Cancer Genetics - Breast Anatomy and GYN System
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
breast anatomy
15 - 20 lobes in each breast
Each lobe has 20 - 40 lobules
Lobules are connected via 6 - 8 ducts
Ducts connected to lobules carry milk to the nipple
Shape of the breast maintained by ligaments and connective tissue
Nerves throughout the breast provide sensation
Lymph nodes and blood vessels help fight infection
The Gynecological system
Ovarian cancer
Epithelial ovarian cancer is the most common malignancy
Primary peritoneal cancer
Lining of the abdominal cavity
Fallopian tube cancer
Uterine cancer
Endometrial cancer
Risk factors for breast cancer
Non-Modifiable
Being female
Aging
Ethnicity
Breast conditions
Hormone exposure
Family history
Inherited mutations
Modifiable
Obesity
Alcohol use
Physical inactivity
Ionizing radiation exposure
Breast findings
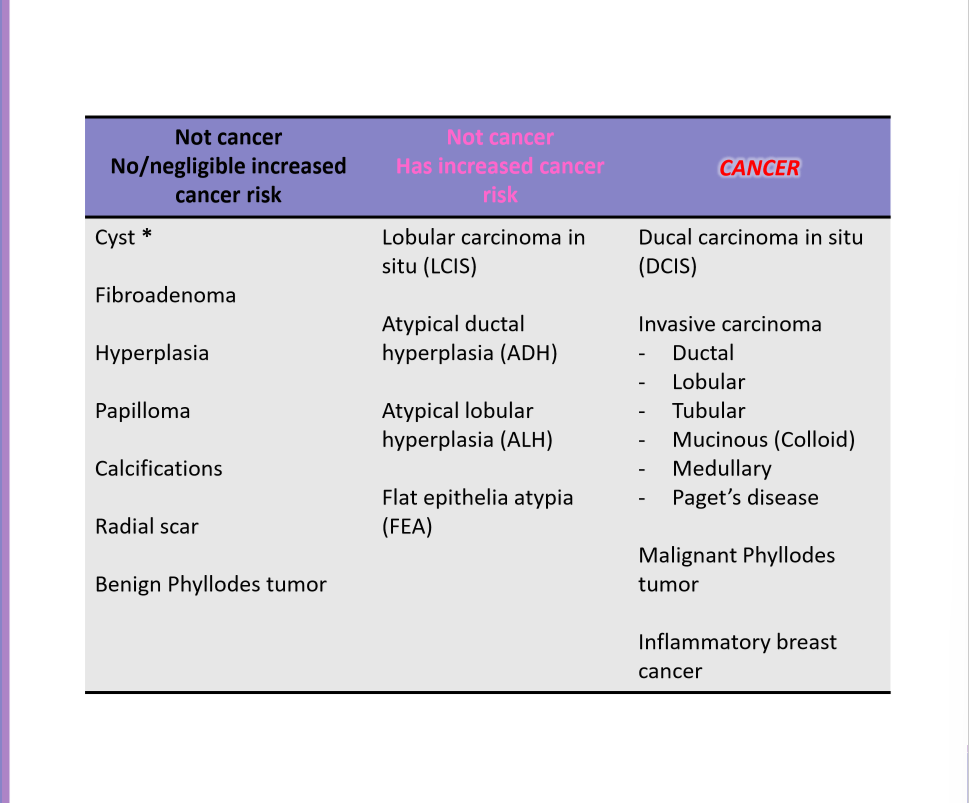
Chemotherapy
Anticancer drugs used after radiation and surgery
Hormonal therapy
Tamoxifen
treat breast cancer with estrogen and/or progesterone receptors on them
Aromatase inhibitors
Used in the treatment of breast cancer in postmenopausal women and men by stopping and enzyme in fat tissue from changing other hormones into estrogen
Immunotherapy
Using the body’s own immune system to help fight cancer
PARP inhibitors
A class of drugs which target cancer cells by exploiting a weakness in their ability to repair DNA damage
Useful for cancers with BRCA1/2 mutations (breast, ovarian, prostate, pancreatic)
Used in maintenance therapy (to prevent recurrence) and active treatment
Drugs target the Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase enzymes
Enzymes that help repair single-stranded breaks through base excision repair
