HN220 - Midterm 3
1/501
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
502 Terms
What are the 3 components of the cardiovascular system?
1) The heart
2) Blood vessels
3) Blood
What is the purpose of blood in the cardiovascular system
acts as the fluid medium that carries nutrients and waste
Blood vessels provide a _____________ system for the cardiovascular system
closed
What is the cardiovascular systems central function?
transportation of substances
What substances does the cardiovascular system transport?
1) oxygen and nutrients to cells
2) waste from cells to liver and kidneys
3) hormones
4) immune cells
5) clotting proteins to specific target cells
Arteries branch into ___________
arterioles
Arterioles branch into ___________
capillaries
Capillaries branch into ____________
venules
Venules branch into ____________
veins
Arties carry blood ____ from the heart
away
Veins carry blood ____ the heart
toward
In pulmonary capiilary beds, O2 ____________ the blood and CO2 ________________ the blood
enters, leaves
In systematic capiilary beds, O2 ____________ the blood and CO2 ________________ the blood
leaves, enters
What are the 2 circuits of the cardiovascular circuit?
1) pulmonary circuit
2) systemic circuit
The pulmonary circuit is supplied by the _________ heart
right side
The systemic circuit is supplied by the _________ heart
left
The blood vessels in the pulmonary circuit run from heart to ____________________, and then from lungs to __________________
lungs, heart
The blood vessels in the systematic circuit run from heart to ____________________, and then from systemic tissues to __________________
systemic tissues, heart
The heart is located in the _________________________
thoracic cavity
What separates the abdominal cavity from the thoraciccavity
diaphragm
The heart is surrounded by the ________________
pericardium
What is the pericardium?
Membranous sac surrounding the heart
What is the function of the pericardium?
Lubricates the heart and decreases friction
True or false: the pericardium is another word for the heart wall
false: the heart wall is different from the pericardium
What is the outer layer of the heart?
epicardium
What is the epicardium also known as?
visceral pericardium
What is the function of the epicardium?
protects the heart
What is the myocardium?
middle layer of the heart, made of muscle
True or false: the myocardium is the thickest layer of the heart
true
The myocardium is made of ____________
cardiac muscle tissue
Great vessels are wrapped around by the _____________________
atrial myocardium
What is the innermost layer of the heart?
endocardium
What is the endocardium made of?
epithelium
What is the function of the endocardium?
Provides protection for valves and heart chambers
What ensures that blood flow is unidirectional?
valves and pressure
What drives blood flow?
pressure difference
Blood moves from ___________ pressure to _________________ pressure
higher to lower
Blood moves from ______________ to ventricles
atria
Blood moves from ventricles to _________________
arteries
What structure prevents the backflow of blood?
valves
Do valves open passively or actively?
passively
What causes valves to open?
pressure gradient
The right AV valve is also known as _____________
tricuspid valve
The left AV valve is also known as _________________
bicuspid valve or the mitral valve
What structures keep the valves from everting?
Papillary muscles and chordae tendinae
Why dont we want valves to evert?
would cause backflow of blood
What are the 2 semilunar valves?
1) pulmonary
2) aortic
The pulmonary valve leads blood to the ____________
lungs
The aortic valve leads blood to the _______________
aorta
What are the 2 types of myocardial cells?
1. Contractile Cells
2. Autorhythmic Cells
Contractile cells are found in the ____________
myocardium
Contractile cells account for ____________ % of the cardiocytes
99
What do autorhythmic cells do?
Can generate/spread AP spontaneously
What are the 2 types of autorhythmic cells?
1) pacemaker cells
2) Conduction fibers
What do pacemaker cells do?
1) Initiate APs
2) Establish heart rate (rhythm; "pace")
What do Conduction Fibers cells do?
Transmit/spread action potentials
How do cardiac muscle cells differ from skeletal cells?
cardiac muscle cells have audtorhythmicity
- the ability to generate own rhythm
Are contractile muscle cells big or small?
small
Describe the structure of contractile muscle cells?
- small
- bifurcate (divide into two branches/forks)
Contractile muscle cells have ____________________ centrally located nucleus
Single
True or false: contractile muscle cells are anaerobic
false: they are aerobic
What allows contractile muscle cells to be aerobic?
- High in myoglobin
- High in mitochondria
- Extensive blood supply
true or false: contractile muscle cell contraction is voluntary
false: involuntary
true or false: contractile muscle cells contract similarly to skeletal muscle
true
How is cardiac muscle similar to skeletal muscle?
- striated
- contains sarcomeres
How is cardiac muscle different than skeletal muscle?
