Maths final
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Float time
The amount of time a task can be delayed without causing a delay to other tasks in the project.
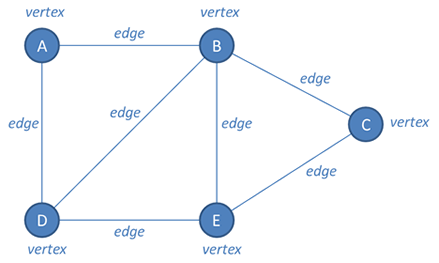
Vertices
A node or point where edges meet
Mean
Calculated by adding up all the numbers in a set, and then dividing by the count of numbers in that set.
Recursive function
A function that repeats or uses its own previous term to calculate subsequent terms and thus forms a sequence of terms.
3 point moving average
We find the mean of the data values for that time period, the previous time period, and the next time period.
Eulerian graph
If all vertices have an even degree then it is this type of graph.
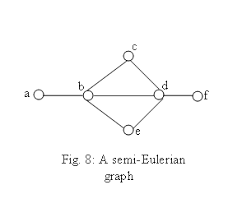
Semi-Eulerian trail
An open trail that includes all edges one time. A graph is this if exactly two vertices have odd degree.
An even vertex…
Has an even number of edges attached to it.
An odd vertex…
Has an odd number of edges attached to it.
Matrix
A rectangular array or table of numbers, symbols, or expressions, arranged in rows and columns, which is used to represent a mathematical object or a property of such an object.
Optimal allocation
As a rule, the optimal allocation equalizes the returns of the marginal (or last) unit to be transferred between all the possible uses.
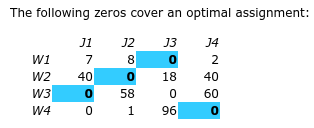
Hungarian method
Is a combinatorial optimization algorithm that solves the assignment problem in polynomial time and which anticipated later primal–dual methods. Used to find optimal allocation.
Interpolation
Determining a value from the existing values in a given data set. Another way of describing it is the act of inserting or interjecting an intermediate value between two other values.
Extrapolation
An estimation of a value based on extending the known series or factors beyond the area that is certainly known. In other words, extrapolation is a method in which the data values are considered as points such as x1, x2,
Spanning tree
Is a connected graph using all vertices in which there are no circuits. In other words, there is a path from any vertex to any other vertex, but no circuits.
Cycle
In graph theory, a path that starts from a given vertex and ends at the same vertex is called a cycle.
Explanatory variable
A type of independent variable. It is what a researcher manipulates or observes changes in. In other words, an explanatory variable is the expected cause, and it explains the results.
Response variable
Is a type of dependent variable. It is the one that changes the results. Furthermore, a response variable is the expected effect, and it responds to explanatory variables.
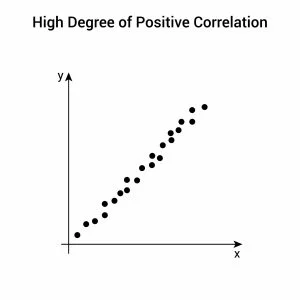
Strong positive association
When one variable moves in one direction, other variables also move in the same direction to the same degree.
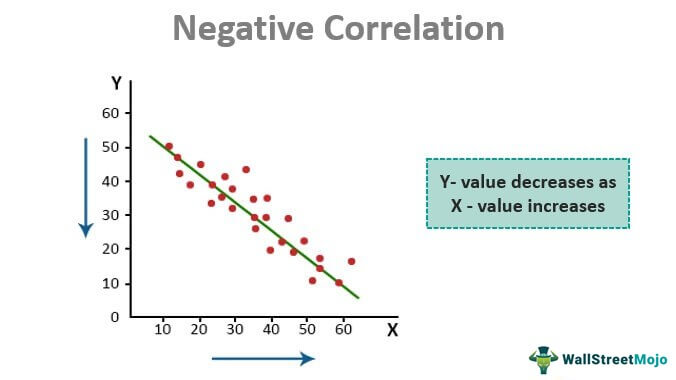
Strong negative association
Meaning that the two variables tend to move in opposite directions.
