Liver- Jones
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
based off pp
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What are the functions of the liver?
filtration and storage of blood
metabolism
bile synthesis
storage of vitamins and iron
formation of coagulation factors
What vitamins are stored in the liver?
A,D,E,K
What cell type of the liver lobule is the epithelial layer and separates the internal from external environment?
hepatocyte
What are the role of Kupffer cells in liver lobules?
macrophage—> identify bacteria
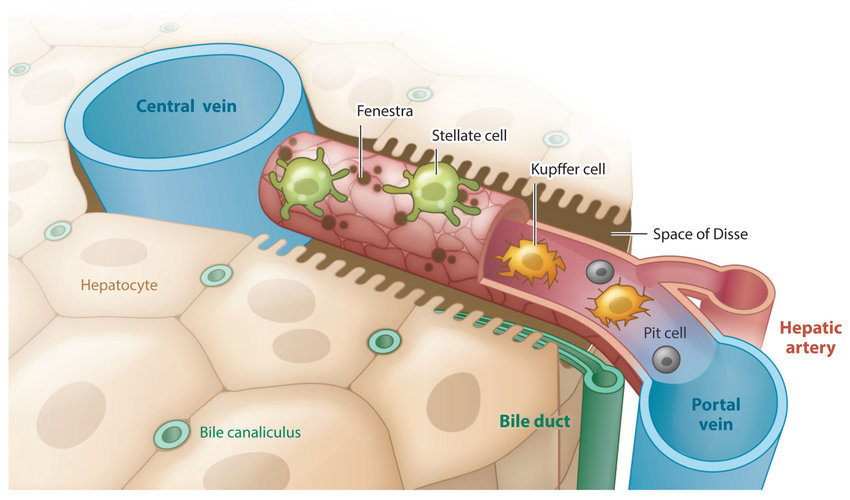
What does this entire structure refer to?
acinus
What the roles of Stellate cells?
Vit A storage
secrete GF
What is the Space of Disse?
interstitial space between blood and hepatocytes
What is a Cholangiocyte?
cells that make up the bile duct
How does blood flow from the GI tract back to the heart?
GI tract
Portal vein
Sinusoid
space of disse
hepatocytes
back out into sinusoid and into central vein to the heart
The lobule of the liver is split into how many zones? What zone receives the most oxygen? In what zone is most of the metabolism done?
3 zones (zone 1, zone 2, zone 3)
zone 1 receives the most oxygen
zone 1 is where most of the metabolism is done
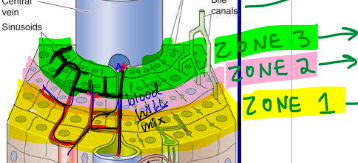
What artery brings oxygen rich blood from the heart?
hepatic artery
How do the sinusoids in the liver lobules respond to meals?
during meals—> dilate to allow for increased metabolism
fasting—> collapse/ smaller
During portal hypertension:
What happens to flow to the liver?
What happens to pressure within the portal vein?
What happens to resistance within the portal vein?
What happens to flow in the surrounding areas?
flow is obstructed/less than normal
INCREASED PRESSURE
INCREASED RESISTANCE
INCREASED FLOW to surrounding areas
What are the 3 classifications of portal hypertension? What are the common causes of each?
pre-hepatic: portal/splenic vein thrombosis
intra-hepatic: fibrosis in the liver, cirrhosis, hepatitis, alcohol abuse
post-hepatic: right-sided HF, vena cava clot
Why is splenomegaly seen in pre-hepatic portal hypertension?
bc of a blockage/clot fluid can’t flow into the liver and flows into the spleen. results in enlarged spleen or splenomegaly
What are the symptoms of portal hypertension?
ascites
jaundice
development of varices
vomiting, diarrhea
In portal hypertension, how does our body react to the increased resistance in the portal vein?
excessive vasodilation to surrounding areas (this becomes a problem)
How does cirrhosis lead to ascites?
cirrhosis causes portal hypertension
we vasodilate to counter the increased resistance
vasodilation increases the pressure in the capillaries and causes lymph to leak out of into the IS = ascites
AT THE SAME TIME—> because all the fluid is leaking out, our body thinks we have arterial hypovolemia
therefore, our body activates the RAAS system, vasoconstricts the arterioles and that leads to more fluid retention, worsening the ascites
When the RAAS system is activated in portal hypertension by conditions like cirrhosis, what hormones are increased?
