NU 321 OB Exam 3
1/145
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
146 Terms
When is the fourth stage of labor?
4-6 hours post-delivery
Includes recovery, freq VS, and fundal exam
Describe involution of the uterus
Process of uterus returning to pre-pregnancy stage/size
Immediately after delivery: 2#
1 wk: 1#
6 wk: 2 oz
Oxytocin is excreted from the
posterior pituitary
Describe uterine/placental healing
Placental attachment is 3-4” in diameter
Heals via exfoliation/sloughing without scar
Autolysis: self digestion
Proteolytic enzymes released into endometrium = cells loosen protein and shrink
Same # of cells, just smaller
What is locia
Postpartum vaginal discharge - uterine shedding lining (decidua) including blood, tissue, and mucus
Describe changes in lochia
Days 1-3: Lochia Rubra
Bright or dark red
Mainly blood, decidual tissue, fetal membranes
Small clots
Heaviest flow
Days 4-10: Lochia Serosa
Pink or brown
Blood, mucus, WBC
Flow is moderate
Days 10-6 wks: Lochia Alba
Whitish or yellowish
Mucus, leukocytes, epithelial tissue
Flow is scant
How many weeks does it take vaginal rugae to return
4 weeks
What does dyspareunia mean?
Painful sex
Describe varying degrees (1-4) of perineal laceration
First degree: skin, superficial tissue
Second degree: + muscles
Third degree: + sphincter muscle
Fourth degree: + anterior rectal wall
Birthing the placenta reverses the diabetogenic effect of pregnancy, resulting in
Lower BGC
HCG is absent by what day postpartum?
Day 14
For a breastfeeding mom, elevated prolactin occurs for 1. how many months postpartum and 2. suppresses what?
6 months postpartum
Suppresses ovulation
For a non-breastfeeding mom, ovulation may be as early as 27 days, but the mean is
70-75 days
Most menstruate within 3 mo
Prolactin levels reach pre-preg norm within few weeks
Colostrum is continued to be produced in the first [ ] days postpartum before transitioning to transitional milk.
2-4 days
2-20mL per feeding
High in IgA, vitamin A, protein
Low in fat and sugar (easier for NB to digest)
Circulatory changes: Postpartum moms remain in a hypercoagulable state, and WBCs are elevated due to
Stress of delivery
Describe the components of “BUBBLE” and what it’s used for
Postpartum assessment
B - breasts
U - uterus
B - bowels
B - bladder
L - lochia
E - episiotomy/laceration/incision
How is postpartum hemorrhage defined?
EBL >1000mL blood loss accompanied by hypovolemia
<24 h after birth
10% change in Hct
Need for RBC transfusion
Increased surveillance requires quantitative blood loss (QBL)
PPH is categorized as early/acute/primary or late/secondary. Define
Early/acute/primary: Within 24 h of birth
Late/secondary: More than 24 h but less than 6 wk postpartum
What is the leading cause of (often early) PPH
Uterine atony
Uterine atony is defined as
marked hypotonia
Treatments for uterine atony include
Pitocin
Methergine - Don’t give to those with HTN**
Hemabate - Don’t give to those with asthma**
Cytotec
Dinoprostone
Tranexamic acid
Surgical management - Tamponade
Methergine can’t be given to those with
HTN
Hemabate can’t be given to those with
Asthma
Retained placenta can cause hemorrhage and requires manual removal, hysterectomy, and/or blood replacement. Define the 3 types of retained placenta.
Placenta accreta: Slight penetration of myometrium by placental trophoblast
Placenta increta: Deep penetration of myometrium by placenta
Placenta percreta: Perforation of uterus by placenta
Inversion of the uterus can be complete or incomplete. Describe assessment findings of both
Complete: large red rounded mass protruding 20-30 cm out of introitus (vaginal opening)
Incomplete: palpated as a smooth mass through dilated cervix
How to calculate corrected/adjusted age
Chronological age - weeks premature = corrected age
Determine weeks premature: 40 weeks - gestational age at birth
Typically used until 2-3y when most preterm infants catch up developmentally
Describe subinvolution of the uterus
Delayed or incomplete return of uterus to pre-preg state (involution distrupted)
Can be caused by retained placenta, endometritis, uterine atony, etc.
Causes LATE postpartum bleeding
Prolonged lochia
Hemorrhage
Large or boggy uterus
A boggy uterus is…
Soft, poorly contracted uterus after birth
Key sign of uterine atony
Uterine massage is first-line treatment
Signs of hypovolemic shock may not occur until [ ] of blood volume is lost.
30-40%
Describe DIC
Consumption of clotting factors = widespread bleeding
Vascular occlusion of small vessels d/t clots
Caused by stillborn, severe pre-e, sepsis, CV arrest, etc.