- Have short and wide T tubules
- Less SR with no terminal cisternae
- Under SNS and PNS control
- Single nucleus
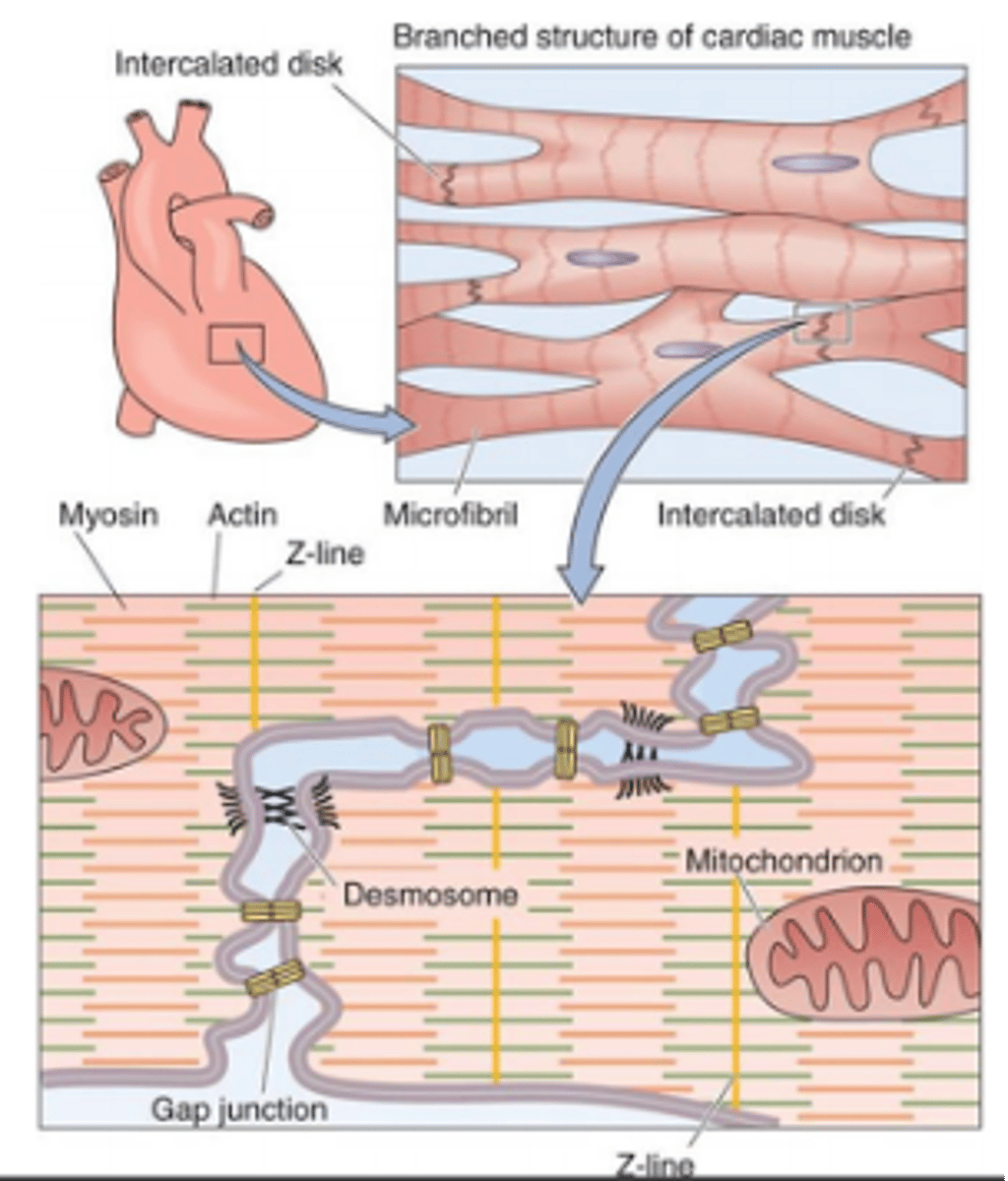
- Have intercalated discs to connect cells
What are intercalated discs?
junctions between cells that anchor cardiac cells
What are the 2 components of intercalated disks
1) Gap junctions
2) Desmosomes
Gap junctions connect ____________ cells _________________
adjacent, electrically
With gap junctions, the cardiac muscle cells functions as ___________
"single-unit" smooth muscle
True or false: gap junctions act as a direct connection
true
What is the purpose of desmosomes?
Provide the 'glue' that holds the cell together
Do desmosomes or tight junctions allow for chemical communication
desmosomes
What is the pacemaker of the heart?
SA node
After the SA node fires, the electrical signal travels to the __________________
AV node
What are the different groups of Conduction fibers of the myocardium
1) internodal pathways
2) Bundle of his
3) Purkinje Fibers
Are desmosomes or gap junctions used for electrical coupling?
gap junctions
Where is the action potential generated in the heart?
SA node
Where does the action potential go after it reaches atrial muscles?
The AV node
What happens after the SA node generates an action potential?
The signal spreads through atrial muscle
How does the signal spread throughout atrial muscle
via interatrial pathways
How does the signal reach the AV node?
via internodal pathways
True or False: There is a small delay once the signal reaches the AV node
true
What is the purpose of the delay at the AV node?
allows time for ventricles to fill
Where does the signal travel after the AV node?