↑ Aldosterone, ↑ Ang II, ↑ ADH
Bile is synthesized from __________________.
cholesterol
How are primary bile acids converted into secondary bile acids?
primary bile acids are synthesized in the liver and go to the GI where they are converted into secondary bile acids by bacteria
When bile acids are being reabsorbed/recycled, they are conjugated in the liver into what 2 things? Why?
conjugated into Glycine or Taurine
conjugated to make them more soluble
How are conjugated and non-conjugated bile acids brought into the HEPATOCYTE from the SINUSOID?
conjugated—> NTCP transporter
un-conjugated—> OATP1B 1/3
How do conjugated bile acids get from the HEPATOCYTE into the BILE?
BSEP transporter
Explain the process of how bilirubin is formed?
RBC dies and is converted to Hgb
In a macrophage, Hgb is converted to bilirubin
In the blood, bilirubin is bound to ___________.
albumin
How does bilirubin get into the HEPATOCYTE from the BLOOD? What happens once bilirubin enters the hepatocyte?
gets into the cell using the OATP transporter
once inside the cell—> conjugated by the UGT enzyme
Once conjugated, how is bilirubin moved from the HEPATOCYTE into the BILE? Where is bilirubin stored thereafter?
bilirubin moves into bile using MRP2 transporter
then store in the gallbladder with bile
Once bilirubin is secreted into the intestine, what happens? What happens after it’s turned into Urobilinogen?
deconjugated and metabolized by bacteria into urobilinogen
THEN either converted into STERCOBILIN and excreted into feces OR returned to plasma
What condition is a yellowing of the skin and tissue as a result of bilirubin accumulation?
jaundice
What are some causes of jaundice?
overproduction—> RBC/hemolysis
genetics:
reduced liver uptake
impaired conjugation
decreased hepatic excretion
impaired bile flow—> gallstone
How can the cause of jaundice be determined?
looking at the form of bilirubin aka is there high unconjugated or conjugated bilirubin
For each cause of jaundice, determine whether there would be higher conjugated or unconjugated bilirubin:
overproduction
reduced uptake
impaired conjugated
decreased hepatic excretion
impaired bile flow
overproduction- ↑ both but more unconjugated
reduced uptake- ↑ unconjugated
impaired conjugated- ↑ unconjugated
decreased hepatic excretion- ↑ conjugated
impaired bile flow- ↑ conjugated
Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia can be caused by:
hemolytic anemia
drugs inhibiting uptake into the liver
Gilberts
Crigler-Najjar
Gilbert’s is impaired _____________ function.
UGT1A1
Crigler-Najjar is impaired ____________ function.
UGT1A1
Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia can be caused by:
Dubin-Johnson
Rotor’s
obstruction in ducts
Dubin-Johnson is a mutation in _____________
MRP2/ ABCC2 transporter
Rotor’s is a mutation in _______________.
OATP1B1/3
Ammonia is toxic to the CNS and can cause what if there is high amounts?
Hepatic encephalopathy (altered mental status)
Hepatocytes play a role of converting ammonia into ______ and _______ to be excreted from the body.
urea and ornithine
A person with Rotor’s will have a problem doing what? (ex: conjugating bilirubin)
transporting conjugated bile into the hepatocyte
A person with Gilbert’s will have a problem doing what? (ex: conjugating bilirubin)
conjugating bilirubin
A person with Crigler-Najjar will have a problem doing what? (ex: conjugating bilirubin)
conjugating bilirubin
A person with Dubin-Johnson’s will have a problem doing what? (ex: conjugating bilirubin)
moving bilirubin from the hepatocyte into the bile