Bones 24: Fractures 3
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What type of fracture is associated most with FOOSH? (Fall on out-stretched hand)
Carpal fractures
What percentage of carpal fractures come from foosh
70-80%
What is the most common radial fracture in adults?
Colles fracture:
radial metaphysis
What type of fracture is characterized by Radial diaphysis fracture and ulnar head dislocation
It happens mostly in children of 9-12 age
Galeazzi fracture
What type of fracture is characterized by ulnar shaft fracture with and radial head dislocation?
It Happens mostly in children of 4-10 age
Monteggia fracture
Which type of fracture can suggest interpersonal violence?
Where does this fracture occur?
Parry fracture/Nightstick
Ulnar diaphysis
What is a bone callus?
What is produced?
Periosteal reaction
Reactive bone as a result of periosteum irritation
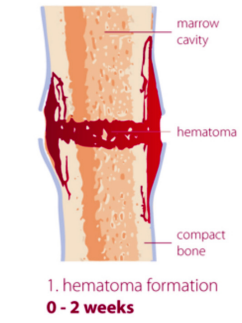
What happens at 0-2 weeks of the callus formation?
Hematoma-blood clot
scaffolding
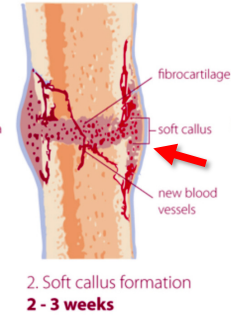
What happens at 2-3 weeks of the callus formation?
Soft callus
cartilage added and bone surface becomes porous and “woven”
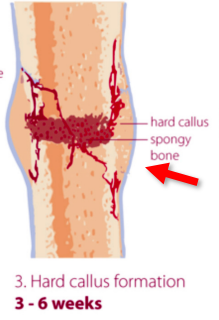
What happens at 3-6 weeks of callus formation?
Hard callus is formed
Thickened
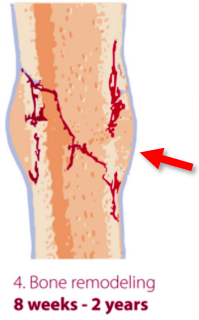
What happens at 8 weeks-2years of callus formation?
Bone remodeling
margins of the callus becomes less distinct
What is the name of a crushing damage to a tissue around bone that can lead to new bone formation?
Myostitis ossificans traumatica

What is “reducing” in fractures?
What happens if it remains unreduced?
Putting the bone back together ex. reduced ulna after parry fracture
Bone will still grow together and the bony tissue will not match up. Displaced
What is it called when the complete fracture fails to heal?
Pseudoarthrosis or nonunion
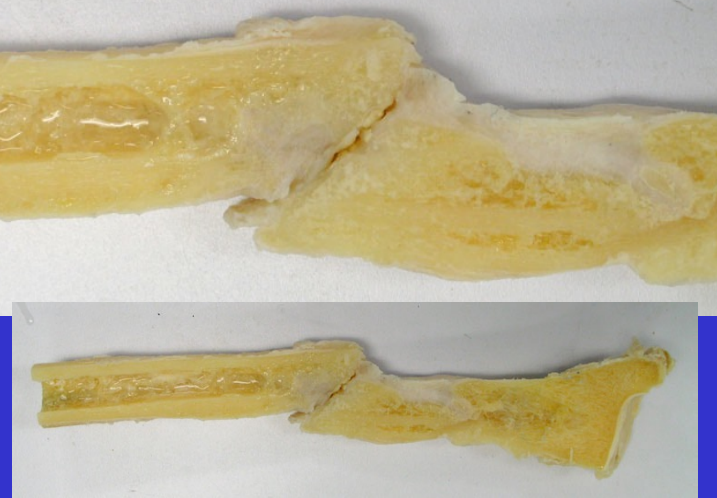
What is the name of this periosteal reaction where reactive bone forms as a result of an infection?
Osteomyelitis
What diseases can lead to bone destruction and reactive bone?
Cancer: Osteoblastoma
Chronic tuberculosis: becomes systemic, originating from the lungs and moving to the bones.
What is the specific name of vertebral degeneration due to tuberculosis
Pott’s disease