Cancer cells with BRCA gene mutations highly depend on PARP enzymes for survival
Lumpectomy
Removal of the tumor from the breast with radiation
Mastectomy
Removal of the entire breast or breasts
May include sentinel lymph node biopsy and axillary lymph node dissection
Risk Factors for Gynecological Cancer
Non-Modifiable
Aging
Being female
Chronic conditions (endometriosis, PCOS, diabetes)
Hormonal factors (early menarche, late menopause, nulliparity)
Infertility
Heredity
Modifiable
Medications (excess estrogen exposure)
Obesity
Smoking
Gynecological tumors
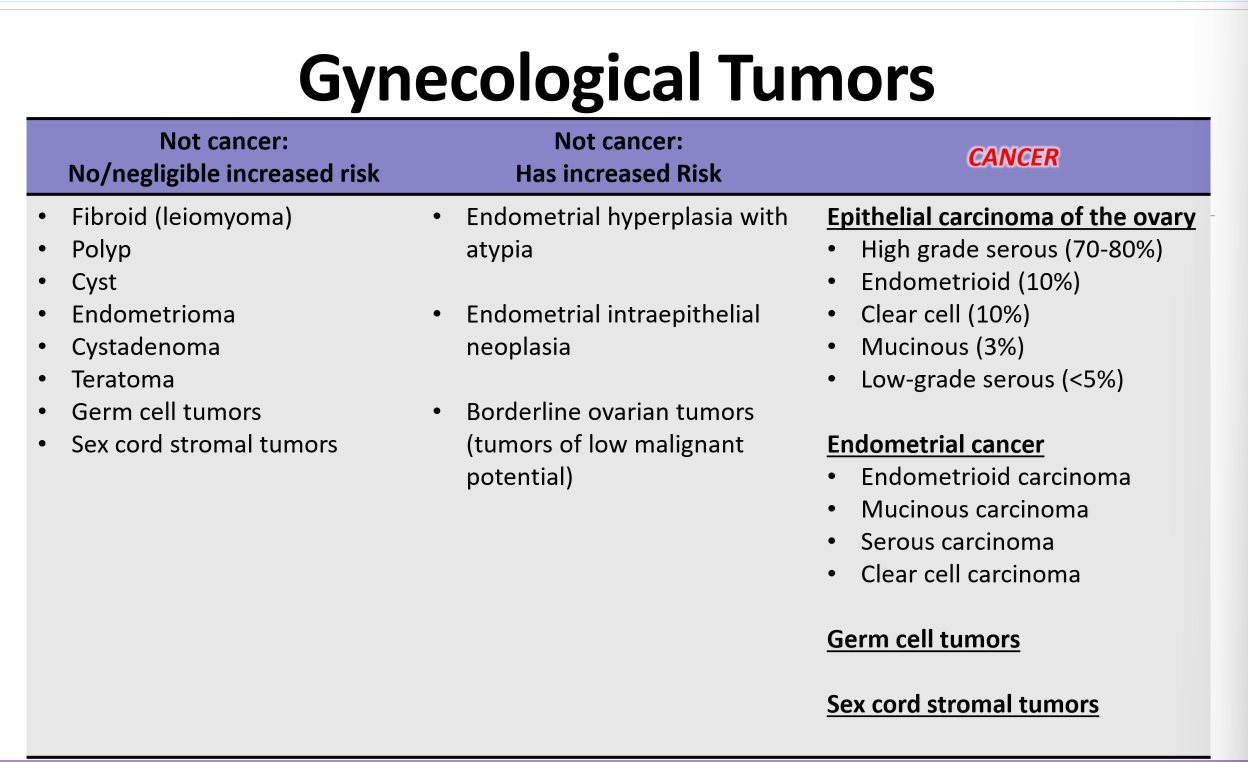
Screening for endometrial / ovarian cancers
Pelvic exam
Ultrasound / sonogram
MRI
Tumor marker (blood test)
Biopsy
Surgery for endometrial / ovarian cancers
Surgery
Hysterectomy (TAH / TH)
Removal uterus
total abdominal hysterectomy - uterus and cervix removed through abdomen
total hysterectomy - removal of uterus and cervix
Bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy
Both fallopian tubes (salpinges) and ovaries are removed
Lymph node biopsy
Omental biopsy
Tissue sample from the omentum, a fatty apron-like tissue that hangs from the stomach and covers the intestines
Pelvic washings
Flushing the pelvic cavity with a sterile solution to collect fluid and tissue samples for analysis
Debulking cytoreduction
Get all visible cancers out
Non-Surgery treatment options for endometrial / ovarian cancers
Chemotherapy
Radiation therapy
Endometrial cancer NOT ovarian
Hormonal therapy
Eg: Progestin
Synthetic version of progesterone, present in birth control
Prevent pregnancy by inhibiting ovulation
Unopposed estrogen can cause an overgrowth of endometrium leading to endometrial cancer
Others
Immunotherapy
PARP inhibitors
HBOC Syndromes
Hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndromes
BRCA1 on 17q21.31
BRCA2 on 17q13.1
Autosomal dominant
Increased risk of breast, ovarian, pancreatic, prostate, melanoma
HBOC Risk vs General
Breast
BRCA1 = 60 - 70%
BRCA2 = 55 - 70%
General = 12 - 13%
Ovarian
BRCA1 = 39 - 58%
BRCA2 = 13 - 29%
General = 1 - 2%
Pancreatic
BRCA1 = <5%
BRCA2 = 5 - 10%
General 1 - 2%
Prostate
BRCA1 = 7 - 26%
BRCA2 = 19 - 61%
General = 12 - 13%
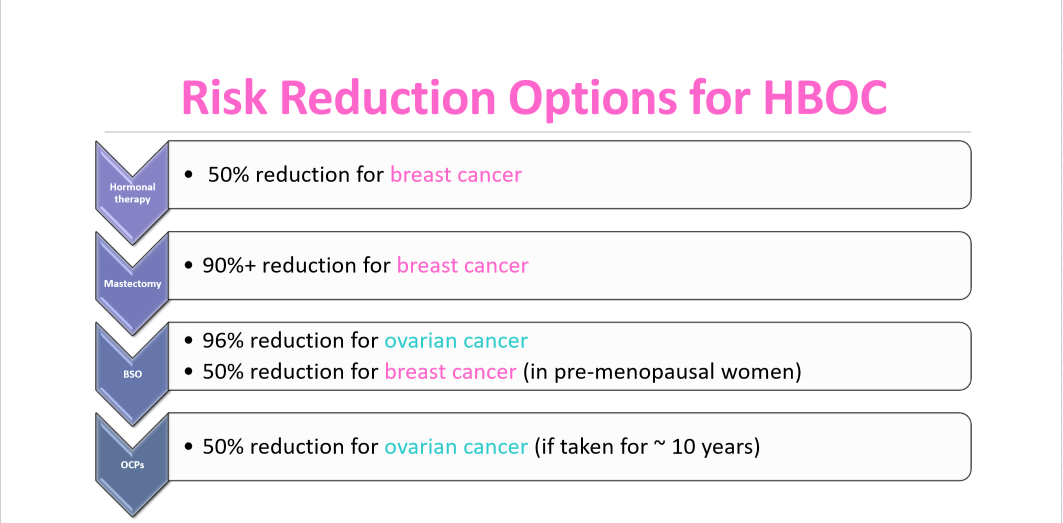
Risk Reduction Options for HBOC
Hormonal therapy
50% reduction in breast cancer
Mastectomy
90%+ reduction in breast cancer
Bilateral Salpingo-Oopherectomy
96% reduction for ovarian cancer
50% reduction in breast cancer (in pre-menopausal women)
Oral Contraceptive Pills
50% reduction for ovarian cancer (if taken ~10 years)
Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
Pancreas imaging
Viewing the bile ducts and the pancreatic duct
It can show the pancreas, gallbladder and liver
MRCP use MRI to produce detailed pictures of these ducts and organs
Founder mutations in BRCA
Ashkenazi-Jewish
Polish
Norwegian
Icelandic
PTEN Hamartoma Tumor Syndrome (PHTS)
PTEN 10q23.3
KLLN at 10q23.31
Autosomal dominant
Increased risk for breast, thyroid, endometrial, colorectal, renal cell, and melanoma cancers
Can cause many benign tumors
PTEN Hamartoma Tumor Syndrome Phenotypes (PHTS)
Cowden syndrome (CS)
Bannyan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome (BRRS)
Adult L’hermite-Duclos disease
Protus-like syndrome
Autism spectrum disorders with macrocephaly
Cowden Syndrome (CS)
Major criteria
Breast cancer
Epithelial thyroid cancer (non-medullary), especially follicular thyroid cancer
Macrocephaly
Endometrial carcinoma
Minor criteria
