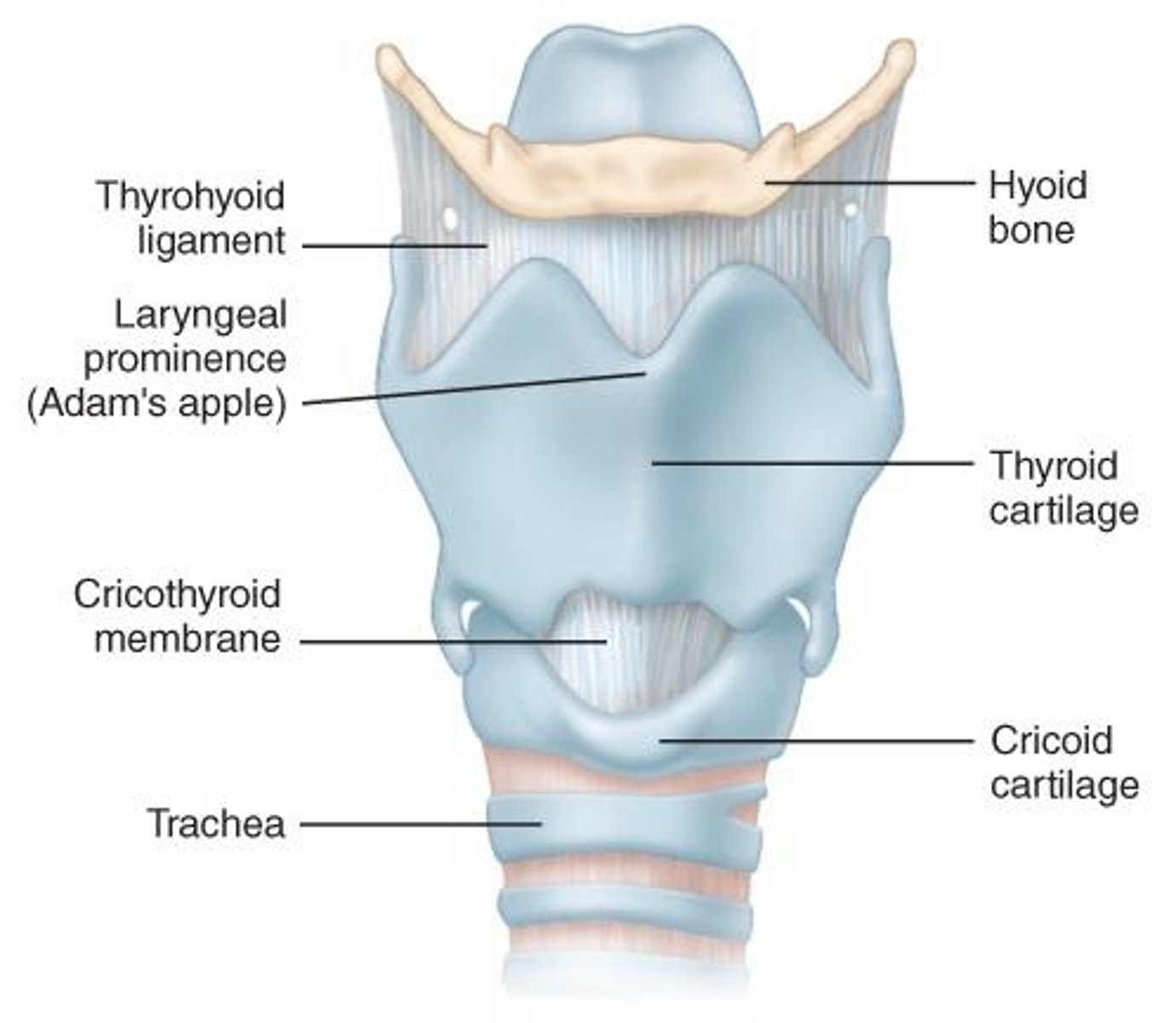
Thyroid Cartilage
Forms 'V' shape in larynx structure.
Cricoid Cartilage
First ring of trachea, supports airway.