Reaches the atrioventricular (AV) bundle (bundle of His)
What do the left and right bundle branches become?
purkinje fibers
What does the bundle of His split into?
left and right bundle branches
What do the left and right bundle branches contract?
ventricles
Describe the initiation and conduction of an impulse in the heart
1) AP initiated in SA node; signals spread through atrialmuscle via interatrial pathways
2) Signal travels to AV node via internodal pathway; AV nodaldelay
3) Atrioventricular bundle (bundle of His)
4) Splits into left and right bundle branches
5) Purkinje fibersThe Conducting System
What's the firing rate of the SA node
-70-80 AP/min
What's the firing rate of the AV node
40-60 AP/min
Cardiac cells are linked by ____ ________
GAP JUNCTIONS
True or False
Slower depolarizing cells control the pace for other cells
False
The faster depolarizing cells set the rate for the rest of the heart
Damage to the SA node causes the ___ _____ to initiate contraction
AV node
AP travel through the conduction system to the ____ of the heart
APEX of the heart
*This allows for the AP to spread upward through the ventricular muscle
What is an ECG
Composite of ALL APs generated by nodal and contractile cells
Waves in an ECG are also called __________
deflections
What are the parts of an ECG
-P wave
-QRS complex
-T wave
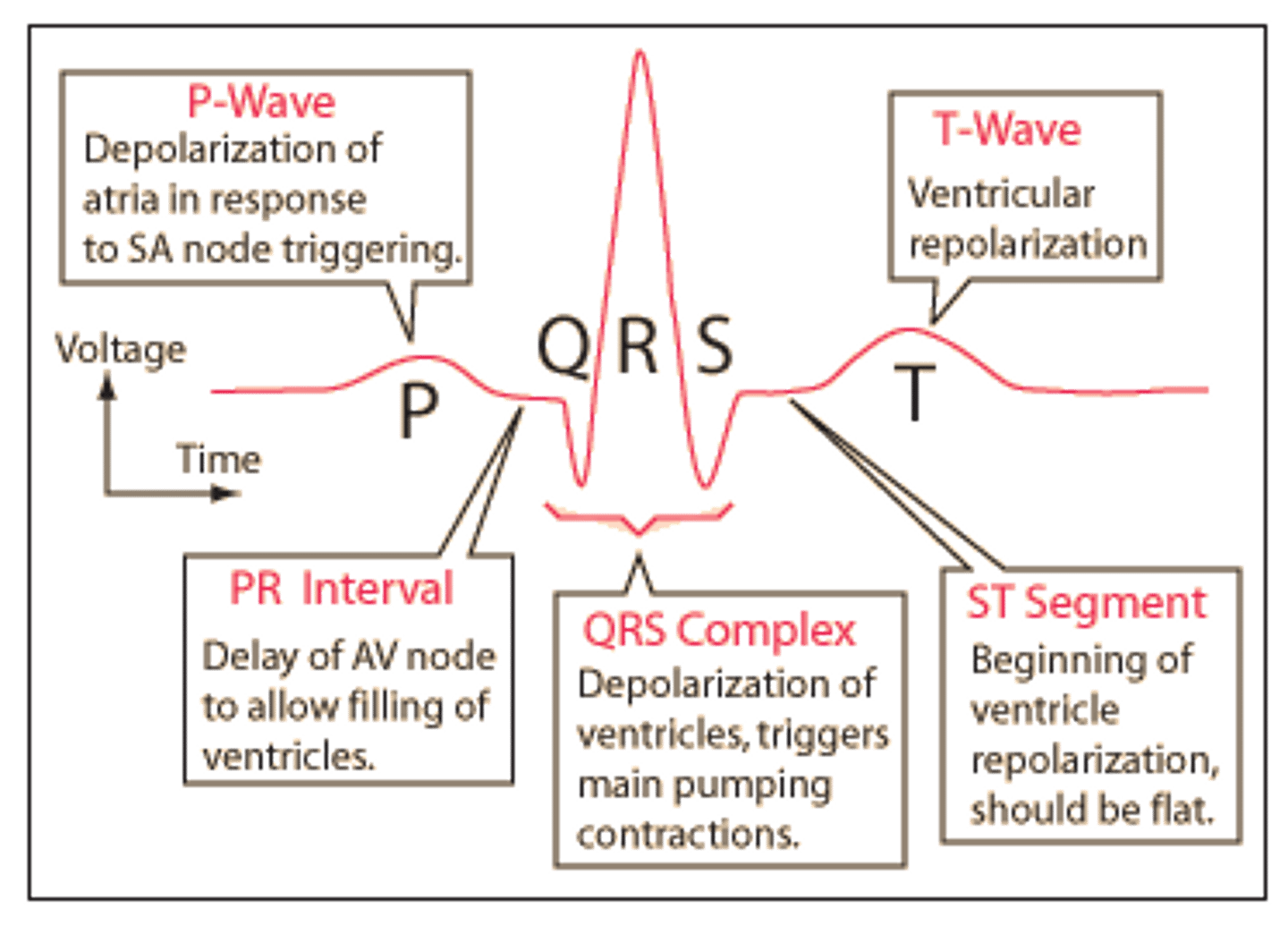
What is a P wave
-Atrial depolarization
-Initiated by SA node
What is the QRS complex
-Ventricular depolarization beginning at the apex
-Atrial repolarization also occurs but obscured by QRS complex