Thyroid lesions (eg. adenoma, multinodular goiter)
Intellectual disability
Hamartomatous intestinal polyps
Fibrocystic disease of the breast
Lipomas
Fibromas
Genitourinary tumors (especially renal cell carcinoma)
Genitourinary malformation
Uterine fibroids

Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba Syndrome (BRRS)
Congenital disorder characterized by:
Macrocephaly,
Intestinal hamartomatous polyposis
Lipomas
Pigmented macules of the glans penis
PTEN-Related Proteus Syndrome
Highly variable
Congenital malformations and hamartomas overgrowth of multiple tissues
Connective tissue nevi (mole), epidermal nevi, and hyperostoses
Li-Fraumeni Syndrome
TP53 at 17p13
Autosomal dominant
7 - 20% de novo
Anticipation
Very high penetrance
Lifetime risk for cancer is >70% for men and >90% for women
Cancer risks
Breast, soft tissue sarcomas, central nervous system cancers, adrenocortical carcinoma, gastrointestinal, hematologic malignancies
Management
Physical exam
Whole body MRI
Suspected when Chrompret criteria
Diagnostic criteria (All three)
Proband with sarcoma diagnosed before 45 years
First-degree relative with any cancer before 45 years
A first or second degree relative with any cancer diagnosed before 45 years or a sarcoma diagnosed at any age
Li-Fraumeni Clinical Criteria
Proband with a sarcoma diagnosed before 45 years AND
First-degree relative with any cancer diagnosed before 45 years AND
First or second-degree relative with any cancer diagnosed before age 45 or a sarcoma diagnosed at any age
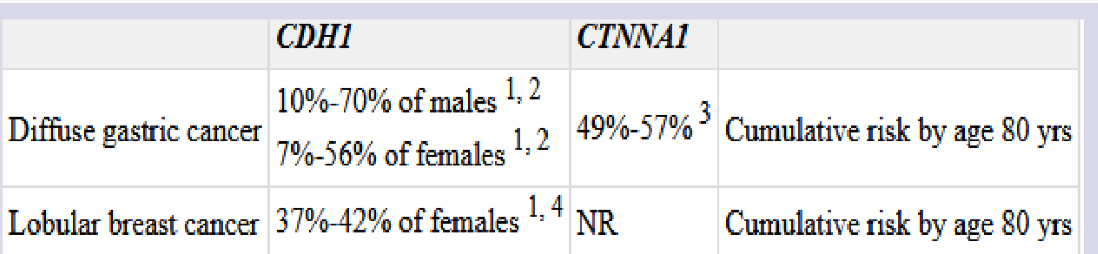
Hereditary Diffuse Gastric Cancer Syndrome
CDH1 at 16q22.1 (e-cadherin protein)
CTNNA1 at 5q31.2
Autosomal dominant
Established in a proband with diffuse gastric cancer and family history of one or more first- or second-degree relatives with GC OR
