Ch 3 - Breathing and gas exchange
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
2.46, 2.47, 2.48, 2.50,2.49
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
How do cells in humans get their energy?
By respiration
What is the difference between breathing and respiration?
Respiration is the chemical reaction that releases energy from glucose
Breathing is a physical mechanism of conducting gas exchange by inhaling and exhaling air
What is the chemical equation for respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP
What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis?
6 CO2 + 6 H2O → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
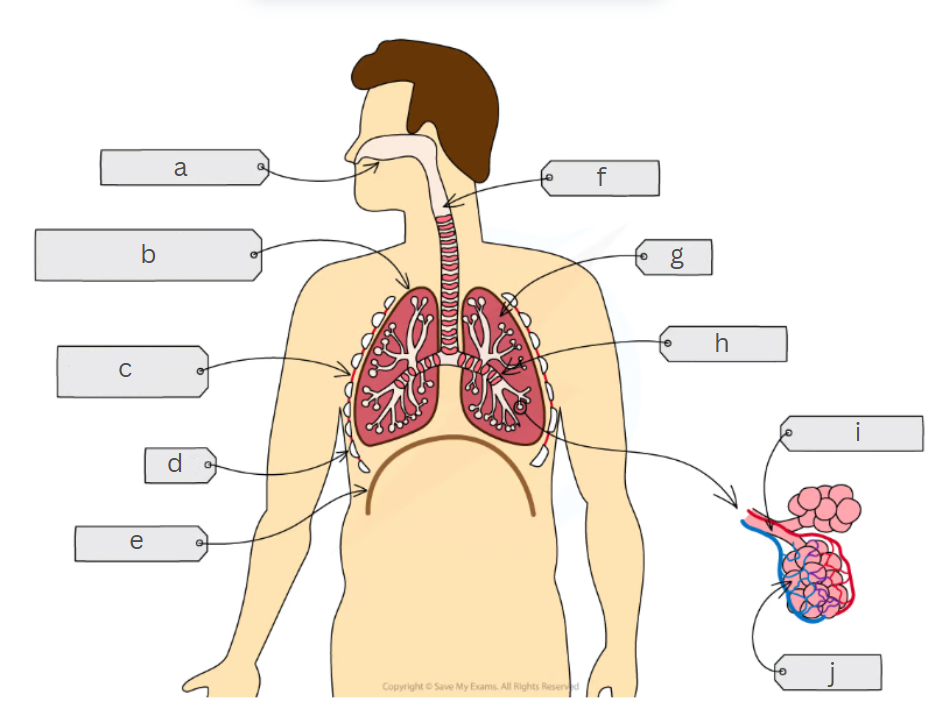
Label the diagram
a - nasal cavity
b - pleural cavity
c - intercoastal muscles
d - ribs
e - diaphragm
f - trachea
g - lung
h - bronchus
i - bronchiole
j - alveoli
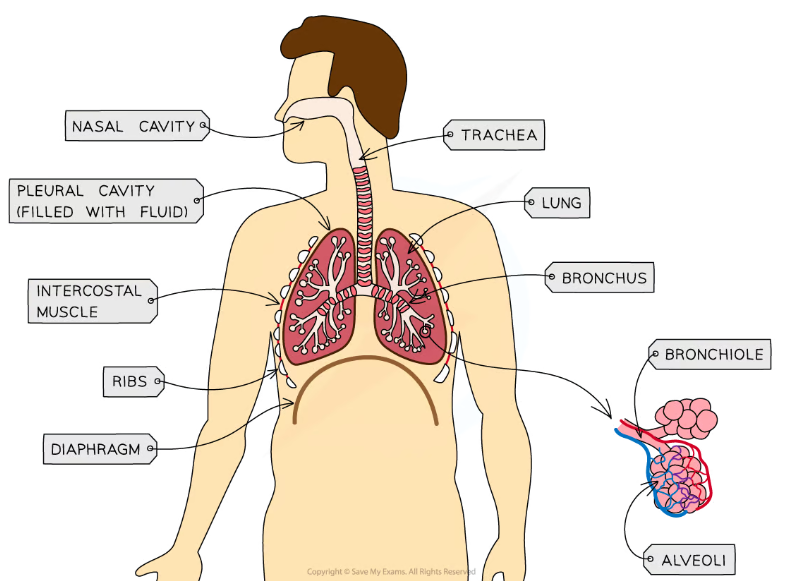
Describe the entire process of gas exchange
We breath in through our nose or mouth
The diaphragm contracts and flattens to increase the chest cavity
The air travels through the trachea and the bronchus to reach the bronchioles and eventually end up in alveoli
Alveoli are surrounded by capillaries that provide oxygen to the blood and take Carbon dioxide through diffusion
The waste gas (CO2) is then exhaled
The diaphragm relaxes, it moves up and the chest cavity decreases to push gas out
The walls of trachea and bronchi contain rings of cartilage. How do the rings help facilitate gas exchange?
They support the airways and keep them open when breathing in and out
How do pleural membranes help gas exchange?
They make an airtight seal to maintain the right pressure needed to inhale and exhale
Where is the plural fluid present and how does it help gas exchange?
It is present in the plural cavity and it provides lubrication so that surfaces don’t rub against each other when inhaling or exhaling
What happens when there is friction in the plural cavity?