Observe bleeding from IV and puncture sites, petechiae (such as under BP cuff)
Postpartum infection is defined as
Clinical infection of genital canal occurring <28 days after miscarriage, abortion, or childbirth
Risk factors: prolonged labor, internal monitoring, DM, immunosuppression
Such as endometritis, mastitis
Risk of postpartum infection is 10-15x higher with…
C-sections
Define endometritis and provide s/sx
Begins as localized infection at placental site, spreads to endometrium
Fever, chills, pelvic pain, foul smelling discharge
Describe mastitis
Most are first time breast feeders
Usually unilateral
Develops after flow of milk established
Staph aureus
Initially nipple fissure, then duct is involved
Edema obstructs flow of milk
Can progress to abscess
May require surgical drainage
PPH is a leading cause of death in US
4.3%
70,000 maternal deaths annually globally
Afterpains are caused by
Oxytocin constricting blood vessels at point of placental separation
Impeded by full bladder
The cervix takes [ ] weeks to heal postpartum
6
Swelling, bruised, red, slit-like appearance
The perineum recovers in
6-8 wk
Describe postpartum changes caused by decreasing estrogen and progesterone
Decreasing estrogen: Diuresis, breast engorgement r/t milk production, postpartum mood changes/depression
Decreasing progesterone: Milk production, return of menstrual cycle, uterine involution
What are typical EBLs of both vaginal delivery and c-section
V: 200-500mL
C: 500-1000mL
Early postpartum has a/n [ ] in platelets, causing a [ ] state
Increase in platelets = hypercoagulability
What are the 4 T’s of PPH
1. Tone (uterine atony)
2. Trauma (lacerations)
3. Tissue (retained placenta)
4. Thrombin (coagulation dysfunction)
Two most common/initial s/sx of hematoma formation
Pain
Shock
empty
Occurrence of postpartum infection is [ ]%
5-7%
Puerperal sepsis is one of the top 5 causes of maternal deaths worldwide, causing [ ]% of deaths in the postpartum period
10-15%
Endometritis is the most common postpartum infection, affecting [ ]% of vaginal and [ ] of c-section deliveries
V: 1-3%
C: 5-10%
2-4% of women develop what type of infection postpartum?
UTI
1% of women will develop…
Mastitis
Neonate is a term used for infants aged…
Birth through 28 days
The postpartum “Transition Period” lasts how many hours?
6-8
How do contractions alter PO2, PCO2, and pH?
PO2: Decreased
PCO2: Increased
pH: Decreased
Cord cutting [increases/decreases] prostaglandins
Decreases
How often and how long can respiratory pauses be and still be considered normal?
Normal is 30-60 pauses of 15 seconds
Typically occur during REM
Longer than 20 seconds is a problem
What causes the closure of the foramen ovale?
First extra-uterine breaths
Initial breathing occurs against increased alveolar capillary distention
Increased pulmonary blood flow causes a closure of the foramen ovale
May have transient murmurs until closure
Where is neonate cardiac PMI?
Fourth intercostal space and to the left of the midclavicular line
Is it recommended to routinely obtain 4 point BPs?
No
When should a nurse obtain a 4 pt BP?
Tachycardia
Persistent murmur
Abnormal pulses
Poor perfusion
Abnormal precordial activity
What are normal BP values for a NB?
Systolic 60-80
Diastolic 40-50
When is a NB considered hypotensive? What about hypertensive?
Hypotensive: Mean BP less than gestational age
Hypertensive: Mean pressure exceeds 50-70
What is a neonate’s blood volume?
85mL/kg
300mL at birth
If delayed cord clamping, increases by 100mL
Causes of NB persistent tachycardia
Anemia
Hypovolemia
Hyperthermia
Sepsis
Causes of NB persistent bradycardia
Congenital HB
Hypoxemia
A significant difference between upper and lower extremity BPs is an early sign of…
Coaractation of aorta
Pathologic jaundice occurs within 24 hours of birth and can be caused by…
ABO or Rh issues
Leukocytosis is [normal/abnormal] at birth
Normal
A NB with sepsis is likely to display [increased/decreased] WBCs
DECREASED WBCs!
What is the normal NB temp range?
97.8-98.8
Slightly higher may be ok if it makes sense clinically (eg wrapped in blankets)
What are the four methods of heat loss?
Convection
Heat to cooler ambient air
Radiation
Loss of heat to cooler solid surface (not in direct contact)
Evaporation
Liquid to vapor
Conduction
Loss of heat to cooler surface in direct contact
Describe convection
Heat loss to cooler ambient air
Describe radiation
Heat loss to cooler solid surface NOT in direct contact
Describe evaporation
Heat loss from liquid to vapor
Describe conduction
Heat loss to cooler surface in DIRECT CONTACT
Infants cannot shiver, and thus have reserves of…
Brown fat, for thermogenesis
Can increase heat production by as much as 100%
Reserves gone by few weeks postpartum
Premature infants have less
What is cold stress?
Pre-hypothermia
Increases metabolic and physiologic demands
BMR increases
Respirations increase
Anerobic glycolysis occurs
Increases production of acids
Metabolic acidosis
Increases risk of hyperbilirubinemia
Describe symptoms of NB hyperthermic sepsis
Stressed
Constricted vessels
Pale
Hands and feet cold
NBs should void within [ ] hours.