Glottis
Space between vocal cords in larynx.
Supplemental Oxygen Therapy
Additional oxygen provided to improve saturation.
Pathophysiology of Respiration
Study of respiratory system dysfunctions.
Mediastinum
Space containing heart, vessels, esophagus, trachea, bronchi.
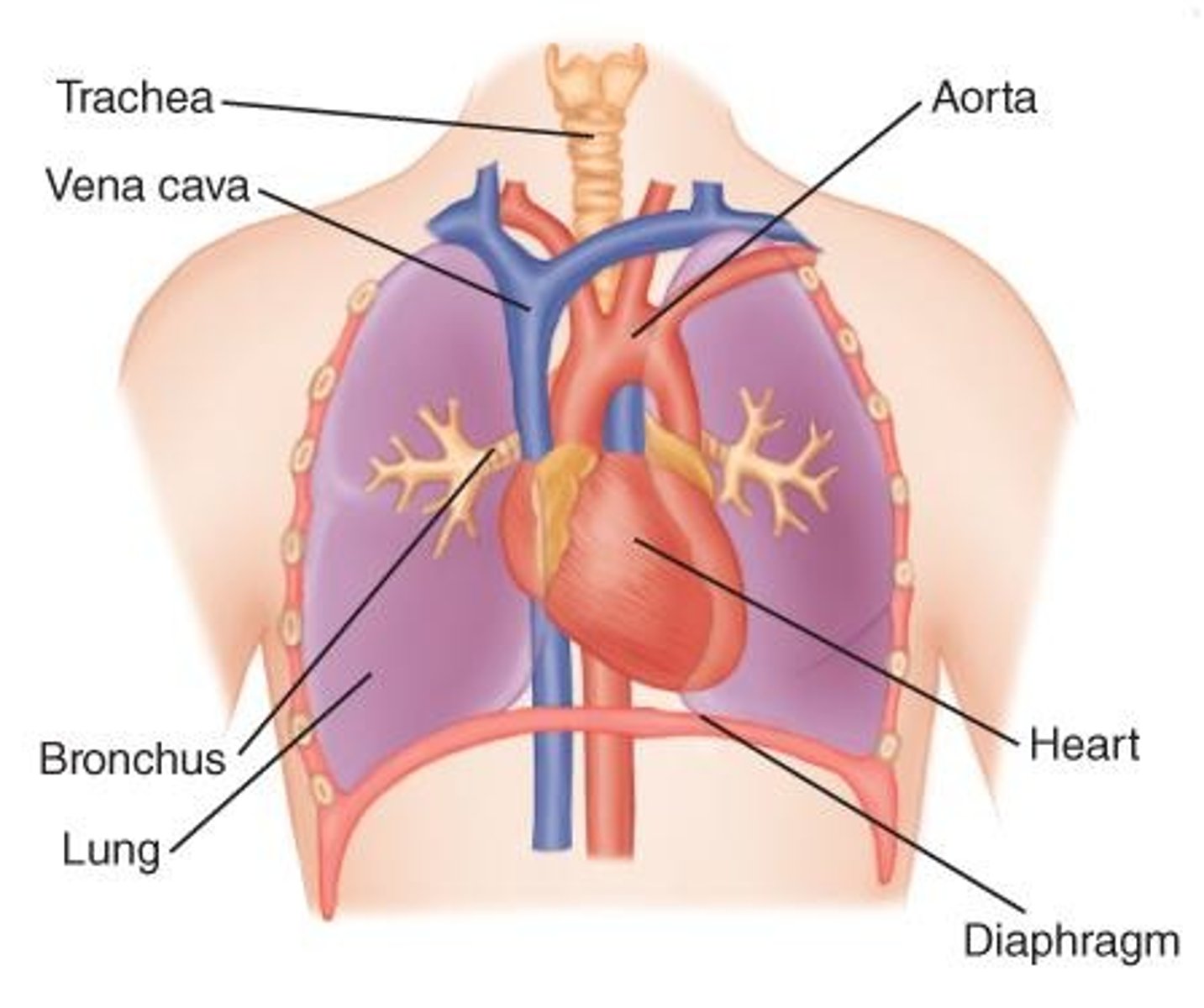
Physiology of Breathing
Collaboration of respiratory and cardiovascular systems.