Friction produces heat, the gas particles will move faster and this will disrupt the maintained pressure in the lungs. It can also cause that area of the lung to swell up.
Explain which features help filter the air that is entering our lungs?
Cilia - sweeps the air back and forth to trap dirt and bacteria from entering the lungs where they might cause infection
Mucus - Sticky liquid that traps particles of dirt and bacteria breathed in
Describe how the intercoastal muscles, the diaphragm and the ribs work together to inhale air
Intercoastal muscles contract
The ribs move outward and upward
The diaphragm contracts and flattens
The thorax has more volume
The pressure inside the lungs is slightly lower than that of the atmosphere, so air moves in
Describe how the intercoastal muscles, the diaphragm and the ribs work together to exhale air
The intercoastal muscles relax
The ribs move inward and downward
The diaphragm relaxes and moves upward
The thorax has less volume
The pressure of the air inside the lungs is slightly higher than that on the outside, so the air moves outside
How is the alveoli adapted for efficient gas exhange?
Large surface area - more area of contact with capillaries
Wrapped in a network of capillaries - Constant supply of blood to maintain the concentration gradient.
Capillaries are one-cell-thick - quicker diffusion across a smaller area
Describe the process of inhalation. Refer to intercoastal muscles, ribs and diaphragm in your answer.
Intercoastal muscles contract
Ribs move up
Diaphragm contracts and flattens so there is more volume in the thorax
There is greater volume so the pressure decreases, it will be less than the pressure outside the body, so air natually moves to an area of high to low pressure, the air moves into the body
Describe the process of exhalation. Refer to intercoastal muscles, ribs and the diaphragm in your answer.
Intercoastal muscles relax
Ribs lower
The diaphragm relaxes and moves up so there is less volume in the thorax
There is less volume so the pressure increases. The pressure inside the lungs will be slightly higher than the air pressure outside the body so the air naturally moves out of the body
Name the two solutions that can indicate the presence of CO2 and their reactions when it is detected
Limewater - turns cloudy in the presence of CO2
Hydrogen carbonate indicator solution - Primarily red, but turns yellow in the presence of CO2
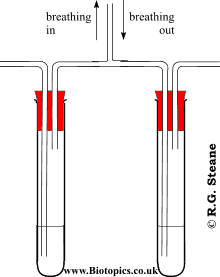
Describe an experiment for comparing the Carbon Dioxide content of inhaled and exhaled air
Two test tubes are filled with either Limewater or Hydrogen Carbonate indicator solution.
Set up the apparatus as follows.
A person should put their mouth to the tube and breathe in gently breathe in and out. This must be done gently to prevent drinking or blowing out and splashing the solution. A clean mouth piece must be used for each person.
If limewater is used, the inhaled air will be clear. The exhaled air will be cloudy.
If Hydrogen Carbonate is used, the inhaled air will be yellow. The exhaled air will be red.
Repeat the experiment for accuracy
Design an experiment to investigate the effect of exercise on breathing rates
Gather many people of the same or similar age, gender, health and athletic experience.
Measure the resting rate of breathing by sitting on a chair relaxed for 5 minutes minimum
After that, measure how many breaths they take in one minute. Take their breathing rate for a few minutes, minimum 5 and make a table and list these measurements
Make them perform a vigorous exercise such as running in place for 3 minutes or 20 push ups, use a stopwatch to record the time.
Make sure everyone does the same exercise for the same duration and at in a room with the same temperature, do not allow any rehydration or break
Immediately after, make them sit down and measure their breathing rate until it returns to their resting rate
Repeat the experiment multiple times and average your results
Plot your readings on a graph
Estimate a line of best fit, do not extrapolate and ignore anomalous points
Explain how smoking effects gas the cilia and mucus
Chemicals in cigarettes damage the cilia that are responsible for filtering out bacteria from air.
The cilia also holds mucus in place, without it, the mucus reaches the lungs so airway is blocked and people have difficulty breathing. Bacteria is also collected there, risk of developing into a disease
Name diseases that are caused by smoking
Lung cancer
Bronchitis
Emphysema
CHD
Why is smoking more harmful for women?
Smoking is more harmful for women because it can result in:
Hormonal fluctuations
Underweight fetuses
An increased risk of certain cancers such as breast cancer or rectal cancer
Fertility issues
Premature menopause
Name and explain the effect of the harmful substances present in cigarettes
Nicotine
Narrows blood vessels increasing blood pressure because the heart now has to pump more blood
High BP can lead to blood clots in the arteries which can result in a heart attack or a stroke
Carbon Monoxide
Hemoglobin binds with Carbon Monoxide because it has a greater affinity for CO than oxygen
Less oxygen is supplied to organs so the heart needs to pump faster to keep up with the lack of oxygen, increasing BP
Risk of CHD or stroke
Tar
Causes cell mutation
Which becomes cancer
Leads to emphysema or chronic bronchitis
Describe the how smoking causes emphysema and its effects on gas exchange
Emphysema is a disease caused by smoke breaking down the walls of the alveoli to fuse together again, causing enlarged, irregular spaces. This greatly reduces the surface area for gas exchange. Diffusion will be significantly less efficient and the body will not receive enough oxygen nor will waste products be exhaled,