98% void within the first 30 hours
If none in 48 hours, consider renal impairment
Describe red brick staining
Caused by washing of uric acid crystals, not blood
Normal in first days after birth
[ ]% of a NB’s body weight is water. [ ]% of body weight is extracellular.
[75]% of a NB’s body weight is water. [40]% of body weight is extracellular.
Describe NB’s daily fluid requirements in 1) first 2 days and 2) following that
1) First 2 days: 40-60mL/kg
2) Following: 100-150mL/kg/24 hours
Babies lose 5-10% of their body weight in the first [ ] days. They regain birth weight within [ ] days after birth.
Babies lose 5-10% of their body weight in the first [3-5] days. They regain birth weight within [14] days after birth.
Sucking calluses disappear by [ ] months.
12 months
What are epsteins pearls?
Whitish-yellow “retention cysts” along the gums or on the roof of a NB’s mouth
Harmless, disappear within weeks
Stomach capacity of a NB is…
30-90mL
Lowest BGC level occurs between [ ] minutes postpartum
30-90 minutes
40-80mg/dL
60% of NBs have…
Hyperbilirubinemia
Can be physiologic or pathologic
Describe kernicterus
Acute bilirubin encephalopathy
Lethargic
Hypotonic
Poor suck
High pitched cry
Fever
Nevi, or stork bites, are [blanchable/nonblanchable]
Blanchable
Describe caput succadaneum
Commonly on occiput
Edematous swelling of fetal scalp
Crosses suture lines
Disappears 3-4 days
Harmless
Occur especially with vacuum-assisted
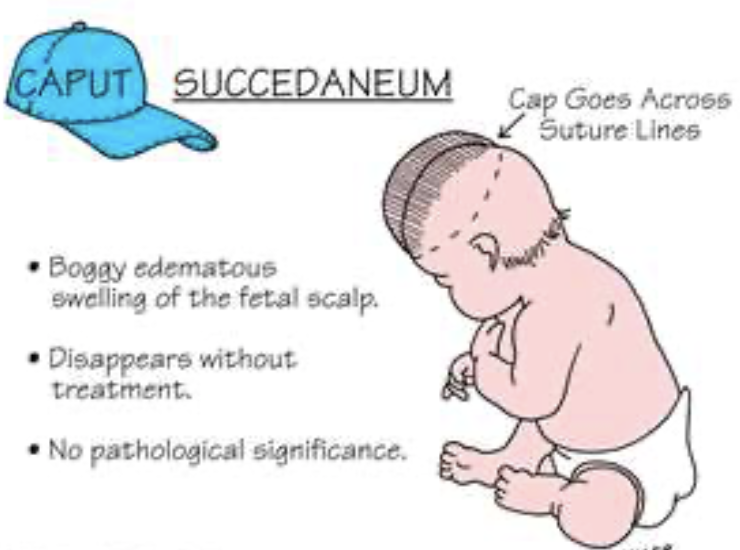
Does caput succadaneum or cephalhematoma cross suture lines?
Caput succadaneum: yes, crosses
Cephalhematoma: no, doesn’t cross
Describe cephalhematoma
Collection of blood between skull bone and periosteum
Doesn’t cross suture lines
What is the Ortolani maneuver?
A physical examination technique used to assess for congenital hip dysplasia
Describe NB reflexes: extrusion, fencing, stepping, babinksi
Extrusion: aka “tongue-thrust,” protects from choking. Pushes tongue forward when touching the lips. At birth.
Fencing: asymmetrical tonic neck reflex. Baby extending the arm and leg on the same side their head is turned towards while flexing the limbs on the opposite side. 18 weeks.
Stepping: occurs when held upright and their feet touch a flat surface.
Babinksi: occurs after the sole of the foot has been firmly stroked. The big toe then moves upward or toward the top surface of the foot. The other toes fan out
Describe a NB’s vision
No tears
Crossed eyes
Tracking
Black and white
12 inches of vision
Prefers patterns
Fluid in the NB’s middle ear can cause…
A failed NB hearing test/false positive hearing loss
Taste develops..
At 25 weeks in utero
Differentiate between caput succedaneum and cephalohematoma
Caput succedaneum is edema (swelling) of the scalp due to pressure, while cephalohematoma is a collection of blood (hemorrhage) under the scalp
Cephalohematoma doesn’t cross suture lines while caput succedaneum does.
Caput succedaneum appears at birth and usually resolves within a few days while cephalohematoma appears shortly after birth and may take weeks or even months to resolve
What four types of factors stimulate the medulla’s respiratory center in order to cause respiration after birth? Give an example of each
Chemical
Contractions causing transient hypoxia and hypercarbia
Decreased PO2 and pH & Increased PCO2
Mechanical
Changes in intrathoracic pressure
Thermal
Skin receptors
Sensory
Handling, suction, drying, sights and sounds
Apgar scores are obtained at…
1 and 5 minutes
Apgar is scored from a total of…
0-10