Ventilation
Physical act of air movement in lungs.
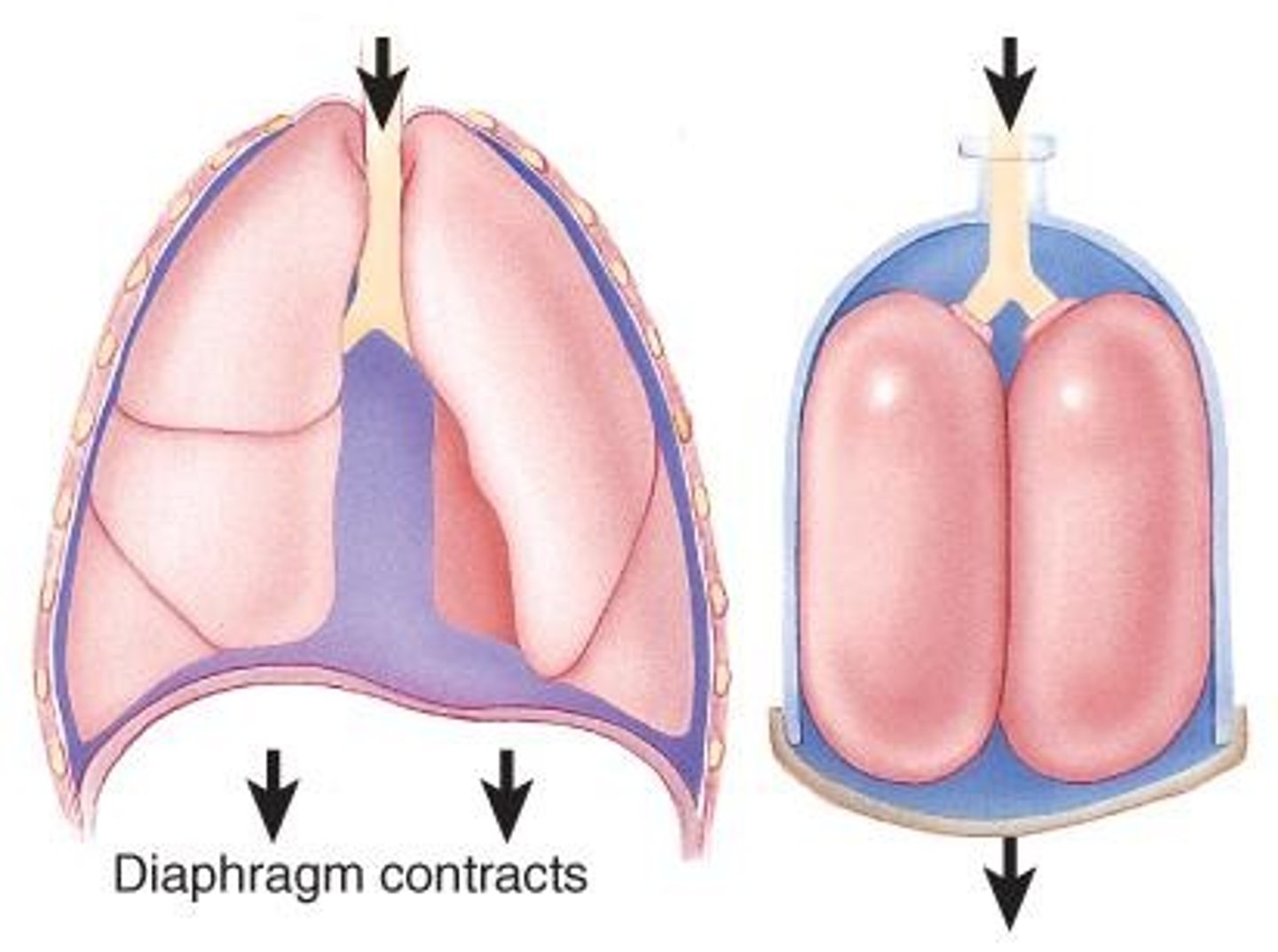
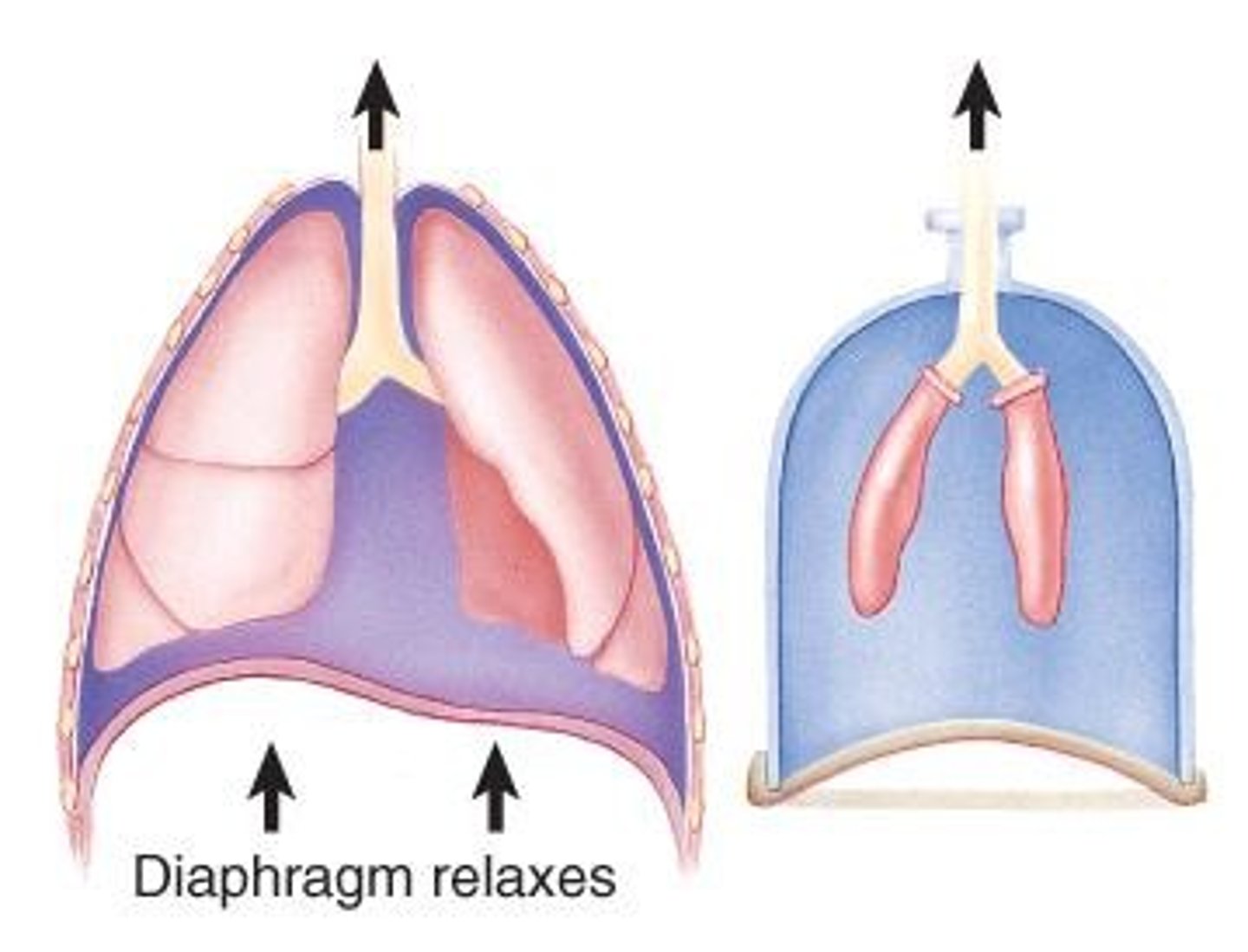
Inhalation
Active breathing phase involving muscle contraction.
Diaphragm
Muscle that aids in inhalation by contracting.