A personal and/or family history of DGC (diffuse gastric cancer) diagnosed before age 40 OR
Personal and/or family history of DGC and LBC, one diagnosed before 50 years
Genetic testing for CDH1 mutations (hereditary Diffuse Gastric Cancer Syndromes)
Genetic testing should be ordered
Diagnosis of DGC (diffuse gastric cancer) and pathologically confirmed in situ signet ring cells and/or pagetoid spread of singet ring cells adjacent to DGC
Diagnosis of DGC and a family history of two first- or second- degree relatives with DGC or LBC (lobular breast cancer)
A diagnosis of DGC and a personal or family history of cleft lip / palate
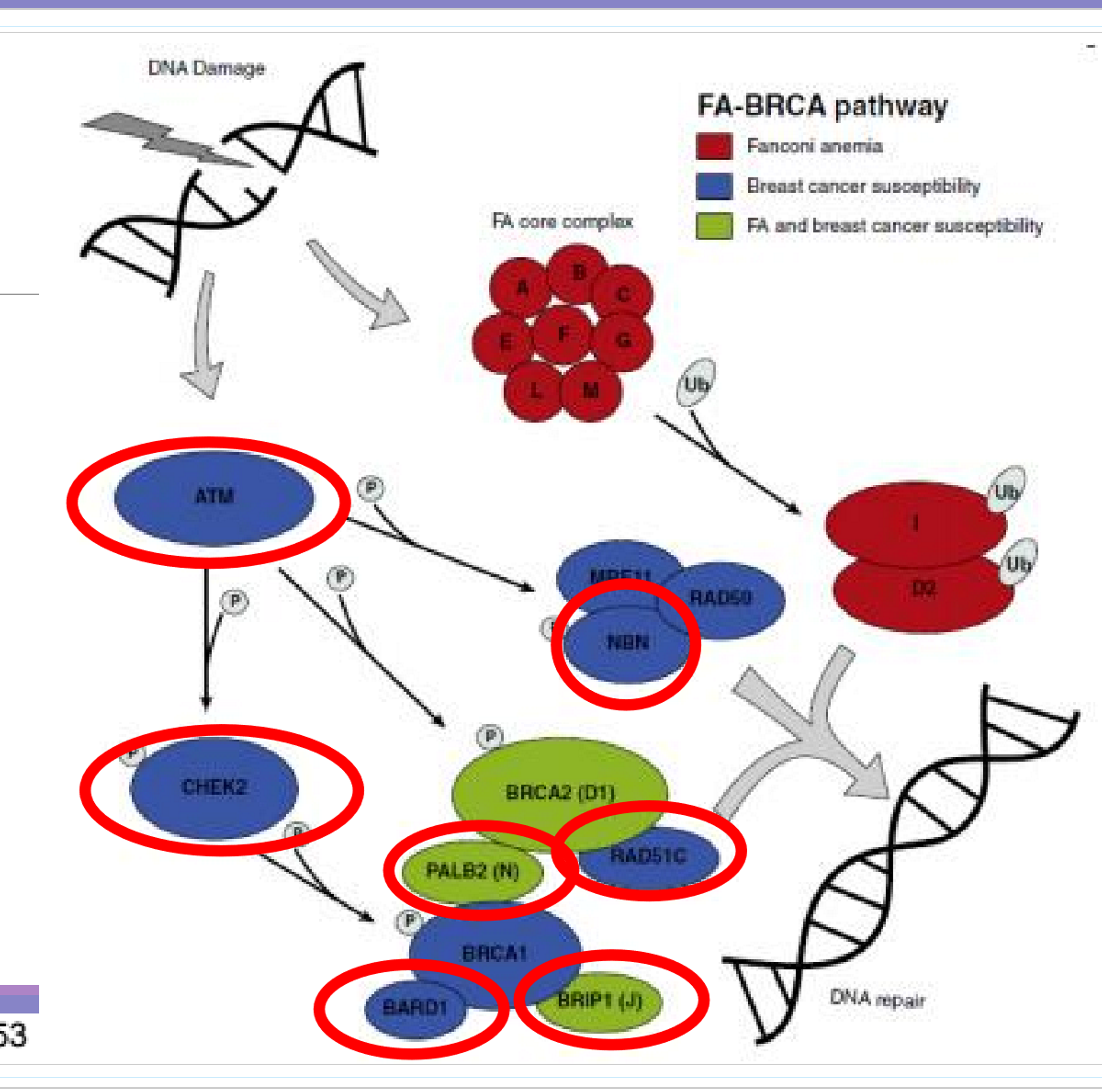
Additional breast / ovarian cancer genes
ATM gene
Bi-allelic mutations in ATM genes is Ataxia telangiectasia
BARD1
BRIP1
CHEK2
MSH2 / MLH1 / MSH6 / PMS2 / EPCAM
NF1
PALB2
RAD51C
RAD51D
STK11
Ataxia Telangiectasia
ATM genes
Bi-allelic, autosomal recessive version of ATM gene mutation
Clinical features
Very sensitive to ionizing radiation
Overall cancer risk of 38%
Progressive gait / truncal ataxia (wheelchair by 10)
Progressively slurred speech
Immunodeficiency
Endocrine abnormalities (diabetes / premature ovarian failure)
Bloom Syndrome
BLM gene
Autosomal recessive
Higher in Ashkenazi Jewish
Clinical Features
Skin, breast, hematological, tongue, laryngeal, GI, cervical cancers
Diarrhea and vomiting in infants
Cafe-au-lait spots
Susceptibility to infection
High-pitched voice
Azoospermia
Learning disability with normal intellect
FA-BRCA Pathway
PTEN-Related Proteus-Like Syndrome
Undefined but refers to individuals with significant clinical features of PS (proteus syndrome?) who do not meet the diagnostic criteria for PS