What is a two way table?
one way to display frequencies for two different categories collected from a single group of people. One category is represented by the rows and the other is represented by the columns.
What is UTC?
Stands for Coordinated Universal Time, a standard used to set all time zones around the world.
UTC example
New York City is in the time zone UTC -5, meaning that it is 5 hours earlier in NYC than the reading on a UTC clock.
Brisbane is in time zone UTC +10, meaning that it is 10 hours later than the reading on a UTC clock.
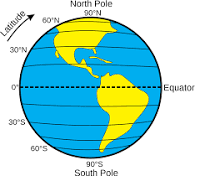
Latitude
A coordinate that specifies the north–south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body.
Longitude
Geographic coordinate that specifies the east–west position of a point on the surface of the Earth,

Least squares line
y = mx + b or y = a + bx
It minimizes the squared distances between the line and our points, we can think of this line as the one that best fits our data.
Recurrence relation
An equation that defines a sequence based on a rule that gives the next term as a function of the previous term(s). The simplest form of this is the case where the next term depends only on the immediately previous term.
Compounding
A powerful investing concept that involves earning returns on both your original investment and on returns you received previously. For compounding to work, you need to reinvest your returns back into your account. For example, you invest $1,000 and earn a 6% rate of return.
Arithmetic sequence
A sequence of numbers such that the difference from any succeeding term to its preceding term remains constant throughout the sequence
Trend
A change/relationship over time
Seasonality
Is the presence of variations that occur at specific regular intervals less than a year, such as weekly, monthly, or quarterly
Hungarian algorithm steps
Subtract row minima.
Subtract column minima.
Cover all zeros with the minimum number of lines.
Create additional zeros by finding the smallest element - call it c - that isn't covered by a line.
Cycle
In graph theory, a path that starts from a given vertex and ends at the same vertex
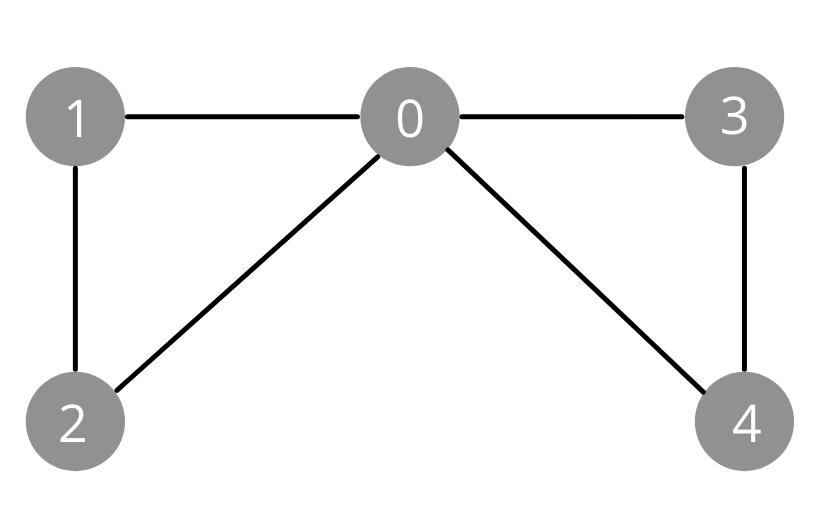
Adjacency matrix
A matrix containing rows and columns which is used to represent a simple labelled graph, with 0 or 1 in the position of (Vi , Vj) according to the condition whether Vi and Vj are adjacent or not.
Seasonal index
A measure of how a particular season through some cycle compares with the average season of that cycle
Equation for seasonal index
Value of season/seasonal average
Network diagram
A representation of a group of objects called vertices that are connected together by lines called edges