Intercostal Muscles
Muscles between ribs that assist breathing.
Negative Pressure
Pressure difference allowing air to enter lungs.
Partial Pressure
Gas concentration in air or fluid.
Tidal Volume
Volume of air inhaled or exhaled in one breath.
Dead Space
Air that does not participate in gas exchange.
Exhalation
Passive process of expelling air from lungs.
Hypoxia
Insufficient oxygen supply to body tissues.
Hypoxic Drive
Breathing stimulus based on low oxygen levels.
Internal Respiration
Gas exchange between blood and body cells.
External Respiration
Gas exchange between alveoli and blood.
Chemoreceptors
Sensors monitoring oxygen, carbon dioxide, and pH.
Ventilation/Perfusion Ratio
Balance of air and blood flow in lungs.
Severe Hypoxemia
Critical deficiency of oxygen in bloodstream.
Cerebrospinal Fluid
Fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord.
Gas Exchange
Transfer of oxygen and carbon dioxide in lungs.
Intrinsic factors
Factors affecting ventilation from within the body.
Extrinsic factors
External influences impacting pulmonary ventilation.
Infections
Pathogens causing inflammation in respiratory system.
Allergic reactions
Immune response leading to airway constriction.
Unresponsiveness
Loss of consciousness causing airway obstruction.
Trauma
Injury affecting respiratory function or structure.
Atmospheric pressure
Weight of air influencing respiratory mechanics.
Partial pressure of O2
Concentration of oxygen affecting gas exchange.
Pneumonia
Lung infection leading to fluid accumulation.
Pulmonary edema
Fluid buildup in lungs impairing gas exchange.
COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, airflow limitation.
Emphysema
Destruction of alveoli reducing respiratory surface area.
Circulatory compromise
Reduced blood flow affecting oxygen delivery.
Pneumothorax
Air in pleural space causing lung collapse.
Tension pneumothorax
Pressure buildup in pleural space, life-threatening.
Open pneumothorax
Air enters pleural space through chest wall.
Hemothorax
Blood accumulation in pleural cavity.
Hemopneumothorax
Combination of air and blood in pleural space.
Blood loss
Reduction of blood volume affecting circulation.
Anemia
Low red blood cell count reducing oxygen transport.
Hypovolemic shock
Severe blood loss leading to organ failure.
Vasodilatory shock
Widespread blood vessel dilation reducing blood pressure.
Aerosol-generating procedures
Medical procedures producing airborne particles.
Agonal gasps
Gasping breaths after cardiac arrest.
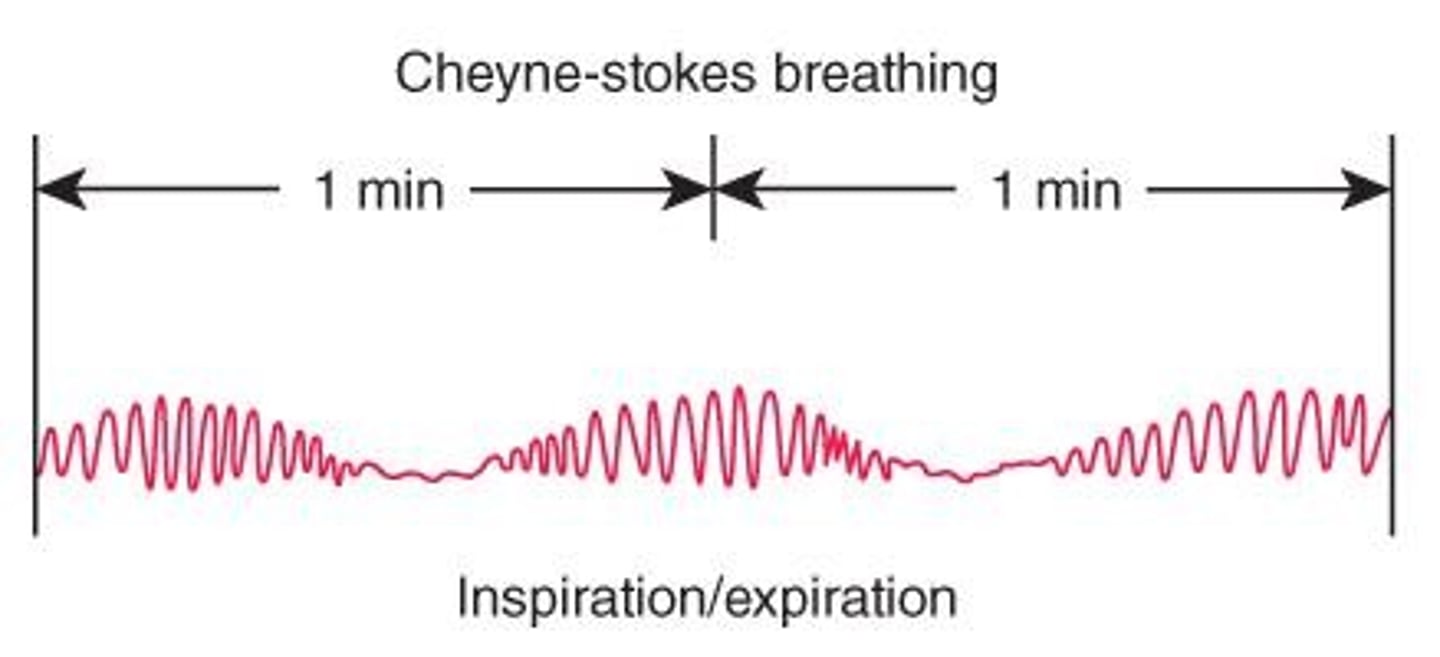
Cheyne-Stokes respirations
Irregular breathing pattern with periods of apnea.
Ataxic respirations
Irregular breathing pattern, often from brain injury.
Kussmaul respirations
Deep, rapid breathing due to metabolic acidosis.
Pulse oximetry
Non-invasive method to measure blood oxygen levels.
End-tidal CO2
Maximal CO2 level at end of exhalation.
Capnometry
Measurement of CO2 concentration in exhaled air.
Capnography
Graphical representation of CO2 levels during respiration.
Head Tilt-Chin Lift Maneuver
Technique to open airway in non-trauma patients.
Jaw-Thrust Maneuver
Airway opening technique for suspected cervical injury.
Cross-Finger Technique
Method to open a closed mouth.
Suctioning Equipment
Essential tools for maintaining airway clearance.
Wide-Bore Tubing
Thick-walled, nonkinking tubing for suctioning.
Pharyngeal Suction Tips
Plastic, rigid tips for effective suctioning.
Nonrigid Catheters
Flexible catheters for delicate suctioning tasks.
Collection Bottle
Nonbreakable, disposable container for suctioned materials.
Suction Pressure
Must exceed 300 mm Hg for effectiveness.
Suction Duration for Adults
Limit to 15 seconds to avoid hypoxia.
Suction Duration for Children
Limit to 10 seconds for safety.
Suction Duration for Infants
Limit to 5 seconds to prevent harm.
Log Rolling Technique
Method to clear mouth using a gloved finger.
Frothy Secretions Protocol
Suction for 15 seconds, then ventilate for 2 minutes.
Oropharyngeal Airways
Prevent tongue obstruction in unresponsive patients.
Indications for Oropharyngeal Airways
Used in unresponsive patients without gag reflex.
Contraindications for Oropharyngeal Airways
Not for conscious patients with intact gag reflex.
Nasopharyngeal Airways
Used in patients with intact gag reflex.
Indications for Nasopharyngeal Airways
For semiconscious patients unable to maintain airway.
Contraindications for Nasopharyngeal Airways
Avoid in severe head injuries with nasal blood.
Recovery Position
Position to maintain airway in unconscious patients.
Supplemental Oxygen
Administer to all hypoxic patients without exception.
Oxygen Cylinder
Contains compressed gas for supplemental oxygen.
Liquid Oxygen
Alternative form of oxygen for medical use.
Pressure Regulator
Device ensuring safe transport of gas cylinders.
Pin-Indexing System
Prevents incorrect gas cylinder connections.